Final Exam Study Guide 1350
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
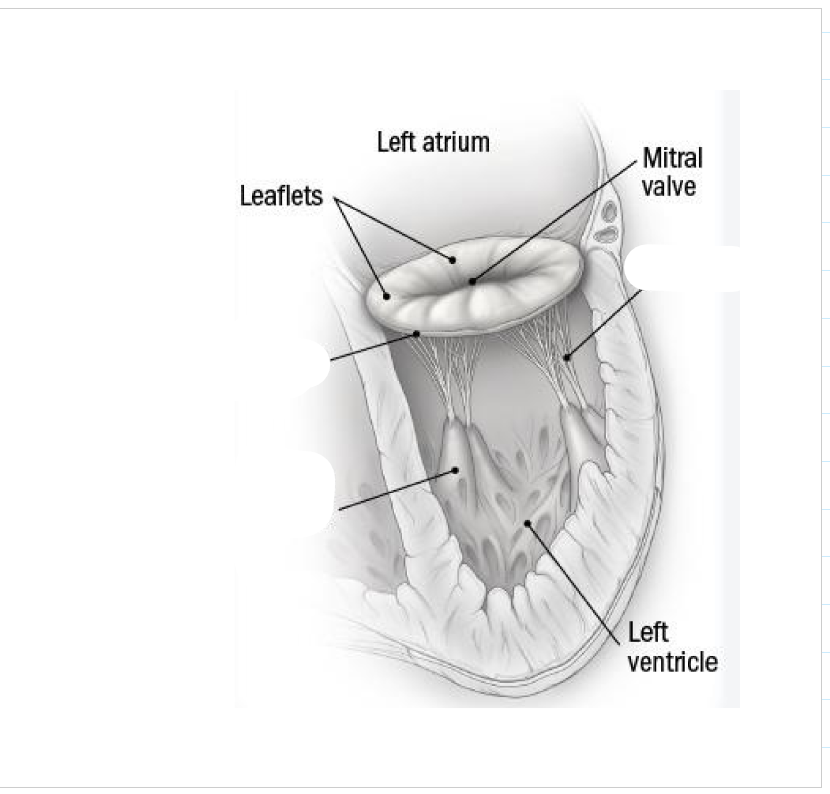
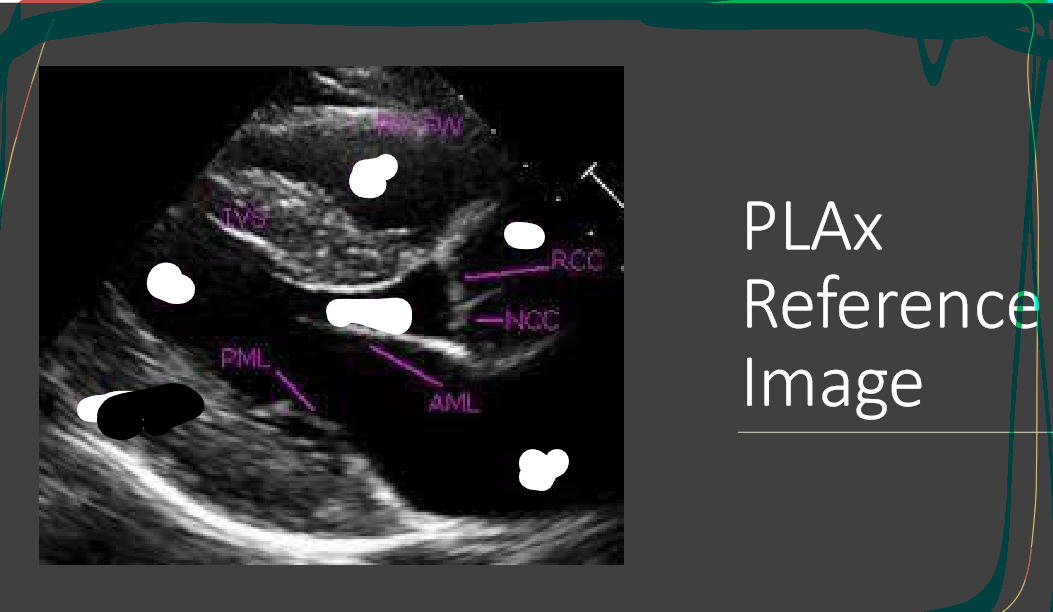
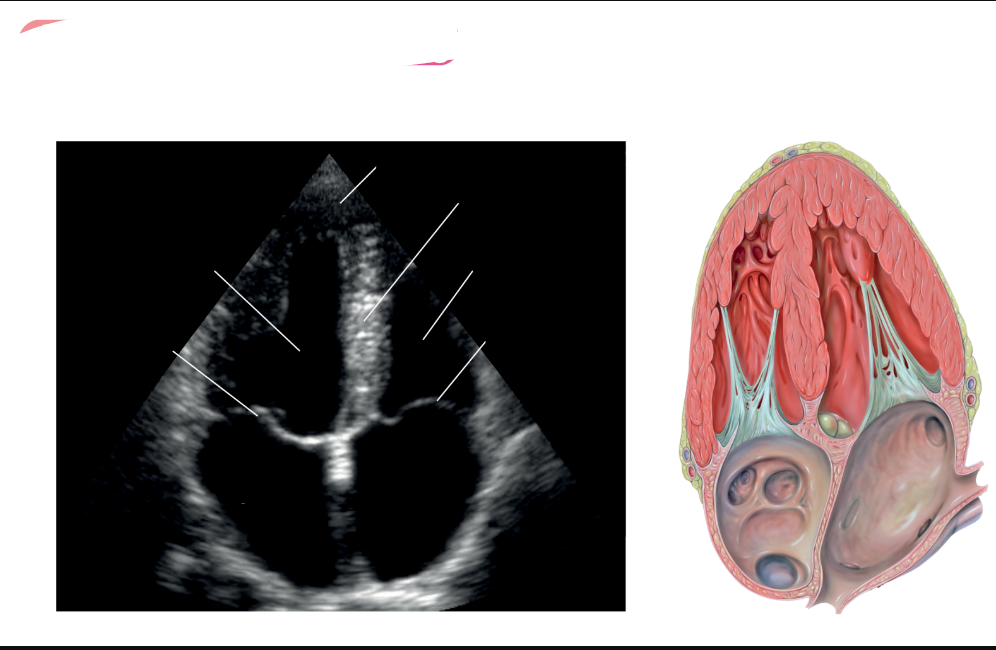
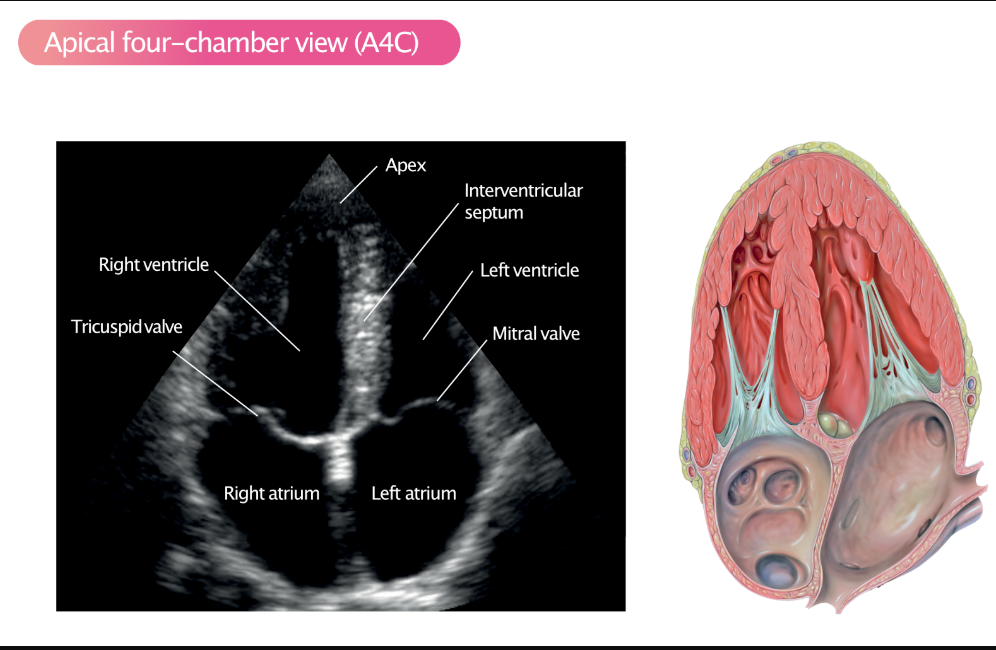
label these 3
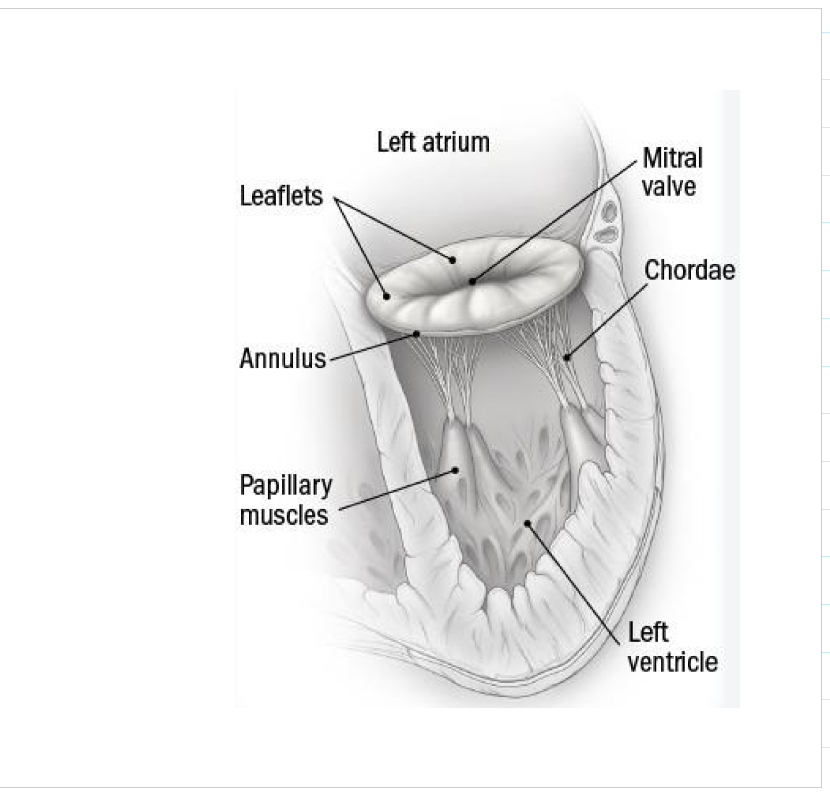
AR
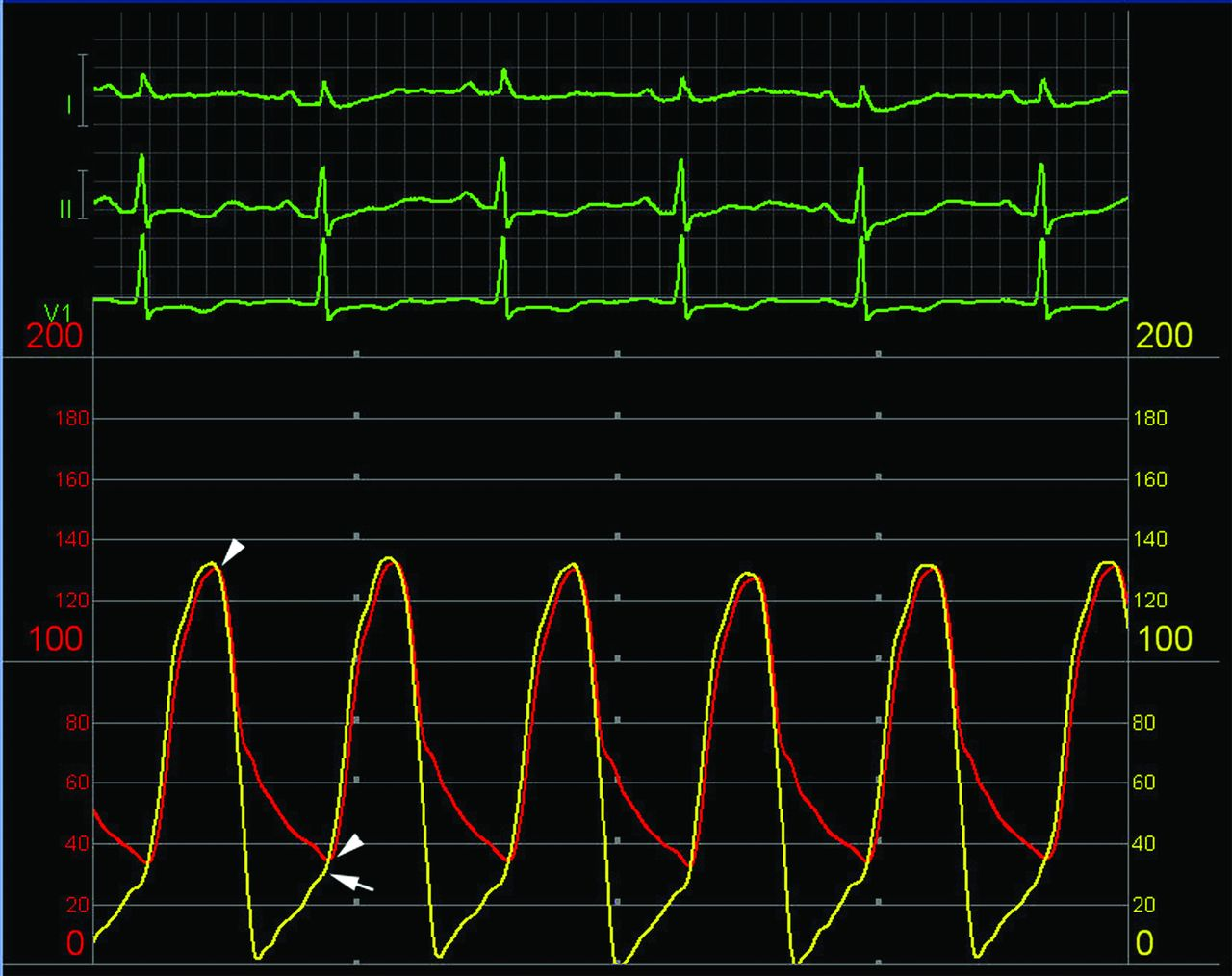
x4 what are these
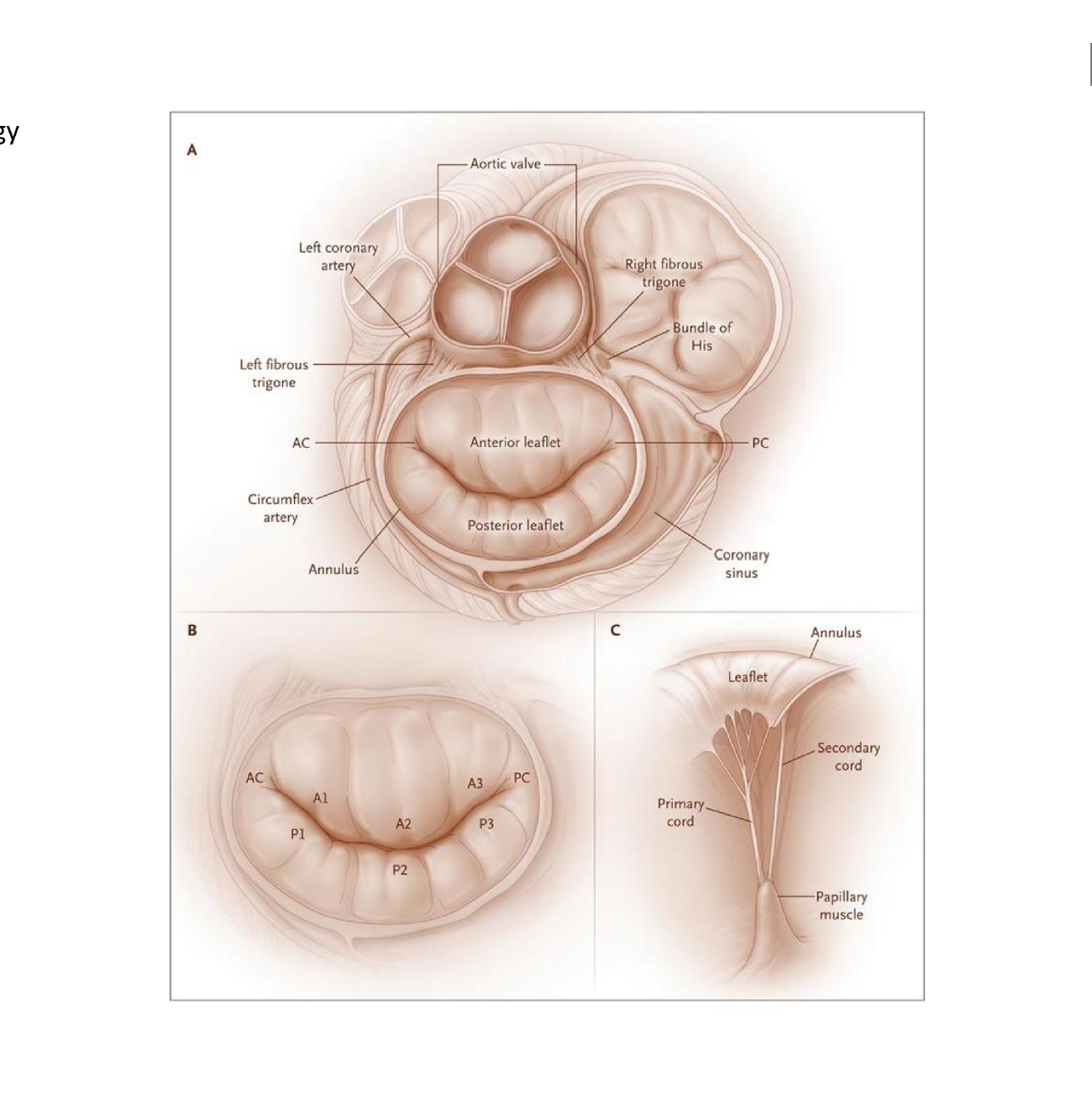
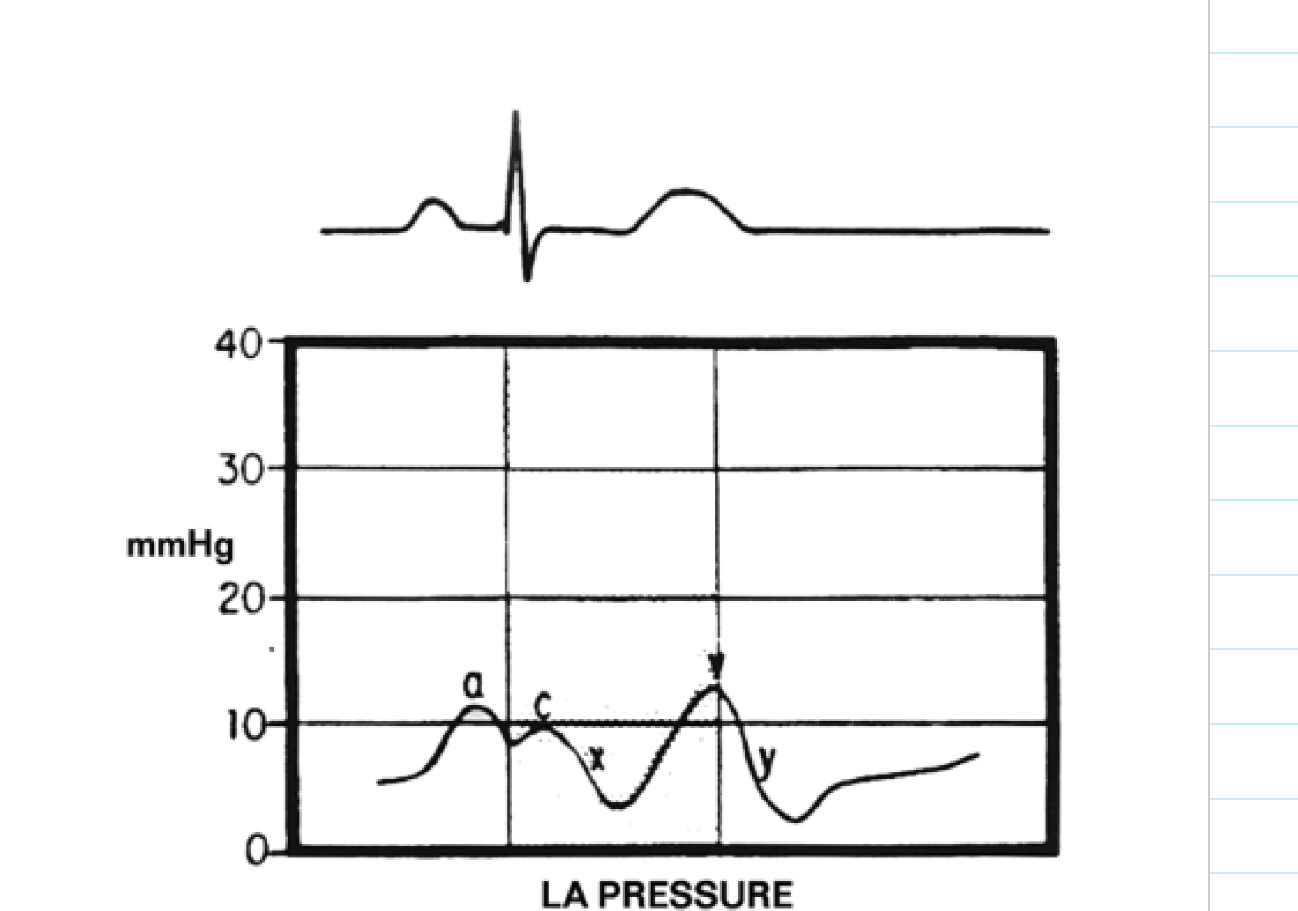
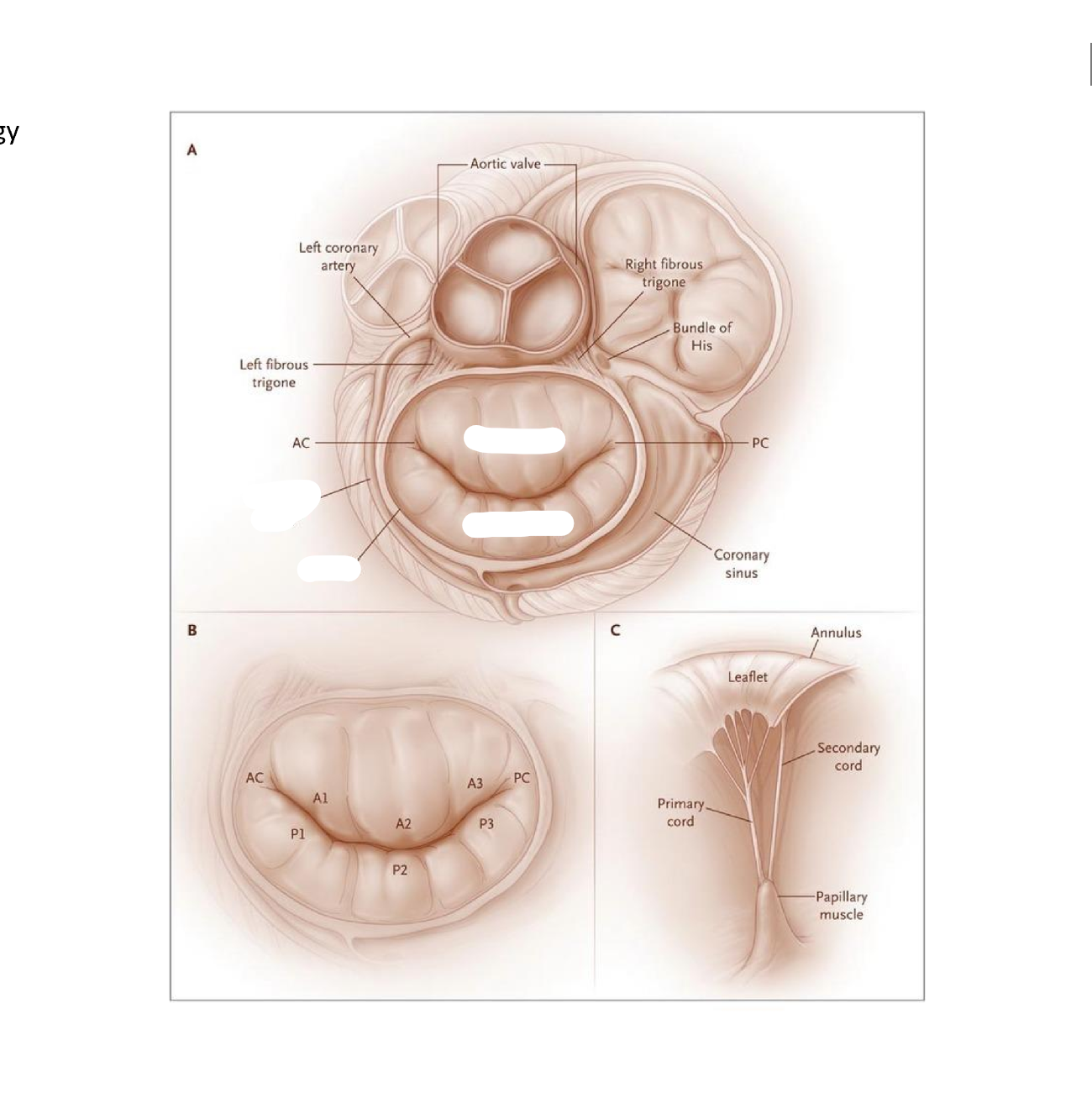
