Chapter 3 (Supply and Demand)
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Demand
The various quantities
of a good or service
which a consumer
is both willing and able
to purchase
at various prices
per unit of time
ceteris paribus
Supply
The various quantities
of a good or service
which a seller
is both willing and able
to sell
at various prices
per unit of time
ceteris paribus
10 Fundamental Principles of Economics
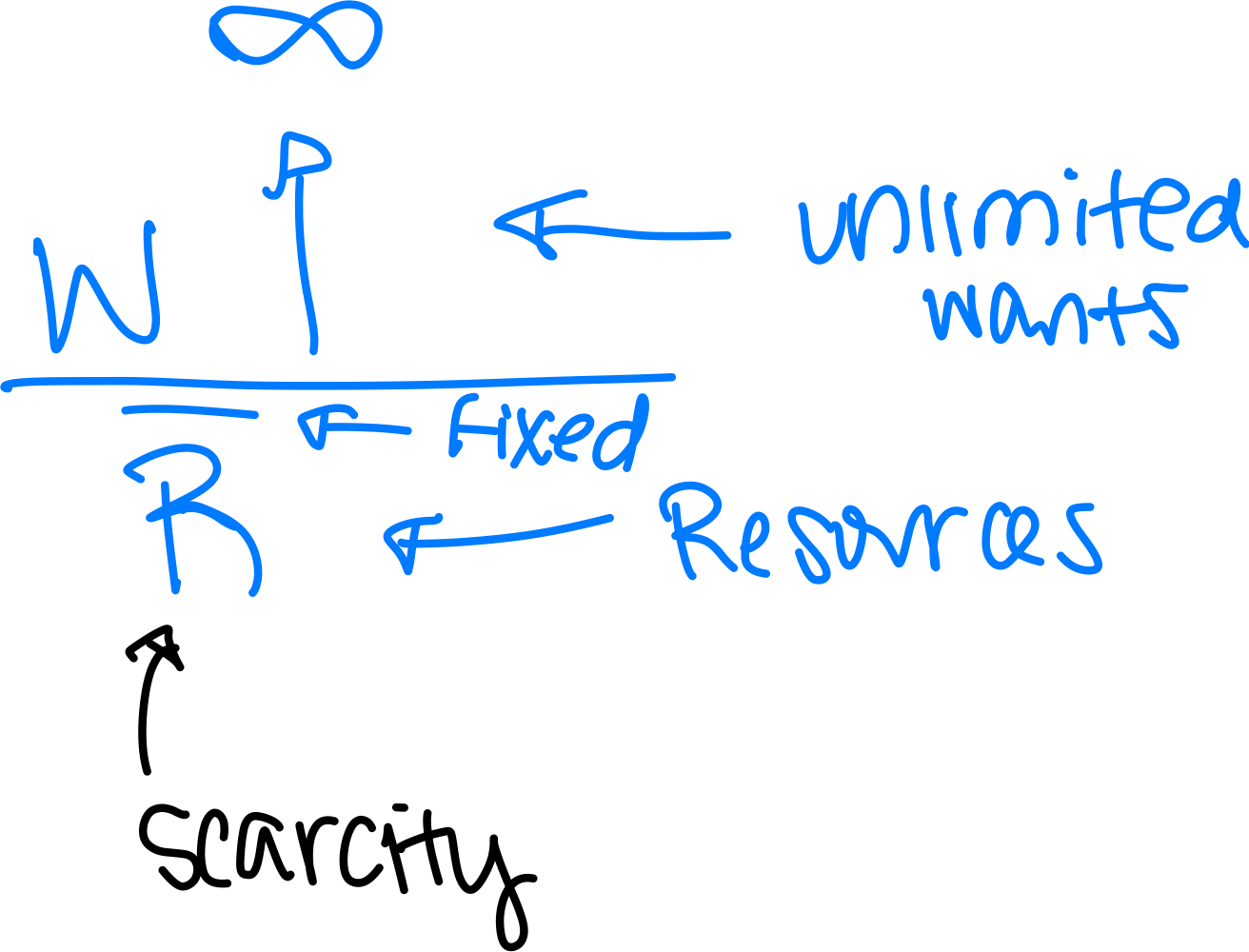
1)Scarcity is Inescapable
2)Risk is unavoidable
3)Therefore all persons must make choices
4)Incentives Matter
5)People generally act in their own self-interest
6)There is often more than one way to produce things
7)Voluntary exchange is mutually advantageous
8)It is wealth not poverty, which has causes
9)Public policies have primary and secondary effects
10)In the end, economic laws tend to prevail
Cobb-Douglas production Function
Y/Q=F(K,L)
Y/Q:Quantity, F:Function of, K:Capital, L:Labor
Economics
A social science that attempts to explain how individuals, firms, and nations allocate scarce resources among competing interests
Economics diagram
Social Science
Defined by the inability to replicate experiments
3 Basic Questions
1)What: What and how much will be produced? Allocation of Inputs
2)How: How will items be produced? Production
3)For Whom: For whom will items be produced? Allocation of Outputs
Centralized Command-Control System
A central authority decides the 3 basic questions.
