PCB4524 UCF MOL BIO 2 EXAM 3 STUDY CARDS (ROY)
1/236
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
237 Terms
Regulation of gene expression is the basis for cellular _________________ and __________________ to the environment of any organism
1. differentiation
2. adaptation
T/F: regulation of expression of genes can be achieved at any step of gene regulation
True
in regard to regulation of gene expression what three steps are specific to ONLY eukaryotes?
1. post-transcriptional processing (RNA maturation)
2. MRNA transport/localization
3. post translational modification
in regard to regulation of gene expression, what steps can be found in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
1. Transcription
2. MRNA degradation
3. protein transport/localization
4. Protein degradation
Gene regulation in prokaryotes is mainly achieved through what three processes?
transcription, mRNA stability, and translation
In regard to prokaryotic gene regulation, what step of transcription is the gene regulated most in? (i.e. initiation, elongation, and termination)
mostly in initiation but can occur and termination as well
bacterial mRNA half-life in regard to mRNA stability is how long? (i.e. time frame)
1.5 minutes
Prokaryotic genes can be regulated in what 2 translational steps?
1. initiation
2. termination
What are the three steps of transcription initiation?
1) Recognition/binding (RNA binds to promoter)
2) Melting open DNA duplex (closed to open complex)
3) Promoter escape
Transcription driven by regulated promoters can exhibit what three different levels of expression?
1. basal transcription level,
2. repressed transcription level,
3. activated or induced transcription level
When there is NO activator or repressor present during initiation of transcription what level of gene expression is typically seen?
A constitutive expression called basal level of transcription (weak binding)
Repressor binding sites are also called:
operators
T/F: Were oppressors physically block RNA polymerase from binding
True (no binding)
Most activators increase the binding of RNA polymerase by what type of binding?
cooperative binding (i.e. recruitment)
what is recruitment in regard to transcriptional activators and RNA polymerase?
- The activator interacts with the DNA near the promoter and RNA polymerase
- deactivator brings the RNA polymerase closer to the promoter) = STRONG BINDING
T/F: transcription is activated is also the same as saying “transcription is induced”
True
T/F: bound repressor facilitates transcription and bound activator inhibits transcription
False, bound repressor = inhibits transcription & bound activator = facilitates transcription
what is the name of the molecule that binds during repression or activation?
The signal molecule is an effector
T/F: Some activators can be activated by systems that sense conditions outside of the cell
True, like TCS (two-component system)
What are two systems that since conditions outside of the cell?
1. two-component systems
2. histidine kinase (HK) /response regulator (RR)
What is the process of signal transduction?
Process by which a signal is transmitted through a cell which results in cellular response
Histidine kinase in the TCS, has ____________ proteins and performs ____________ which transfers a phosphate group from HK’s histidine residue onto ___________ residue of the response regulator
1. Transmembrane
2. Autophosphorylation
3. aspartate
T/F: Response regulators are often repressors and not activators
False, they are most often activators of reg of transcription
T/F: Two components systems enable bacteria to sins and adapt to their environment
True
T/F: bacteria generally exhibit up to 100 two-component systems
False, ~30 TCS
The lactose operon is positively regulated by what molecule?
Lactose
The lactose operon is negatively regulated by what molecule?
glucose
What is an operon?
Cluster of genes control by single promoter
T/F: Both CAP and the lac repressor are ____________-binding proteins and each binds to a specific site on ____________ at or near the lac promoter
1. DNA
2. DNA
what is catabolite repression?
