organic chemistry 3: bonding
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
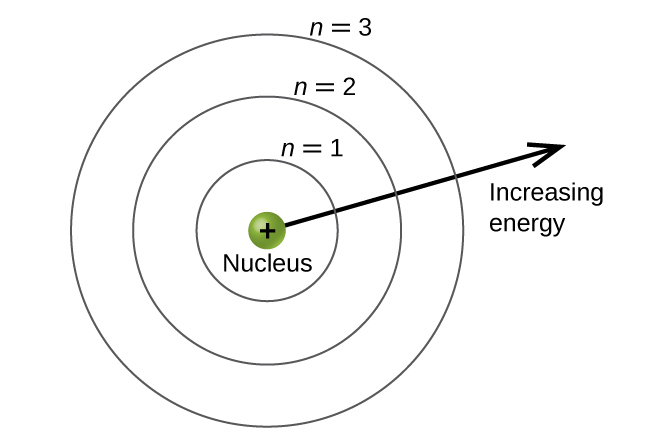
Quantum number n is the [...] quantum number and gives the electron [...]
principal
energy level or shell number
1,2,3….
expect doe d- and f-orbits the shel # matches the row of the periodic table

Quantum number l is the [...] quantum number and gives the [...] of an orbital
azimuthal
3D- shape (subshell)
0, 1, 2, …, n-1
0 = s orbital
1 = p orbital
2 = d orbital
3 = f orbital
4 = g orbital

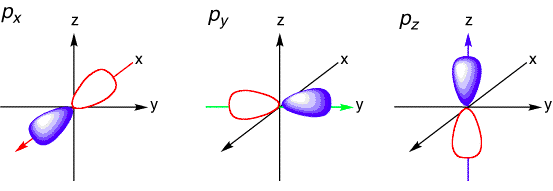
Quantum number ml is the [...] quantum number and gives the orbital [...]