Capitalism (Price) System
Price answers the 3 basic questions.
Compromise System
Government and Price answer the 3 basic questions
Customary (traditional) System
Tradition answers the 3 basic questions
Post hoc ergo propter hoc
“After this therefore because of this” First economic warning that states that just because one event proceeds another, it doesn’t mean it caused the second event. Time-series data.
Fallacy of Composition
Second economic warning that states that what holds true for an individual does not always hold true for the whole.
Correlation does not necessarily equal causation
Third economic warning. Cross-sectional data.
Violation of Ceteris Paribus
Fourth economic warning that says “other things being held constant” should not be violated.
Inclusion of an irrelevant variable
Fifth economic warning that states unrelated factors should not be taken into consideration
Exclusion of relevant variables
Sixth economic warning
Cause of bowed outward shape
Law of increasing opportunity cost
Consumer sovereignty
Actions in the marketplace dictate what is being made
Allocative efficiency
Right mix of goods, dictated by consumer sovereignty
Economic good
More of the good is preferred to less
Economic Bad
Less of the good is prefered to more
Consumer durable goods
Goods that are around for a long time
Consumer non-durable goods
Goods that dont last
Capital goods
Goods that create other goods. They allow for faster further development
Non-Price parameters of demand
Income, price of other goods, tastes/preferences, advertising, number of buyers, expectations
Formula for demand
Q^d=F(P|
Q^d:Quantity demanded, F:function of, P:price, |:Ceteris Paribus “all other things constant”
*Q and P are inverse (-)
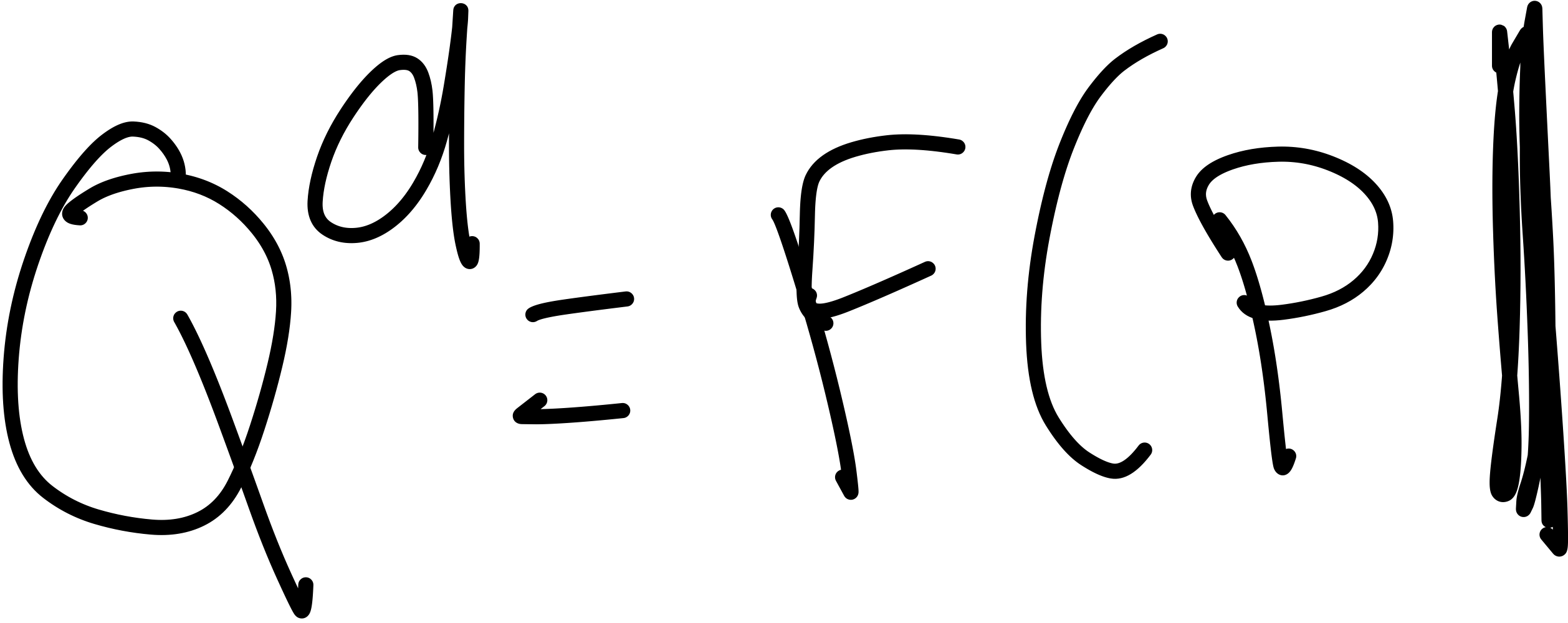
Positive Statement
Statement of fact. EX “If the price of gas goes up, people will buy less”.
