Kinesiology Final
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
Humeroradial joint
Identify 1 (joint)
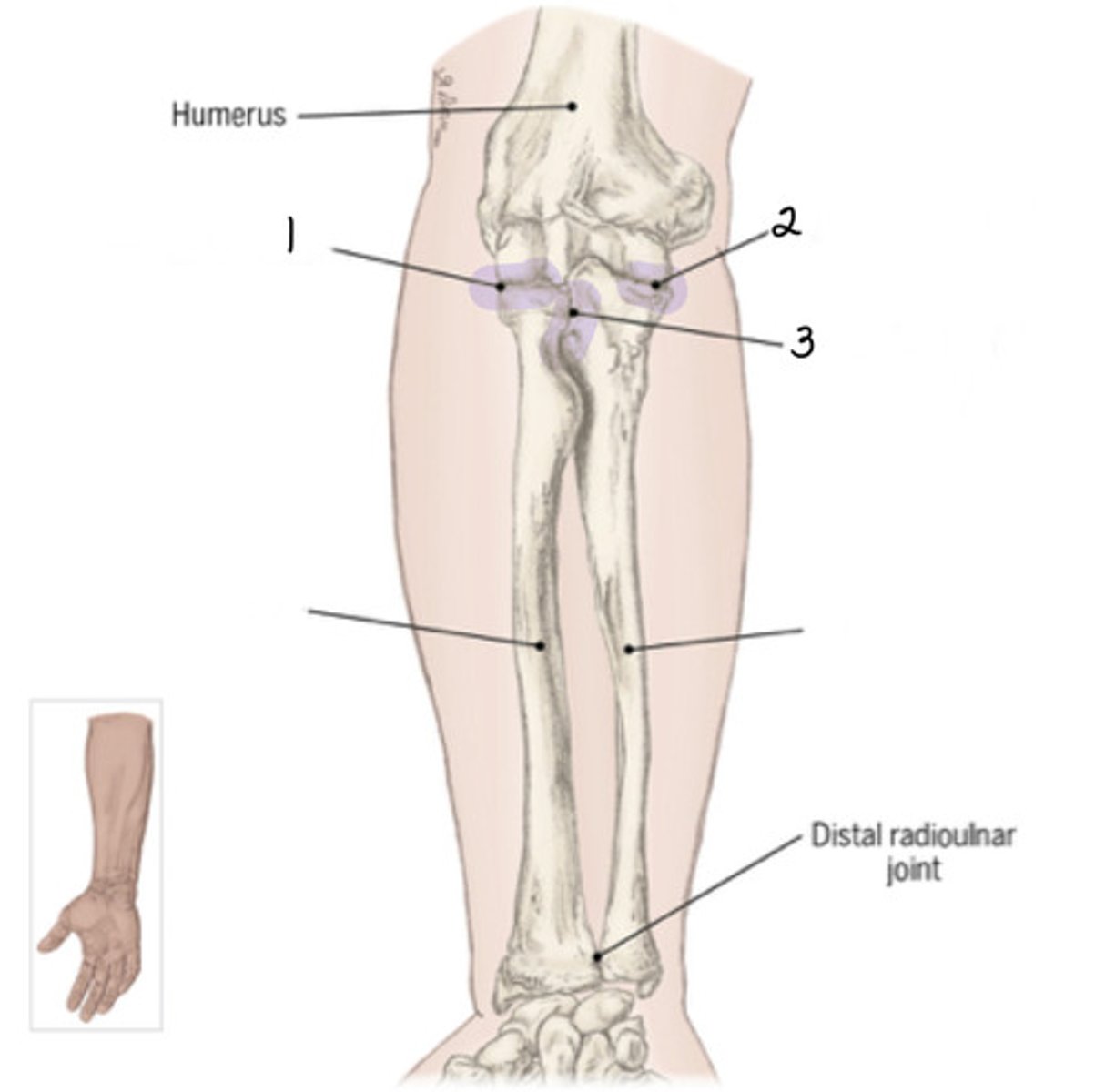
Humeroulnar joint
Identify 2 (joint)
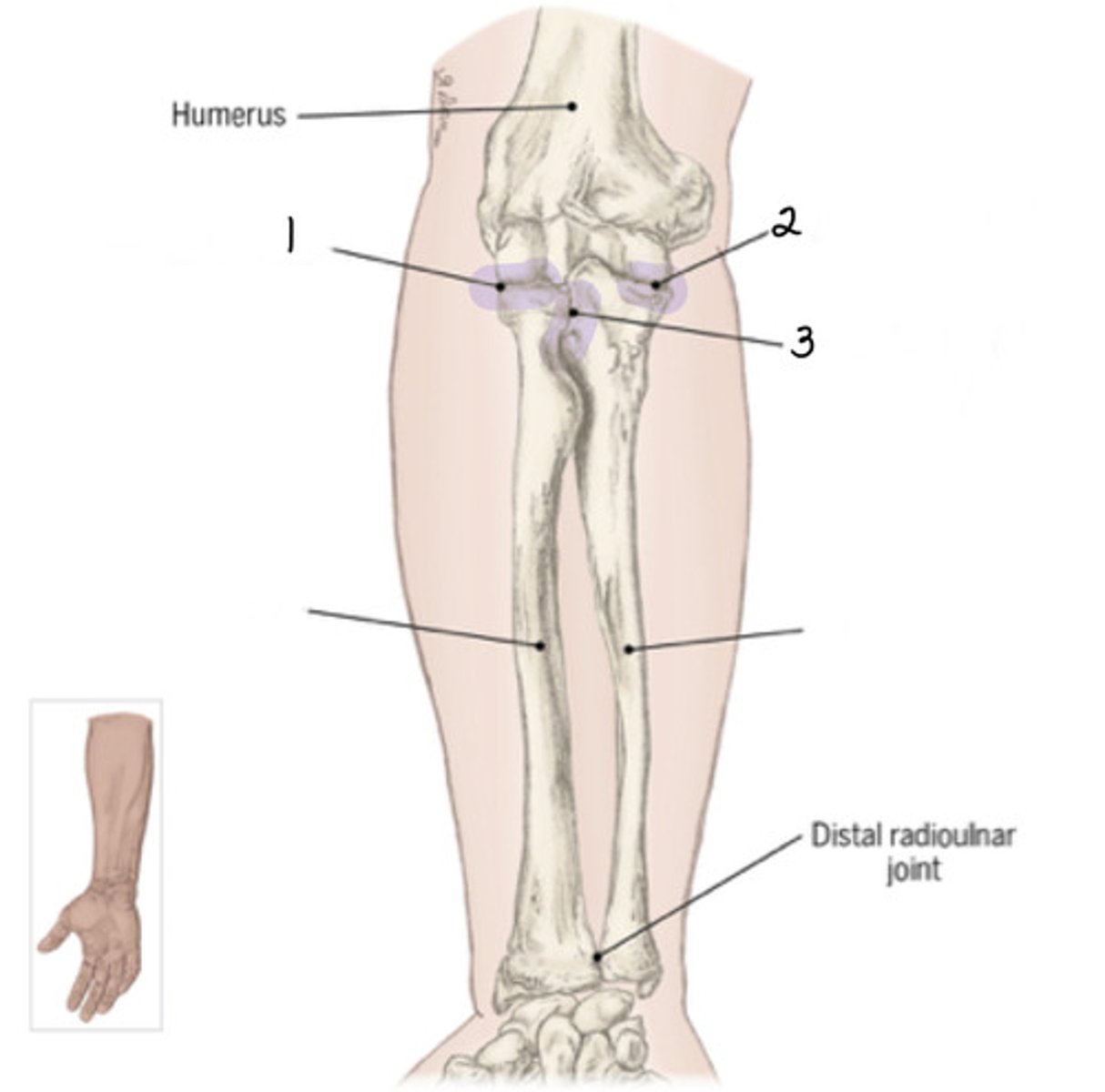
Proximal radioulnar joint
Identify 3 (joint)
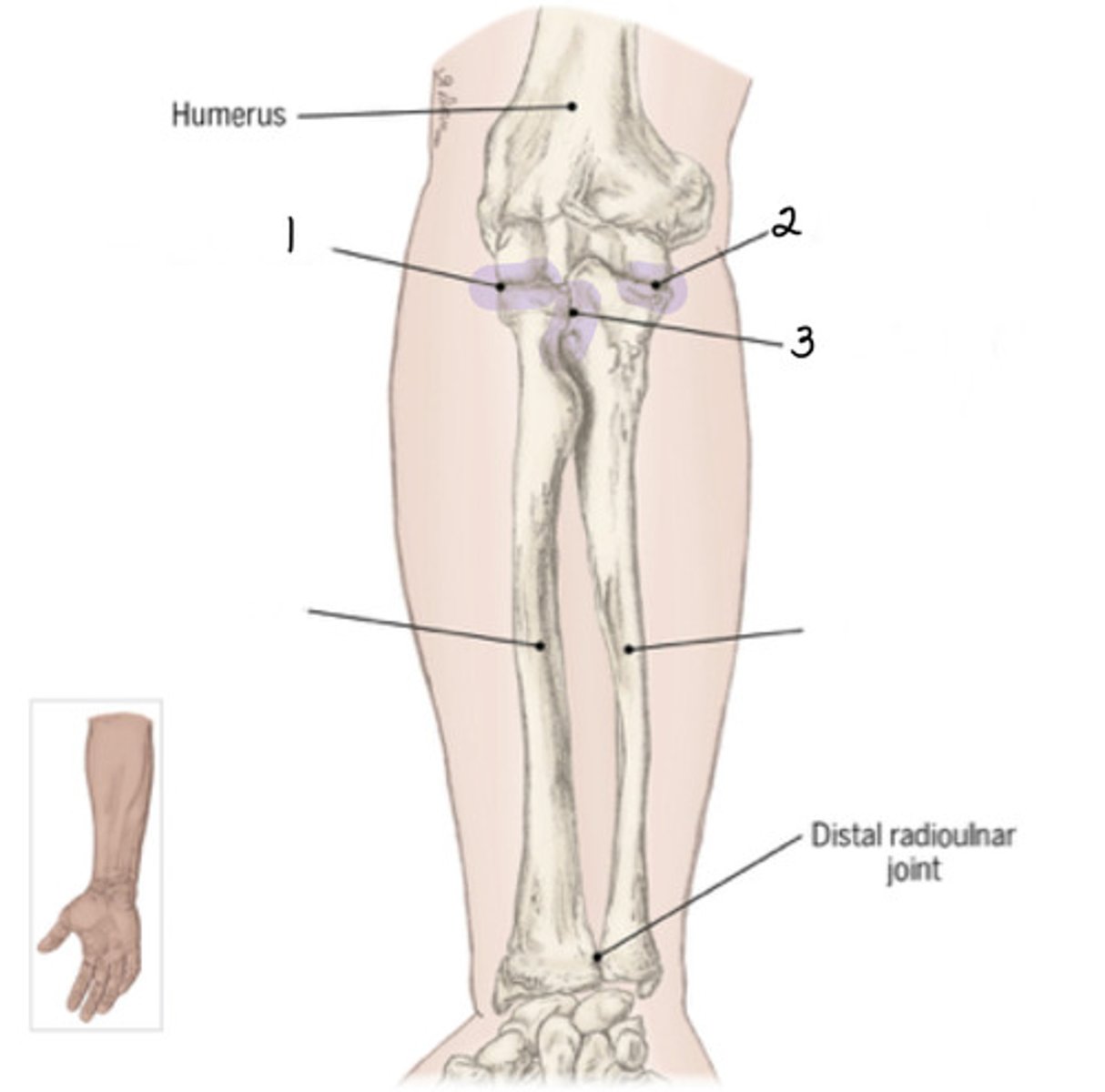
Humeroulnar joint
Primary hinge joint of elbow; articulates between trochlea and trochlear notch; virtually no translation occurs here; has 1 degree of freedom (flexion/extension)
Humeroradial joint
Important joint for transmitting loads, takes on 60% of loads on the elbow; articulation of capitulum of distal humerus with head of radius; has 1 degree of freedom (flexion/extension)
Proximal radiolunar joint
Articulation of radial notch of ulna with radial head and rim; responsible for rotation movement for supination and pronation
In pronation, the radius rotates over the ulna
In pronation, the ________ rotates over the __________
Middle radioulnar joint
Articulation of the shaft of the radius, shaft of ulnar and membrane; synarthrodial; important for stabilization of elbow and joint, transmitting force from hand to humerus, and attachment for muscles
Distal radioulnar joint
Articulation of the head of the ulna and the ulnar notch and articulate disk of the radius; responsible for rational movement for pronation and supination
Stabilizers
The Humeroradial joint, medial collateral ligament, and lateral collateral ligament are primary __________ of the elbow
False - greater stability in flexion than extension
T/F? The elbow has greater stability in extension than flexion
The ulnar/medial collateral ligaments prevent excessive valgus (lateral angulation) at the elbow
The ulnar/medial collateral ligaments prevent excessive ___________ at the elbow
The radial/lateral collateral ligaments prevent excessive varus (medial angulation) at the elbow
The radial/lateral collateral ligaments prevent excessive __________ at the elbow
Elbow flexion
What are these muscles responsible for?
Brachialis
Biceps brachii
Brachioradialis
Triceps
Primary muscle responsible for elbow flexion
sagittal plane, frontal axis
Elbow flexion/extension occur in the ________ plane, around the ________ axis
Pronation
What are these muscles responsible for?
