principles of diagnosis
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what is health?
The WHO defines it as a state of physical , mental or social state of wellbeing and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity
health exists on a spectrum - sickness to wellness to then fitness
the more fit you are the greater buffer to declining into sickness

health - the numbers
out of 544k people who died in the UK in 2023, 21.6%were considered avoidable as they were from preventable conditions
what does health mean to you?

the consultation
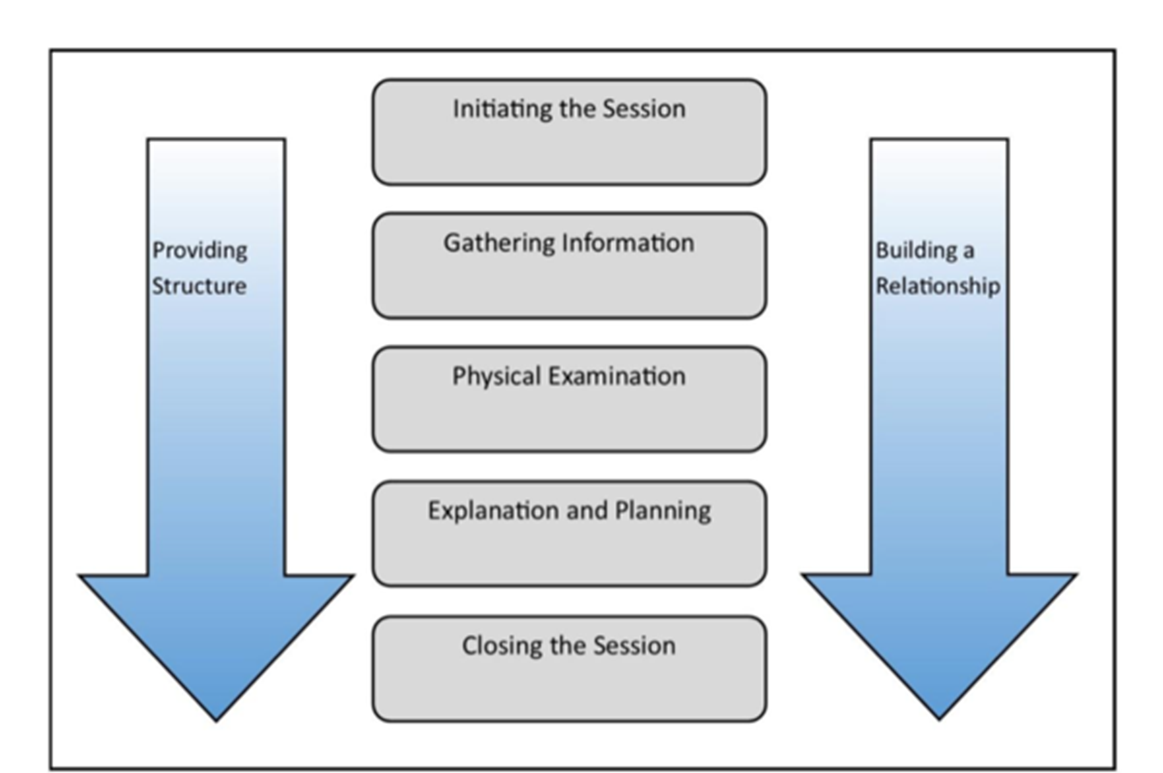
Calgary - Cambridge model
name the steps in the Calgary-Cambridge method 5
initiation
gathering information
physical examination
explanation and planning
closing the session
Initiating the session
1
•Consider this like a first impression - sets the tone
•Introduction - how you/they want to be addressed
•Check the patient identification
•Ascertain the purpose of the consultation
•Explain how you intend to continue the consultation
Gathering information – The History
•Presenting complaint
•The patient’s reason for attending in their own words
•History of presenting complaint
•Further details to elicit signs and symptoms. Further questioning by the clinician
•Medical History
•Details of the patient’s past and ongoing medical problems.
