Nursing Care of the Client with Endocrine Disorders: Thyroid Gland
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Where is the thyroid located?
a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the neck, just below the Adam's apple
What is the function of the thyroid?
-Produces 2 main hormones: T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine)
What do T3 and T4 hormones do?
regulate metabolism, energy production, growth, and body temperature
T3
triiodothyronine
The active hormone that directly influences metabolism
T4
thyroxine
Mostly converted to T3 in the body
What kind of feedback loop is hypothyroidism?
negative feedback
How does the normal thyroid negative feedback loop work?
1. When thyroid hormone levels (T3 and T4) are low, the hypothalamus releases TRH, which signals the pituitary to release TSH.
2. TSH stimulates the thyroid to produce more T3 and T4.
3. Once levels are normal, high T3 and T4 stop the release of TRH and TSH (negative feedback).
How does the hypothyroidism negative feedback loop work
1. In hypothyroidism, the thyroid doesn’t produce enough T3 and T4 (due to damage or dysfunction).
2. The hypothalamus detects low levels and releases more TRH, signaling the pituitary to release more TSH.
3. Despite high TSH, the thyroid cannot produce enough hormones, so T3 and T4 remain low.
4. This leads to symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, and cold intolerance.
What is the key difference between the normal thyroid negative feedback loop and the hypothyroidism negative feedback loop?
In hypothyroidism, the feedback loop is disrupted because the thyroid gland doesn't respond to TSH properly, causing low thyroid hormone levels despite high TSH.
What hormones are affected in hypothyroidism?
T3, T4, TSH
In hypothyroidism, there is a decrease in...?
T3 and T4 (Decreased metabolism and SNS response- fight or flight- tie this in with the symptoms)
In hypothyroidism, how does our body compensate?
Hypothalamus and anterior pituitary gland increase TSH levels in attempt to compensate
-attempting to stimulate the thyroid gland to produce more thyroid hormone
In Hypothyroidism, are TSH levels elevated or decreased?
elevated
In hypothyroidism, are T3 and T4 levels increased or decreased?
decreased
What is the most common cause of hypothyroidism?
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
What is Hashimoto's thyroiditis?
autoimmune destruction of thyroid gland, decreases negative feedback loop and T3 and T4 levels
Who is most commonly affected by hypothyroidism?
-Females
-Ages 30-60
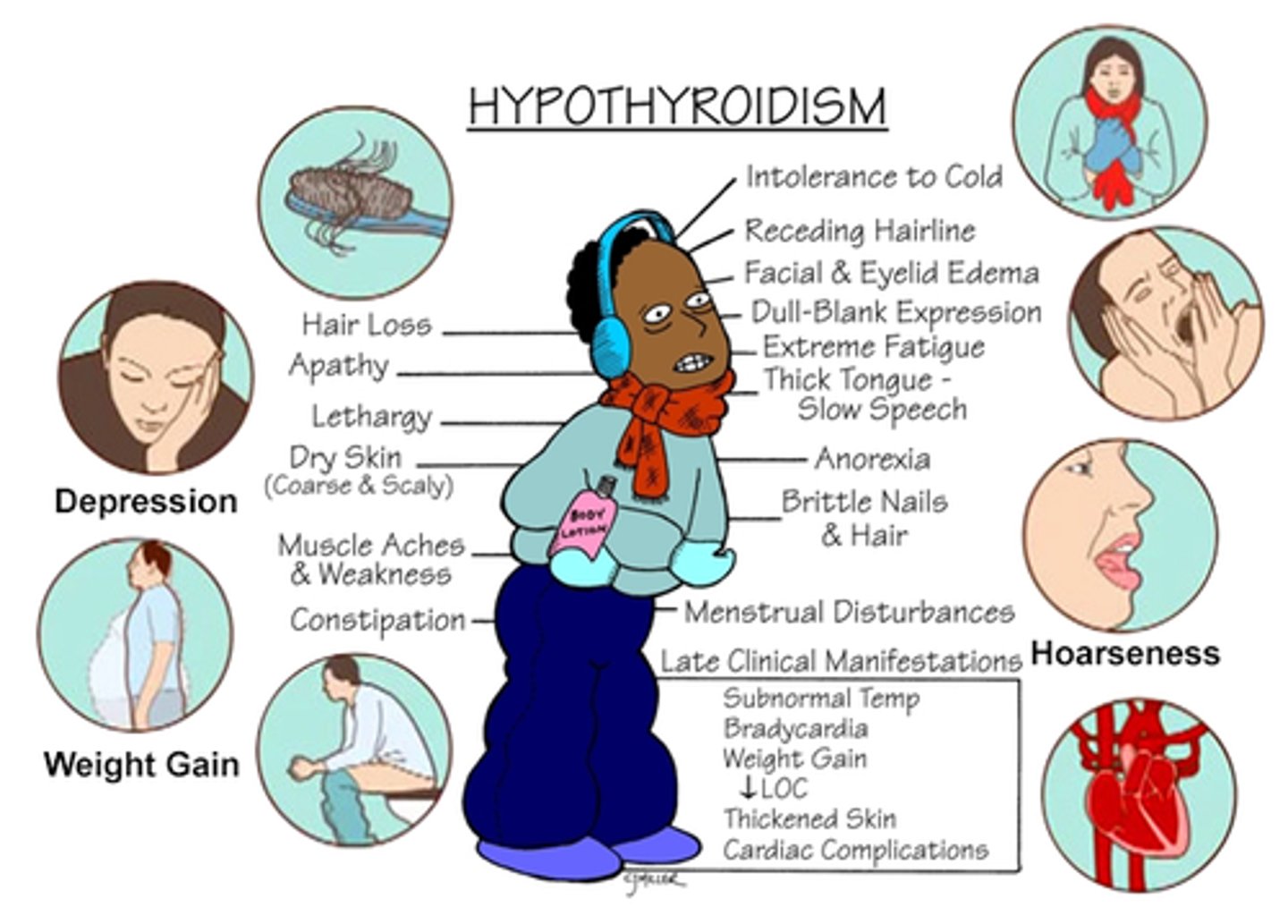
What is a common symptom of hypothyroidism related to energy levels?
Extreme fatigue
How much more frequently does hypothyroidism affect women compared to men?
5 times more frequently
What skin and hair characteristics are associated with hypothyroidism?