Pronator teres
Pronator quadratus
Supinator and biceps
Identify the muscles (2) responsible for supination
Transverse plane, frontal axis
Forearm supination/pronation occurs in the ______ plane, around the ______ axis
True - there is a natural carrying angle at this joint
T/F? The axis of the humeroulnar joint is not horizontal
Cubital tunnel syndrome
Numbness and tingling in ring and small fingers caused by increased pressure and tension on the ulnar nerve with elbow in a flexed position
Cubits valgus
An abnormal outward/lateral deviation at the elbow
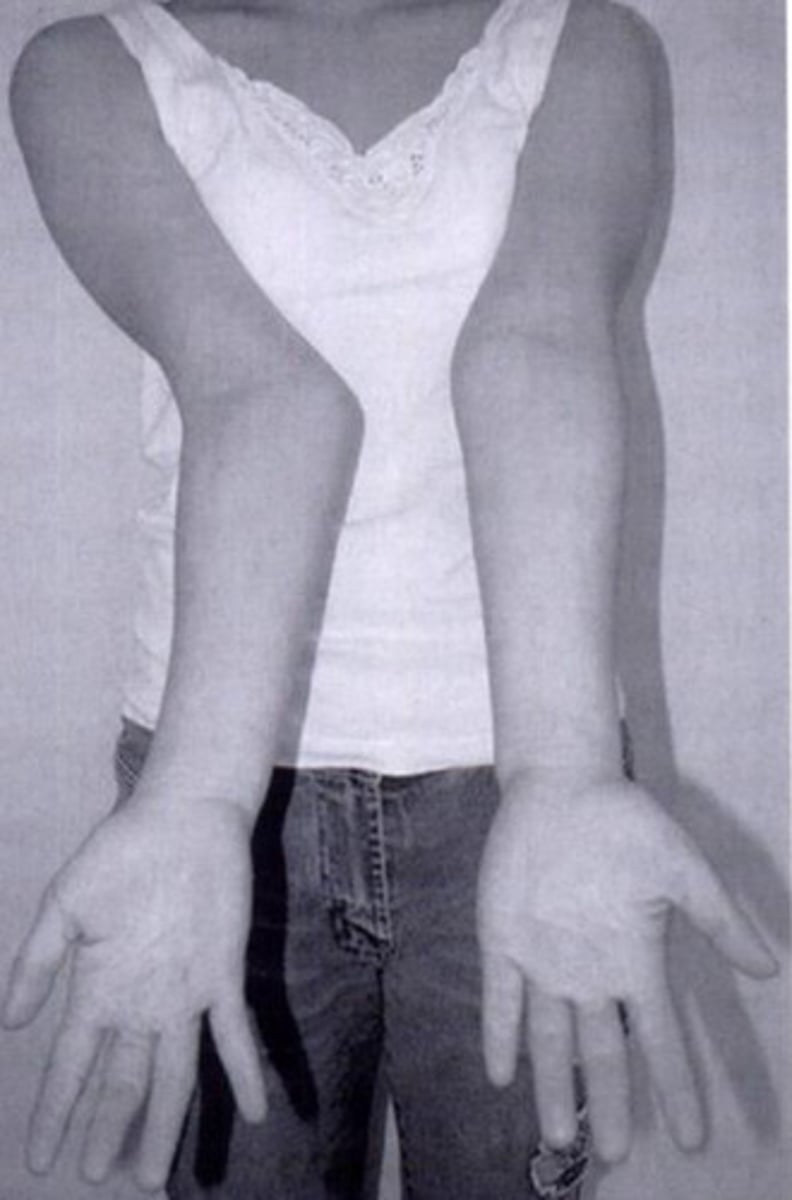
Cubits varus
An abnormal inward/medial deviation at the elbow
Lateral epicondylosis
Tennis elbow; pain outside of elbow and sometimes forearm and wrist; caused by repetitive wrist and arm motions
Medial epicondylosis
Golfer's elbow, pain on inner side; caused by excess or repetitive stress