•Dental History
•Details of their dental health problems, ongoing maintenance etc
•Social History
•External factors which impact on oral and systemic health…and vice versa
•Ideas, concerns and expectations
Things to remember
•Patients don’t always know all the details
•The history is not always chronological
•They may only tell you what is important to them and not what you need to know
•The history may not come from the patient, or may be assisted by another party - ask who they are at the start
•Communication difficulties and disabilities - language/cultural barrier
Presenting complaint
”What can I do for you today?”
“I have broken my front second tooth”
“What brings you to see us?”
“I have a swelling under my chin and toothache”
“How are you?”
”Fine!”
History of presenting complaint - SOCRATES
•Site: Where exactly is the pain?
•Onset: When did it start, was it constant/intermittent, gradual/ sudden?
•Character: What is the pain like e.g. sharp, burning, tight?
•Radiation: Does it radiate/move anywhere?
•Associations: Is there anything else associated with the pain, e.g. sweating, vomiting.
•Time course: Does it follow any time pattern, how long did it last?
•Exacerbating / relieving factors: Does anything make it better or worse?
•Severity: How severe is the pain, consider using the 1-10 scale?
Medical History
•Open question
•Systems review - General, CVS, RS, GI, GU, CNS, MSK
•Medications -Names, dosage, indication and duration
•Allergies
•Allergen and type of reaction
•Previously hospitalised?

Dental history
•Current hygiene regimen
•Toothbrushing
•Interproximal cleaning
•Adjuncts - mouthwash
•Topical fluorides
•Mouthwashes
•Toothpastes
•Previous treatment (none, simple, complex)
•Extractions, RCT, crowns, bridges, dentures
•Sedation
Social History
•Smoking
•What and how much? have they ever smoked? how long for?
•Alcohol
•What and how much? (Units / Beer is better than spirits for teeth, wine spirits / Alcohol-free days)
•Recreational drug use
•Occupation -
•Travel
•Hobbies - diving - fillings need to be a specific type