Cool, dry, coarse skin; hard, decreased hair growth; brittle nails; cold intolerance
What are two common gastrointestinal symptoms of hypothyroidism?
Weight gain and constipation
What should be encouraged for managing weight gain and constipation in hypothyroidism?
Consultation with a nutritionist, increased movement, and increased fiber and fluids
What neurological symptoms can occur with hypothyroidism?
Muscle weakness, paresthesia (numbness and tingling in the fingers), and joint discomfort
What cardiovascular symptoms are associated with hypothyroidism?
Hypoventilation, hypotension, bradycardia, and decreased activity tolerance
What cognitive and emotional symptoms may be present in hypothyroidism?
Forgetfulness, slow speech, confusion, and depression
What reproductive changes can occur in both men and women with hypothyroidism?
Changes in menses, decreased libido, and impotence
What is a physical sign of thyroid dysfunction that can occur in both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism?
Goiter (enlarged thyroid)
What are some long-term effects of untreated hypothyroidism?
Elevated cholesterol, atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease, and poor left ventricular function
Hypothyroidism symptoms
For Hypothyroidism, what is the replacement drug?
-Levothyroxine (generic name)
-Synthroid or Levothroid- brand name
How much levothyroxine should you give
25mcg-50 mcg PO QD (once a day)
Levothyroxine is increased how frequently and what is the increase based on?
-Increased normally by 25mcg every 4-6 weeks
-based on patient's response (TSH level)
-also ask the pt. how they are feeling. After 4-6 weeksm blood work is done and based on the levels you can decide whether the dose needs to be increased or decreased.
If the starting dose of Levothyroxine is too high, what can it cause?
severe hypertension or heart failure
How should pt take Levothyroxine and why?
on an empty stomach one hour before breakfast so the stomach is empty and absorption is better and more effective
What should you teach the patient about their medication?
that they will need to take the medication for the rest of their lives
Levothyroxine care with other medication
may increase absorption of Coumadin (anticoagulant- increase INR) and decrease effect of insulin and oral anti-diabetics (increased blood glucose)
Levothyroxine effect on cardiac function
-with longstanding patients on meds
-medications may cause increase in cholesterol > atherosclerosis > coronary artery disease
What is myxedema coma?
severe deficiency of thyroid hormone
What are some symptoms of myxedema coma?
accumulation of mucopolysaccharides in SQ and interstitial tissues... mask-like expression, puffy eyelids, thick lips and an enlarged tongue
What are rare but emergency complications of untreated or poorly treated hypothyroid disease?
