unit 1-6
1/55
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
functions of the nervous system (6)
perception
special senses (5 modalities), somtosensory (5 submodalities), visceral)
movement
life-sustaining
cognition
emotion
arousal
LAMPCE
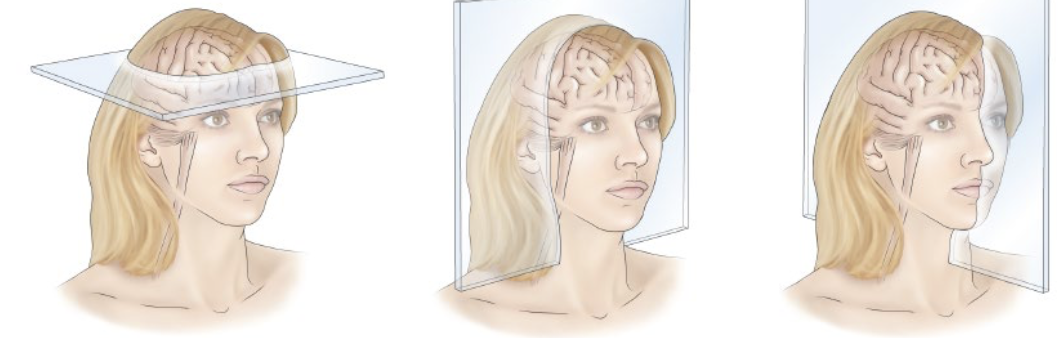
3 neuroanatomical planes
horizontal plane
coronal plane
sagittal/midsagittal plane
4 components of central nervous system with subcomponents if applicable
forebrain - cerebrum/cerebral hemisphere, diencephalon
brainstem - midbrain, pons, medulla
cerebellum
spinal cord
peripheral nervous system: somatic vs autonomic components (2 each)
somatic = sensory nerves/ganglia, motor nerves
sensory nerves = afferent fibers
motor nerves = efferent fibers
autonomic = sympathetic nerves/ganglia, parasympathetic nerves/ganglia
number of cranial nerves vs spinal nerves
cranial = 12
spinal = 31
developmental origins of neuroanatomy
3 vesicle stage (3 wks post-fertilization, cephalic/cervical flexure)
prosencephalon (forebrain)
mesencephalon (midbrain)
rhombencephalon (hindbrain)
5 vesicle stage (5-6 wks post-fertilization)
telencephalon (cerebral hemisphere), diencephalon (thalamus and hypothalamus)
mesencephalon (midbrain)
metencephalon (pons), myelencephalon (medulla)
Number corresponds to each other
4 classifications of neurons by function
sensory
motor
autonomic
interneuron
4 classifications of neurons by morphology (# extensions from cell body) + 2 classifications by shape of cell body
unipolar = 1 extension from cell body
bipolar = 2 extensions from cell body
multipolar = 3 dendrites + 1 axon from cell body
pseudo-unipolar = cell body and extensions merge (dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord)
shape of cell body
pyramidal cell and star-like cell
8 classifications by neurons and synapses by pharmacology: glutamate, gaba, acetylcholine, dopamine, glycine, serotonin, norepinephrine, histamine
glutamate - glutamatergic (most common NT)
gaba - gabaergic
acetylcholine - cholinergic
dopamine - dopaminergic
glycine - glycinergic
serotonin - serotonergic
norepinephrine - noradrenergic
histamine - histaminergic
(also pharmacologic classification of synapses)
3 qualifications to be a NT?
manufactured by presynaptic neuron
requires Ca to release into synapse
receptor in postsynaptic membrane
Match the neuronal structures and functional zones:
Terms: input zone, integrative zone, conducting zone, transmitting zone, insulation, action potential regeneration, transmitter release, transmitter uptake
Functional zones: axon, axon terminal, myelin, postsynaptic membrane, nodes of ranvier, initial segment axon hillock, presynaptic membrane, dendrites/sensory endings,
input zone = dendrites, sensory endings
integrative zone = initial segment axon hillock
conducting zone = axon
transmitting zone = axon terminal
insulation = myelin
action potential regeneration = nodes of ranvier
transmitter release = presynaptic membrane
transmitter uptake = postsynaptic membrane
synapse morphology and functional classifications (2)
chemical synapse = presynaptic and postsynaptic neuron separated by synaptic space
electrical synapse = cytoplasmic continuity between presynaptic and postsynaptic neuron
types of macroglia vs microglia cells
macroglia: astrocytes, ependymal cells, oligodendrocytes, schwann cells
microglia: from yoke sacs of embryo, macrophages, bone marrow, hematopoetic
how many glial cells are in the human CNS? different function of glial cells in PNS vs CNS?