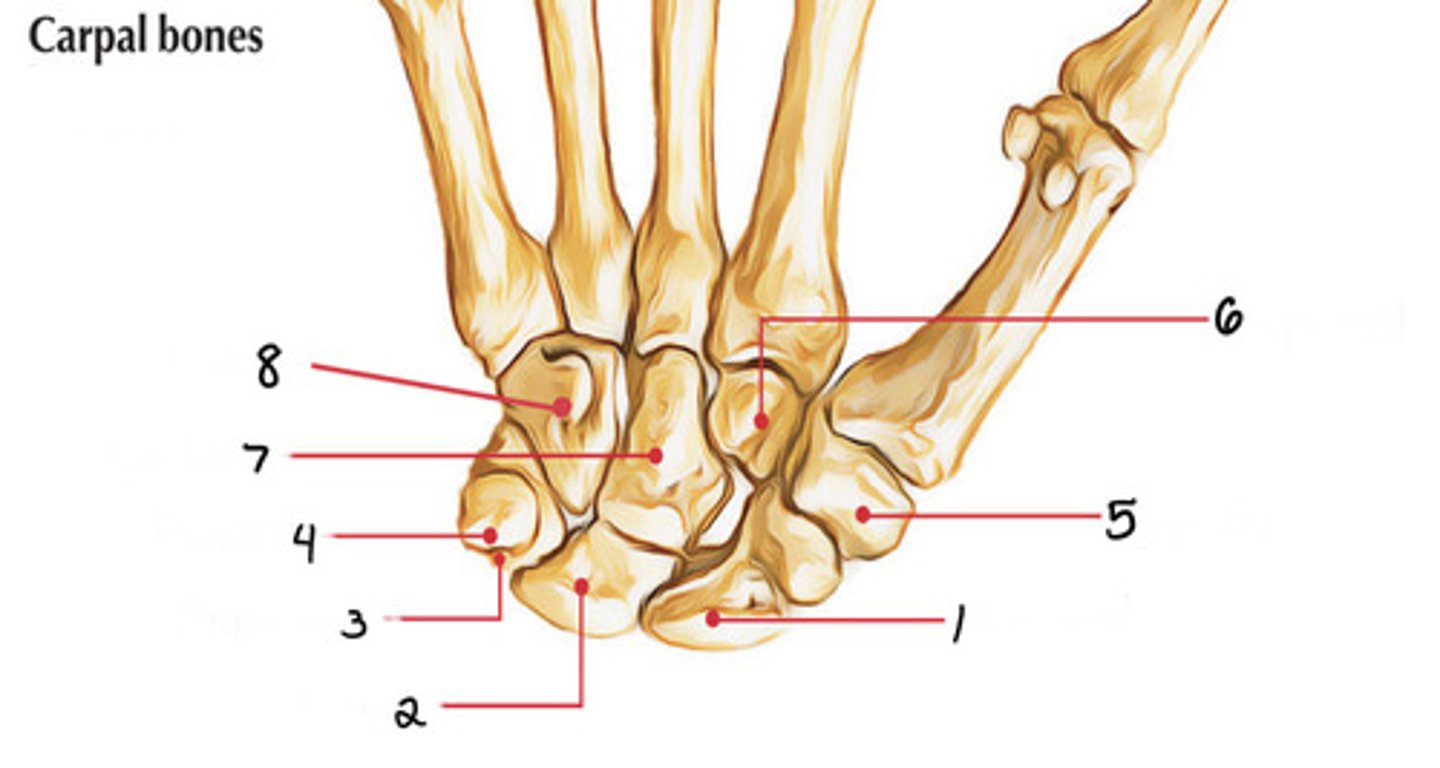
Scaphoid
Identify 1
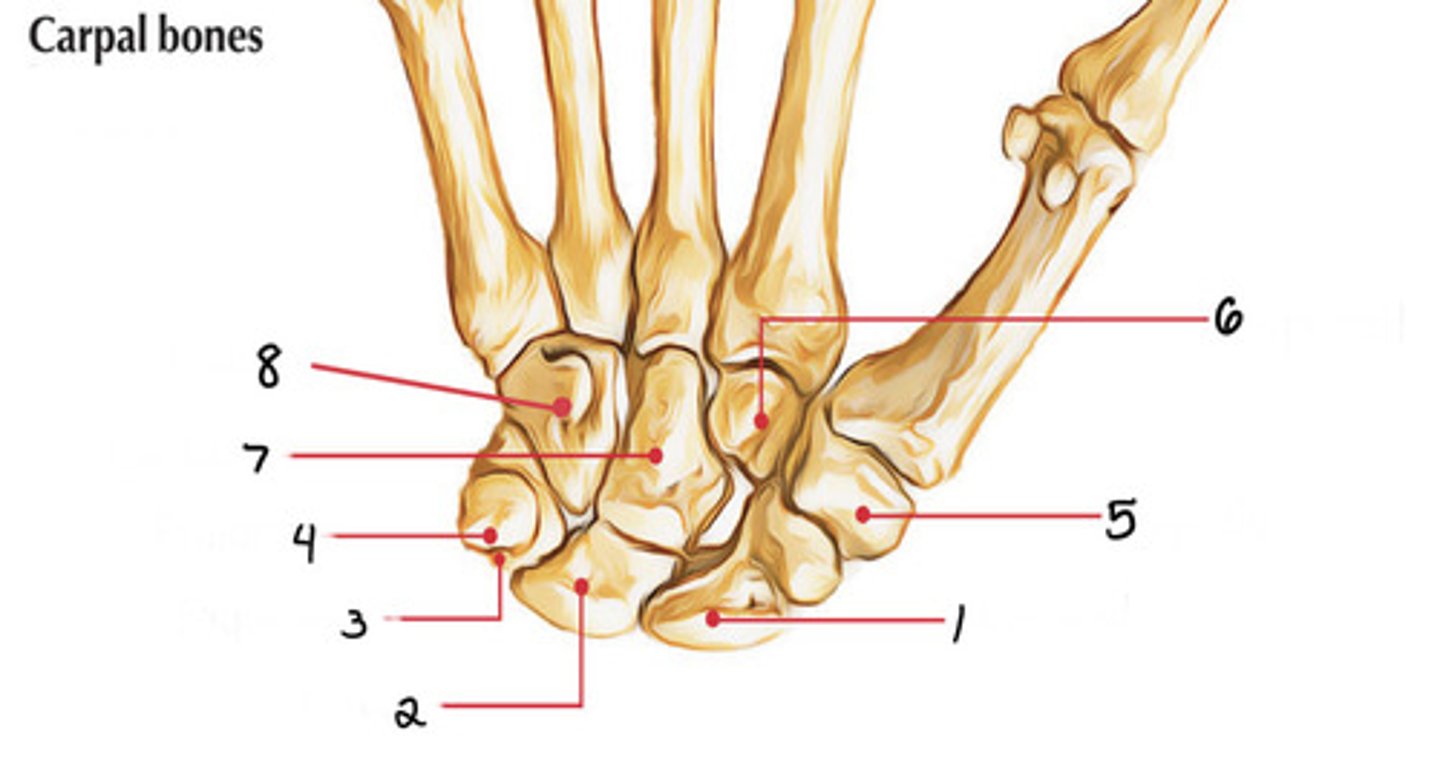
Lunate
Identify 2
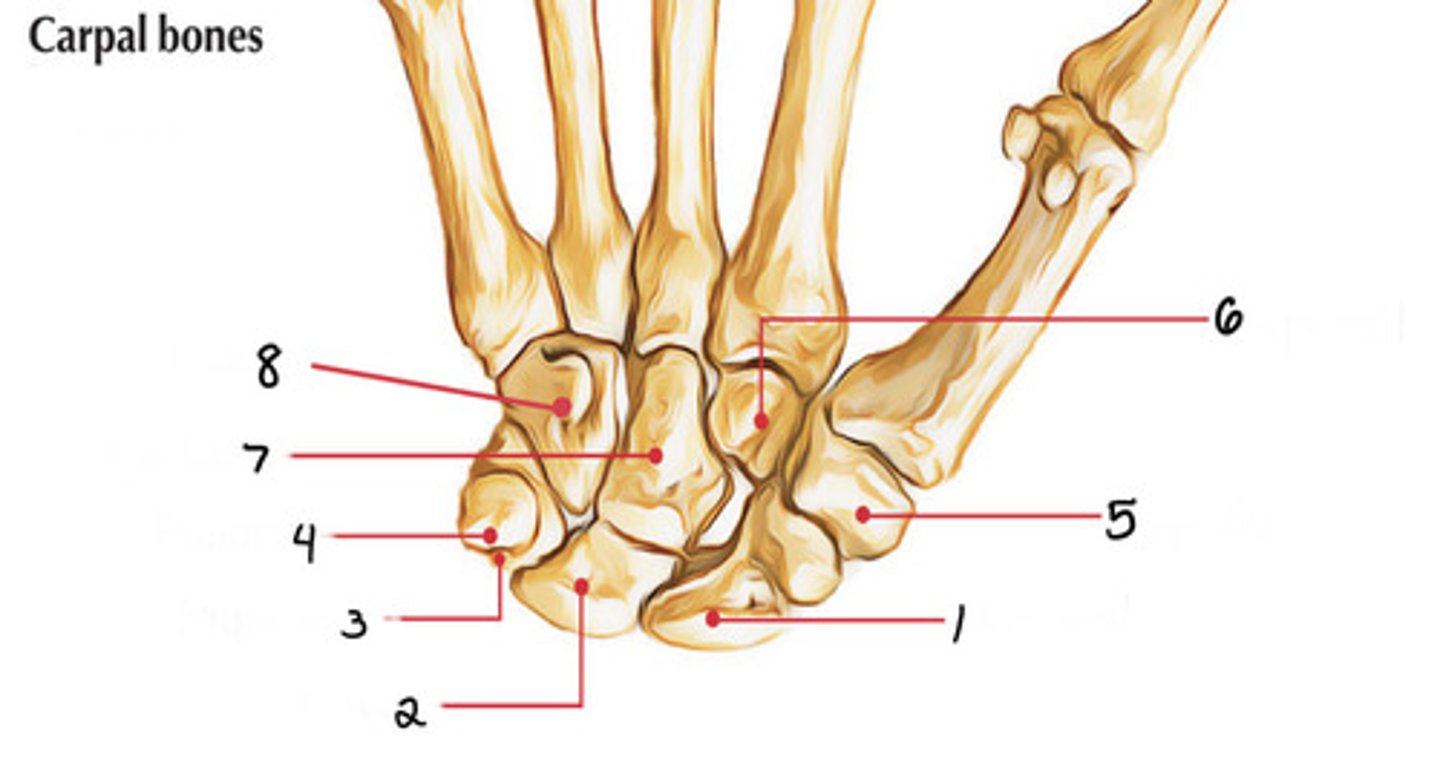
Triquetrum
Identify 3
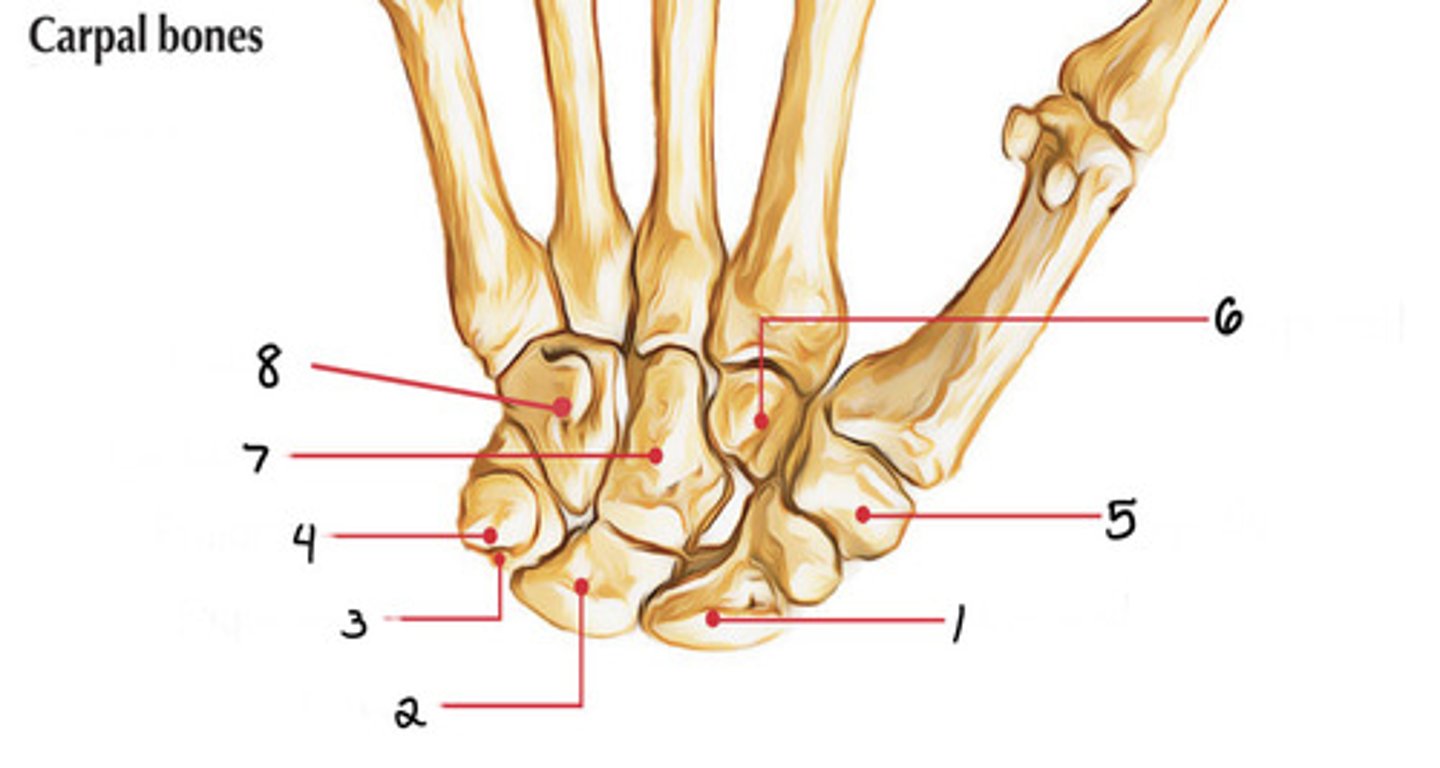
Pisiform
Identify 4
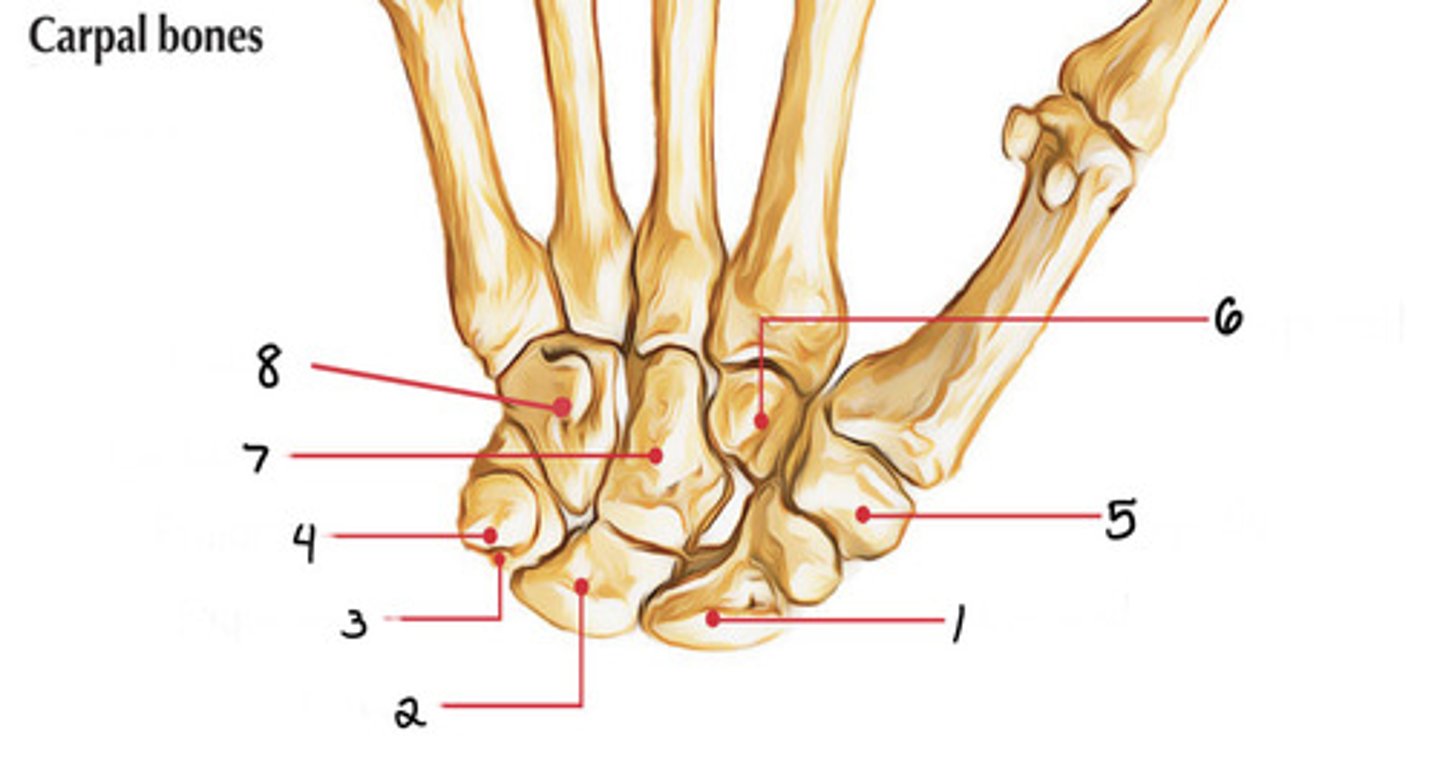
Palmar aspect, ulnar side
Pisiform: Pea shaped bone can be found on the (palmar/dorsal) aspect of the hand near the (radial/ulnar) crease
Trapezium
Identify 5