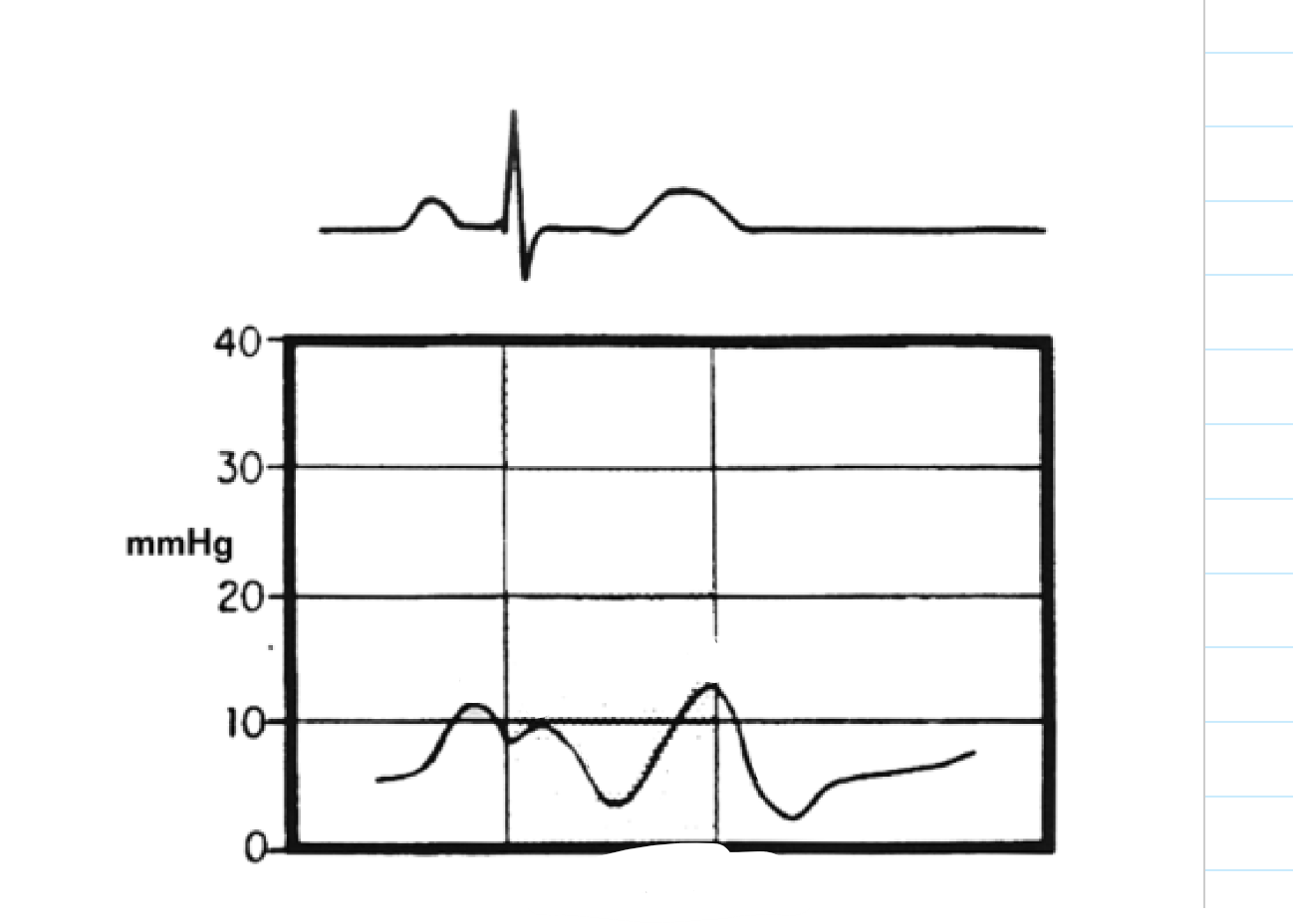
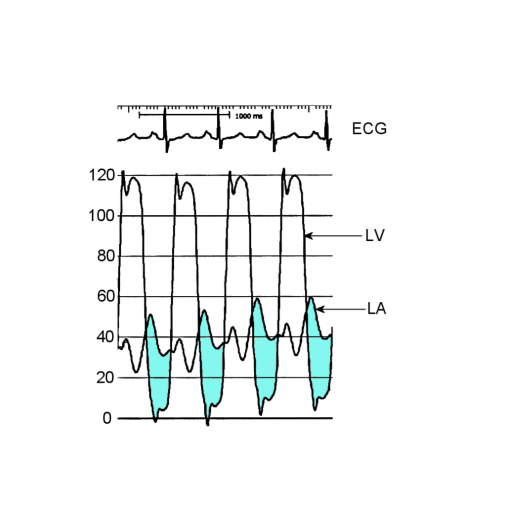
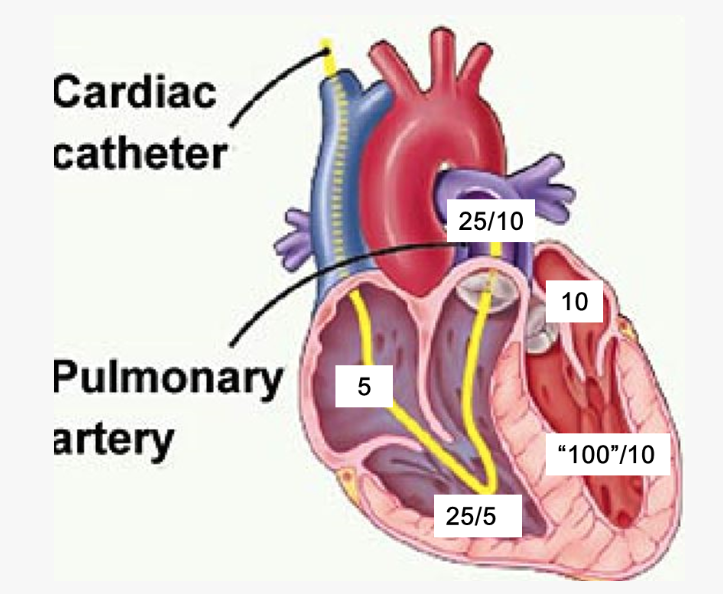
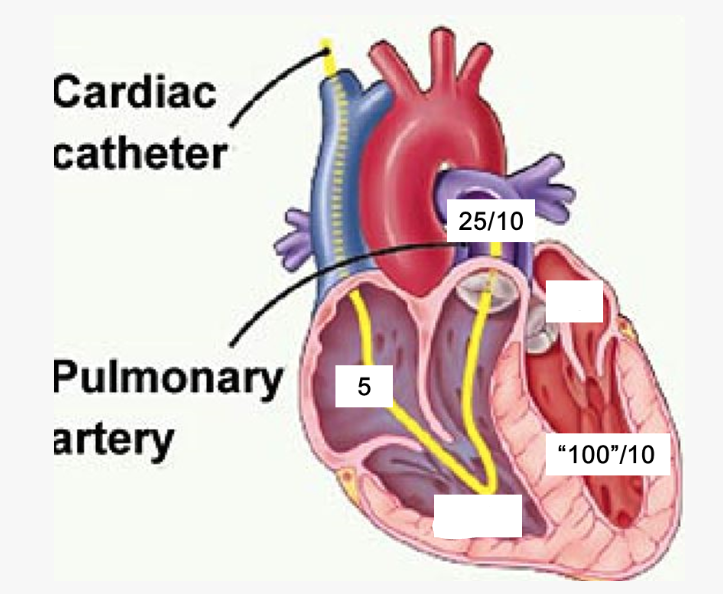
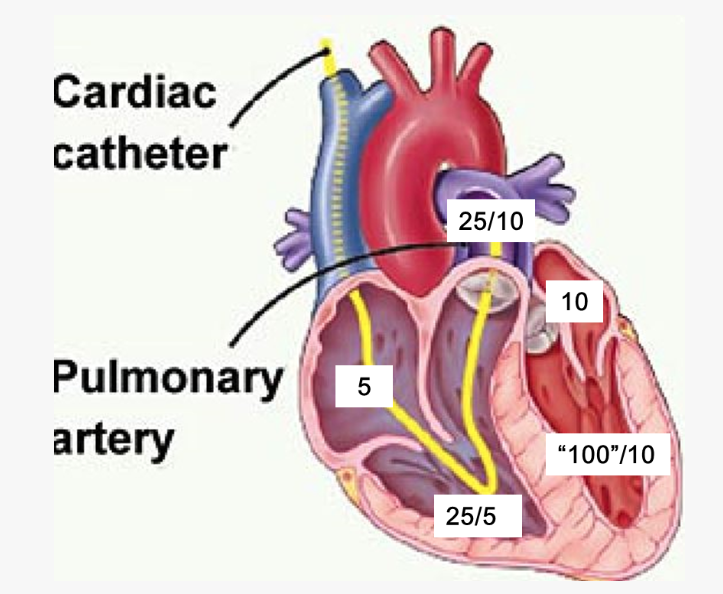
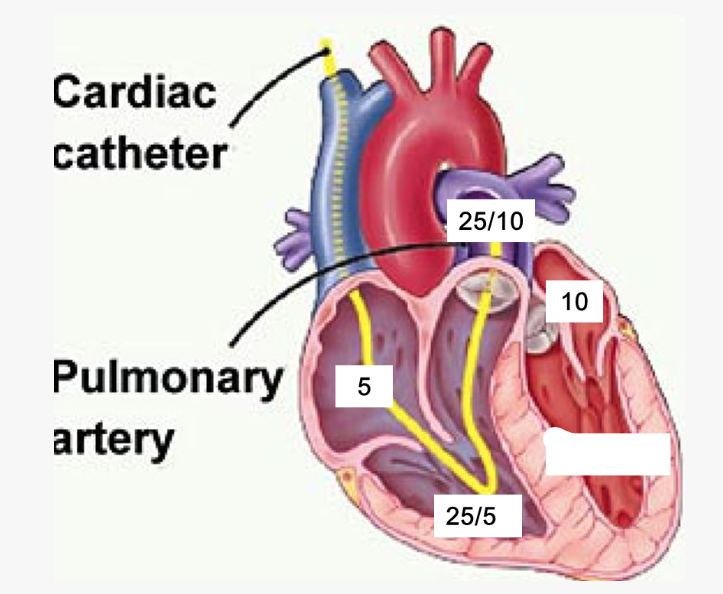
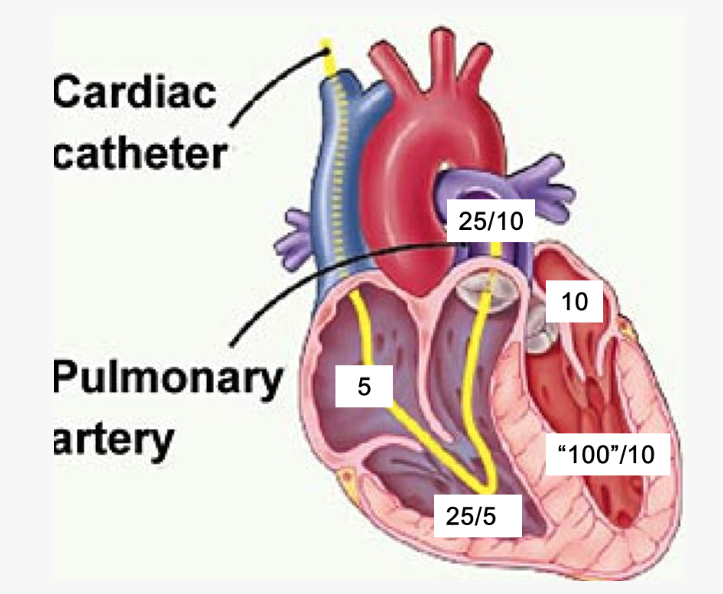
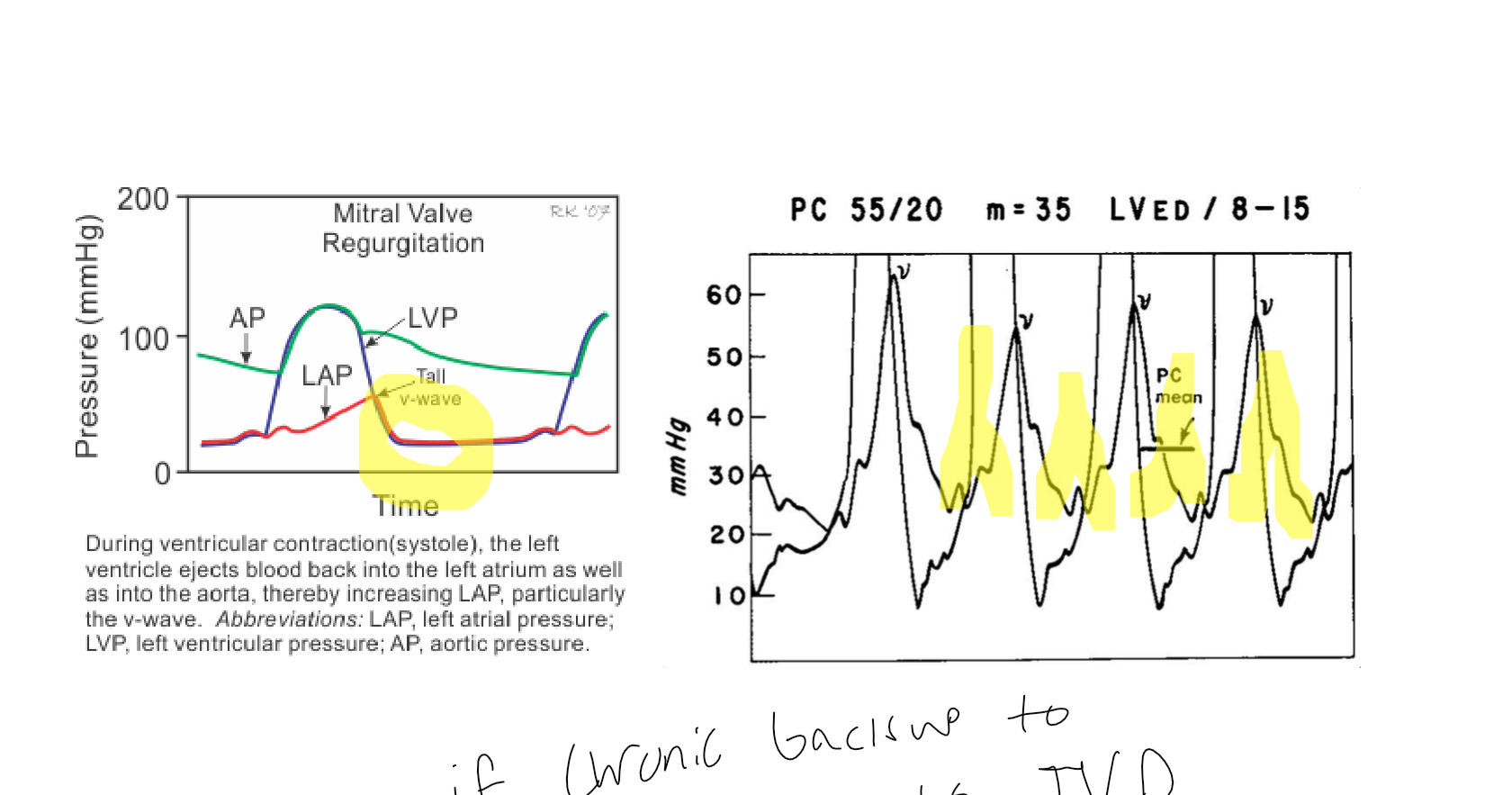
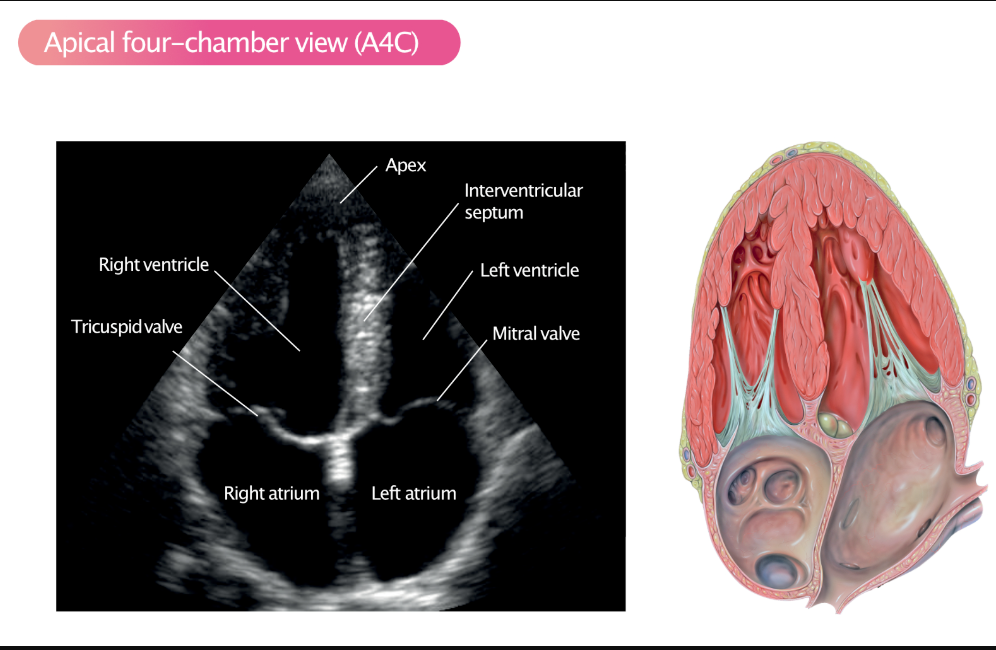
label these 6 including where the pressure is being measured
What disease is the biggest contributor to mitral valve stenosis
