Business Studies OCR: Marketing
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Main purposes of marketing
Identifying and understanding customers
Informing customers
Increasing sales
What is marketing?
Finding out the needs of customers and demonstrating how a business fulfils those needs, so that its sales increases
What is market research?
The collection of data on customer habits to help decision-making in marketing
What are the 4p’s of marketing?
Price
Product
Place
Promotion
What information does market research aim to find?
Age
Economic status
Culture
Location
Wants and needs
What information is needed from market research to avoid expensive mistakes?
The product or service customers want
The prices customers are willing to pay
The design of the product that will be attractive to customers
How many products customers will buy
How to target customers
Where and how to sell goods and services
Primary research methods
Questionnaire
Interview
Trialing
Focus group
What is primary research?
Data that is collected first hand
What is secondary research?
The collection data using research and information provided by others
Secondary research methods
Methods of secondary research | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
UK census data | The national census data finds out about all UK households every 10 years Includes information about the numbers of people living in the household, their income and where they live | Information comes from a lot of people-almost the whole population of the country It is already collected ad analysed, reducing the cost to the business | Information has not been collected for the specific needs of the business Information will need careful interpretation |
Data from newspapers and magazines | Articles in publications often describe peoples interests and current fashions | Such information is up to date, cheap and a good source of ideas | Information will be general and not specific to the business |
Data from websites | Information about other companies can be found, including what they sell and the prices they charge | Cheap to collect and readily available. Such data can help a business decide what to produce and what to charge | Information will be general and not specific to the business |
Internal data | This data is collected by the business for certain purposes | Cheap to collect and readily available and is specific to business | Data is historical-its looks at what has happened not what will happen |
How to choose what research to conduct?
How much the business can afford to spend
What information is required
Location of customers
How quickly the information is needed
What is quantitive data?
Data collected that is based on facts or numbers, it is usually easier to analyse than qualitative data
What is qualitative data?
data based on the opinions of those being asked
What is market segmentation?
Splitting the market for a product or service into different parts or segments
Ways of segmenting a market
Age
Gender
Income
Lifestyle
Location
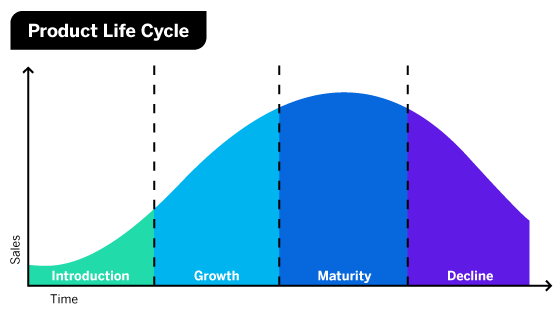
Define decline
When sales are falling as the product or service is seen by customers to be old and they switch to new products and services
Define design
An important element in a number of products, especially where style and technology work together
Define growth
When sales are growing strongly as the new product or service becomes known
Define innovation
The improvement of an original idea, which will often involve using a new process
Define maturity
When sales are at their highest level
Define the product life cycle
The life cycle of a product, usually shown as a graph divided into four stages: introduction, growth, maturity, decline
Pricing methods of a product
Skimming
Cost-plus pricing
Promotional pricing
Competition pricing
Penetration pricing
Define competition pricing
a price is set based on prices charged by competitors for a similar product
Define cost-plus pricing
a pricing method that adds a percentage for profit to the total costs of making the product. This gives the selling price
Define penetration pricing
A price is set lower than those of competitors.Often used by new businesses to break into the market. It is a short-term strategy only
Define promotional pricing:
Prices are reduced to give products a boost or to sell off old stock
Define skimming
Where a new product is more advanced than that of its competitors, a price is et high as consumers are willing to pay higher prices to own the newest technology
Point of sale promotions
Price reductions
Competitions
Loss leaders
Free samples
Ways of advertising
Social media
Websites
Television
Print media
Radio
Physical distribution
the distribution of a good or service using physical presence
Digital distribution
the distribution of goods and services digitally by downloading from a website
Define market data
Information that can help marketing decisions
Define market share
The % of total sales of a product that a business has made