Biochem Exam 2
1/327
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
328 Terms
DNA is the
genetic molecule
nucleotides are comprised of
a base, (deoxy)ribose (sugar) and PO4 (phosphate)
in nucleotides, sugar-phosphodiester forms a polynucleotide ______
backbone
nucleotides can be _____ stranded or _____ stranded
single, multi
base stacking in nucleotides
stabilizes polynucleotide structures
purine and pyrimidine bases pair via
hydrogen bonding
base conformation affects ________ between bases
hydrogen bonding
________ affects nucleic acid tertiary structure
sugar pucker
DNA structure
double stranded in cells
2 stands form an anti-parallel, right handed helix
RNA structure
single stranded in cells
widely variable secondary structures
multi-functional molecule
nucleotide structure is essential to
DNA based activities
ex: genome replication, gene expression
phosphodiester bonds link nucleotides in
the polynucleotide backbone
glycosidic bonds link the base to the
ribose ring
hydrogen bonds form between
bases
5'=
the 5' carbon of a nucleotide
3'=
the 3' hydroxyl of a nucleotide
sugar pucker determines
the distances between phosphates in the phosphodiester backbone
the conformation of the base (syn vs anti) determines
how nucleotide bases interact
nucleotides are added in a
5' to 3' manner
hydroxyl initiates
nucleophilic attack
nucleic acids are polymers built from
nucleotides
two base types
purine and pyrimidine
Purine structure
shorter word=bigger structure
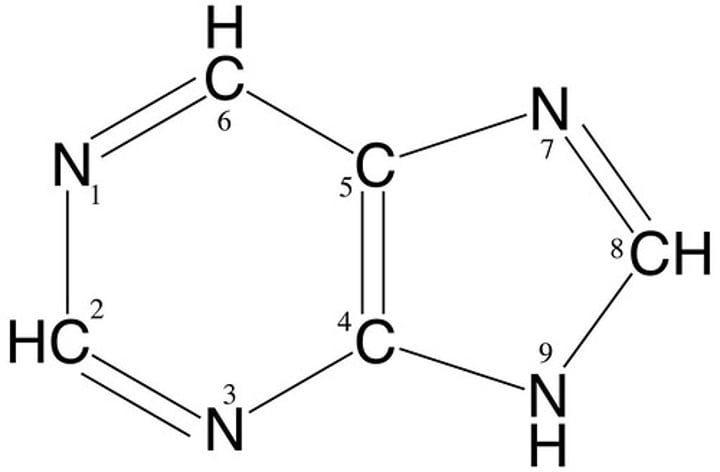
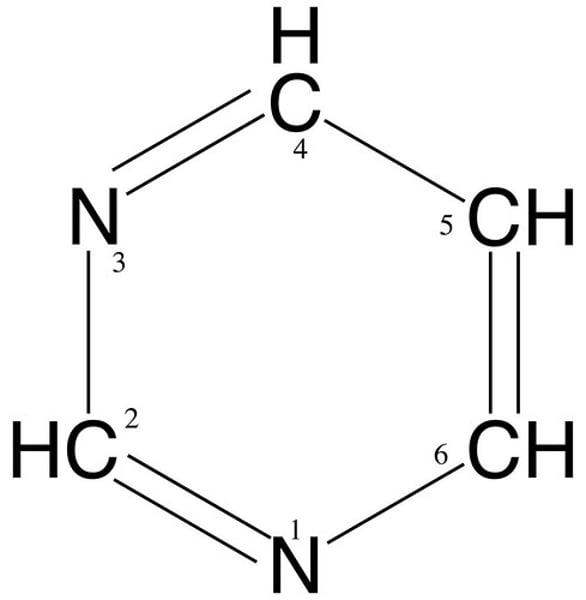