rheumatic fever
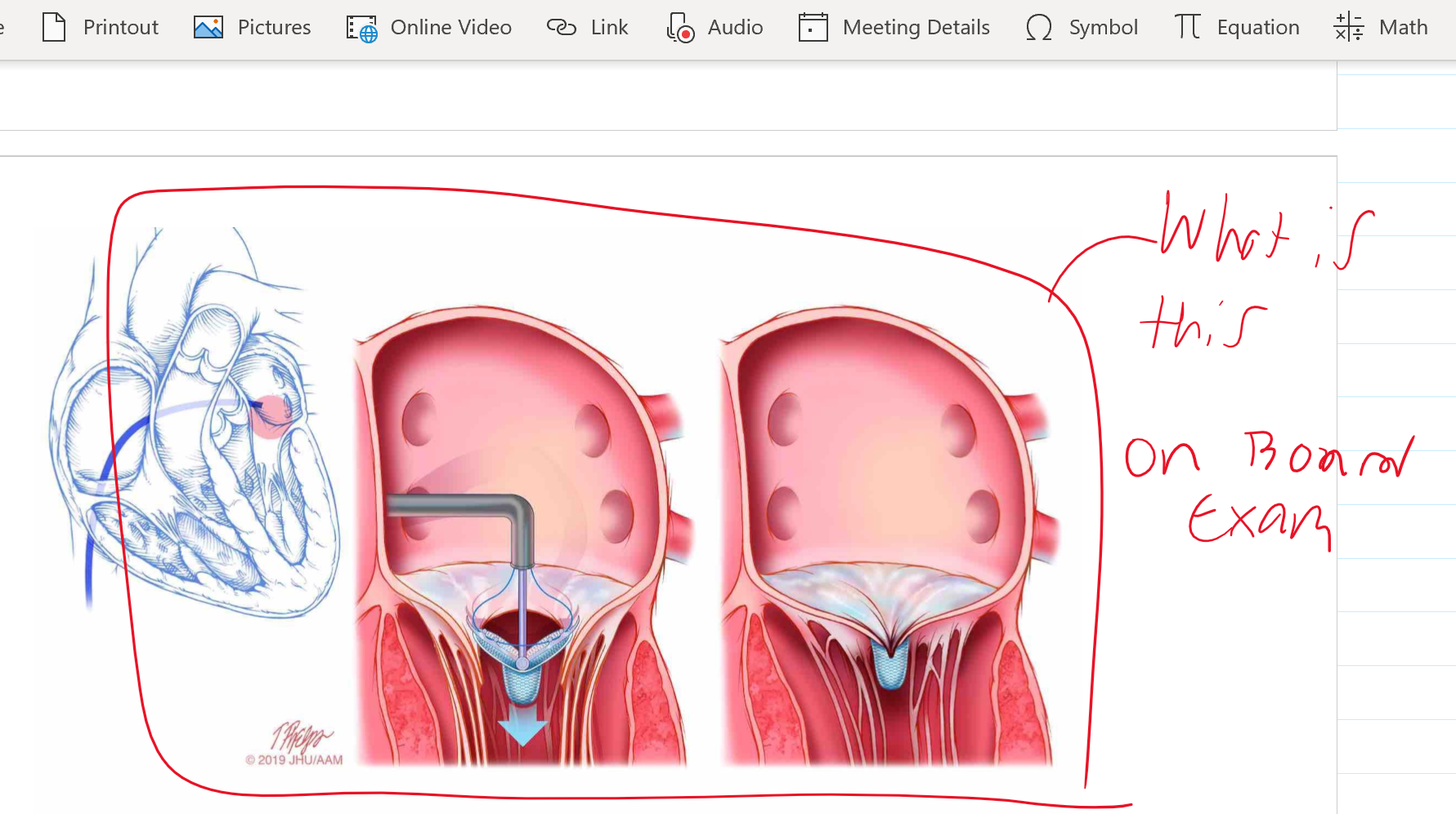
what is occurring here
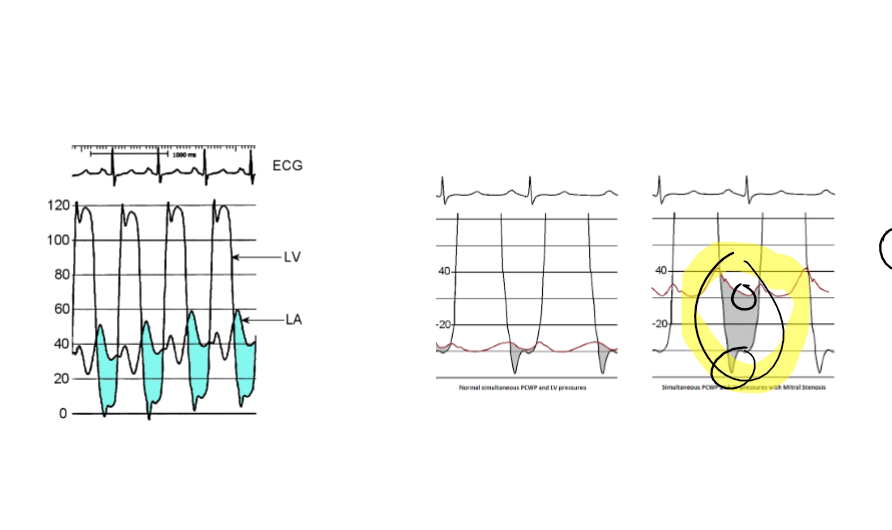
Mitral Stenosis
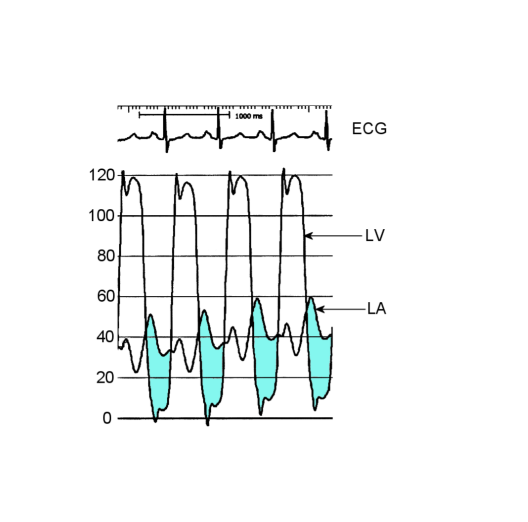
What is being observed a systolic or diastolic gradient
A diastolic gradient is being observed due to the pressure difference between the left atrium and left ventricle during diastole.
Regurgitant contrast that clears with every beat and never opacifies the entire LA
what grade of severity is this
1+ Mild
