Biology
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Photosynthesis equation
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
Cell differentiation
The process by which a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell type.
Morphogenesis
The biological process that causes an organism to develop its shape.
Bottleneck effect
A sharp reduction in the size of a population due to environmental events or human activities, resulting in a loss of genetic diversity.
Founder effect
A loss of genetic variation that occurs when a new population is established by a small number of individuals from a larger population.
Directional selection
A mode of natural selection in which a single phenotype is favored, causing the allele frequency to continuously shift in one direction.
Sexual selection
A mode of natural selection in which certain traits increase an individual's chances of attracting mates.
Disruptive selection
A mode of natural selection that favors extreme phenotypes over intermediate phenotypes.
Stabilizing selection
A mode of natural selection that favors intermediate phenotypes over extreme phenotypes, reducing variance.
Genetic drift
A mechanism of evolution that involves random changes in allele frequencies, particularly in small populations.
Speciation
The evolutionary process by which populations evolve to become distinct species
Cyclin
A regulatory protein whose concentration fluctuates throughout the cell cycle, activating cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) to regulate cell cycle progression.
Cyclin-dependent Kinase (CDK)
An enzyme that, when activated by binding to a cyclin, can phosphorylate various target proteins to regulate the cell cycle.
Morphogenesis
The biological process that causes an organism to develop its shape.
Cell differentiation
The process by which a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell type.
Cytoplasmic determinants
Molecules located in the cytoplasm that influence the development and differentiation of cells by regulating gene expression.
G1 phase of the cell cycle
The first gap phase in the cell cycle where the cell grows and prepares to duplicate its DNA.
S phase of the cell cycle
The synthesis phase in the cell cycle where DNA replication occurs, resulting in two sets of chromosomes.
G2 phase of the cell cycle
The second gap phase in the cell cycle where the cell continues to grow and prepares for mitosis.
Mitosis
The phase of the cell cycle where the replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei.
Cytokinesis
The process that occurs after mitosis, where the cytoplasm of a parental cell is divided into two daughter cells.
Prophase
The first stage of mitosis where chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes and the mitotic spindle begins to form.
Prometaphase
The stage of mitosis following prophase where the nuclear envelope breaks down and spindle fibers attach to chromosomes.
Metaphase
The stage of mitosis where chromosomes line up along the metaphase plate in the center of the cell.
Anaphase
The stage of mitosis where sister chromatids are pulled apart toward opposite poles of the cell.
Telophase
The final stage of mitosis where the chromatids arrive at the poles, and the nuclear envelope re-forms around each set of chromosomes.
G1 Checkpoint
A control point in the cell cycle that assesses whether the cell is ready to move into the DNA synthesis phase.
G2 Checkpoint
A control point in the cell cycle that checks for DNA damage and ensures all of the DNA is replicated before mitosis.
M Checkpoint
A control point during mitosis that ensures all chromosomes are properly attached to the spindle apparatus before proceeding with cell division
Silent mutation
A mutation that does not affect the amino acid sequence of a protein due to the redundancy in the genetic code.
Frameshift mutation
A mutation caused by insertion or deletion of nucleotides that shifts the reading frame, leading to changes in the entire amino acid sequence downstream.
Nonframeshift mutation
A mutation that does not shift the reading frame, typically caused by nucleotide substitutions or insertions/deletions in multiples of three nucleotides.
Nonsense mutation
A mutation that changes a codon into a stop codon, resulting in premature termination of protein synthesis.
Missense mutation
A mutation that results in the substitution of one amino acid for another in the protein sequence.
Result of the Krebs cycle
The Krebs cycle produces carbon dioxide, ATP, NADH, and FADH2 as it processes acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins
Oxidation
The process in which a substance loses electrons, leading to an increase in its oxidation state. It is commonly associated with the addition of oxygen or the removal of hydrogen from a compound.
Reduction
The process in which a substance gains electrons, resulting in a decrease in its oxidation state. It is typically associated with the addition of hydrogen or the removal of oxygen from
Products of light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis
The products of the light-dependent reactions are ATP, NADPH, and oxygen.
Start and end products of the Calvin cycle
The Calvin cycle starts with carbon dioxide and ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) and ends with glucose and ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) being regenerated
Intraspecific competition
Competition between individuals of the same species for limited resources, such as food, space, or mates.
Interspecific competition
Competition between individuals of different species competing for the same resources, which can lead to changes in population dynamics and
Maturation promoting factor (MPF)
Maturation promoting factor (MPF) is a cyclin-dependent kinase complex that triggers the transition from the G2 phase to the M phase of the cell
Helicase
An enzyme that unwinds and separates the two strands of DNA during DNA replication.
Topoisomerase
An enzyme that alters the supercoiling of DNA; it relieves strain in the DNA helix ahead of the replication fork by cutting the DNA, allowing it to unwind, and then rejoining it.
DNA polymerase I
An enzyme involved in DNA replication that removes RNA primers and replaces them with DNA nucleotides.
DNA polymerase II
An enzyme that is involved in DNA repair and also helps in DNA replication; it can also proofread and correct errors during DNA synthesis.
RNA polymerase (primase)
An enzyme that synthesizes short RNA primers complementary to the DNA template, which are necessary for DNA polymerase to initiate DNA replication.
Ligase
An enzyme that joins DNA fragments together by forming phosphodiester bonds, essential for sealing nicks in the DNA backbone during replication and repair.
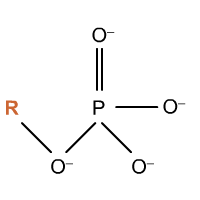
Which functional group is this?
Phosphate- participates in energy transfer that drives cellular processes

