B1.2 and A1.2- Proteins and nucleotides
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
monomer of nucleic acid
nucleotide
protein
A three dimensional polymer made of monomers of amino acids.
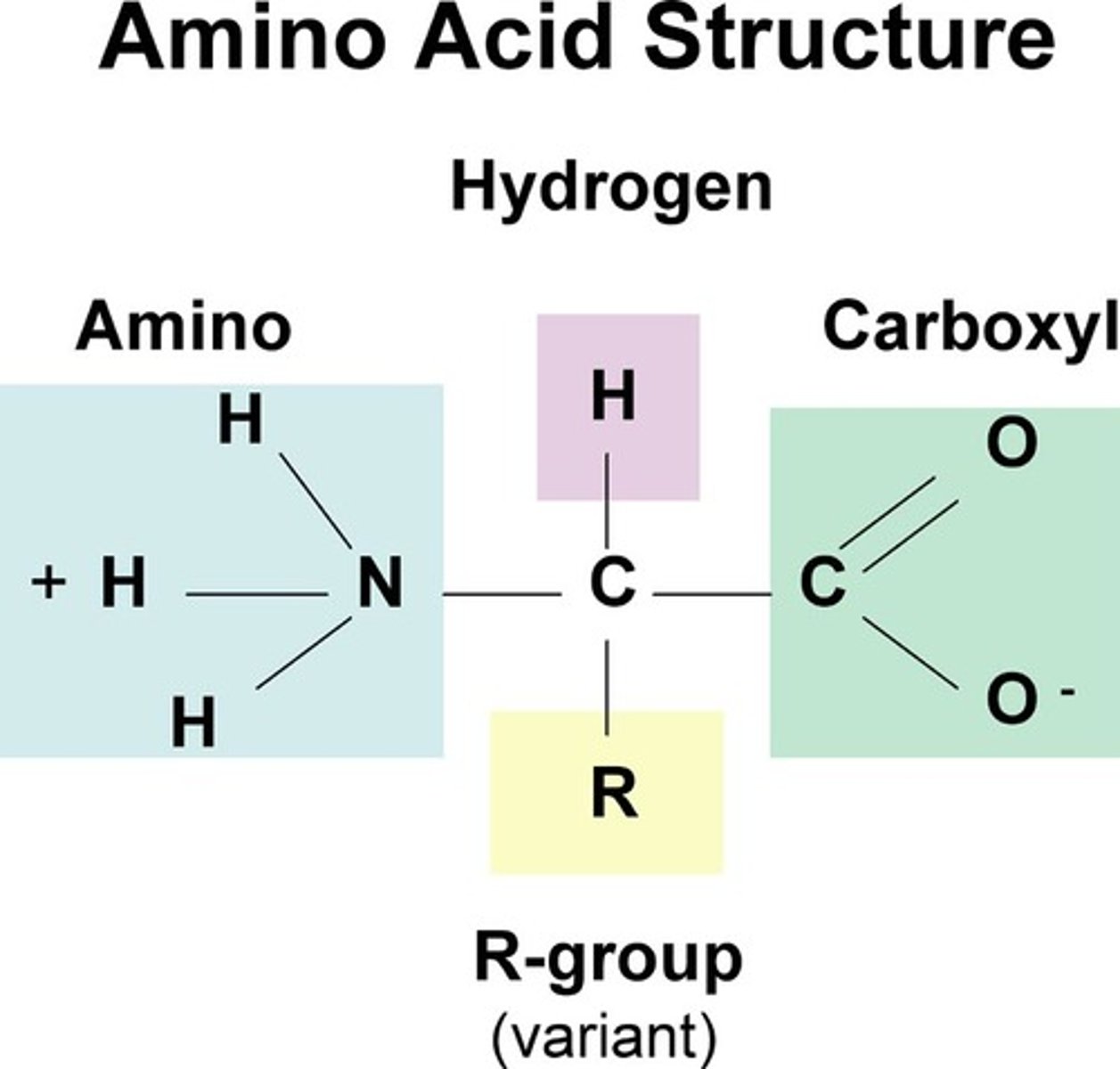
draw amino acid structure
carboxyl group, amino group, and variable group
r groups effects in amino acids
can make them acidic polar, basic polar, polar, or non polar
bond between amino acids
peptide bond- formed through condensation
essential amino acids
need to be obtained in our diet as the body can't synthesize them
non-essential amino acids
amino acids that the body can synthesize on its own; does not need to get from diet
Conditionally non-essential amino acids
amino acids that are synthesized when healthy, but not when you're ill.