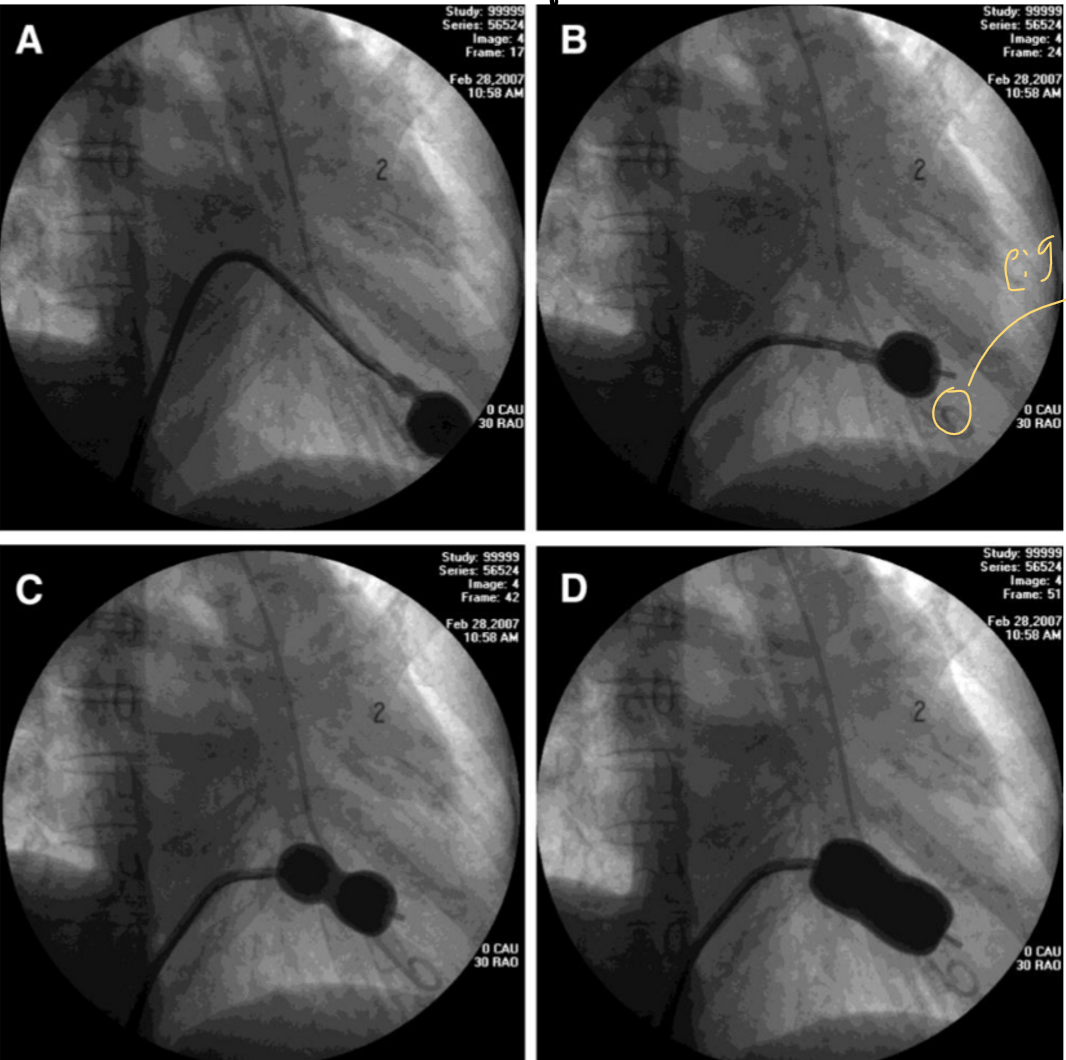
what is occurring in this image
Balloon mitral valvuloplasty
Regurgitant contrast faintly opacifies the LA after several beats but the opacification never equals that of the LV
what grade of severity is this
2+ Moderate
Regurgitant contrast completely opacifies the LA after several beats and the density of the opacification equals that of the LV.
This indicates 3+ Severe regurgitation.
regurgitant contrast opacifies the entire LA after a single beat, with the opacification becoming denser with subsequent bears. Additionally contrast can be seen opacifying the LAAA and PV.
what grade or severity would this be considered.
4+ Very Severe
hypogastric as also known as
internal iliac artery, supplying pelvic organs.
What are the main focuses for Aortic Valve Disease?
Anatomy, Stenosis/Regurgitation, Hemodynamics, Signs & Symptoms, Treatment options.
List the conditions associated with Structural Heart Disease. (4)
ASD, PFO, PDA, LAA.