magnetic
sub-type
integers -L to +L
the orientation of electrons orbitals with respect to the three axes in space x, y,z
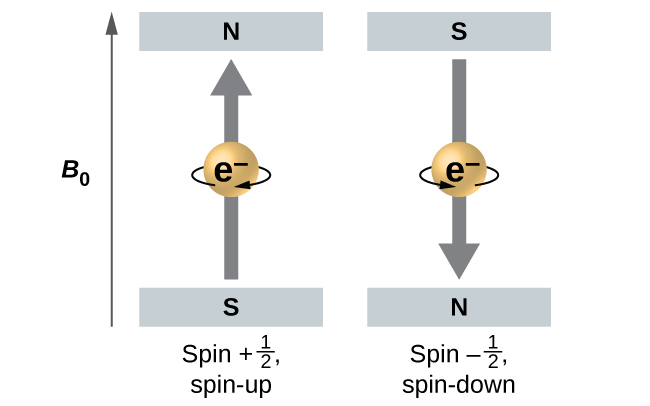
Quantum number ms is the [...] quantum number and gives the [...] of the electron
spin
electronic spin
+1/2, -1/2
[...] orbitals are obtained by combining the [...] orbitals from the individual atoms that make up the molecule
molecular, atomic
molecular orbital theory is able to explain why some bonds between atoms are observed to be in between a single and aboudle bond valence-bond theory, the more traditional theory cannot explain these “hybridized” bonds