effect of ph and temperature on protein structure
- when temperature increases beyond its optimum, the protein becomes denatured
- if ph is increased or decreased beyond its optimum, the protein denatures
denaturation
a change in the 3d structure of a molecule, making it fail to function
sugar phosphate backbone
when many nucleotides join together through condensation
How is the sugar-phosphate backbone formed?
by covalent bonding between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the pentose sugar of the next nucleotide.
condensation reaction (h20 released)
bond forming between nucleotides
phosphodiester bond- phosphate groups join with the pentose sugar of another nucleotide
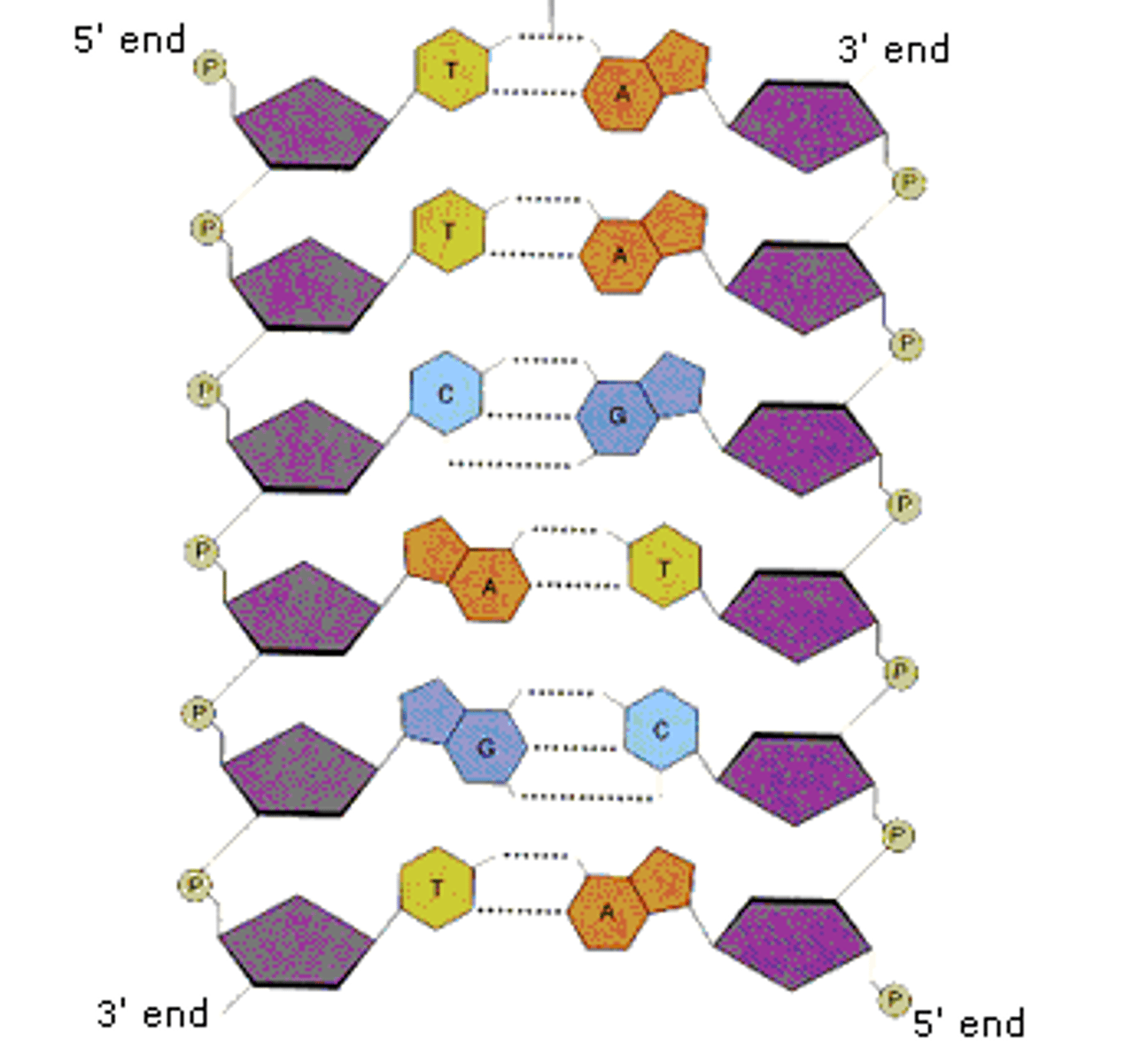
Complementary pairing in a double-strand structure of DNA.