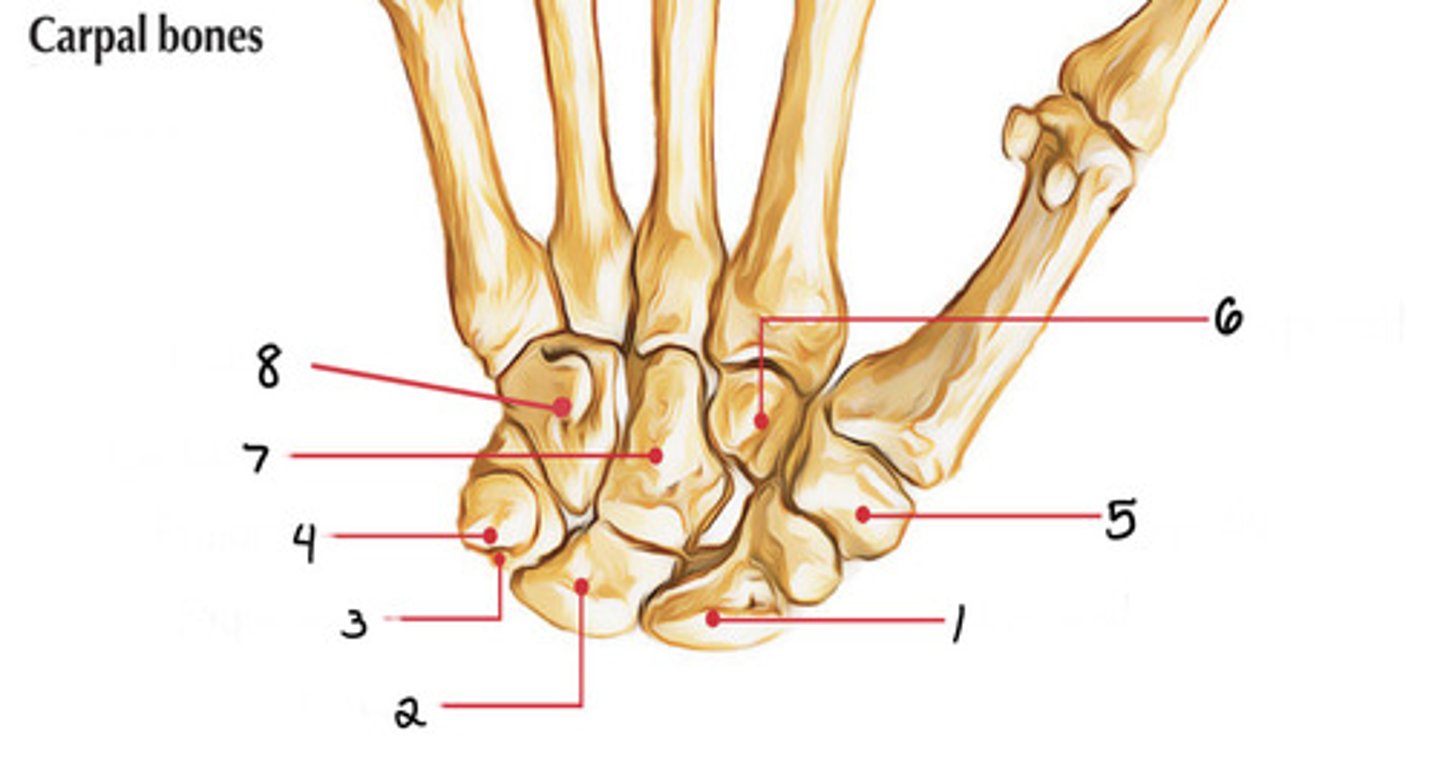
Capitate
Identify 7
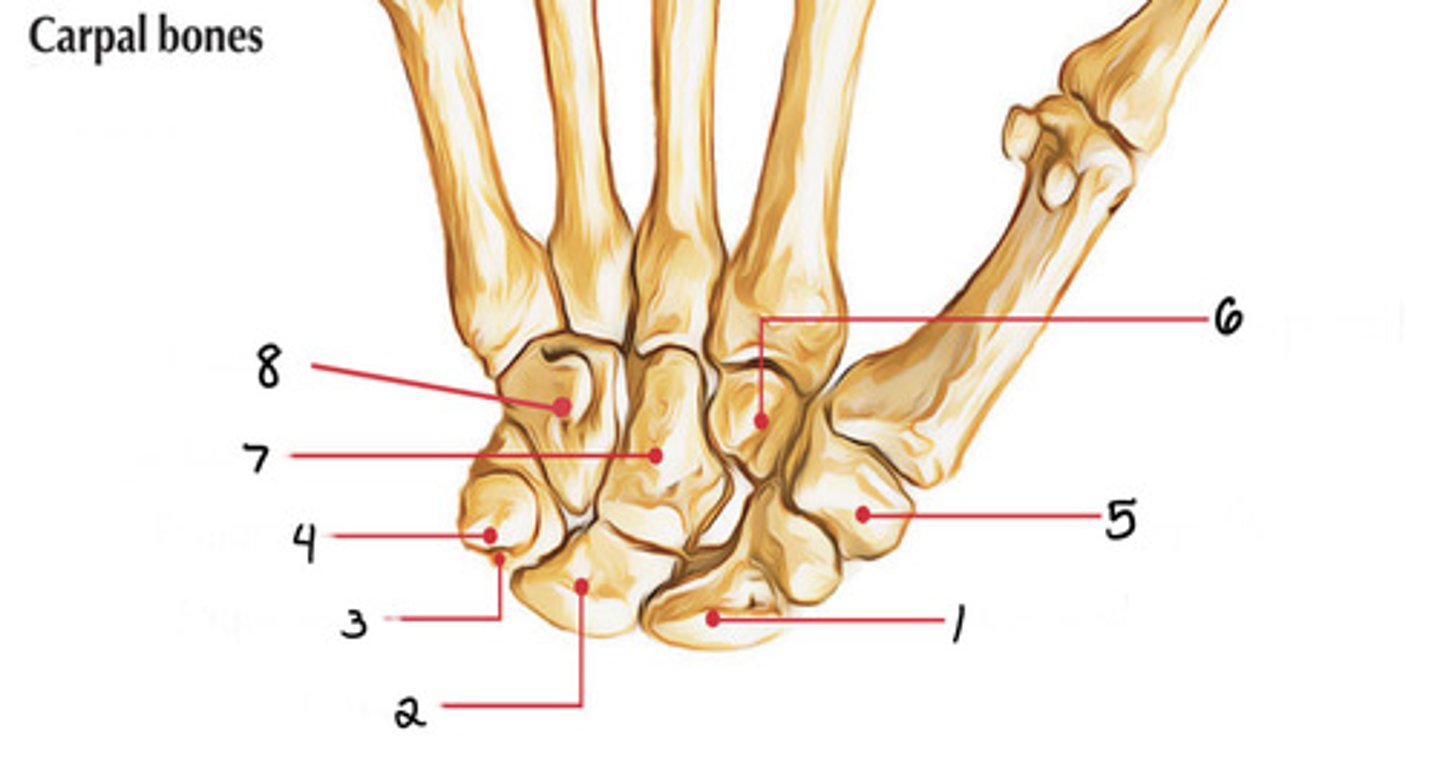
Trapezoid
Identify 6
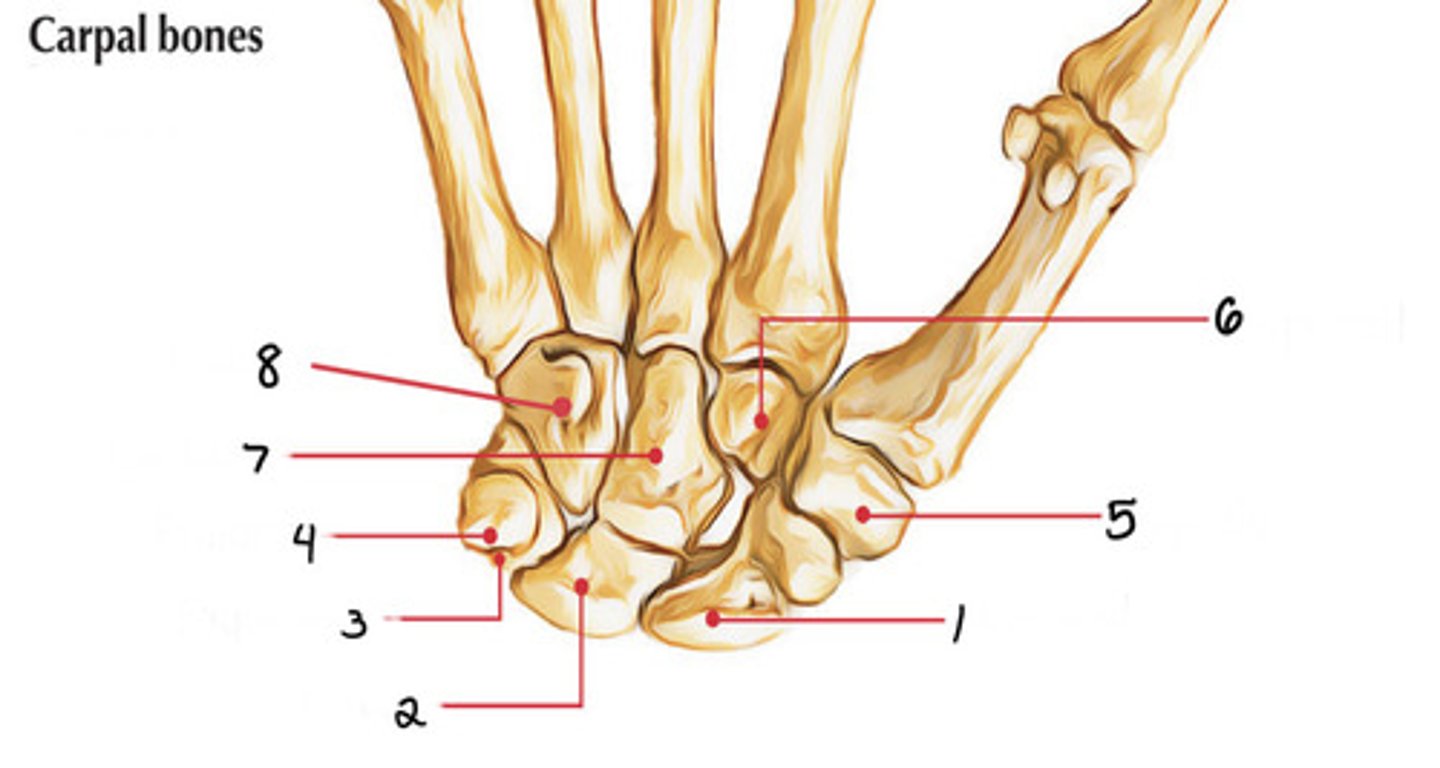
Pisiform
Insertion for the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon
False- it is attached to the triquetrum
T/F? The pisiform is attached to the trapezium
Hamate
Identify 8
Scaphoid
Most frequently fractured carpal bone
Trapezium
Carpal bone distal to the scaphoid
Capitate