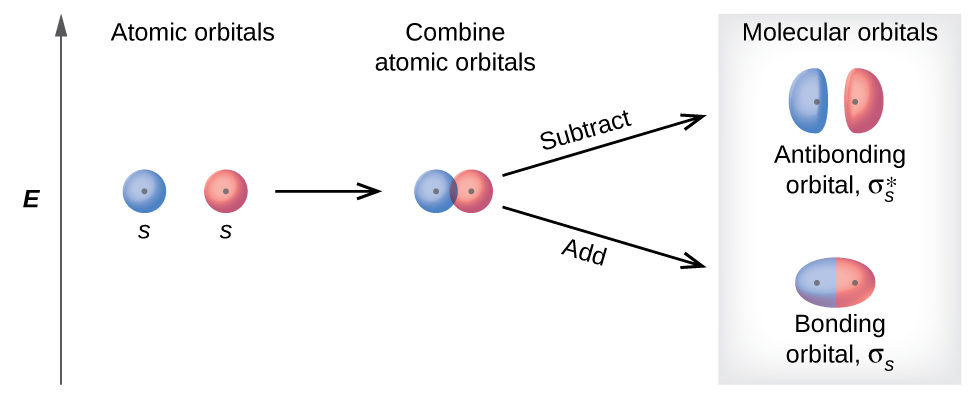
Bonding orbitals are created by overlap of atomic orbitals of the [same or opposite] sign
same

Antibonding orbitals are created by overlap of atomic orbitals of the [same or opposite] signs
opposite

![<p>Give the number of sigma and pi bonds for each bond order</p><p><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[...]</strong></span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9f919f64-caca-4227-8c4c-93e0ca7cdd9f.png)
Give the number of sigma and pi bonds for each bond order
[...]
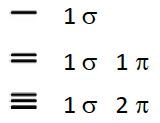
