Chapter 12 - Conception & Fetal Development
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Conception
Union of a single egg and single sperm
Oogenesis
Egg (ovum) formation
begins during fetal formation in the female
degenerative process until menopause
Zygote
united egg and sperm
How is a trisomy/down syndrome produced?
Gamete with 24 chromosomes unites with normal gamete with 23 chromosomes
How is monosomy produced?
Gamete with 22 chromosomes unites with a gamete with 23 chromosomes
Zona Pellucida
Thick, inner layer of the ovum
Corona Radiata
Outer layer of the ovum
How long is an ovum considered fertile after ovulation?
24 hrs
Average viable time for sperm to be viable in a woman’s vagina
2 to 3 days
Capacitation
removal of protective coating from the head of the sperm
Hylauronidase
enzymes that allow the sperm to penetrate the protective layers of the ovum before fertilization
Where does fertilization take place in?
In the outer third of the fallopian tube/ampulla
Cleavage
Mitotic cellular replication
Zygote destinations
In the ampulla (outer third) of the tube for 1st 24hrs
Propelled by ciliary action
Travels thru tube into the uterus
Morula
Solid ball of cells surrounded by the protective zona pellucida
Further development as it flows freely within the uterus
Trophoblast
Gives rise to the placenta
Embryoblast
Gives rise to the embryo
Blastocyst
Structure of the developing embryo
What happens to the zona pellucida at the implantation site?
It degenerates
Describe what goes during implantation?
Trophoblast secrete enzymes to set into the endometrium until the blastocyst is covered
Endometrial vessels erode →
Implantation bleeding
Spotting
Bleeding @ the time of 1st missed menses
Chorionic Villi
Finger like projections out of the trophoblast
Obtain oxygen and nutrients from maternal blood
Dispose of waste & co2
Decidua
Name for the endometrium after implantation
Length of pregnancy (how is it measured)
From 1st day of LMP until day of birth
Intrauterine Developmental Stages
Ovum Stage: conception to day 12
Embryonic Stage: day 15 to 8 weeks
Fetal Stage: 9 weeks until end of pregnancy
Embryonic Disk & Layers
Endoderm
Mesoderm
Ectoderm
Ectoderm (Components)
CNS
Epideremis
Glands
Nails
Mesoderm (Components)
Bones/teeth
Muscles
CV/Spleen
Urogenital
Endoderm (Components)
Respiratory
Digestive
Glandular Cells
Roof of yolk sac?
Stage of the Embryo
Around 3cm
Critical time in the development of organogenesis & main external features
Areas with rapid cell division at risk for malformation by env.teratogens
At the end of 8 weeks = human igs
Chorion
Develops from the trophoblast
Increases in size and complexity
Covers fetal side of placenta
Contains major umbilical blood vessels
What happens to the chorionic villi?
Atrophy & degeneration → Smooth chorionic membrane
Amnion
Inner cell membrane from the cells of the blastocyst
Amniotic Cavity
Cavity between inner cell mass and outer layer of cells (trophoblast)
What does the embryo do to the amnion?
Draws it around itself and forms a fluid filled sack
Volume of amniotic fluid
Increases weekly
Steadily decreases after term
Functions of Amniotic Fluid
Fetal Thermoregulation
Source of oral fluid & waste storage
F&E balance
Fetal movement
Cushions from trauma
Antibacterial factors
Prevents membrane tangling
✅ for symmetric growth
Otherwise, amputations/malformations
Oligohydramnios
< 300mL of amniotic fluid
Fetal renal abnormalities
Hydramnios/Polyhydramnios
> 2L of amniotic fluid
GI or other malformations
How can fetal lung maturity be determined?
By analysis of pulmonary surfactant
Yolk Sac
Secondary cavity
Transfers nutrients & oxygen
Vessels form to aid transport
When does the embryo curve inward?
By the 5th week
Stalk becomes compressed
Narrow cord formed
Umbilical Cord Components
2 arteries
1 vein
What happens when umbilical cords only have 2 vessels (1 artery:1 vein)?
Congenital Malformation
Fetal CV/GI/Urinary Tract Anomalies
The umbilical cord..
Rapidly increases in length
False knots can compromise circulations
Whartons Jelly
Surrounds umbilical vessels and prevents compression
Nuchal Cord
Cord wrapped around the fetal neck
Placenta & Metabolic Function
Minimal, 2 layers make it too thick
Permeability increases later on
By the 8th week, genetic testing may done via aspiration biopsy
**Limb defects associated if done b4 10 weeks
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
detected in urine 8 to 10 days after ovulation (used in preg.tests)
ensures supply of estrogen and progesterone to maintain pregnancy
How does miscarriage occur?