adenine-thymine
cytosine-guanine
purines: adenine and guanine
pyrimidines: cytosine and thymine
purines always pair with prymidines
purine vs. prymidine
purines have two rings, prymidines have one
shape of DNA molecule
double helix, with antiparallel strands
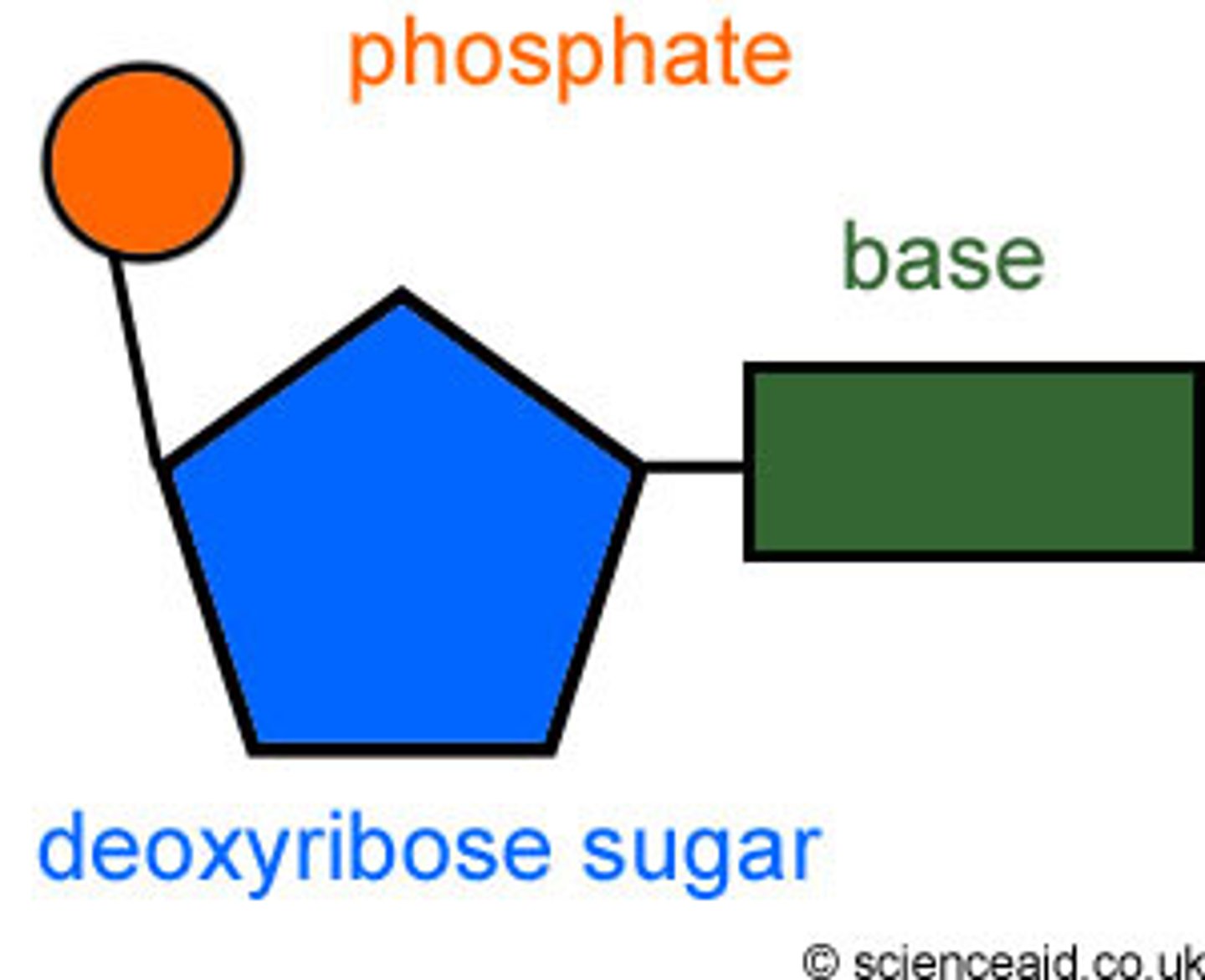