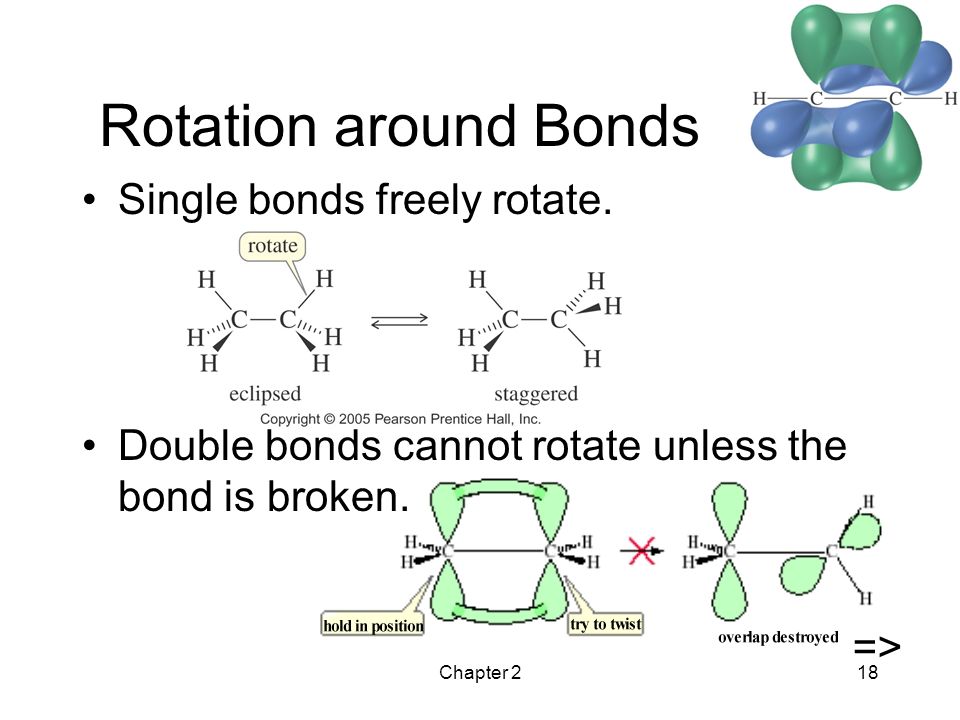
Multiple bonds are [more or less] flexible than single bonds
less
this is because rotation is not permitted in the presence of π bond
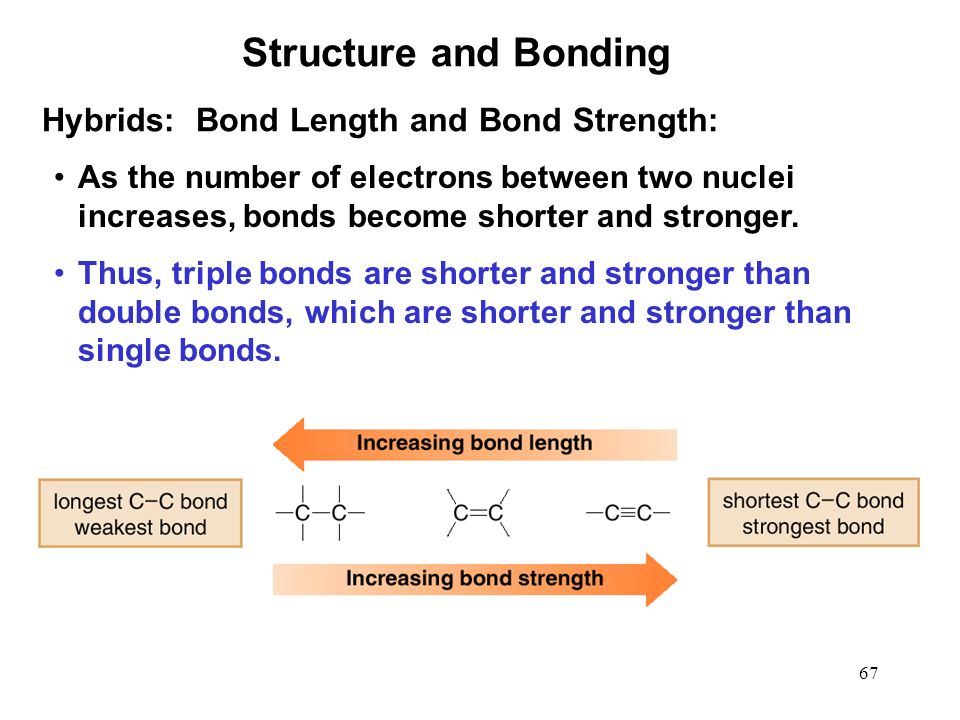
Multiple bonds are [shorter or longer] than single bonds
shorter
[...] is the idea that atomic orbitals fuse to form newly hybridized orbitals
orbital hybridization
included sp3 sp2 sp
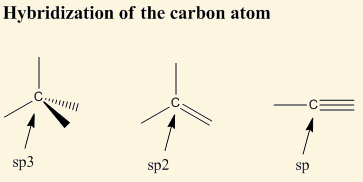
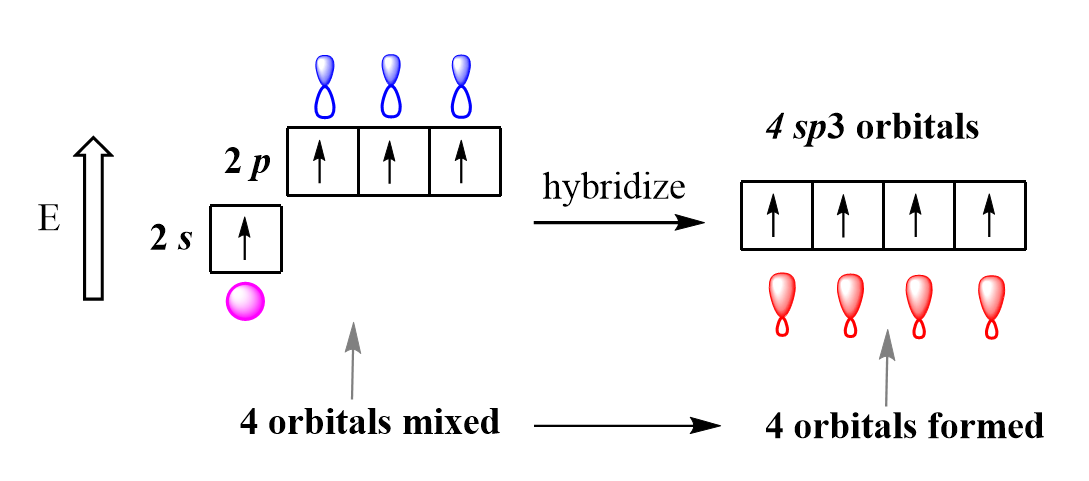
sp3 hybridization is [%] s character and [%] p character
25% s character and 75% p character
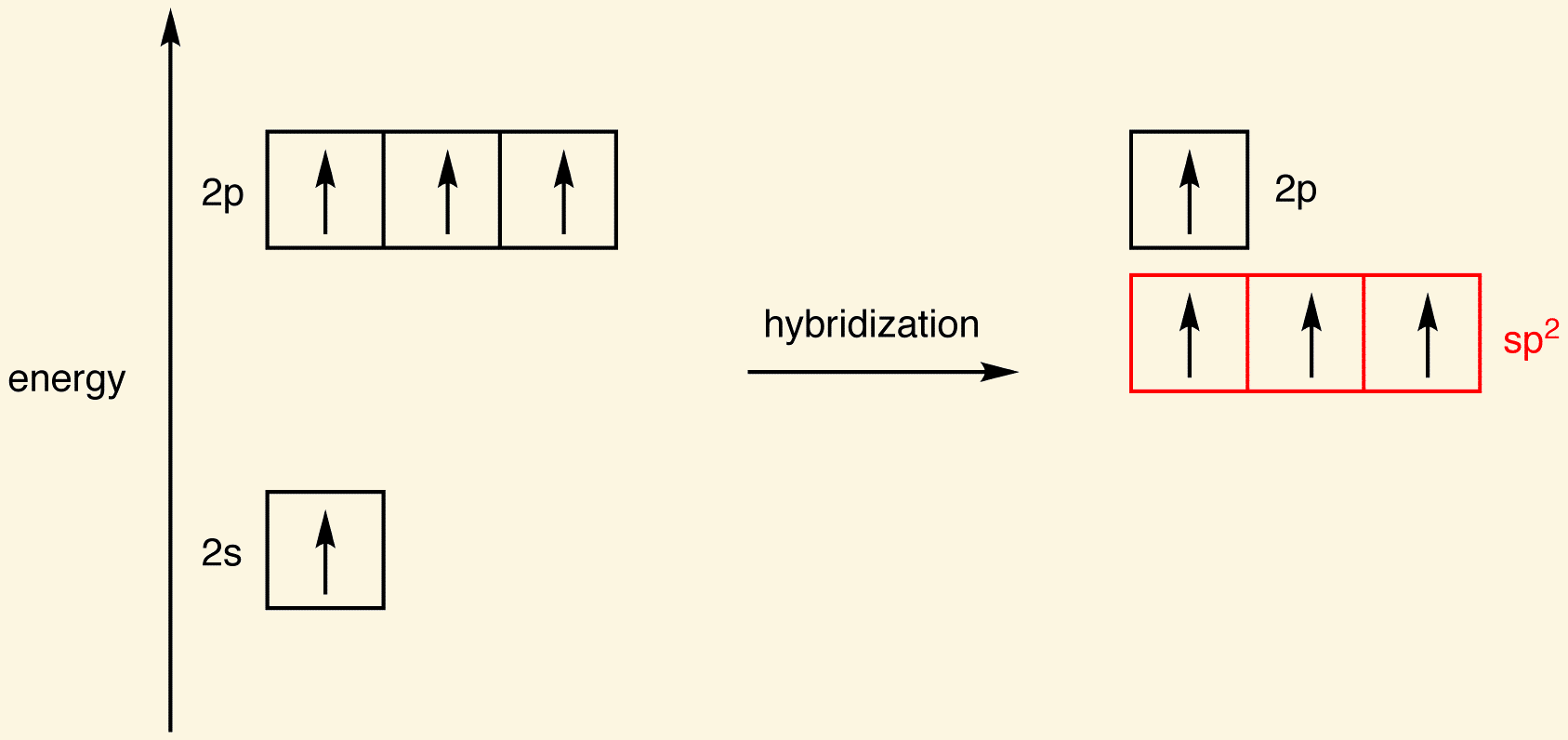