Which functional group is this?
Methyl- can affect gene expression when bound to DNA (turn them off)

Which functional group is this?
Hydroxyl- polar, makes a molecule hydrophilic/water soluble; Often forms hydrogen bondsd with neighboring molecules
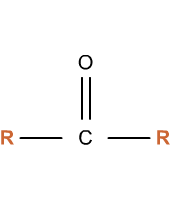
Which functional group is this?
Carbonyl- makes a molecule hydrophilic, often found in sugars

Which functional group is this?
Carboxyl- behaves as an acid by donating H+
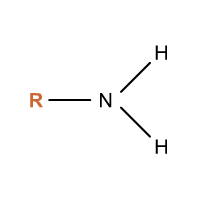
Which functional group is this?
Amino- behaves as a base by accepting H+
Sylfhydryl group
important in protein structure, creates a stabilizing bond that holds proteins in a specific 3-dimensional shape
Acetyl
Used to activte DNA through acetylation
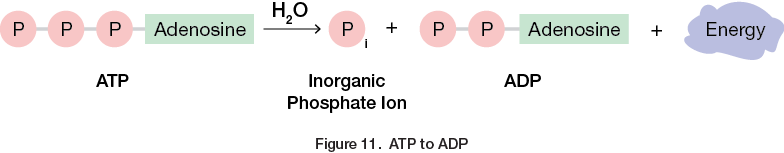
What does this illustration depict?
Hydrolysis of ATP to release energy that can be used by the cell
Phosphorylation
The process of adding a phosphate group to a molecule, typically a protein, which can alter the function and activity of that molecule, often playing a key role in regulating cellular processes
Transcription factors
Proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences, regulating the transcription of genes by enhancing or repressing RNA polymerase's ability to initiate transcription.
Phosphodiester bonds
Covalent bonds that link the 5' phosphate group of one nucleotide to the 3' hydroxyl group of another nucleotide, forming the backbone of DNA and RNA molecules.
Oxidative phosphorylation
The metabolic pathway that uses energy released by the oxidation of nutrients to generate ATP, occurring in the mitochondria of cells.
Histone phosphorylation
The addition of a phosphate group to histone proteins, which can affect chromatin structure and gene expression by altering the interactions between histones and DNA.
Lac operon
A set of genes in bacteria that are regulated together, involved in the metabolism of lactose; it is an example of an operon that is turned on in the presence of lactose and off in its absence
Intron
Non-coding sections of a gene that are removed during the RNA splicing process before translation, meaning they do not code for proteins.
Exon
Coding sections of a gene that remain in the final mRNA after splicing, and are translated into the amino acid sequence of a protein.
RNA splicing
The process by which introns are removed and exons are joined together in a pre-mRNA molecule to produce a mature mRNA transcript that can be translated into a protein
Glycosidic linkage
A type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which can be another carbohydrate.
ATP synthase
An enzyme that creates the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). It is found in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells
Peptide bond
A chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule, releasing a molecule of water (H2O).
Convergent evolution
The independent evolution of similar features in species of different lineages, creating analogous structures.
Fitness
An organism's ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment.
Genetic variation
The presence of differences in sequences of genes between individual organisms of a species.
Selective pressure
Any cause that reduces reproductive success in a portion of a population, potentially leading to evolutionary change.
Analogous structures
Biological structures that have similar functions but do not share a common evolutionary origin. These structures arise due to convergent evolution, where different species independently evolve similar traits under similar environmental pressures.
Homologous structures
Structures in different species that are similar because of common ancestry. They may have different functions but share a similar underlying structure.
Quorum sensing
Cell-to-cell communication system used by bacteria to coordinate gene expression and behavior based on population density