Axis for ulnar and radial deviation; distal to lunate
Hamate
Carpal bone distal and lateral to the pisiform
Scaphoid
Distal to the styloid process of radius, opposite the pisiform; transmits forces from hand to the forearm
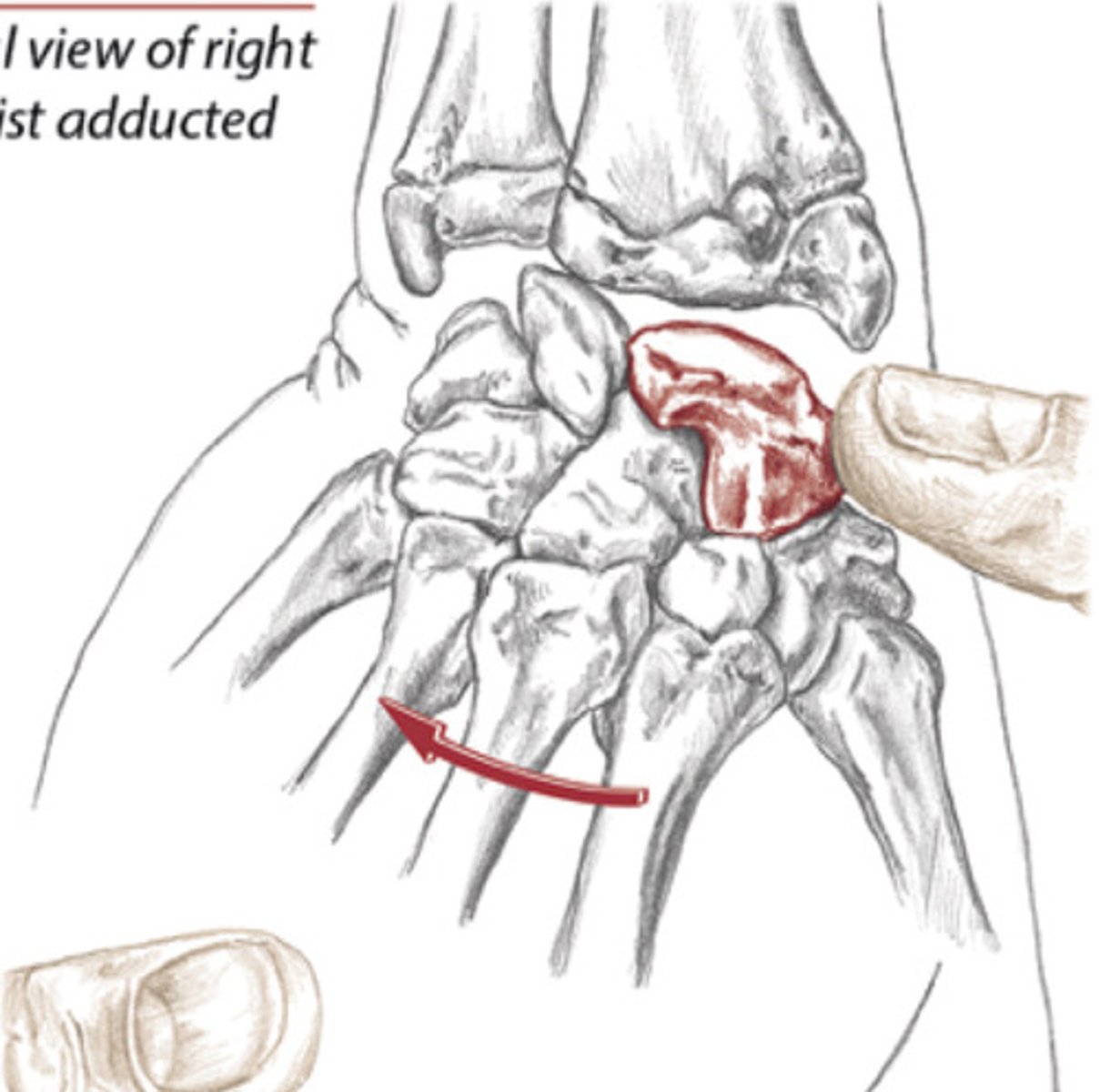
Pisiform, Ulnar nerve
Tunnel of guyron: channel between _________ and hook of hamate where ________ nerve passes
Lunate
Most frequently dislocated carpal bone, distal to Lister's tubercle