pyrimidine structure
longer word=shorter structure
The purine bases are
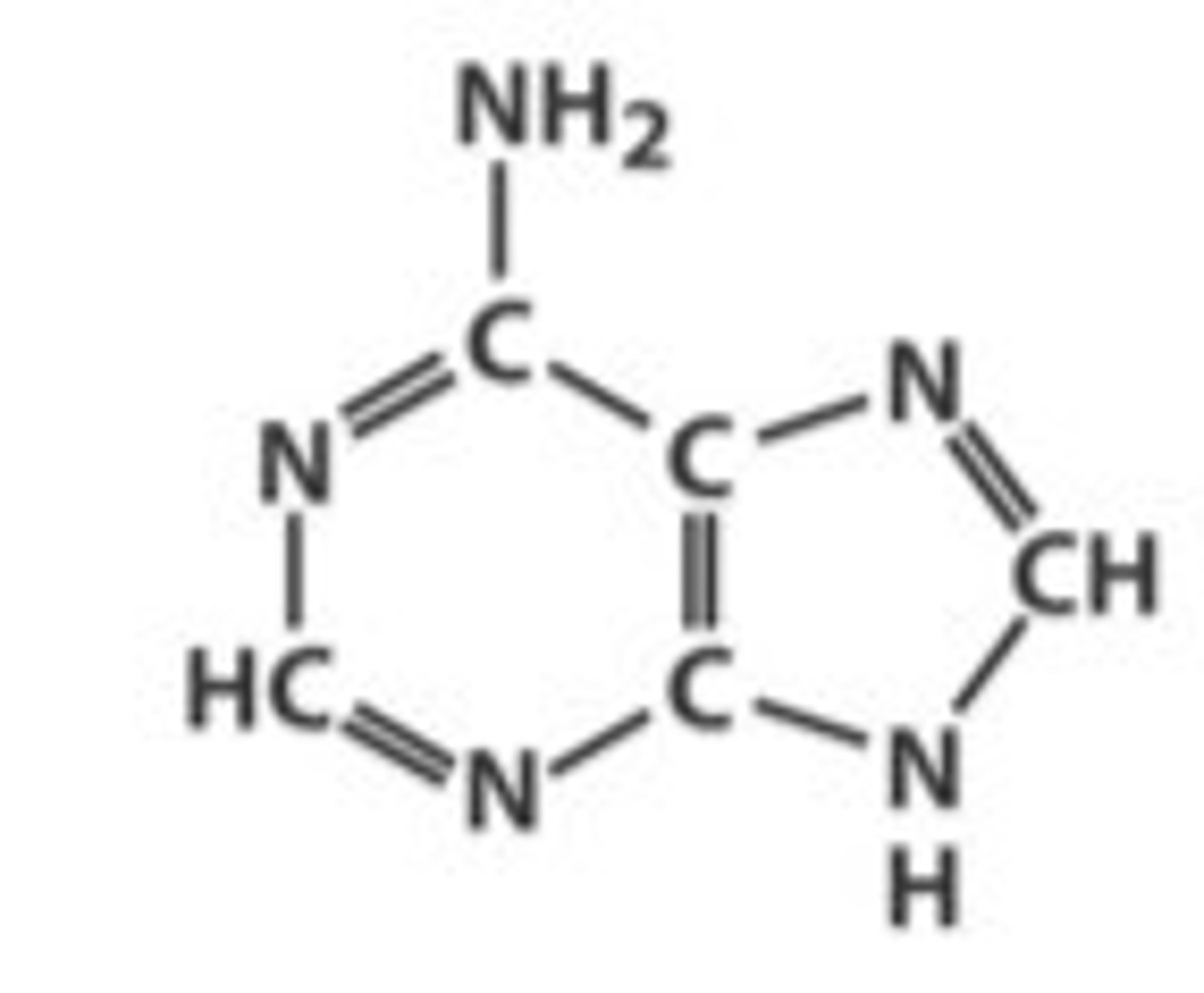
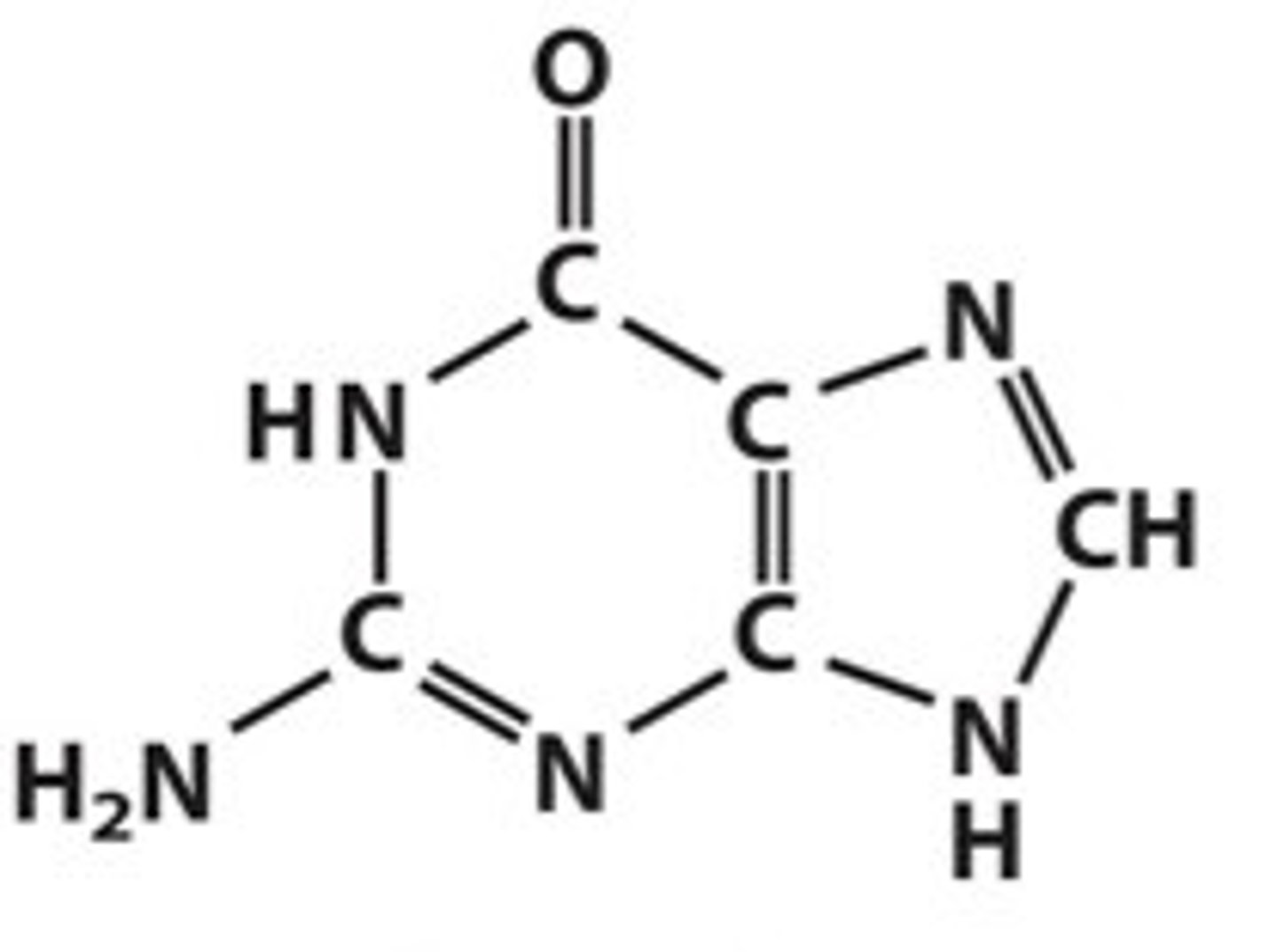
Adenine and Guanine
The pyrimidine bases are
cytosine, thymine, uracil
Adenine
Guanine
Cytosine
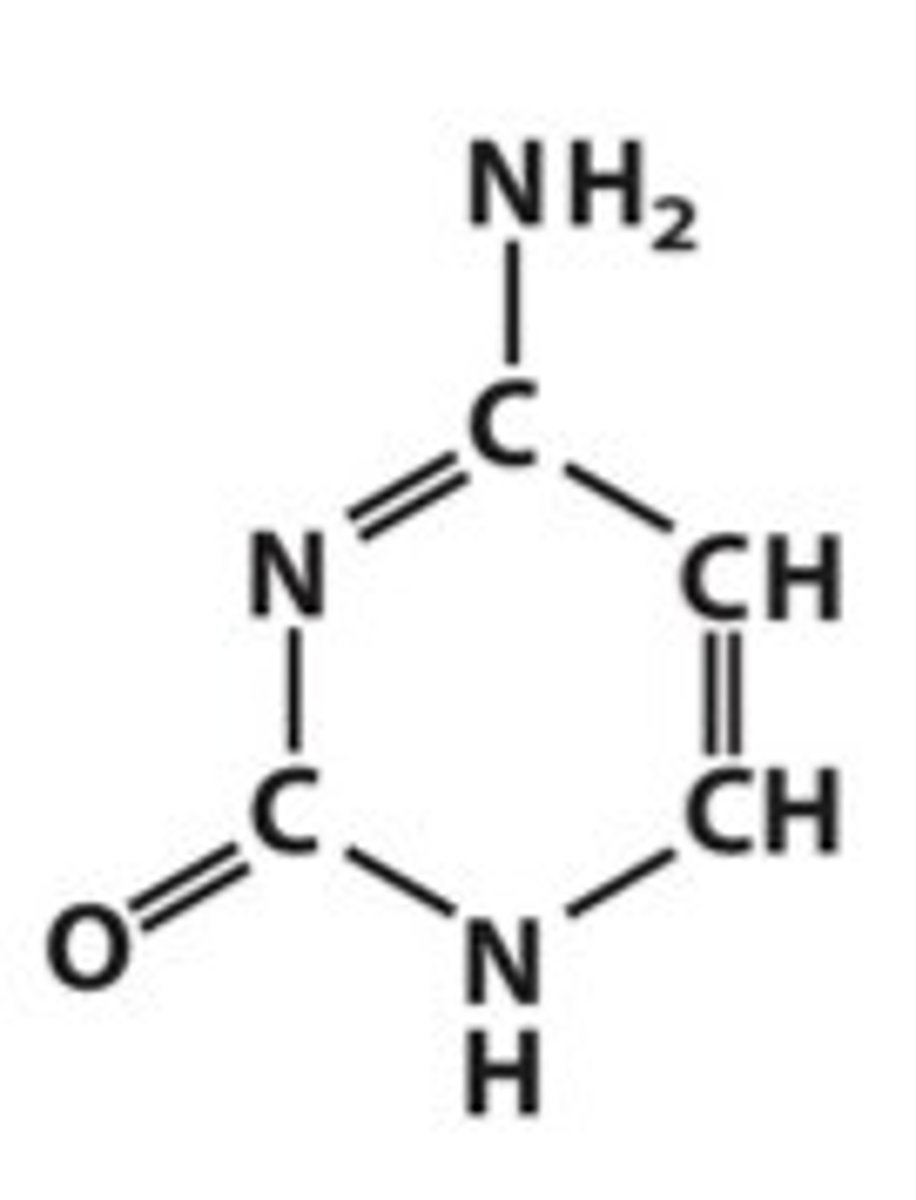
Thymine (DNA)
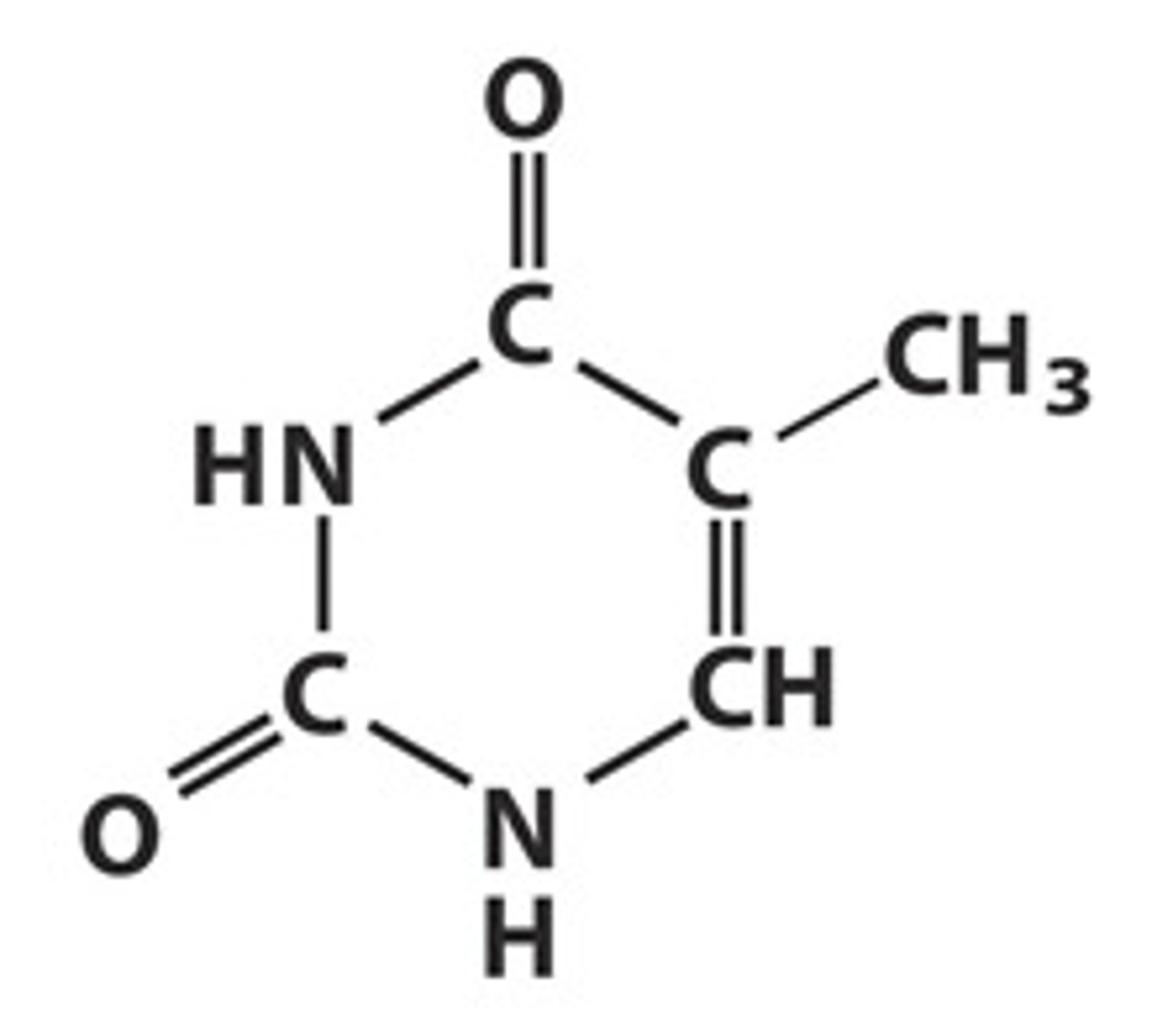
Uracil (RNA)
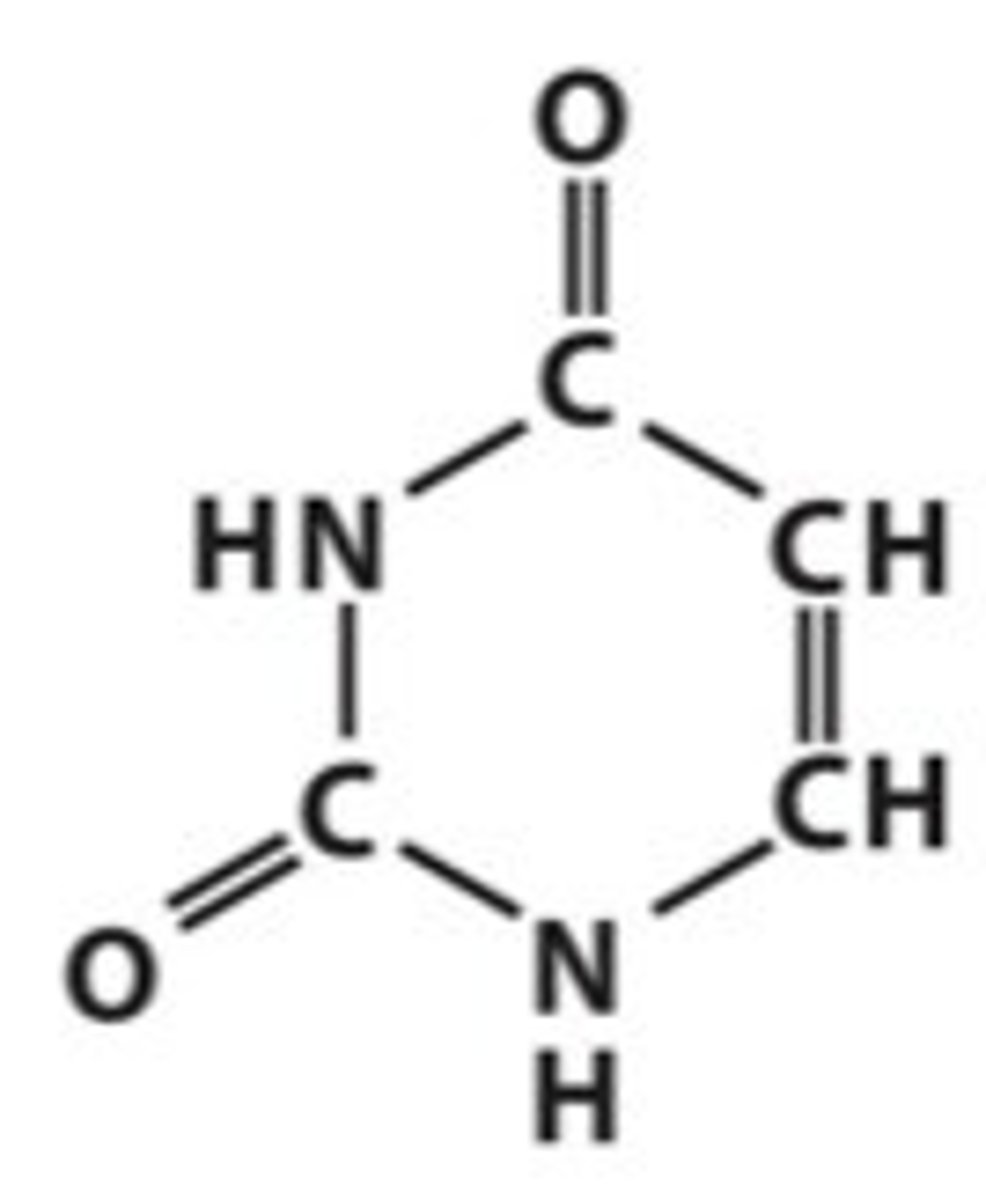
The presence or absence of the _______ is the defining difference between RNA and DNA
2' OH
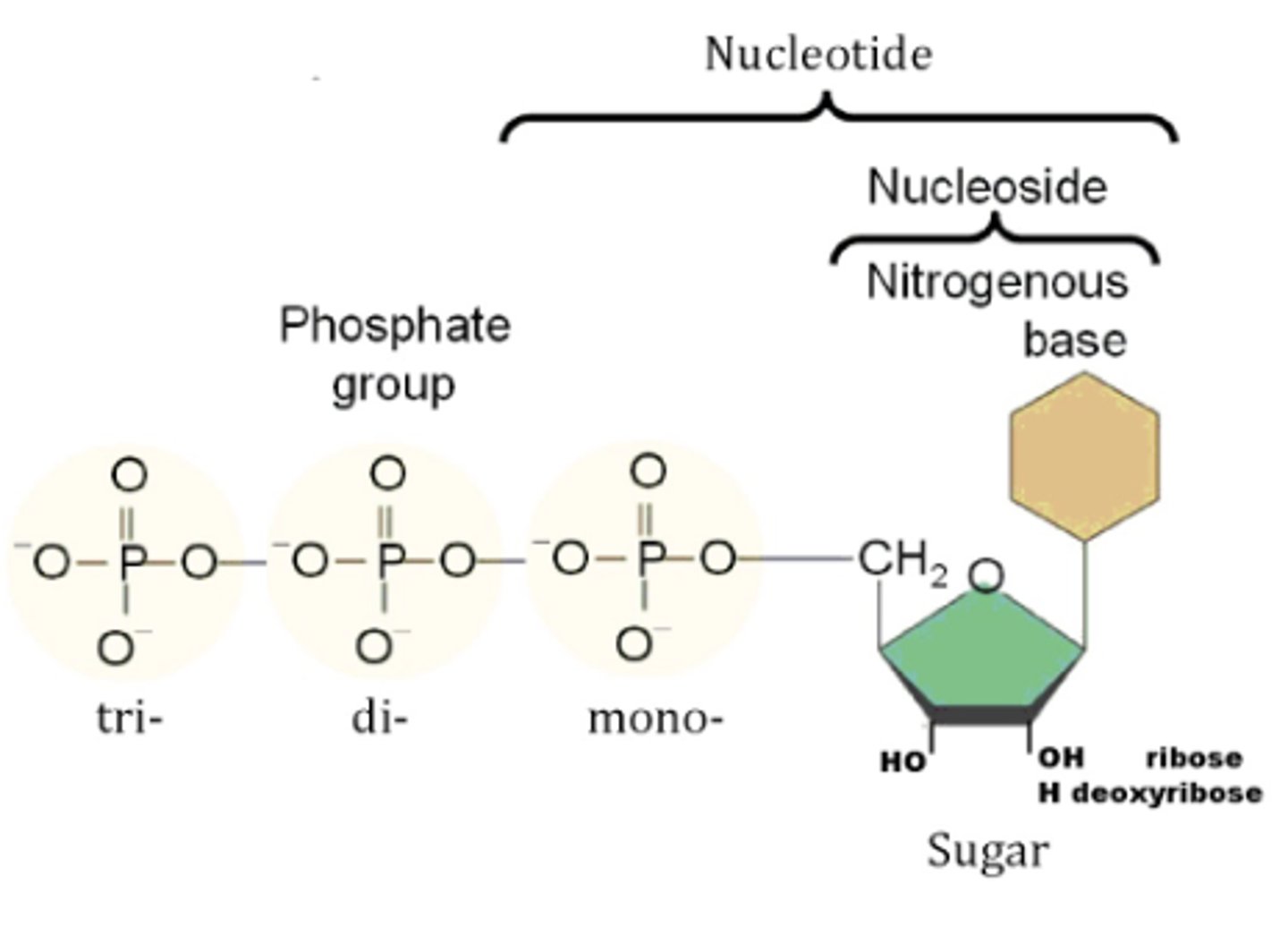