nucleotide
phosphate, pentose sugar, nitrogenous base
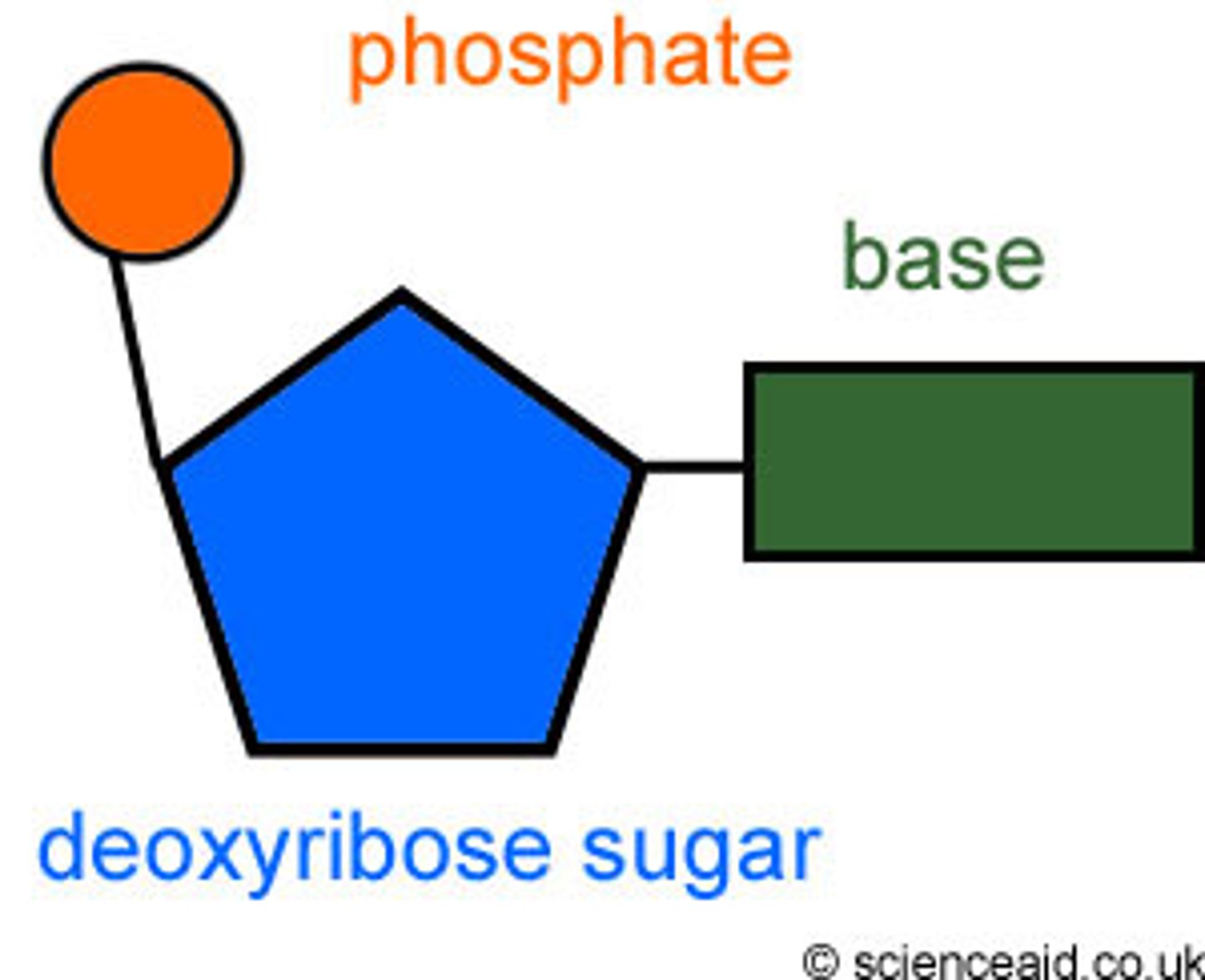
The nitrogen-containing bases found in DNA
Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine
The nitrogen-containing bases found in RNA
Adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil
RNA vs DNA