Normative Statement
Value judgement, what “ought’ to be. EX “If the price of gas goes up, people will buy less. So we should not allow the price to go up”.
Household Macroeconomic Sector
Supplies the inputs, demands the output
Business Macroeconomic Sector
Demanding the inputs, supplying the outputs
4 Factors of Production
1)Land (Rent, smallest)
2)Labor (Wages, biggest)
3)Capital (Interest)
4)Entrepreneurship (Profit)
National Income
Sum of the 4 factors of production
Complementary goods
As the price of one good goes down, demand for the other goes up. (-).
Substitute good
As the price of one good goes up, the demand for the other also goes up. (+).
Normal Good
Increase in income=Increase in demand (+)
Inferior good
Increase in income=decrease in demand
Non-price parameters of Supply
Number of sellers, expectations of sellers, price of inputs, taxes and subsidies, technology, weather
Law of supply Equation
Q^s=f(P|
Consumer surplus
You have money left over from what you were willing to pay
Producer Surplus
More product left over from what you were willing to sell
Shift of the curve (Change in demand/supply)
Change in non price parameters
Shift along the curve (change in quantity demanded/supplied)
Change in price
Equalibrium
no shortage or surplus
Comparative statistics
1) Identify the original equilibrium price and quantity
2)Identify the shift (demand or supply)(left or right)
3)identify the new equilibrium price and quantity
Price floor
A case in which the government says, “you must charge at least ____”
The seller
Side the Government takes with a Price Floor
Effective price floor
Must be set above the equilibrium price and must result in a surplus and unemployment
Price ceiling
A case in which the government says “you can charge no more than___”
The buyer
Side the Government takes with a Price Ceiling
Effective price ceiling
Must be put below the equilibrium price and must result in a shortage
Case #1
D→ S→
P*=? Q*=up
Case #2
D← S←
P*=? Q*=down
Case #3
D→ S←
P*=up Q*=?
Case #4
D← S→
P*=down Q*=?
Output
Deals with GNP and GDP
Price Level
Deals with CPI(most controversial), PPI, and GDP deflator
Fair’s model
Output+Price
Predicts popular vote using output and price
Phillips curve
Price+Unemployment
When inflation is high, unemployment is low
Oken’s Law
Output+Unemployment
%changeGDP=3%-2 X A changeUnemployment
As unemployment goes down, GDP goes up
Full Employment Act of 1946
Pursued all 3 goals, Output, Price Level, Unemployment
Output increase, Price steady, Employment increase
Gross Domestic Product
1) The total dollar value
2)of all FINAL goods and services
3)Produced by ANYONE
4)within US BOARDERS
5)in a given calendar year
Gross National Product
1)The total dollar value
2)of all FINAL goods and services
3)produced by US CITIZENS/FIRMS
4)ANYWHERE in the world
5)in a given calendar year
Shift from GNP to GDP
Caused by texaco in Saudi Arabia in 1991
Nominal GDP
(CPa X CQa)+(CPo X CQo)
Real GDP
(BPa X CQa)+(BPo X CQo)
CPI
Fixed market basket of goods. Consumer goods, can include foreign products
CPI formula
((CPa X BQa) + (CPo X BQo))/((BPa X BQa) + (BPo X BQo))
Everything is base except Price in numerator
Laspeyres Price Index
Another name for CPI
GDP Deflator
Changing market basket. All goods and services produced within US borders.
GDP Deflator formula
((CPa X CQa) + (CPo X CQo))/((BPa X CQa) +(BPo X CQo))
Everything is current except for price in the denominator
Inflation
Increase in the overall price level
Deflation
Decrease in the overall price level
Hyperinflation
Extremely rapid increase in the overall price level
Disinflation
Slowing of the inflation rate
Arthur Oakum misery index
Inflation rate + unemployment rate
One-to-one trade off
The opportunity cost of receiving one grade higher in economics, is one grade lower for math
Comparative advantage
Ability to perform an activity at a lower opportunity cost
Only thing that matters when allocating time
Absolute advantage
If you were to spend a given amount of time on any duty, you could produce more than anyone else