A global regulatory mechanism that inhibits the expression of genes for the use of secondary carbon sources (like lactose) when a preferred carbon source is present (like glucose)
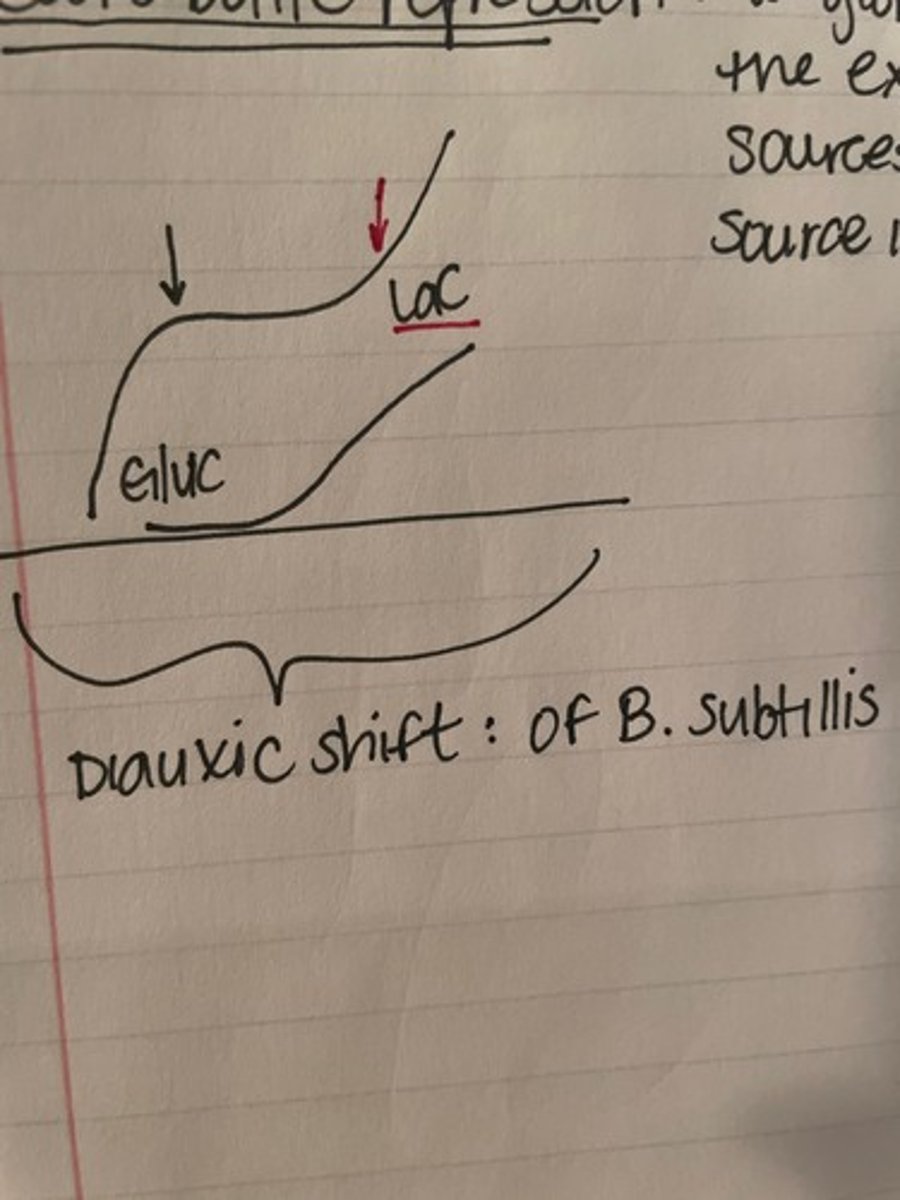
what is a diauxic shift? And what is an example?
- when the curve shifts from the preferred carbon source to the 2ndary carbon source (i.e. glucose —> lactose)
- seen in Bacillus subtillis
T/F: The presence or absence of sugars controls the lac operon activity
True
T/F: Both CAP and lac repressor are DNA binding proteins and each binds to a specific site at or near the lac repressor
True
What does CAP stand for?
catabolite activator protein
When can the lack repressor bind to DNA and repress transcription?
Only in the absence of lactose
When can CAP bind DNA and activate the lac of genes?
only in the absence of glucose
What is the true inducer of the lac operon?
allolactose
Lac__ is the repressor of the lac operon
LacI
The lacZ gene encodes the enzyme: _____________
beta-galactosidase
What does beta-galactosidase do?
cleaves lactose into glucose and galactose
LacY gene encodes: ___________ ____________
lactose permease
What does lactose permease do?
A protein that inserts into the cell membrane and transports lactose into the cell
The lacA gene encodes: _______________ ____________
galactose acetyltransferase or thiogalactoside transacetylase
What does galactoside acetyltransferase do?
rids the cell of toxic thiogalactosides that also get transported in by LacY
CAP binds DNA as a ________ and the lac repressor binds DNA as a __________
1. dimer
2. tetramer
T/F: The lac operator is a palindrome
True
Various DNA binding proteins are used for recognition of specific DNA sequences which is achieved thru a conserved region (a secondary structure) called a:
helix-turn-helix
LacI is a ______________ protein and has ____ operators
1. homeotetrameric
2. three
What are the names of the 3 operators in the LacI repressor?
1. auxiliary operator
2. major operator
3. 2nd auxiliary operator
What two transcriptional activators work through allostery rather than recruitment?
1. NtrC
2. MerR
What transcriptional activator is involved with nitrogen metabolism?