Single-stranded vs. Double- stranded,
Uracil vs. Thymine
Ribose sugar vs. Deoxyribose sugar
Draw RNA Polymer
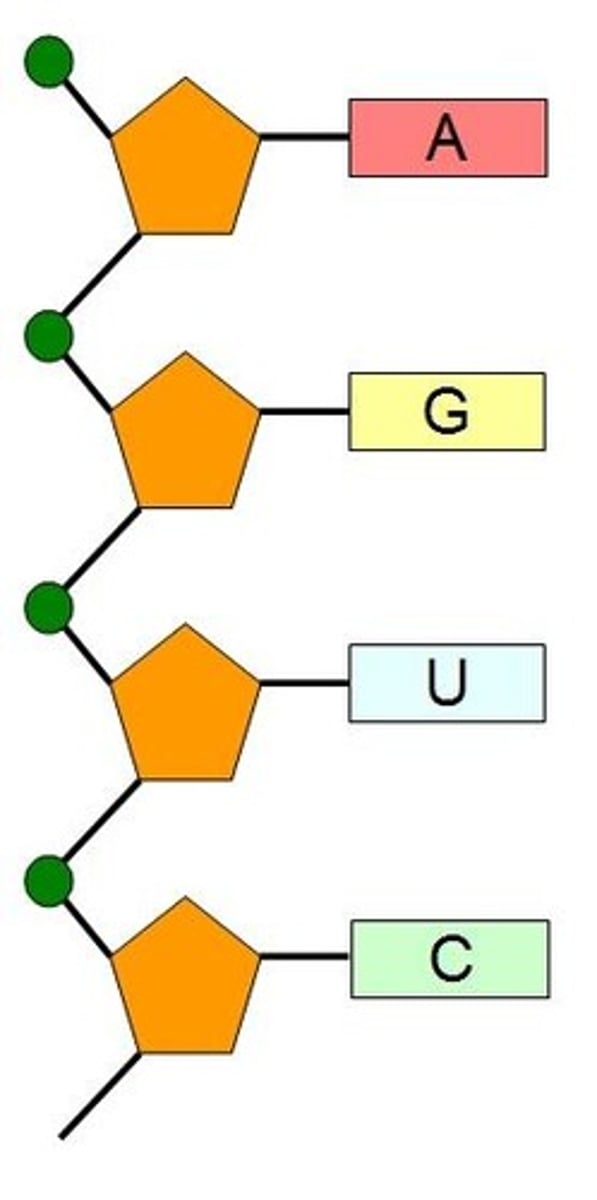
Draw DNA Polymer.
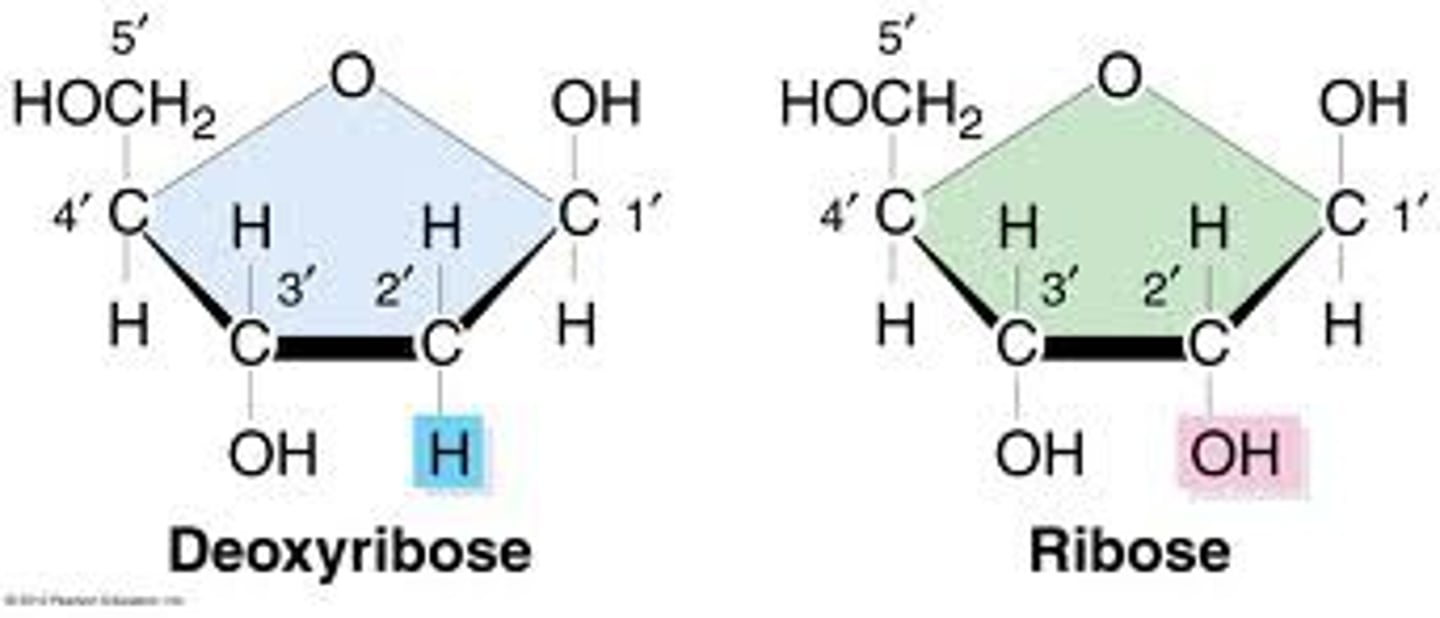
ribose vs deoxyribose chemical difference
ribose has oxygen on bottom, deoxyribose doesn't