~1 trillion
PNS glial cells = support, insulate
CNS glial cells = support, insulate, filtrate, communicate
smooth brain → addition of cerebral cortex, sulci and gyri fancy names
lissencephalic → gyrencephalic
how many lobes of the cerebral cortex? structure and function?
5 lobes of the brain (frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, *insula)
structure: surface has sulci, beneath is nuclei
function: perception and movement they drive (learning their names ain’t no jive)
what is the 5th lobe and what is it covered by?
insula hidden by opeculum (frontal, parietal, temporal) aka “lips”
functional areas of cerebral cortex: primary cortex, secondary cortex, association cortex, homunculus
primary cortex = sensorimotor, M1, S1, A1, V1
secondary cortex = S1 → S2, A1 → A2, V1 → V2
association cortex = complex integrative analysis (i.e executive functions via insights, planning)
homunculus = body map (somatosensory and motor homunculus)
brodmann areas
BA 1-3, 5, 7 ~ somatosensory cortex
BA 4, 6, 8 ~ motor, premotor cortex
BA 39-40 ~ receptive language (reading, speech)
BA 44-45 ~ speech generation (grammar, planning)
gray and white matter: cerebral hemisphere (4), diencephalon (2), brainstem/cerebellum (3), spinal cord (2)
cerebral hemisphere: cortical mantel, basal ganglia, hippocampus, amygdala
diencephalon: thalamus, hypothalamus
brainstem/cerebellum: motor nuclei, relay nuclei, modulatory nuclei
spinal cord: motor nuclei, interneurosn
gray matter vs white matter
gray matter = clustered cell bodies form nuclei (nuclear groups)
white matter = myelin enveloping axons
white matter fibers form (7)
tract
pathway
funiculus
faciculus
leminiscus
penduncle
stria
cerebral cortex + neocortex, paleocortex, archicortex
cerebral cortex = a laminated mantel of gray matter
lamina history varies across cortical regions
neocortex = 6 layers
plaeocortex = <6 layers
archicortex = 3 layers
subcortical white matter: association fibers, commissural fibers, projection fibers
association fibers = anterior → posterior, posterior → anterior
commissural fibers = left → right, right → left
projection fibers = vertically oriented cortex → subcortical or thalamus to cortex
naming conventions for fiber tracts: cell body location to synapse location → name
definitions: corona radiata, internal capsule
corona radiata = regions of axons to/from cortex fanned out
internal capsule = region same axons are compressed
choroid plexus
filtration → CSF
CSF (ventricles)
lateral and medial apparatus → subarachnoid space → CSF pools in cisterns = expanded regions within subarachnoid space, CSF in perivascular space
Diecephalon and brainstem ventral surface structures
diencephalon (ventral/inferior)
CN II, optic chiasm, optic tract, infundibulum, mammilary bodies
brainstem (ventral/anterior)
midbrain: cerebral peduncle, interpendicular fossa, CN III
pons: CN V-VIII
medulla: CN IX-XII, pyramids, pyramidial decussation, olives
length of spinal cord
~17-18”
spinal cord regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral distinguishing features
cervical (n=8): axons from UE/trunk/LE, greatest total white matter, large ventral horns (LMNs for UE muscles)
thoracic (n=12): all axons from trunk/LE, very small ventral horns (LMN for trunk muscles)
lumbar (n=5): all axons for LEs, large ventral horns (LMNs for LE muscles)
sacral: few axons for LEs, ventral horns appear prominent but cord very small in diameter, more gray than white matter
how many fasciculi does the cervical cord vs thoracic-lumbar-sacral have?