Depression, diminished cognitive status, lethargy, somnolence- stupor, CV collapse, and shock which will require agressive supportive hemodynamic therapy
precipitating factors of a patient with hypothyroidism that can trigger a myxedema coma?
Acute illness, infection, surgery, anesthesia, hypothermia, hypoglycemia, chemotherapy, sedatives, opioids
treatment for myxedema coma
-AIRWAY, IVF, IV synthroid, Glucose (increase sugar), corticosteroid administration (decrease inflammation), warming blankets
-Assess/ re-assess- vitals, LOC
What is the nurses role for a patient with hypothyroidism
-obtaining blood samples and reviewing lab results
-administering medication
-assessing vital signs. Vital sign assessments can reveal potential signs of overtreatment such as tachycardia
-Advocate for and specialist if needed
-monitor client's appetite and any changes in weight
-assess clients activity level and ancourage them to increase exercise
-encourage fluids and consult with dietitian
-educate clients on taking levothyroxine as prescribed. Emphasize the importance of lifelong treatment, recognizing signs of overtreatment (rapid HR, weight loss) and managing symptoms like constipation with fiber or moisturizers for dry skin
What happens during a hyperthyroidism negative feedback loop?
1. The thyroid produces too much T3 and T4, often because of conditions like Graves’ disease, toxic nodules, or thyroiditis.
2. The excess T3 and T4 tell the hypothalamus and pituitary to stop releasing TRH and TSH.
3. As a result, TSH levels drop very low, but the thyroid ignores this signal and keeps making too much hormone.
4. Negative feedback is working, but the thyroid gland is malfunctioning and won’t “turn off.”
What is a key difference between normal thyroid negative feedback loop and hyperthyroidism negative feedback loop?
Normal: High T3/T4 shuts off TSH, and the thyroid slows down.
Hyperthyroidism: High T3/T4 still shuts off TSH, but the thyroid continues producing excess hormone despite low TSH.
What is the second most prevalent endocrine disorder?
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a form of ______
thyrotoxicosis
-Excessive levels of thyroid hormone secretion
Who does hyperthyroidism affect?
women
In hyperthyroidism, is the metabolic rate and sympathetic nervous systerm response increased or decreased?
increased
What does an increased metabolic rate and sympathetic nervous system due to hyperthyroidism cause?
increased vitals, pt. will feel anxious, jittery, on edge, and losing weight
What are the diagnostic studies for hyperthyroidism?
- laboratory assessment
-thyroid scan
-thyroid ultrasound
What does the laboratory assessment show for a patient with hyperthyroidism?
-Increased free T4 (good indicator)
-Decreased TSH
-Increased thyroid antibodies (Grave's disease)
What information does the thyroid scan show?