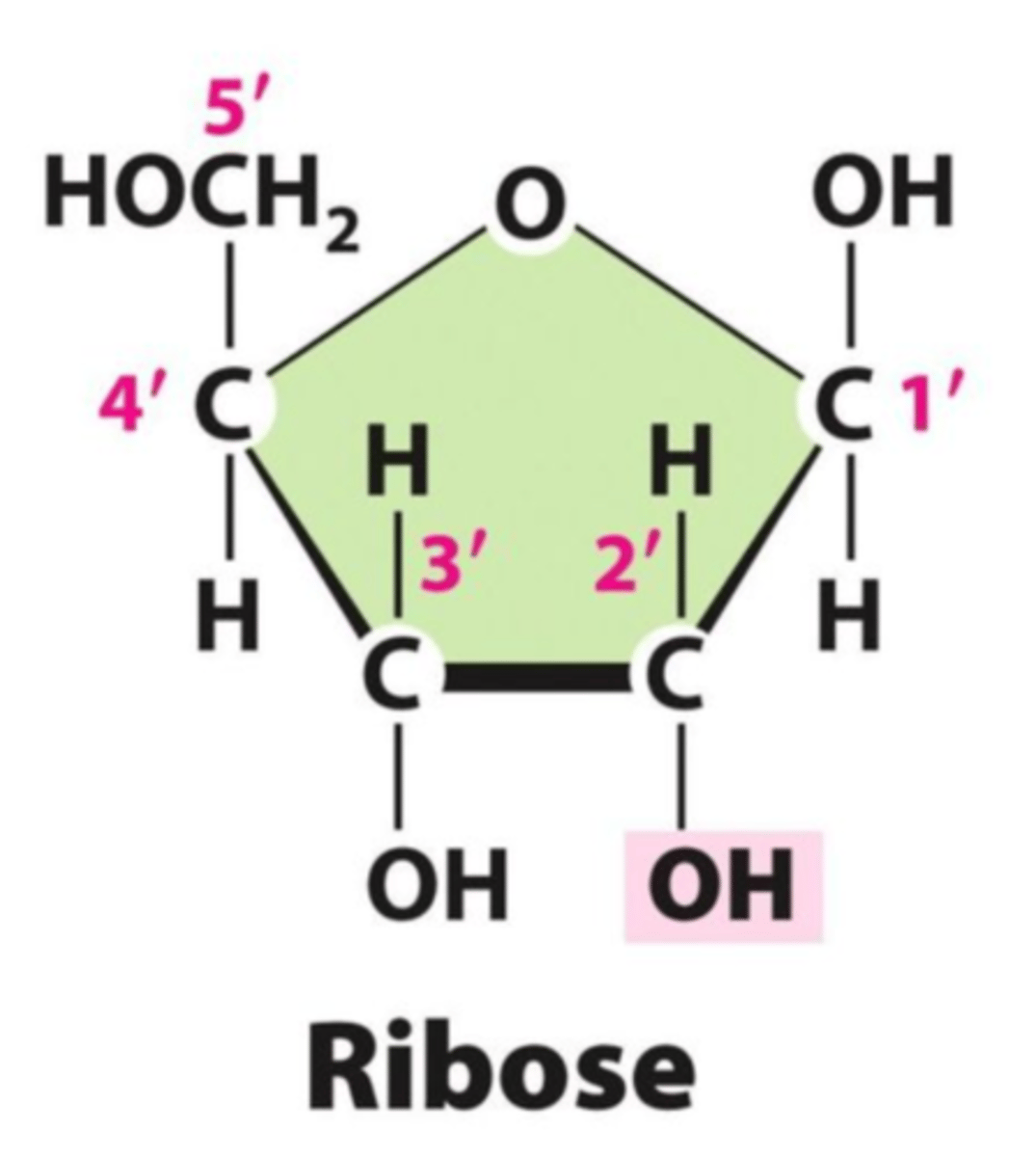
draw ribose sugar
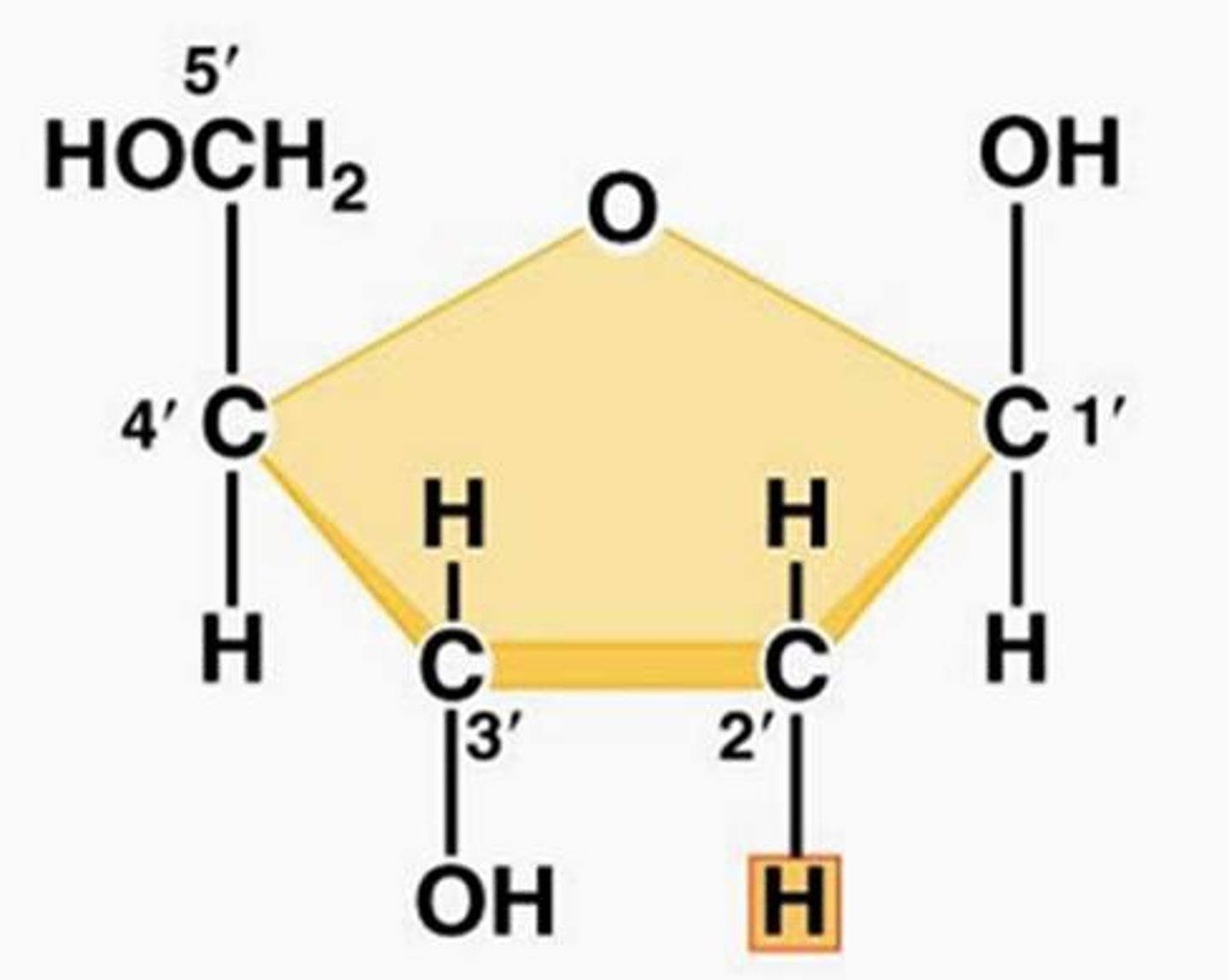
Draw deoxyribose sugar
Explain the importance of complementary base pairing in allowing genetic information to be replicated and expressed.
Maintains the specificity required for accurate copying and reading of genetic information.
Why are DNA sequences diverse
DNA can hold a lot of information (enormous capacity for storing data), so it can have many different sequences and lengths, giving rise to diversity.
DNA is a universal code?
Yes, it is. It is common to all organisms. Evidence of universal common ancestry.