N-glycosidic linkage
the connection between the base and the sugar occurs between the 1' position on the sugar and a nitrogen on the base
nucleoside
base + sugar
DNA uses
A, T, C, G
RNA uses
A, U, C, G
nucleotides are joined together through
phosphodiester bonds
the nucleic acid polymer grows in the
5' to 3' direction
-nucleic acids will always be added on the 3' end
Core mechanism of joining nucleotides together
1: base activation of 3' OH
2: nucleophilic attack of 3' OH on the alpha phosphate of a nucleoside triphosphate
3: pyrophosphate acts as a leaving group to drive the rxn forward
nucleotides can interact through
complementary base pairing
Watson-Crick-Franklin Base Pairs
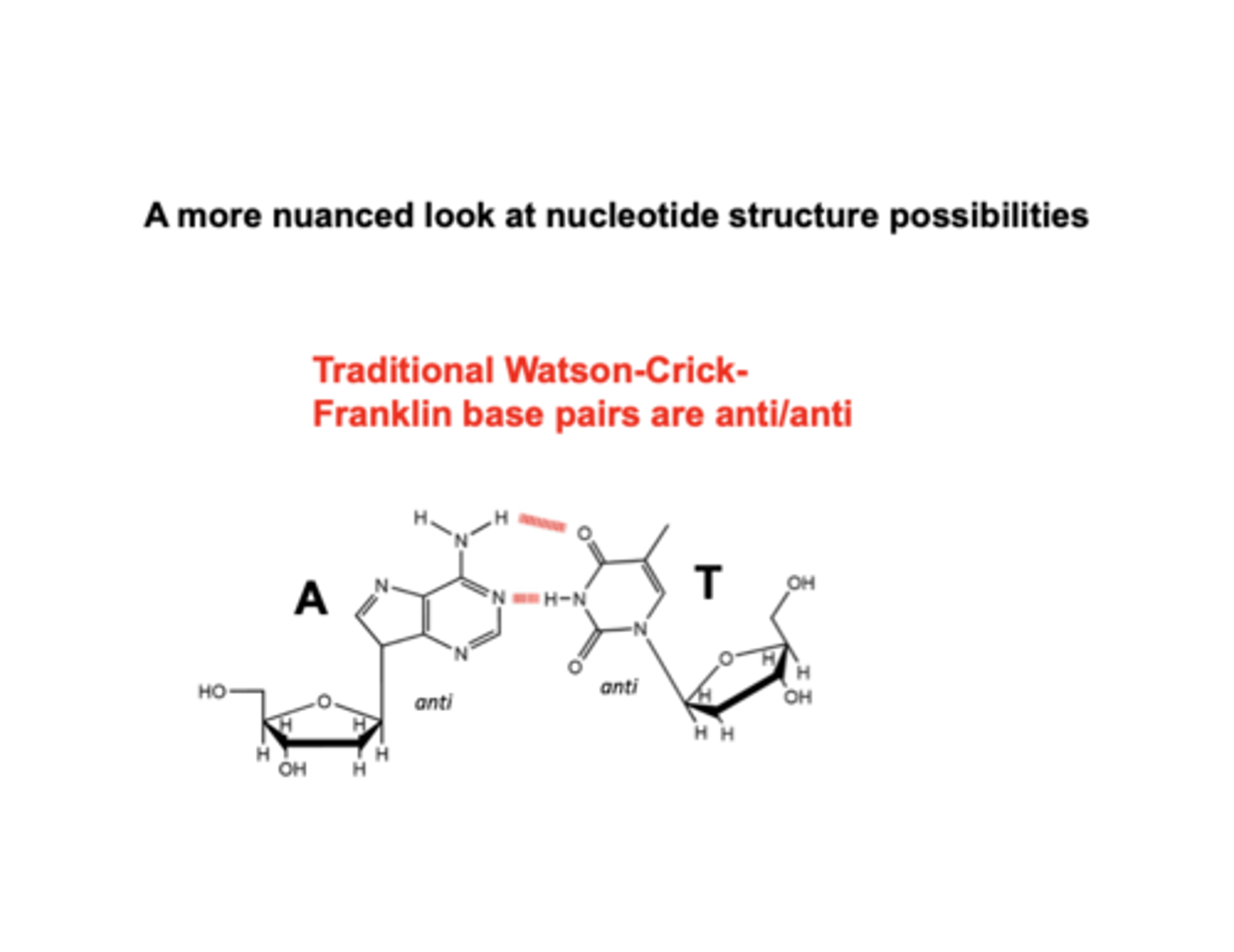
In watson-crick-franklin, adenine forms ______ with thymine
2 H bonds
In watson-crick-franklin, guanine forms ______ with cytosine
3 H bonds
A/T and C/G base pairing interactions are completely
orthogonal
-they will not pair with something that isnt their match
B-form dna double helix
right handed dna helix, 2 antiparallel strands, held together via hydrogen bonding in A-T and C-G base pairs
*****asymmetrical
Major groove (in b-form DNA) is __________
wide and deep
minor groove (in b-form DNA)
shallow and narrow
proteins can bind to dsDNA through the ________ in a sequence specific manner
major groove
C3'-endo
position 3 is up
-RNA
-tighter
C2'-endo
position 2 is up
-DNA
-looser
the ____ conformation of a nucleotide is more energetically favorable
anti
Only _________ nucleotides can adopt the syn conformation.