cervical = 2
t-l-s = 1
intermediolateral nucleus
clark’s nucleus T1-L2/3 and lateral horn
lateral horn vs sympathetic chain (each side of SC)
lateral horn = cell bodies for sympathetic preganglionic neurons
sympathetic chain = cell bodies for sympathetic postganglionic neurons
meninges 3 layers, 3 spaces, 2 vascular supplies
meninges: dura (makes up cerebral falx and cerebellar tentorium), arachnoid, pia
spaces: epidural, subdural (common site in bleeding), subarachnoid (normal space contains CSF)
vasculature: blood vessels, dural sinuses
tumor + herniations within dura
tumor location: hemotoma of cingulate gyrus, medial temporal lobe, cerebellar tonsil
herniations: herniates under cerebral falx, under cerebellar tentorium → compress brainstem, into foramen magnum
perosteal dura ends at ____ ____
meningeal dura envelopes _____ ___ and ____
periosteal dura ends at foramen magnum
meningeal dura envelopes spinal cord and nerves
name of anterior artery: ____ % of blood supply to brain
name of posterior artery: ____ % of blood supply to brain
internal carotid; 80%
vertebral; 20%
anterior communicating artery vs posterior communicating artery
anterior = joins left and right circulation
posterior = joins anterior and posterior circulation
motor homunculus (order)
hand, face, jaw, tongue, throat
what two arteries overlap with middle cerebral artery (MCA)?
ACA, anterior chordial artery
somatosensory fibers: dorsal….
as
all LMN functions and some somatosensory: lateral, intermediate, ventral…
somatosensory fibers: dorsal columns, roots, horns
all LMN functions and some somatosensory: lateral column, intermediate column, ventral column, roots, horns
circumventricular organs (3), lipid soluble molecules (3), active transport (3)
circumventricular organs: ion [ ], hormones, signalling molecules
soluble: alcohol, caffiene, nicotine
active transport: glucose, enzymes, essential proteins and amino acids
choroid plexus 3 layers, key components for CSF production (3)
choroid plexus: capillary, endothelial wall, fragmented pia and collagen (for filtration of blood plasma), ependymal choroid epithelium
key for CSF production: vascular fenestrations, tight junctions, choroid fronds/villi
plexus produces ____ ml CSF/day
500
note: total CSF volume = 150 ml (ventricles/subarachnoid space)
CSF circulation
lateral ventricles → 3rd ventricle → 4th ventricle → subarachnoid space -(arachnoid granulations) → superior sagittal sinus (mixes with venous blood)
somatosensory functions (5)
motor control = posture, coordination of movement, object manipulation
objetive identification
avoidance of itssue damage
formation of body schema
psychosocial = emotional wellness, communication
conscious sensory perception
first order neurons: sensory neurons, pseudounipolar/unipolar neurons, cell bodies form ganglion (DRG/PNS), peripheral region of axon forms peripheral nerve, central region of axon forms tract
second order neurons: interneurons, multipolar neurons, cell bodies forms CNS nucleus, axons may/may not decussate, axons form (fiber) tract
third order neurons: interneurons, cell bodies form thalamic nucleus, axons form tracts and cortical radiation, axons synapse in primary sensory cortex
skin mechanoreceptors vs muscle mechanoreceptors
skin:
alpha-beta: merkel cells, meissner’s corpuscle, ruffini corpuscle, pacinian corpuscle, hair receptor
muscle:
1a, II: muscle spindle
1b: golgi tendon
contraction for muscle proprioceptors
contraction shortens muscle fiber length → gamma motor shortens intrafused fibers to maintain spindle sensitivity
__ fiber senses changes in tendon tension ~ muscle contractile force
afferent fiber
sensory endings of first order neurons have mechanoreceptors embedded in _____ ____
afferent endings
receptive fields are maps of individual sensory neurons. they vary ini
location, density, spatial area size, neuron responses
dermatomes are composed of multiple RF, modalities, submodalities.
1 dermatome =
2 dermatomes =
1 dermatome = 2 receptive fields, 2 submodalities
2 dermatomes = 2 receptive fields, same modality
proprioception vs touch: receptor type, afferent axon type
proprioception:
muscle spindle/golgi tendon organs
Ia, II, Ib
touch:
merkel, meissner, pacinian, ruffini
AB
caudal receptive fields:
as
rostral receptive fields:
caudal receptive fields: medial gracilus fasiciculus (LE, trunk)
rostral receptive fields: lateral cuneate fasiciculus (UE)
DCML pathway
cortex (BA)
subcortical: corona radiata, internal capsule - posterior limb
thalamus: VPL thalamus
midbrain
pons: medial leminiscus
rostral medulla
caudal medulla: arcuate fibers, gracilis nucleus
cervical
thoracic
lumbar: dorsal column, gracilis fasciculus, DRG, AB fiber, peripheral nerve
sacral