The monomer of a protein
Amino acid
Polypeptide
A polymer (chain) of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
Dipeptide
Two amino acids bonded together
word equation for condensation reactions between amino acids to form dipeptides
Amino acid + amino acid >> dipeptide + water
Draw a dipeptide
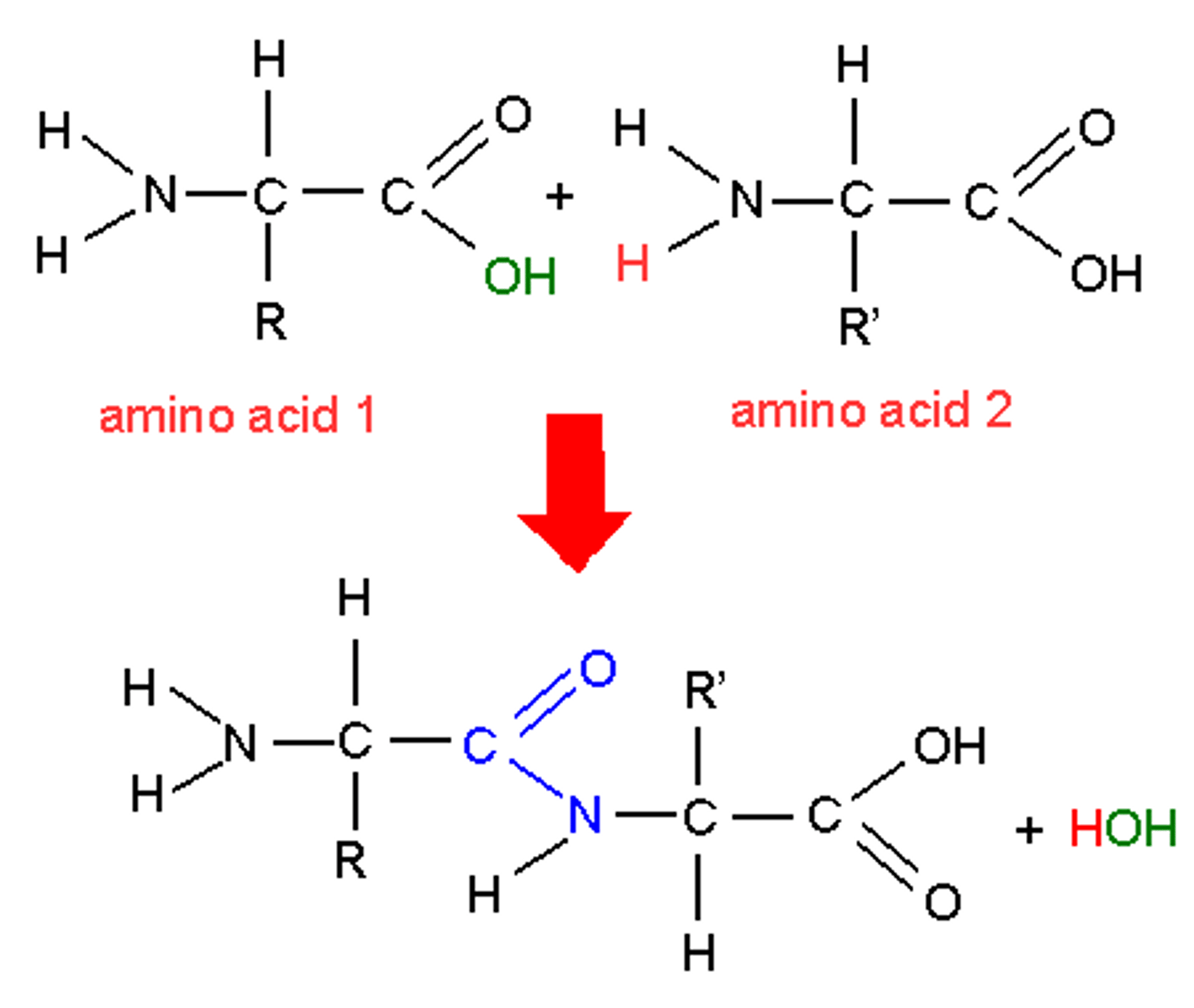
How many amino acids are coded for in the genetic code?
20
examples of polypeptides and function
Collagen: Structural proteins in tendons, ligaments, skin and blood vessel walls. Fibrous proteins.
Harmoglobin: Binds oxygen in the lungs and releases it in tissues with reduced oxygen. Globular protein.