Bioavailability II
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Which of the following is false in regards to Extraction ratio (E)?
a. Value ranges from 0 to infinity
b. A fraction of drug eliminated by a drug-eliminating organ during single pass metaboism
c. Efficiency of a drug-eliminating organ to eliminate a drug
d. Drug-dependent (property of drug)
a. Value ranges from 0 to infinity
Values range from 0-1
Which of the following is true about Extraction ratio (E)? (Select all that apply)
a. High EH drugs have EH > 0.7
b. High EH drugs have EH < 0.7
c. Low EH < drugs have EH < 0.3
d. Low EH < drugs have EH > 0.3
a. High EH drugs have EH > 0.7
c. Low EH < drugs have EH < 0.3
Which of the following are Low EH drugs? (Select all that apply)
a. Verapamil
b. Rifampin
c. Cimetidine
d. Warfarin
e. Theophylline
f. Propranolol
d. Warfarin
Has HIGH plasma protein binding
e. Theophylline
not a good substrate for drug-metabolizing enzymes
Which of the following are High EH drugs? (Select all that apply)
a. Verapamil
b. Rifampin
c. Cimetidine
d. Warfarin
e. Theophylline
f. Propranolol
a. Verapamil
Good substrate of drug-metabolizing enzymes (takes precedence)
Has high plasma protein binding
What determines if a drug is LowH?
a. If a drug is a good substrate of drug-metabolizing enzymes
b. If the drug is high protein-binding.
c. If the drug is present in small amounts.
d. If a drug has low enzyme activity (not a good substrate for drug metabolizing enzymes)
b. If the drug is high protein-binding.
d. If a drug has low enzyme activity (not a good substrate for drug metabolizing enzymes)
What determines if a drug is High EH?
b. If the drug is high protein-binding.
c. If the drug is present in small amounts.
d. If a drug has low enzyme activity (not a good substrate for drug metabolizing enzymes)
a. If a drug is a good substrate of drug-metabolizing enzymes
Is not limited by protein binding unlike low EH drugs
Which is true about CLint (intrinsic clearance)?
a. It reflects the natural ability of the liver to metabolize a drug in its free form (unbound form)
b. Drug-dependent (property of drug)
c. Values are greater than 0, goes to infinity
d. Drugs with large CLint are rapidly metabolized by the liver while Drugs with small CLint take longer to metabolize
e. All of the above are true
e. All of the above are true
True or false: CLint can be measured directly from plasma concentrations.
False. CLint is typically determined from in vitro systems (using liver tissues).
Cp gives CL (systemic) and CLH (hepatic
Which of the following are enzyme inducers? (Select all that apply)
a. Erythromycin
b. Cimetidine
c. Phenobarbital
d. Rifampin
c. Phenobarbital
d. Rifampin
Which of the following are enzyme inhibitors? (Select all that apply)
a. Erythromycin
b. Cimetidine
c. Phenobarbital
d. Rifampin
a. Erythromycin
b. Cimetidine
Which of the following is false?
a. CLint of a drug reflects how good a substrate a drug is to drug-metabolizing enzymes
b. CLint reflects the ability of the liver to metabolize a drug also dependent of binding restrictions
c. Enzyme inhibitors inhibit activities of drug-metabolizing enzymes (i.e. Cimetidine)
d. Enzyme inducers induce expression of drug-metabolizing enzymes. (i.e. Rifampin)
b. CLint reflects the ability of the liver to metabolize a drug also dependent of binding restrictions
If verapamil has high protein binding and high intrinsic clearance, what will happen to its hepatic extraction ratio (EH) if its free fraction (fu) increases?
a. significant effects on EH
b. insignificant effects on EH
b. insignificant effects on EH
Verapamil is a high EH drug, and in high EH drugs, metabolism is not limited by protein binding. What matters is if a drug is a good substrate of drug-metabolizing enzymes.
Verapamil is a good substrate
Which of the following has low enzyme activity against a drug limit hepatic elimination?