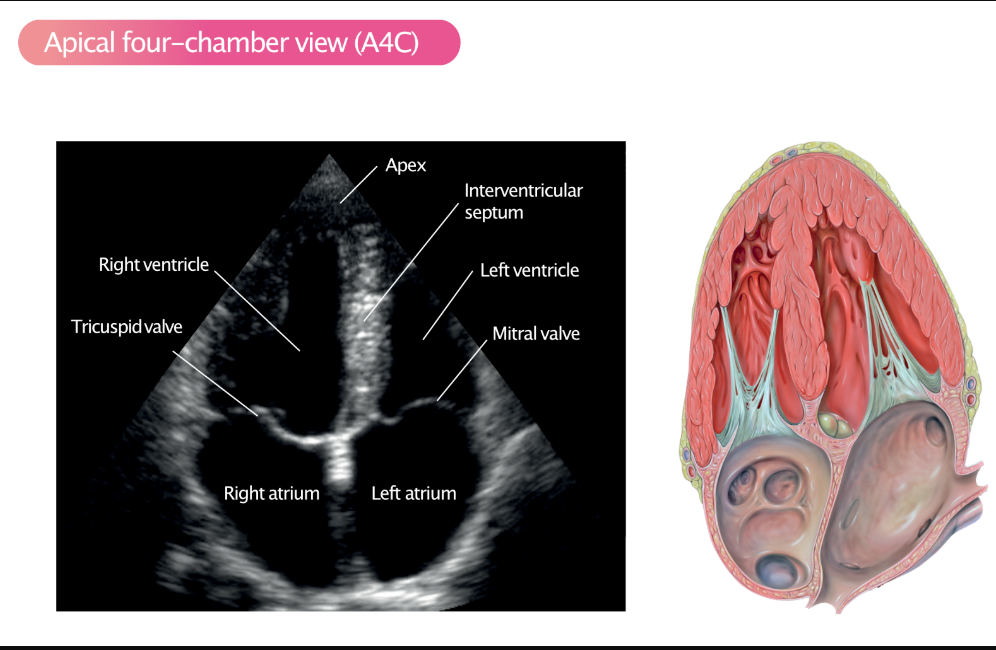
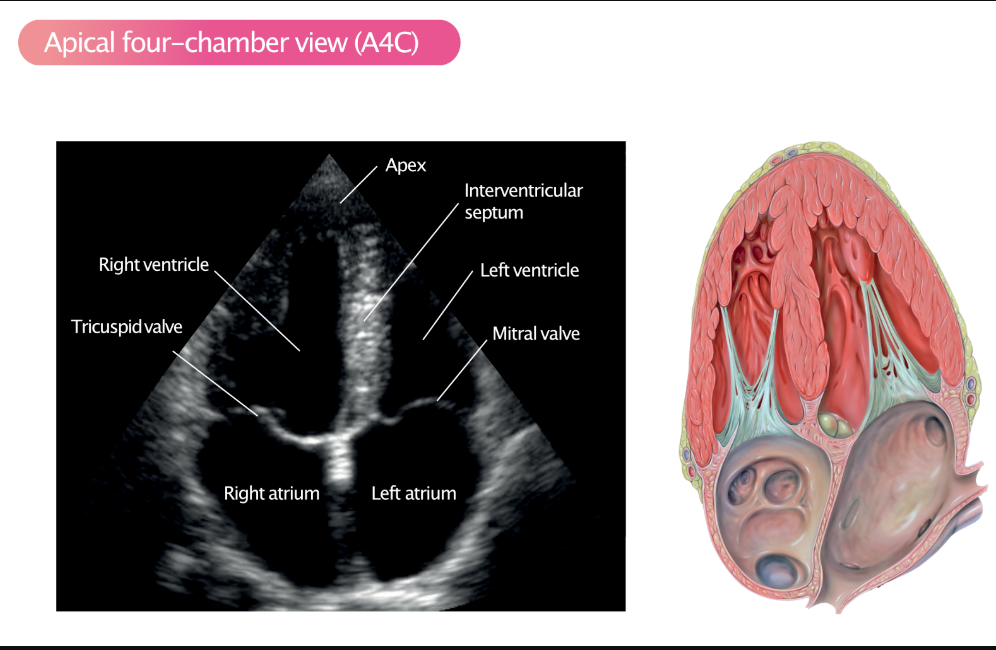
What echo imaging views are important in cardiovascular studies? (3)
Apical 4 chamber, Parasternal short axis, Parasternal long axis.
How do PAD and PVD differ?
PAD refers to Peripheral Arterial Disease, while PVD refers to Peripheral Vascular Disease.
What is the purpose of ABI testing?
To assess peripheral artery disease by comparing blood pressures in the arms and legs.
What does cine imaging differ from DSA imaging?
Cine imaging provides continuous visual frames, while DSA (Digital Subtraction Angiography) uses digital imaging to visualize blood vessels.
What does Carotid PTI refer to?
Percutaneous Transluminal Interventional procedures for the carotid arteries.
What is ‘Regurgitation’ in the context of heart valves?
Backflow of blood due to improper closure of the valve.
List two imaging methods used in vascular studies.
Cine imaging and DSA imaging.
What is the purpose of distal arterial pulse assessment?
To evaluate blood flow and detect blockages in peripheral arteries.
Identify a characteristic symptom of Peripheral Vascular Disease.
Intermittent claudication or pain in the legs during exercise.
Explain the term LAA in cardiac context. what can it lead to
Left Atrial Appendage, a pouch in the heart that can lead to clot formation.
Define the acronym ABI test what does it test
Ankle-Brachial Index, a test comparing blood pressure in the ankle and arm.
cine imaging captures *** ****moving images of the heart and blood vessels.
Real-time moving images of the heart and blood vessels.
List one advantage of using DSA imaging.
Provides clearer images of blood vessels by removing background structures.
What is the primary risk associated with AAA?
Rupture of the aneurysm, leading to potentially fatal hemorrhage.
What are the symptoms associated with stenosis of the aortic valve?
Dizziness, fainting, angina, and heart failure symptoms.
Identify a complication associated with mitral valve regurgitation. (2)
Heart failure or pulmonary hypertension due to volume overload.
**** pulse pressures and ***** murmur (heart sound) are common signs in a patient with aortic regurgitation? (2)
Widened pulse pressure and diastolic murmur upon examination.
What does PTI stand for in the cath lab