sp2 hybridization is [%] s character and [%] p character
33% s character and 67% p character
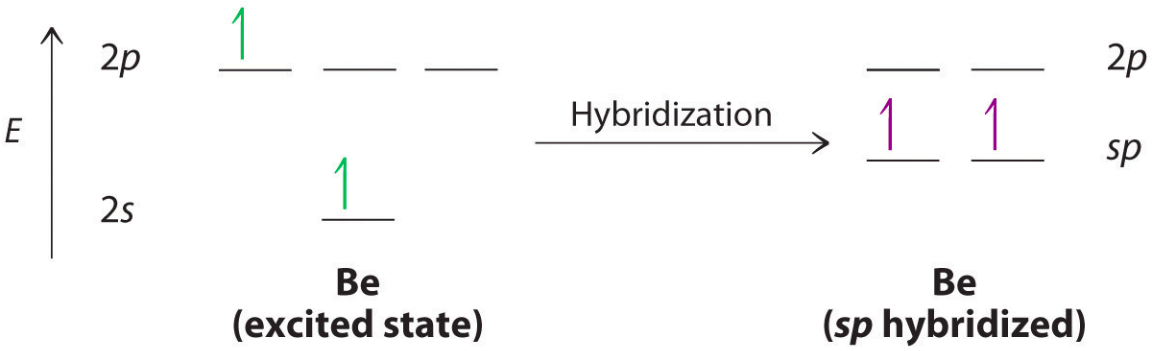
sp hybridization is [%] s character and [%] p character
50% s character and 50% p character
[...] occurs when single and multiple bonds alternate
conjugation
this creates a system of unhybridized p orbitals down the back the backbone of the molecule through which p electrons can delocalize
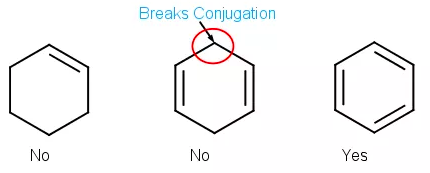

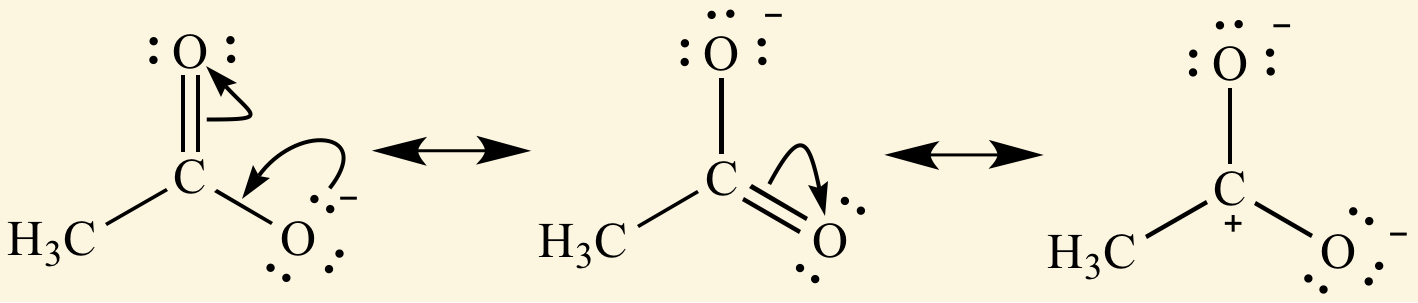
[...] is the delocalization of electrons in molecules that have conjugated bonds
resonance