Corpus luteum stops functioning b4 placenta produces sufficient estrogen & progesterone
Human Placental Lactogen (hPL)
Stimulates maternal metabolism to supply nutrients
Progesterone & Pregnancy
Maintains endometrium
Decreases uterus contractility
Stimulates maternal metabolism
Development of breast alveoli
Hormone produced by placenta and ovaries?
Placenta - Estriol
Ovaries - Estradiol
What does the placenta function as for the fetus?
As the lungs
Fetal concentration of glucose
Lower than maternal glucose lvl (bc of the rapid metabolism of glucose by the fetus)
Fetal glucose demand = high
Although many viruses can cross placenta
Bacteria & protozoa first infect placenta and then the fetus
Since only one layer separates the maternal & fetal blood…
Breaks can occur and fetal blood leaks into maternal circulation
Mother may develop antibodies (isoimmunization)
Since placental functions depends on maternal BP…
HTN & cocaine use diminishes uterine blood flow
Why are pregnant woman told to not lay on their backs?
Applies pressure to the uterus, vena cava & blood return to r.atrium is diminished
Otherwise, growth restrictions or small infants
Braxton Hicks Contractions
Painless contractions after 1st trimester that ENHANCE blood flow
**prolonged contractions/short intervals between contractions REDUCE blood flow to placenta
During the fetal stage…
They are less vulnerable to teratogens except for those affecting functioning of CNS
Viability
Capability of the fetus to survive outside uterus
1st organ to function in the developing human
CV system
Alcohol can cause
growth restrictions
microcephaly
fetal alc syndrome
Androgens can lead to
Masculinization of female
Organic mercury (ex.sushi) can cause
cognitive impairment
blindness
Formane ovale
opening in l.atrium
mixes with the deoxygenated blood
Fetal HR (Range)
110 - 160
Lecithin
Alveolar surfactant required for postnatal lung expansion
Once the L/S ratio is 2:1
Lungs are deemed mature
The prescense of Phosphatidylglycerol
Indicates VERY LOW risk for respiratory depression
A count > 50k lamellar bodies
Indicates lung maturity (mercer)
Gestational DM & chronic glomerulonephritis can
Inhibit lung maturity
Neonates born b3 39 weeks via cesarian
Increased transient tachypnea risk
Likely to have crackles first 24 to 48 hrs
Omphalocele
intensines protrude from the umbilicus
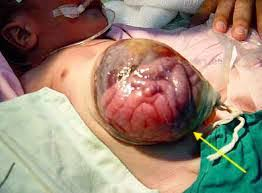
Meconium
fetal waste
passed thru rectum within 24hrs of birth
How does the fetus prepare for extrauterine cold stress?
It lays down stores of brown fat
Since the placenta clears unconjugated billirubin
Enzyme for conjugation is needed LESS
Predisposes neonate to hyperbilirubinemia
Why is vitamin K given to neonates at birth?
Their gut cannot produce vitamin K which is necessary for the synthesis of coagulation factors
@ birth, kidneys lack ability to concentrate urine
Increasing risk for
Dehydration
Overhydration
Acoustic stimulation can evoke
Fetal HR response
Flavors from maternal diet are
Transferred to the fetus thru amniotic fluid
When the fetus swallows amniotic fluid in the 5th month
sweeteners in fluid causes baby to swallow faster
bitter substances results in decreased swallowing
cold substances causes fetal hiccups
Congenital hypothyroidism if untreated can cause
Severe intellectual disability
(why we screen for hypothyroidism at birth)
Mothers with uncontrolled DM
leads to fetal hyperglycemia
hypperinsulemia
islet cell hyperplasia
large fetus
What does hyperinsulinemia do to the neonate?
Blocks lung maturation → respiratory distress & hypoglycemia
Sutures & fontanelles allow
Bones of skull to mold & enables head to pass thru birth canal
Vernix Caseosa
protects fetal skim
thick at 24 weeks, scant by birth
Lanugo
fine hairs that may disappear by term gestation

Fetus produced
IgM
Breast milk precursor, colostrum has large amount of
IgA
Hearing is fully developed
At birth
Fraternal/Dizygotic Twins
same sex or different sex
increased frequency with maternal age
increased incidence following discontinuation of oral contraceptives
With conjoined twins,
Cleavage is incomplete and occurs late
Assistive Reproductive Therapy increases
incidence of monozygotic twinning
Multifetal gestation comes with
Increased perinatal complications & fetal anomalies
Since the brain has the longest developmental period
It is extremely vulnerable to teratogens & more defects can occur
Teratogens have greatest effect during
1st 3 months