Percutaneous Transluminal Intervention
What does left atrial appendage (LAA) assessment focus on?
Risk of thrombus formation and potential stroke from thrombus
Ao stenosis waveform
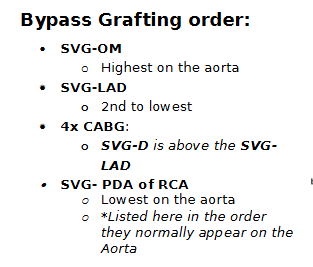
Bypass grafting order
1
2
3
4
OM
DIAG
LAD
RCAA surgical procedure that creates an alternative route for blood flow around blocked arteries, specifically using the left internal mammary artery (LIMA) for the left anterior descending artery (LAD) and saphenous veins for the right coronary artery (RCA).
What condition creates an equalization of pressures
cardiac tamponade
CRANIAL views are best for the
LAD A
CAUDAL VIEWS ARE BEST FOR THE
circumflex U
what is included in a radial access cocktail
verapamil
nitro
heparin
which antiplatelet agent has the quickest platelet recovery time
cangrelor
What is the most common ASD
Ostial Secundum
In pulses alternans the arterial pressure waveform show the heart is ******
every other beat pressure is reduced
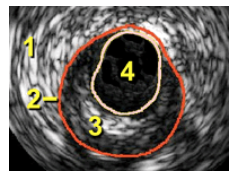
adventitia
media
intima (plaque)
lumen
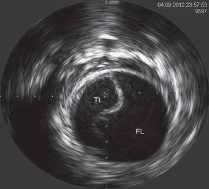
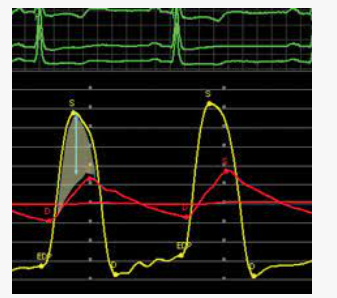
what is happening in this image
is iFR or FFR with medication
FFR is used with medication
one sided occlusion
Eccentric
completely surrounded or encapsulating lumen
concentric
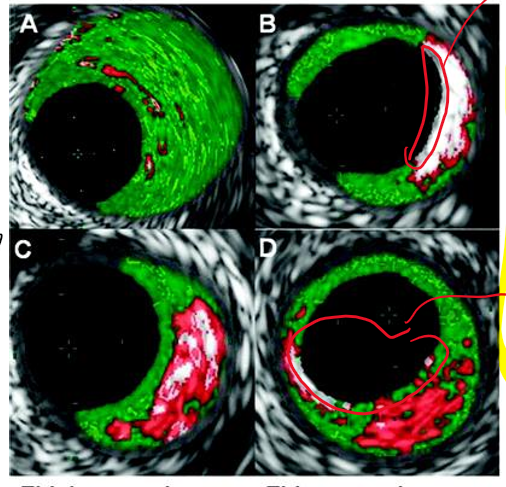
red?
necrotic core
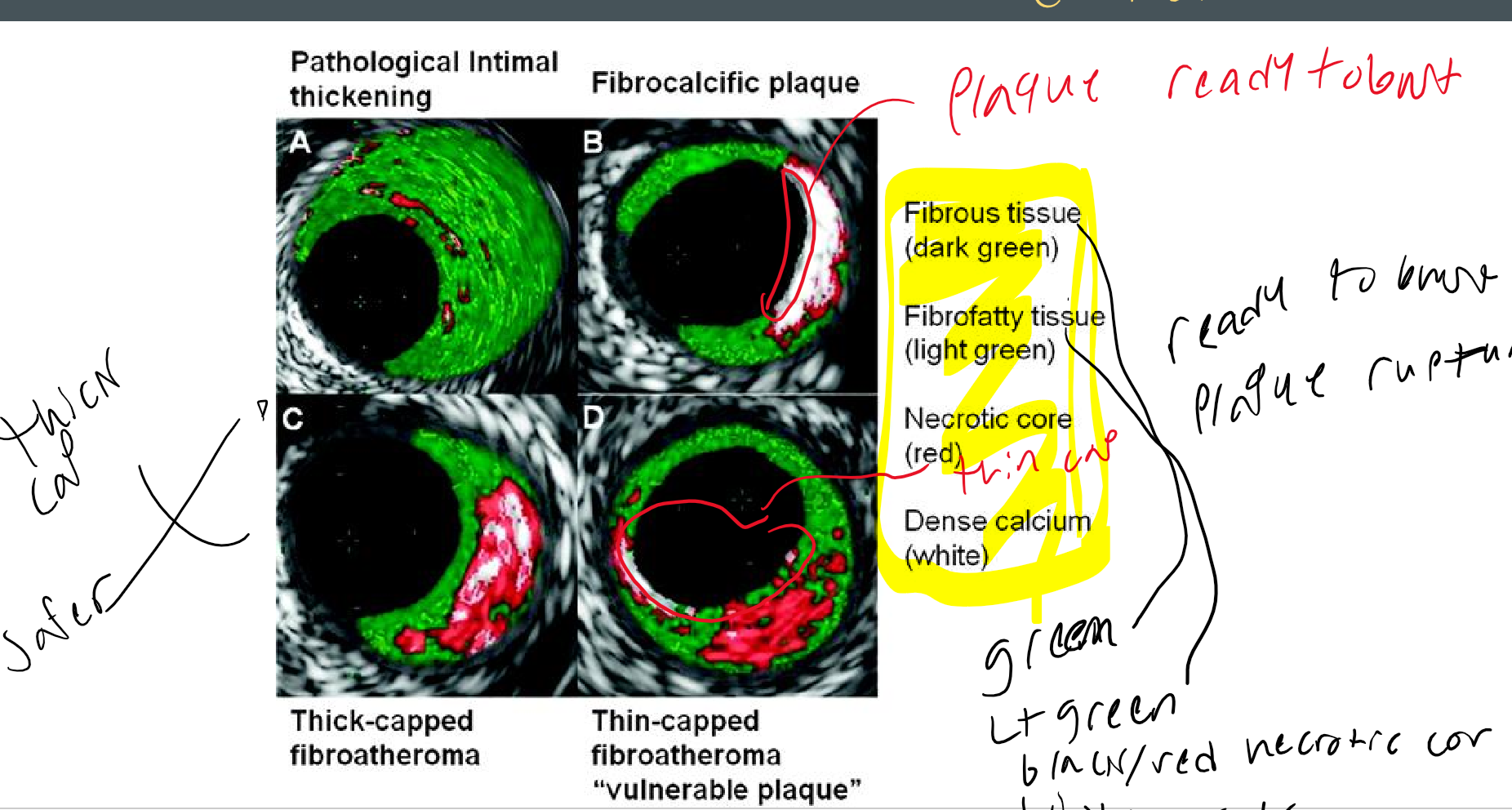
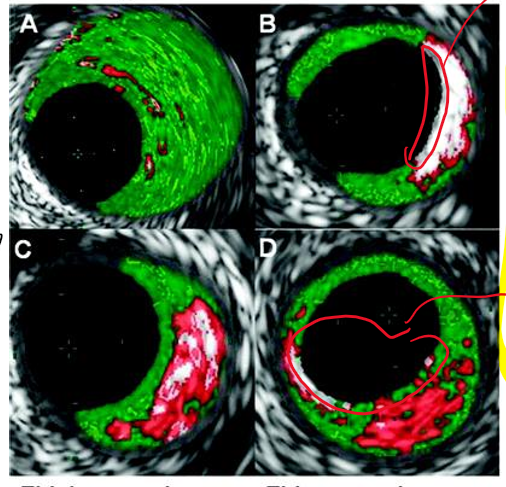
white
calcium
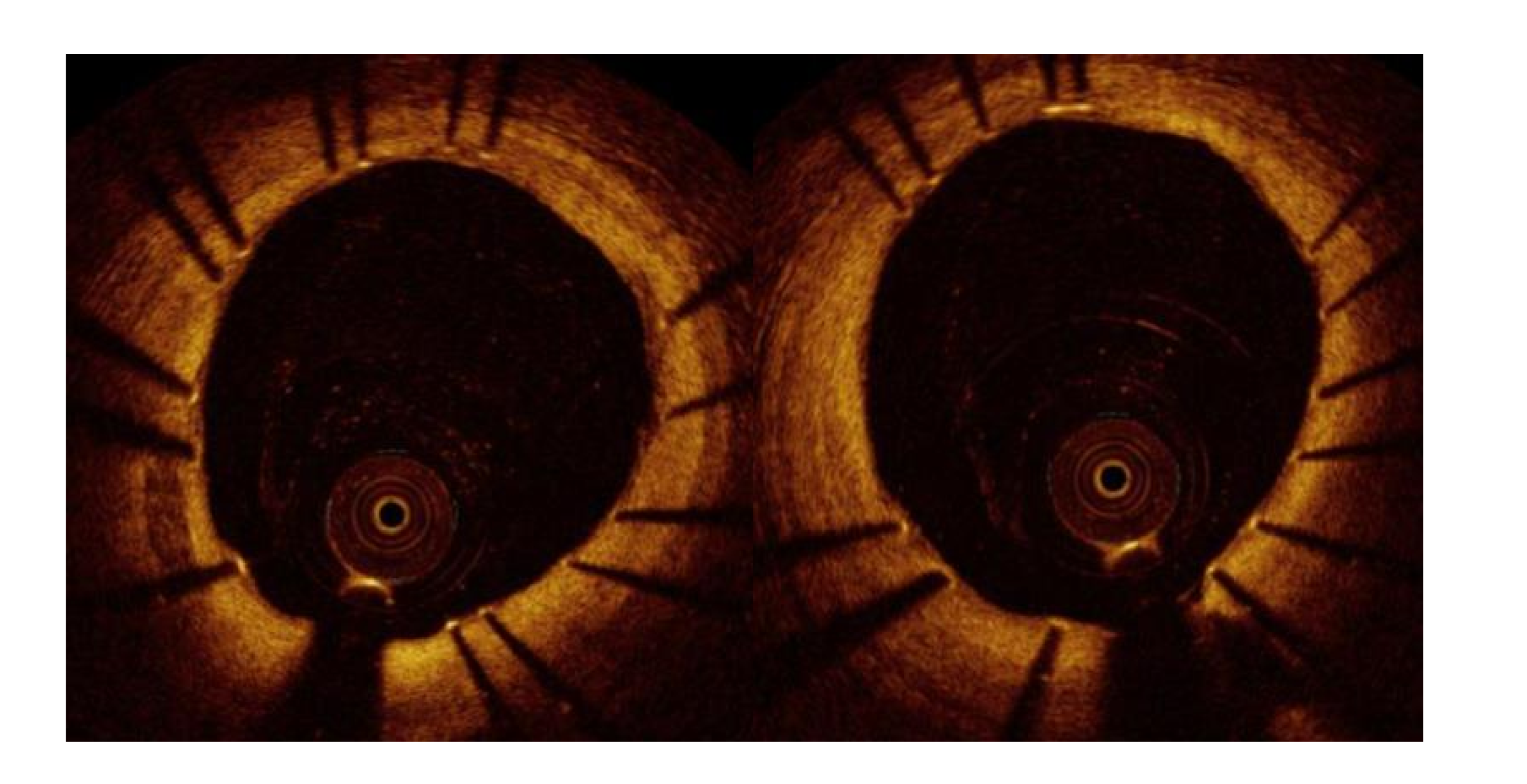
what is this
oct stent
behind ankle medial is what pulse
medial malleolus
which of the following is not a symptom of severe mitral stenosis
angina
JVD
fatigue
SOB
JVD
what is the most common cause of mitral stenosis
rheumatic fever
what gradient can be observed in severe aortic stenosis
SYSTOLIC LV/AO gradient
what imaging modality is considered the gold standard for diagnosing mitral regurgitation
endocardiography
echocardiography
in mitral stenosis a ****** gradient is observed between
diastolic gradient
LV and LA
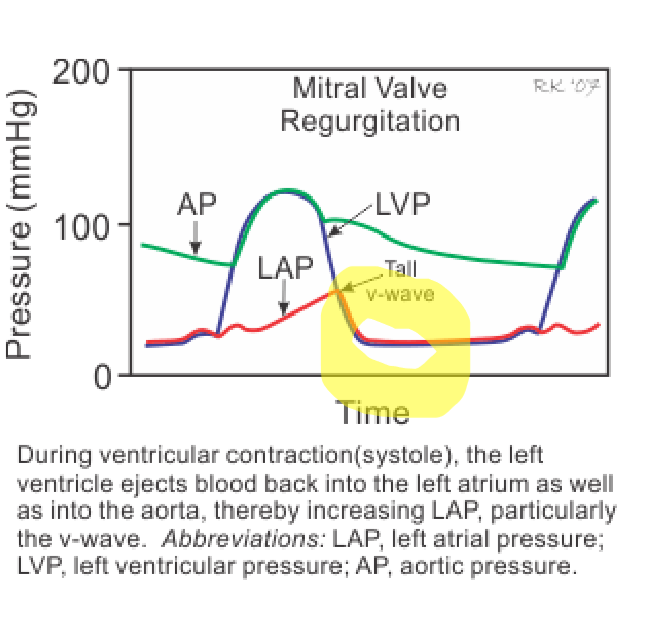
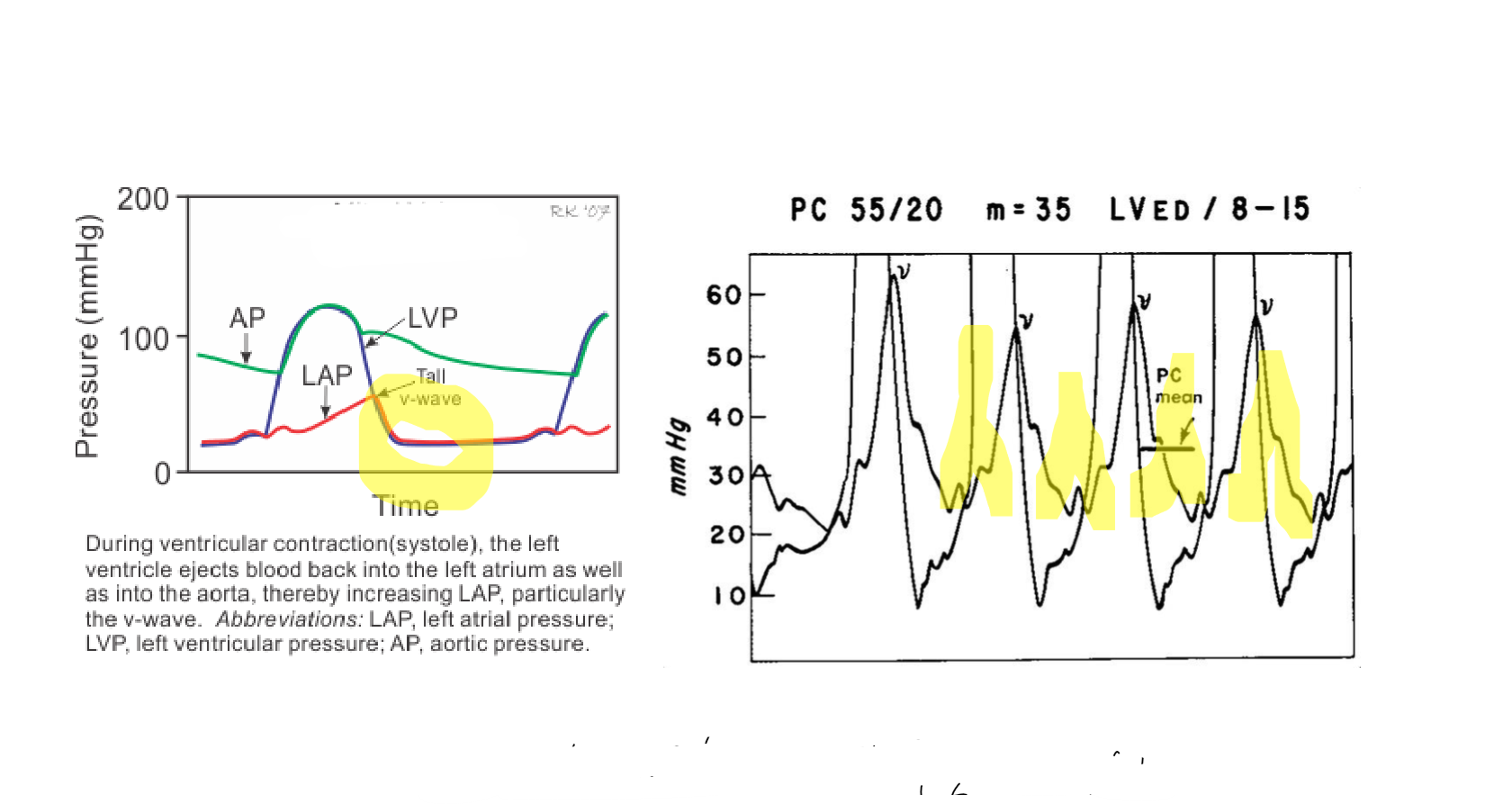
the main hemodynamic consequences of severe MR is
increased preload
and decreased afterload, leading to volume overload of the left atrium and ventricle.
