Information Processing
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What is information processing in sport?
The process of gathering sensory data, prioritising stimuli, making decisions, and producing movement.
What are the four main stages of information processing?
Input → Decision making (CNS) → Output → Feedback.
What senses contribute to input during skill execution?
Sight, hearing, touch, balance, and kinesthesis.
What information do Golgi tendon organs provide?
Feedback on muscle tension and posture.
What information does the vestibular apparatus provide?
Body position and movement in space.
What information do muscle spindles provide?
Muscle stretch, length, and velocity of lengthening.
What is decision making in information processing?
Perceiving sensory input and selecting a response, aided by memory and DCR.
What does DCR stand for in decision making?
Detection, Comparison, Recognition.
What occurs during the output stage?
Motor programmes send impulses through nerves to muscles to produce movement.
What is the most common type of feedback in sport performance?
Internal feedback (knowledge of performance).
Welford’s Model
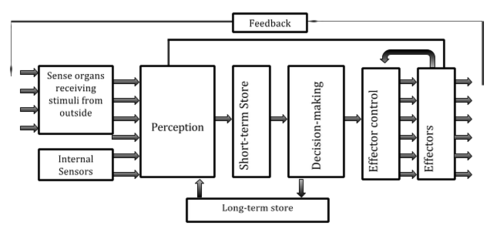
In Welford’s model, what do sense organs do?
Receive stimuli from the environment.
What do internal sensors do in Welford’s model?
Provide information from within the body.
What is perception in Welford’s model?
The brain making sense of stimuli.
What role does short-term memory play in Welford’s model?
Temporarily stores information for selective attention before decision making.
What role does decision making play in Welford’s model?
Choosing the best response from available options.
How does long-term memory contribute in Welford’s model?
Draws on past experiences and skills to aid decisions.
What is effector control in Welford’s model?
Brain sending signals to muscles about how to move.
What are effectors in Welford’s model?
Muscles carrying out the movement.
What are the three stages of the signal detection process?
Detection, Comparison, Recognition.
What determines whether a signal is recognised?
The intensity of the stimulus.
What effect does background noise have on signal detection?
It interferes with perception of the signal.
How does intensity affect detection?
Stronger, more intense signals are easier to detect.
How does efficiency of sensory organs affect detection?
Better sensory organs improve signal processing, impairment degrades it.
What is early stimulus detection?
Identifying a signal quickly to distinguish it from noise.
How does arousal affect signal detection?
It enhances sensory sensitivity and reduces internal noise.
What is the short-term sensory store (STSS)?
Initial stage storing raw sensory data briefly.
What is the capacity and duration of STSS?
Large capacity, very short duration (a few seconds).
Does STSS allow information retrieval?
No, information only passes to STM via selective attention.
What is the role of selective attention?
Filters relevant stimuli from STSS into STM.
How can selective attention improve?
By learning from past experiences.
What is short-term memory (STM or working memory)?
A temporary store that processes information.
What is the capacity and duration of STM?
About 7±2 items, lasting 6–12 seconds.
What inputs does STM receive?
From STSS via selective attention and from LTM retrieval.
How is retrieval from STM?
Relatively easy.
What is long-term memory (LTM)?
The storage of information for long duration.
What is procedural memory?
Unconscious memory of how to perform skills.
What is episodic memory?
Memory of specific events at times and places.
What is declarative memory?
Conscious recall of facts and events.
What is the capacity and duration of LTM?
Unlimited capacity and duration.
What does retrieval from LTM require?
Effortful processing.
How does selective attention interact with memory?
It ensures relevant info reaches STM and helps overcome its limited capacity.
What is required for information to be retained in LTM?
Rehearsal.