size, position and function
What information does the thyroid ultrasound show
-most common
-size (goiter)
-position
-nodules
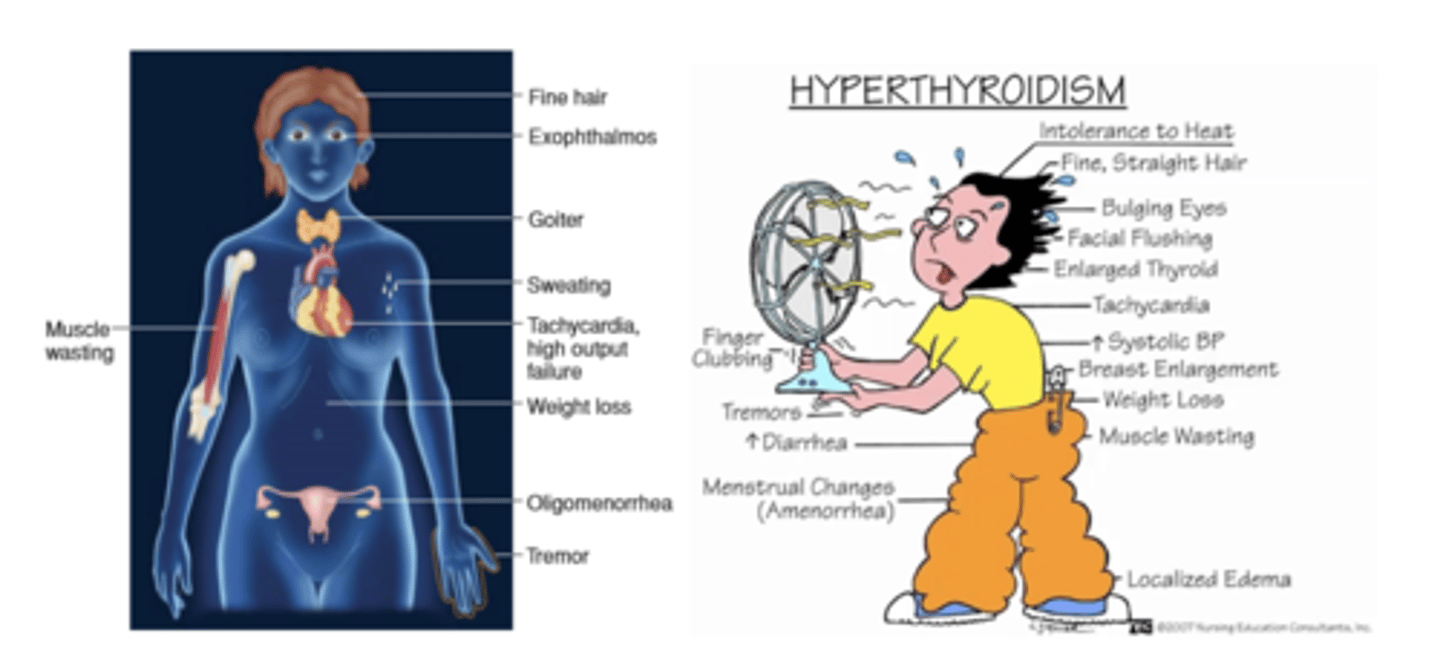
What is a common physical finding in hyperthyroidism?
Thyroid gland enlarged, positive bruit
What is a presenting symptom of hyperthyroidism?
Nervousness
What are some symptoms of hyperthyroidism related to skin and hair?
Diaphoresis, soft, fine and thin hair, heat intolerance, and warm, flushed skin
What weight-related symptom is associated with hyperthyroidism?
Weight loss even with an increased appetite
What gastrointestinal symptom can occur in hyperthyroidism?
Frequent soft stools
What are potential complications of undiagnosed hyperthyroidism?
Shortness of breath, palpitations, tachycardia, chest pain, increased systolic BP, widening pulse pressure, and dysrhythmias
hyperthyroidism symptoms
what is the most common causes of hyperthyroidism?
-Grave's disease
Grave's Disease
-autoimmune disorder
-Antibodies stimulate the thyroid to produce too much thyroid hormone- increased serum T3 and T4
What kind of people does hyperthyroidism normally occur in?
women between age 20 and 40
Most common symptoms of hyperthyroidism?
-Exopthalmos- bulging eyes
-Goiter- enlarged thyroid
Drug therapy for hyperthyroidism
-Thioamides (anti-thyroid meds) reduce excessive secretion of thyroid hormones
(won't fix hyperthyroidism but will be started and patient will end up getting thyroid removed and have to take levothyroxine forever)
What are the 2 types of thioamides used for hyperthyroidism?
-Propylthiouracil (PTU)
-Methimazole (MMI) (Tapazole)
With Propylthiouracil (PTU) and Methimazole (MMI) (Tapazole), what do you want to be aware of and monitor for?