•Support networks and Family
•Pets
ICE
Really helpful for getting back on track, or trying to establish the patient’s agenda
•Ideas
•“What do you think is going on?”
•Concerns
•“You seem worried about this?”
•Expectations
•”What do you hope to get out of today’s consultation?”
Additional parts of the history
•Family History
•Inflammatory bowel diseases, recurrent ulceration, common illness/conditions
symptoms
a physical or mental feature which is regarded as indicating a condition of disease, particularly such a feature that is apparent to the patient
signs
a clinical feature whose presence or occurrence indicates the probable presence or occurrence of something else - eg facial swelling
may overlap with symptoms
Examination – “End of bed”
•As the patient walks into the room, what do you see?
•Walking independently - ? Walking aids
•Unstable gait
•Tremors
•Skin tone – pallor / erythema
•Shortness of breath
•Hands – deformity
Examination - General
•Respiratory rate
•Blood pressure
•Pulse
•Temperature
Examination - Extra oral
•Bony symmetry
•Ears
•Nose
•Soft tissues
•Lacerations / Scars / Ecchymosis
•Lips
•Competency (rest together) / Contour / Fissuring
•Lymph nodes
•Submental / Submandibular / Preauricular / Postauricular / Occipital / Cervical / Supraclavicular
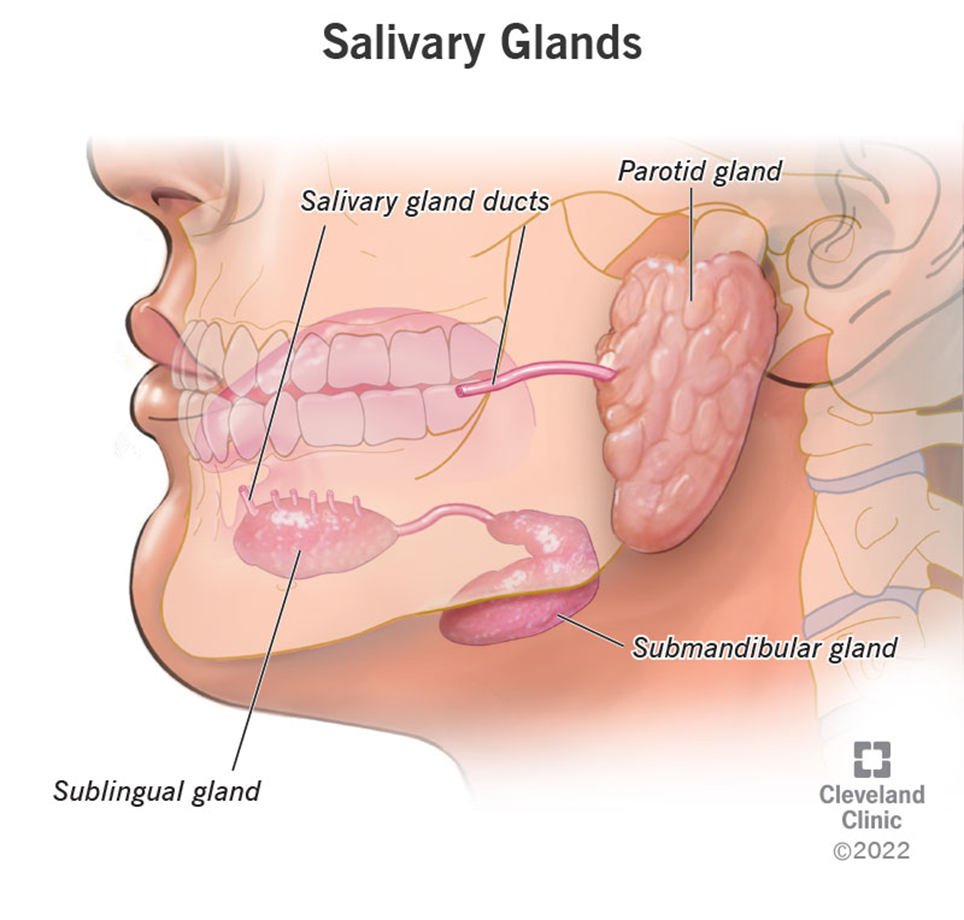
•Salivary glands
•Parotid / Submandibular / Sublingual
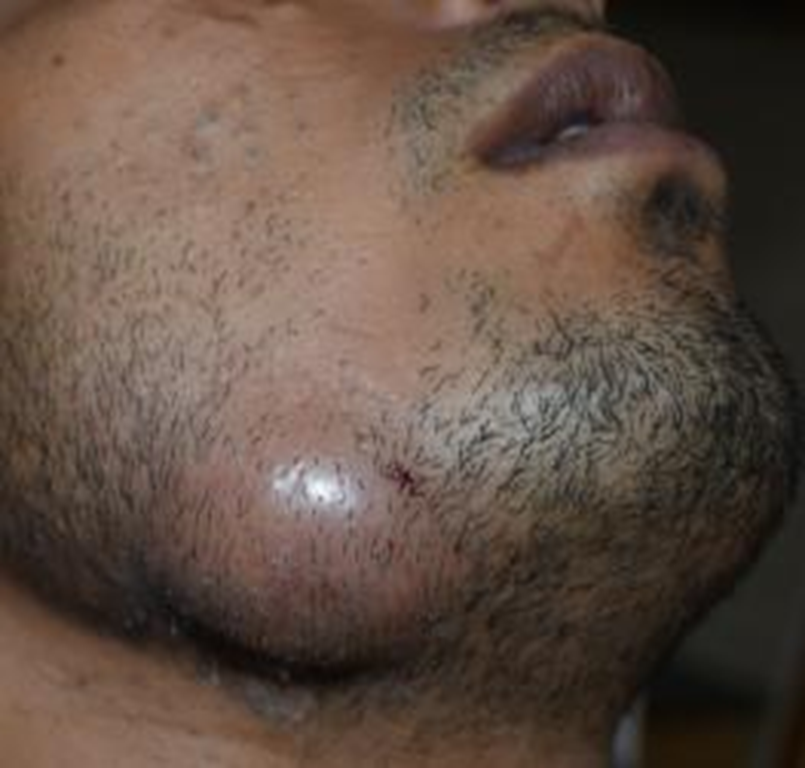
Examination - Swellings
Site
Size
Shape
Colour
Consistency
Hard/Soft/Fluctuant
Fixed/Mobile
Outline/Border
Surrounding tissues
Broad based/Pedunculated - stalk with stump
Transillumination
Examination – Intra-oral
•Mucous membranes
•Buccal mucosa / Labial mucosa / Palate /
Floor of mouth / Oropharynx /
Retromolar fossa
•Tongue
•colour, texture
•Salivary gland ducts
•Tonsillar tissue
•Periodontal tissues
•Teeth
•Edentulous ridges
•Occlusion
•Dentures
Diagnosis
•Following your history taking and examination must decide on the likely diagnosis
•The provisional diagnosis is your initial or working diagnosis
•A differential diagnosis is a list of possible diagnoses