NtrC, does so by inducing a conformational change in a pre-bound RNA polymerase > triggers change to open complex
What does adenylate cyclase synthesize?
cAMP and pyrophosphate as a byproduct
What type of system is the Phosphotransferase System (PTS)?
a glucose-specific transport system
What does the PTS (Phosphotransferase system) regulate?
catabolite expression
The PTS controls the synthesis of: ___________
cAMP
What is inducer exclusion?
when glucose transported into the cell leads to the formation of a protein intermediate that binds to the lactose permease and prevents the transport of lactose into the cell
what to transcriptional activators work by allostery?
1. NtrC
2. MerR
NtrC is involved with: _________ ___________; MerR is controls the expression of a gene involved with ___________ ___________.
1. Nitrogen Metabolism
2. Mercury Resistance
T/F: attenuation is an RNA regulatory mechanism controlling early termination of transcription at a site located before the first structural gene (in the 5'UTR region)
True
T/F: Riboswitches can be used as a type of an continuation mechanism in RNA regulation
True
Signa factors activate a: __________
regulon
Sigma factor cascades is a type of: _____________ ___________
regulatory network
What are sigma factor cascades?
where the activation of one sigma factor causes the activation of another save a factor and so on and so forth (sigma70 > sigma32 for hear shock)
Activators and oppressors are regulatory: ____________
networks
what is a regulon? What's an example?
A group of genes regulated by the same regulator seen in sigma-E-dependent extracytoplasmic stress response
Sigma factors are organized in a cascade during expression of what phase?
Lytic phase
When the sigma-E regulon is expressed, what happens to the envelope associated functions?
1. folding & degradation
2. biosynthesis
assembly of LPS and OMP's
3. sRNA (inhibit OMP's)
4. Other IMP, OMP, lipoproteins
when the sigma-E regulon is expressed, what happens to to cytoplasmic functions?
1. transcription
2. translation
3. replication
4. DNA/RNA modification
5. cell division
Sigma factor cascades allow what type of gene regulation?
temporal regulation of genes
What are 2 examples of temporal regulation of genes?
1. Life cycle of bacterial viruses like: bacteriophages (T4, T5, T7)
2. Sporulation of B. subtilis
_________ involves the ______________ Of a vegetative bacterium into a mother cell that is lysed in a sport that is released
1. sporulation
2. differentiation
The steps of sporulation are regulated by __________ factor cascade
sigma
The early genes of phage ____________ are transcribed by host RNA polymerase
SPO1
In the expression of sigma factors during the lytic phase, one of the early genes codes for a __________ sigma factor that causes RNA polymerase to transcribe the middle genes
viral
What are the two lifestyles of the lambda phage?
lytic or lysogenic
The lacZ gene encodes the enzyme: __________________
beta-galactosidase
What is the definition of a prophage?
is a phage genome covalently integrated as a linear part of the bacterial chromosome
Induction refers to the ability of bacteria or yeast to synthesize certain enzymes only when their ____________ are present this is applied to gene __________ and it refers to switching on transcription as a result of interaction of an inducer with a regulatory signal
1. substrates
2. expression
The excision step in an excision - repair system consist of removing a __________ stranded stretch of DNA by action of a ___________ exonuclease
1. single-stranded
2. 5' —> 3'
What is a virion?
complete virus particle outside the host cell
T:F: Bacteriophages are viruses that infect bacteria
True
What is lysogenic induction?
When a prophage switches from lysogenic to lytic growth, its called this
The lambda repressor CI is: a _________ of PR and an ________ of PRM
1. repressor
2. activator
The __________ cycle is the default state of the lambda phage
lytic
T/F: The Cro only represses transcription like the lac of repressor
True
Cro stands for control of repressor's operator and represses:
PRM
T/F: The cooperative binding of the lambda repressor (CI) allows greater binding (and greater effects) from small changes in concentrations
True
___________ concentration of lambda repressor turns off its own transcription
higher
T/F: The CI gene stabilizes the lysogenic state
True
T:F: Epigenetic gene regulation allows inheritance of expression pattern or phenotype in absence of the initial stimulus and without alteration of the genetic sequence
True
In eukaryotes, promoters display proximal and _______ regulatory elements
distal
where are distal and proximal elements located?
distal - located within 400 kb (can be up or downstream of promoters
proximal - located near 200 bp (are upstream of promoters)
Which [distal or proximal] elements are orientation-dependent?
proximal elements
Enhancers are DNA elements that bind specific __________
activators
Enhancers are ______ - 1500 bp long region
50
Activators are proteins and some attract the transcription _________ complex
initiation
Some activators activate _________ remodeling systems
chromatin
T/F: Silencers are only found in distal elements
False, distal and proximal
DNA insulators block the effect of _________
enhancers
CpG islands regulate via DNA __________________
methylation