-monitor for hypothyroidism (educate pt. on these symptoms)
-Can increase effect of Coumadin (increase INR) and decrease effect of insulin and oral antidiabetics
What is another drug used to manage hyperthyroidism, but isn't directly related to the thyroid
-Beta-adrenergic blockers decrease tachycardia, diaphoresis and anxiety
-Propanolol (Inderal)
-Does not treat thyroid
-Treats cardiac issues because it helps people with hyperthyroidism decrease HR, and diaphoresis which can decrease anxiety
-Must monitor BP and diaphoresis before and after administration
What is Iodine essential for?
the creation of thyroid hormones
What can be a cause of hypothyroidism related to iodine?
insufficient iodine can be a cause of hypothyroidism
What is a type of therapy that is used to treat hyperthyroidism?
radioactive iodine therapy
radioactive iodine therapy
destroys the overactive thyroid cells that are producing excessive hormones (Decrease T3 and T4 hormones and increases TSH)
What is a contraindication for radioactive iodine therapy?
Iodine allergies
Can radioactive iodine therapy be done as outpatient?
yes!
How many weeks can it take for radioactive iodine therapy to show improvement?
-3-4 weeks
Radioactive Iodine Therapy nursing interventions
-push fluids to flush kidneys (to get radioactive material out of the body)
-Educate: Care with contamination from saliva or urine- do not share utensils and cups
-Educate: Avoid sexual contact, sleeping in the same bed with other persons, having close contact with children and pregnant women
What is a thyroidectomy indicated for?
large goiters- tracheal or esophageal compromise, patients not responsive to drug therapy or thyroid cancer
What are the types of thyroidectomy
total or subtotal thyroidectomy
What are you concerned for after a thyroidectomy?
airway
What are other things that thyroid cancer surgery may include?
modified or radical neck dissection, and may include treatment with radioactive iodine to minimize metastasis
pre-op considerations for thyroidectomy
-achieve euthyroid state prior to surgery
-Control abnormal VS and rhythms (give a beta blocker)
-Post-operative teaching
beta blockers function
A decrease in heart rate and a decrease in blood pressure
Postoperative care for a thyroidectomy
-monitor respirations and protect airway: check O2 saturation
-Position: Semi-fowlers (30 degrees) position and support head with pillows, avoid neck flexion and extension
-proximity to throat: Assess voice but discourage talking (have the pt. hum)
-Assess pain and provide pain relief measures
-Monitor dressing for potential bleeding and hematoma formation; check posterior dressing
Why may a patient not be able to hum and what can you do about this?
because of tissue swelling around the larynx. Steroids cam be administered to decrease swelling
how can the nurse assess for hematoma formation?
light palpation around the neck
What is the nurses role for a patient with hyperthyroidism
-monitoring vital signs
-administering antithyroid medications and educating the patient about their treatment plan
-Watch for complications like thyroid storm or heart problems and provide comfort measures for symptoms like tremors or itching
-After treatments, such as surgery, nurses focus on airway monitoring and calcium level checks
What are the 4 major complications of thyroidectomy
-Hemorrhage
-Respiratory Distress
-Laryngeal nerve damage
-Parathyroid damage
Hemorrhage
-because of movement of neck
-most common within 24 hours, assess drainage
-pt. has sensation of fullness at operation site (can be a sign of internal hemorrhage)
-want to do a neuro assessment- is there blood flow to the brain?
-Want to take VS: increased HR, Decreased BP if there is bleeding
Respiratory Distress
-assess for stridor
stridor
strained, high-pitched sound heard on inspiration caused by obstruction in the pharynx or larynx
How to assess for stridor?
-listen to lung sounds
-pulse ox (only perfusion)
-RR (ventilation)
If the pt has respiratory distress, what should you have at the bedside?
trach set
Laryngeal nerve damage
hoarseness is normally temporary, assess voice every 2 hours
-have then hum, eventually have them say short words
Parathyroid damage
-decreased parathyroid hormone and calcium (no ability to secrete calcium)
-tingling of mouth, toes, and fingers- hypocalcemia
-muscle twitching (tetany)- hypocalcemia
What is thyroid storm?
severe hyperthyroidism
How serious is thyroid storm? Is it common?
life threatening event, uncommon today
What is thyroid storm due to?
injury, infection, stress
What are symptoms of thyroid storm?
-fever >101F
-tachycardia (>130bpm)
-chest pain (related to tachycardia. anxiety)
-palpitation> altered LOC > delirium > psychosis > coma (heart is squeezing but decreased cardiac output (not enough blood flow)
Thyroid storm treatment
cool pt (with ice packs in armpits and groin), tylenole, IV fluids, oxygen, meds (PTU and Tapazole)