a. Warfarin
b. Verapamil
a. Warfarin
Low EH drug
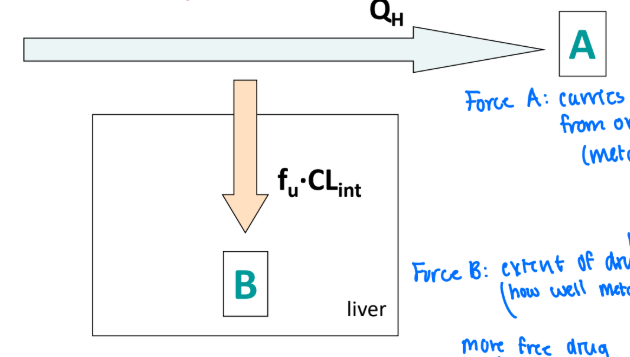
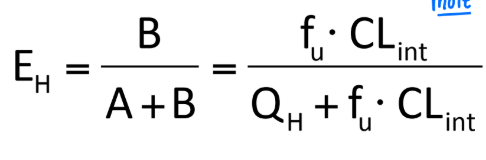
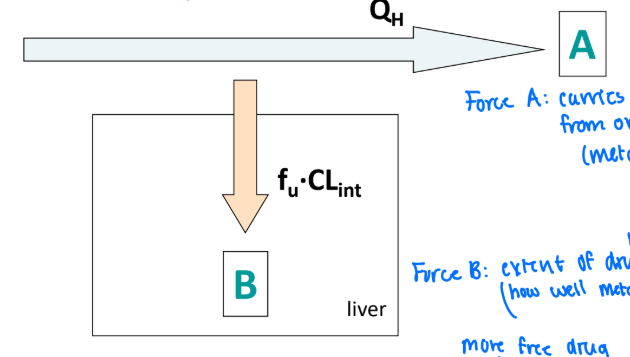
Define the variables included in the Well-Stirred Model (EH)
B (Force B) = extent of hepatic drug metabolism
how well metabolism is show
more free drug, more metabolism
A (Force A) = carries drug away from organ/metabolism site
fu = unbound fraction
QH = hepatic plasma flow
CLint = intrinsic clearance
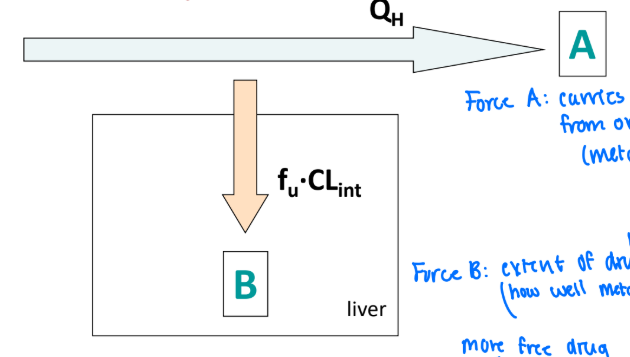
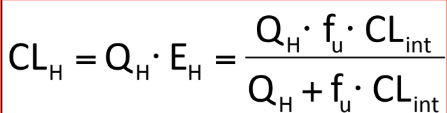
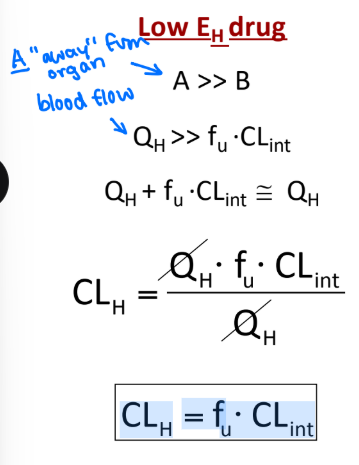
Given this image and equation, what can you say about Low EH drugs?
(Select all that apply)
a. Force A > > > Force B
b. has low enzyme activity; blood flow dominates (QH)
c. CLH = fu * CLint
d. CLH = QH
a. Force A > > > Force B
b. has low enzyme activity (fu * CLint ); blood flow dominates (QH)
c. CLH = fu * CLint
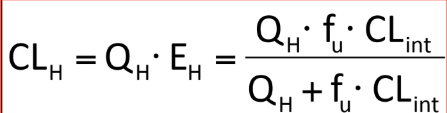
Given this image and equation, what can you say about High EH drugs? (Select all that apply)
a. Force A < < < Force B
b. has high enzyme activity (fu * CLint ) > QH
c. CLH = fu * CLint
d. CLH = QH
a. Force A < < < Force B
b. has high enzyme activity (fu * CLint ) > QH
d. CLH = QH
Which affects Hepatic Plasma Flow (QH)?
a. Increased by food
b. Increased by enzyme inducing drugs (i.e. Rifampin, phenobarbital)
c. Decreased by liver disease, dietary deficiencies, & enzyme inhibiting drugs
d. Decreased by disease states (<3 failure, liver disease, propranolol)
a. Increased by food
d. Decreased by disease states (<3 failure, liver disease, propranolol)
Which affects Hepatic Enzyme Activity (CLint)?
a. Increased by food
b. Increased by enzyme inducing drugs (i.e. Rifampin, phenobarbital)
c. Decreased by liver disease, dietary deficiencies, & enzyme inhibiting drugs
d. Decreased by disease states (<3 failure, liver disease, propranolol)
b. Increased by enzyme inducing drugs (i.e. Rifampin, phenobarbital)
c. Decreased by liver disease, dietary deficiencies, & enzyme inhibiting drugs
Which of the following is false about plasma proteins?
a. synthesized in the liver
b. drugs with higher affinity for the same protein binding site do not displace the drug already on the site
c. albumin is a plasma protein
d. chronic liver disease (cirrhosis) decrease plasma protein concentrations
b. drugs with higher affinity for the same protein binding site do not displace the drug already on the site
False. Aspirin has higher binding affinity so it displaces Warfarin from Albumin.
True or false: For Low EH, CLH is affected only by changes of QH.
False. Low EH —> CLH is affected by changes in CLint and fu.
Rate-limited by the concentration of unbound drug that enters hepatocytes and metabolic activity
True or false: For High EH, CLH is affected only by changes of QH.
True! CLH is rate limited by rate of drug presentation to liver