purine
(A and G)
traditional watson-crick-franklin base pairs are
anti/anti
Hoogsteen base pairs
less common than watson-crick
occurs when one base is in the syn conformation
allows 3-4 strands to be present
found in damaged DNA
single stranded nucleic acid can
fold to form a secondary strcuture
genome
all of an organism's genetic material
double stranded dna=
2 stands annealed together
separation of 2 dna strands requires
hydrogen bonds to break
A/T base pairs are ____ to break than C/G base pairs
easier
2 H bonds vs 3 H bonds
Topoisomerase
corrects "overwinding" ahead of replication forks by breaking, swiveling, and rejoining DNA strands
In eukaryotes, DNA is further packaged by wrapping the DNA around proteins called ______ to form _______
histones, nucleosomes
nucleosomes are further compacted into _______ in _______ chromosomes
chromatin, linear
chromatin is good for
storage
acetylation of histones makes DNA
more accesible (euchromatin)
methylation of histones makes DNA
less accessible (heterochromatin)
3' OH attacks
5' triphosphate
why is the genome (the principal storage) DNA and not RNA?
RNA is more susceptible for destruction
The 2' OH can lead to breakdown of the chain
What sets the relative stability of the two strands being annealed together versus separated as free strands?
the annealed form is good for long term storage but also need to separate the strands to be able to make use of base-pairing for replication, transcription etc
which base pairs form stronger interactions?
C/G
3 hydrogen bonds
closer together in the alphabet, so stronger bond
Tm=
temperature at which the helix is half double stranded and half single stranded
-50% denatured
stable helix=
high Tm
unstable helix
low Tm
more _____ base pairs makes it harder to separate bonds
C/G
-bc they have more hydrogen bonds per pair
melting
process of unwinding strands of DNA
topology
number of cross-overs in the material
topology of a DNA fragment is described by the
Linking number (Lk)
Lk=Tw+Wr
Linking number=twist+writhe
DNA in the B-form configuration has an ______ to it
intrinsic twist
DNA being in a B-form geometry is a very
energetically favorable state
if the change in Lk=0, then
the DNA is relaxed
if the change in Lk
underwound, negative-supercoiling
if the change in Lk>0, the DNA is _________ and _________ will result
overwound, positive-supercoiling
supercoiled DNA is more ______ than relaxed DNA
compact
if you were to cut the dna structure, add or remove some twist you could change the
linking number
what can change the structure and add/remove some twist?
topoisomerase
as a general rule, most DNA inside the cell is
negatively supercoiled
topoisomerases are also needed to resolve _______ that develops when the genome is locally unwound for DNA replication or transcription
supercoiling
the linking number cannot be changed by
deformation alone
topoisomerases play important roles in DNA _______, and dealing with disruptive structures that form during _______ and ________
compaction, replication, transcription
dna wraps around _____ proteins to form nucleosomes
histone
histone modification impacts
chromatin compaction
euchromatin vs heterochromatin
Euchromatin - available for transcription;
Heterochromatin - not available for transcription
packaging DNA into chromatin makes it
inaccessible
histone acetylation makes DNA
more accessible
histone methylation makes DNA
less accessible
topological constraints on dna cause it to ______ if you try to unwind or overwind it
supercoil
base activation of the 3' OH leads to
nucleophilic attack on a nucleoside triphosphate
DNA polymerases are the enzymes that catalyze
DNA synthesis
DNA polymerases require a
primer to extend off
DNA synthesis requires 3' OH in order to add the next
dNTP