rapid upstroke and downstroke in aortic pressure waveform
indicates aortic regurgitation
MS
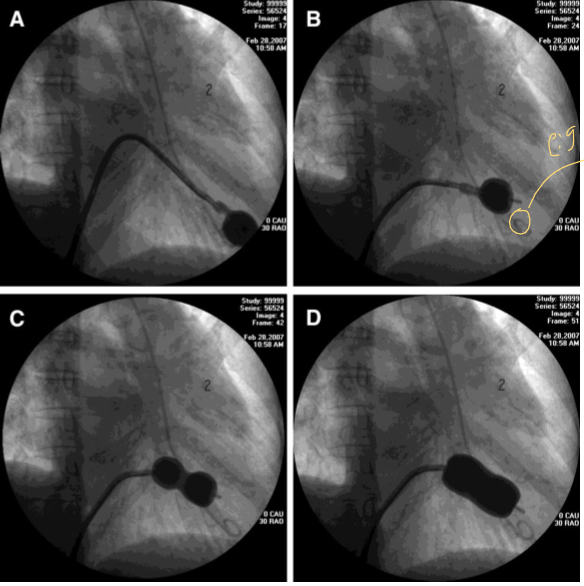
WHAT PROCEDURE IS HAPPENING
MITRAL VALVULOPLASTY
Large v waves in the left atrial pressure waveforms indicate what valve issue
MR
what are the white labels
RV
LA
LV
LVOT
AO
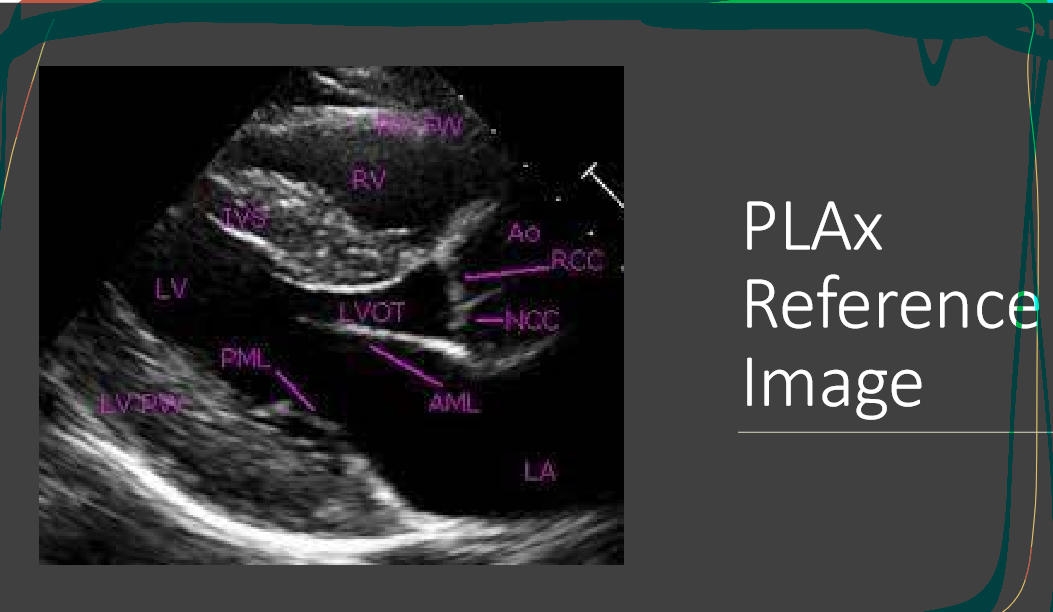
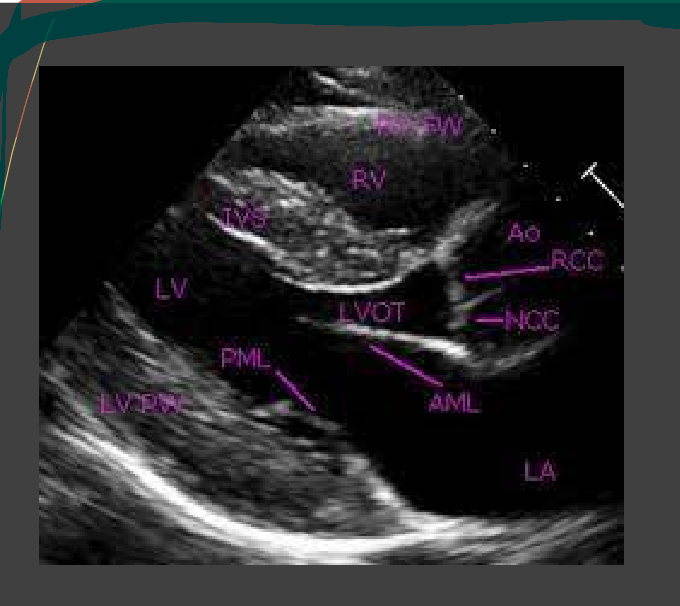
What is this view
parasternal long axis of the heart
what is normal aortic valve area
3.0-4.0 cm²
is 3.5 cm² a normal valve area?
yes
What is a normal MVA?
4.0 cm²
to treat mitral stenosis the **** balloon must go *****
Inoue balloon must go transseptal
an INOUE balloon is used to treat what
mitral valve stenosis
paravalvular leak occurs between implanted valve and surrounding aortic tissue
paravalvular
TAVR valvular leak where the leak occurs within the cage or scaffold of the implant but above the implanted valve tissue
supravalvular leak
What view is this
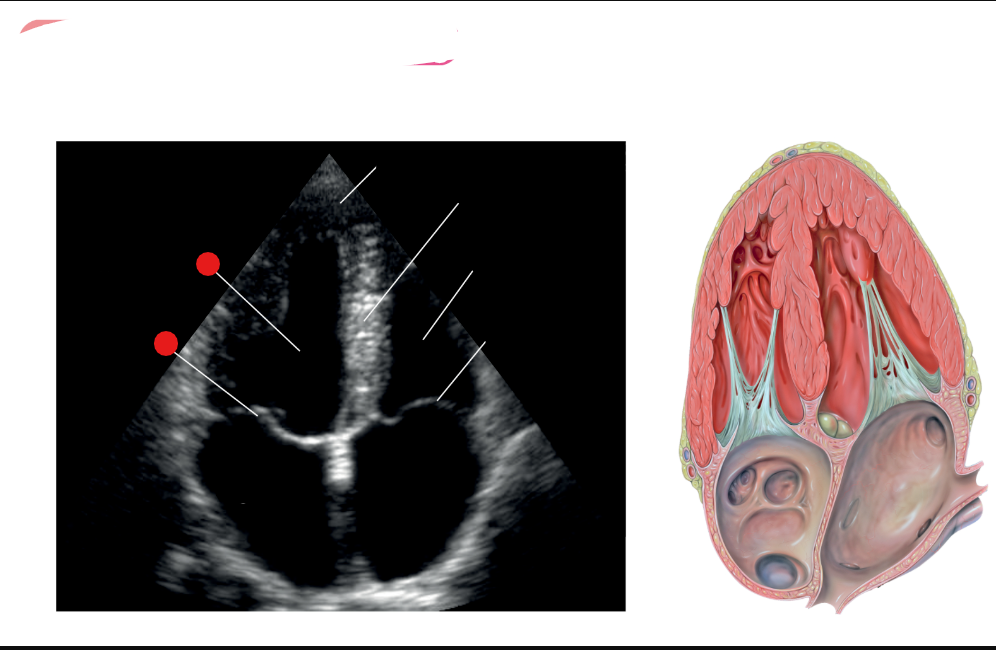
label red
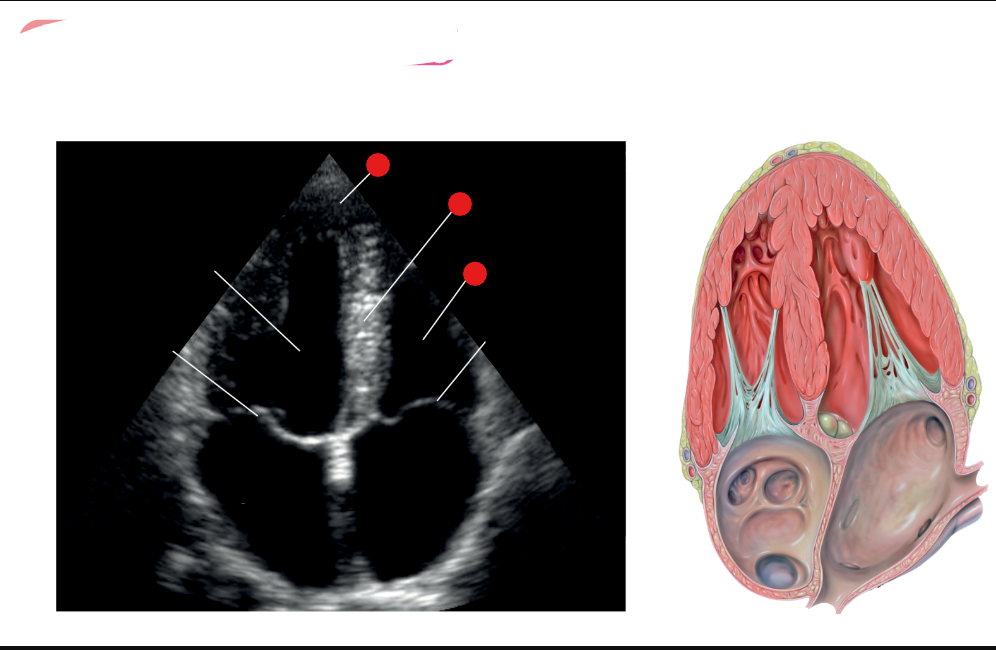
label red
label red
In the radial cocktail how much verapamil is used
verapemil 2.5 - 5mg
in radial cocktail how much nitro and heprin is given
nitro 100 - 200 mcg
heparin 40 u/kg
what are the two universal access catheters
choose two
tiger
jl4
kimmy
EBU
kimmy
tiger
which of the following is a direct thrombin inhibtor
aspirin
biviliruden
coumadin
eptifibitide
bivilirudiin
what two meds comprise dapt
aspirin and clopidogrel (plavix)
CLOPIDEGROL (Plavix) loading and maintenance dose
loading 300 - 600
m. 75 mg
brilinta (Angiomax) loading and maintenance
180 loading
90 mg maintenance dose.
PRASUGRAL (Effiant) loading and maintenance
l 60 mg
m 10 mg
aspirin loading and maintenance
L 325 mg
M 81 mg
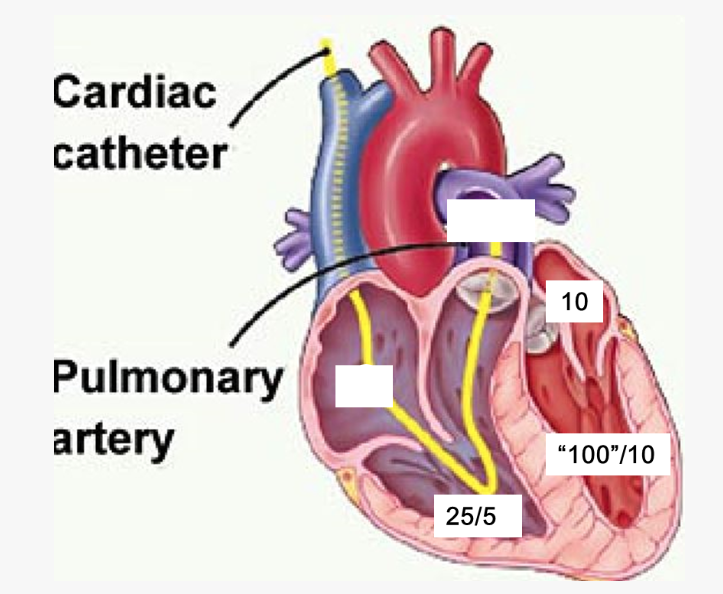
When performing a thermodilution cardiac output, 10 cc of injectate enters into the ___, and the temperature change is measured in the ___.
RA
PA
Afterload is most impacted by ________?
SVR
Place the grafts in the correct order as they would appear on the Aorta in a patient with 4 X CABG (quadruple bypass).
OM
DIAG
LAD
RCA
unless you have a 4 vessel bypass and you stick LAD between OM and DIAG (double check this to be sure)
excluding the 3rd degree heartblock which one is likely to become lethal
2nd degree type 2