•Investigations are then required to confirm your diagnosis or exclude a possible diagnosis
Developing a list of differential diagnosis - •Use of surgical sieve
VITAMIN CDEF
VITAMIN CDEF
•V – Vascular
•I – Infective
•T – Trauma
•A – Autoimmune
•M – Metabolic
•I – Iatrogenic
N – Neoplastic
•C - Congenital
•D – Degenerative
•E – Endocrine
•F - Functional
VITAMIN CDEF - example, submandibular swelling , possible diagnosis
Submandibular swelling
•V – Vascular - Arteriovenous malformations
•I – Infective / Inflammatory – Dental Abscess / Tuberculosis / Sarcoidosis
•T – Trauma – Recent injury / mandibular fracture
•A – Autoimmune – Sjogren’s syndrome / lupus
•M – Metabolic – Diabetes
•I – Iatrogenic – Surgery / dental procedure – extraction
•N – Neoplastic – Squamous cell carcinoma, tumors of the salivary glands
•C – Congenital – Branchial cysts, thyroglossal duct cysts
•D – Degenerative – sialadenitis – see autoimmune
•E – Endocrine – thyroid cysts / goiter
•F – Functional – Blockage, stone
Investigations
•Chairside
•Labs
•Imaging
Chairside
•Vitality testing of teeth - ethyl choloride
•Transillumination
•Cranial nerve examination
•Saliva flow assessment
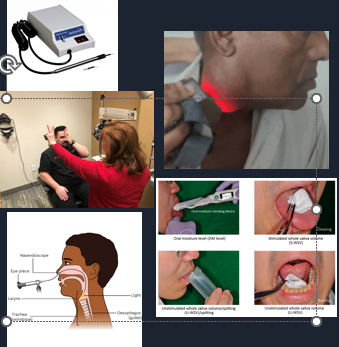
Labs
bloods - haematology - full blood count
biochemistry - renal function
virology
immunology
swabs and saliva samples - microbiology
virology - swabs
biopsy - histology - incisionalsample/excisionalwholething , FNA(take a sample from a lump by sticking a needle in it)

imaging - radiation
dental radiographs
OPT
Periapical
cephalogram - ortho
CBCT
CT
non radiating
ultrasound
MRI - timely -takes long
definitive diagnosis - is overall based on…..
History
Clinical Examination
Investigations
Lifestyle factors
management plan
Explanation and patient factors considered
Agreed management plan - sign a consent form
Lifestyle advice
Short term / Medium term / Long term
Medical / Surgical treatment
Referral for specialist opinion / management
treatment
Treatment is tailored to each patients needs
Many factors must be considered eg., Patient factors , Prognosis