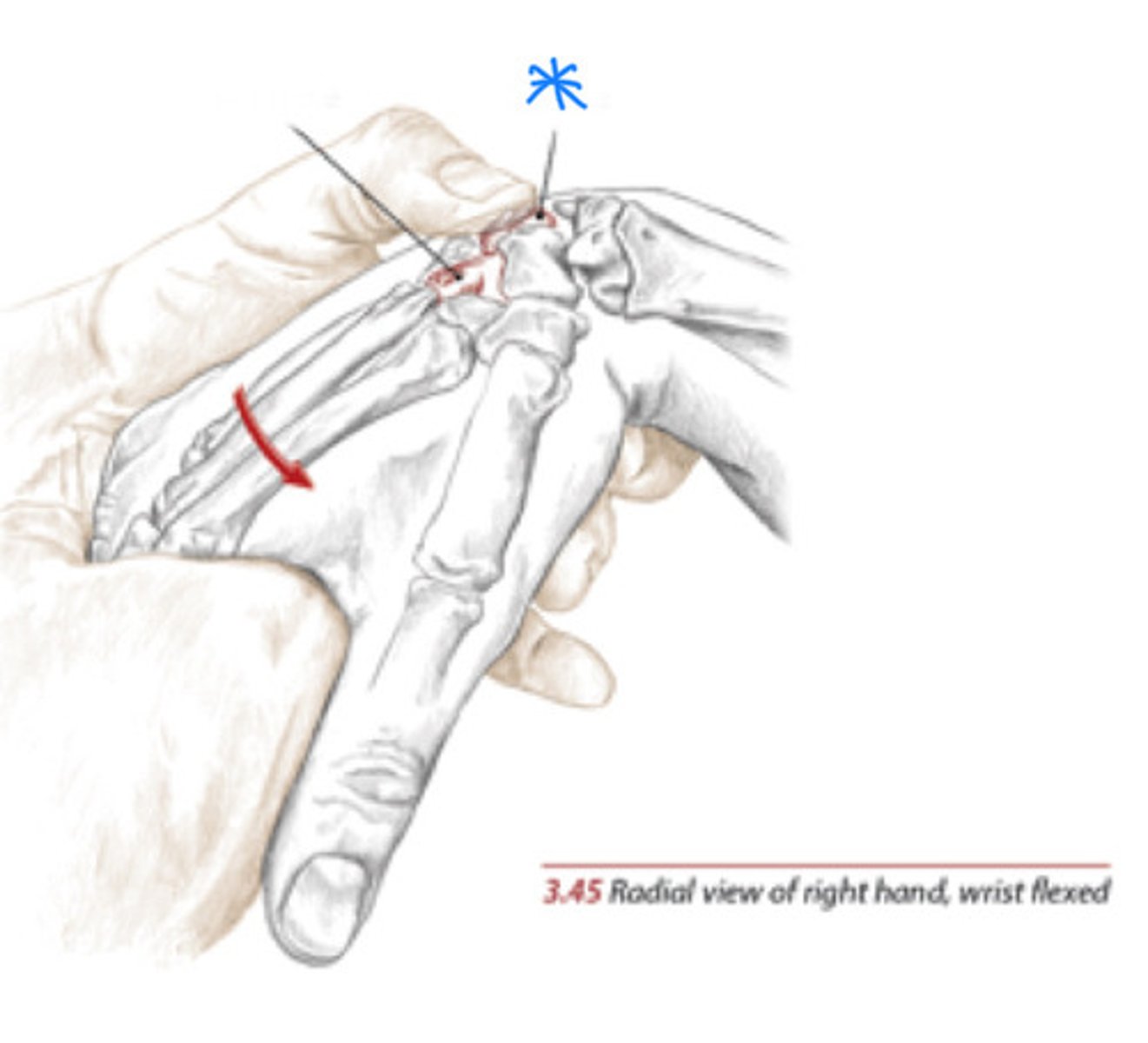
Flexion/extension, radial/ulnar deviation
What movements occurs at the radiocarpal joint? (2 sets)
Triquetrum
Distal to styloid process of ulnar; best to palpated when wrist is radially deviated
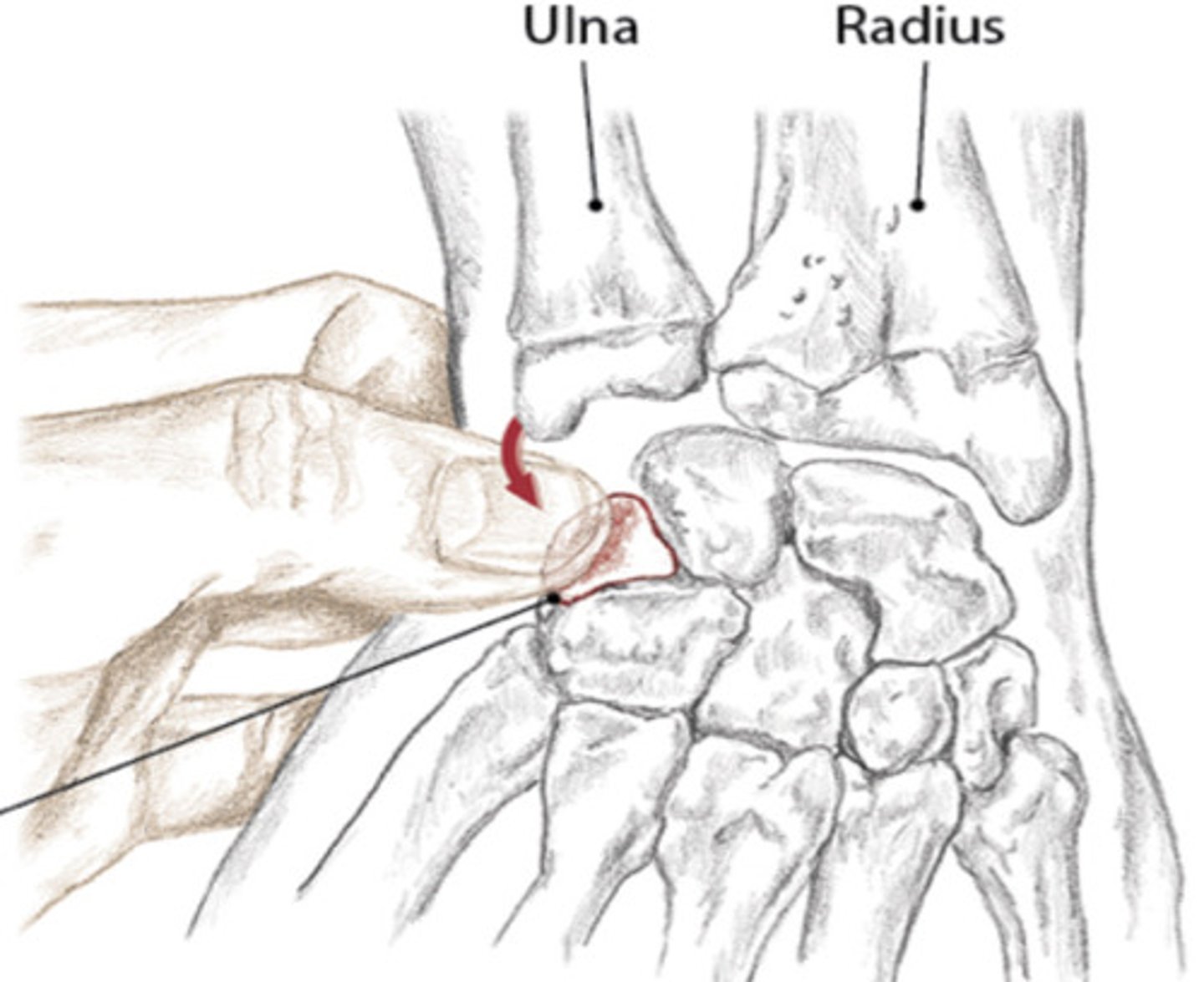
True
T/F? The intercarpal joints are where the individual carpal bones articulate with each other
Flexion/extension, rotation
Movements that occur at the midcarpal joint
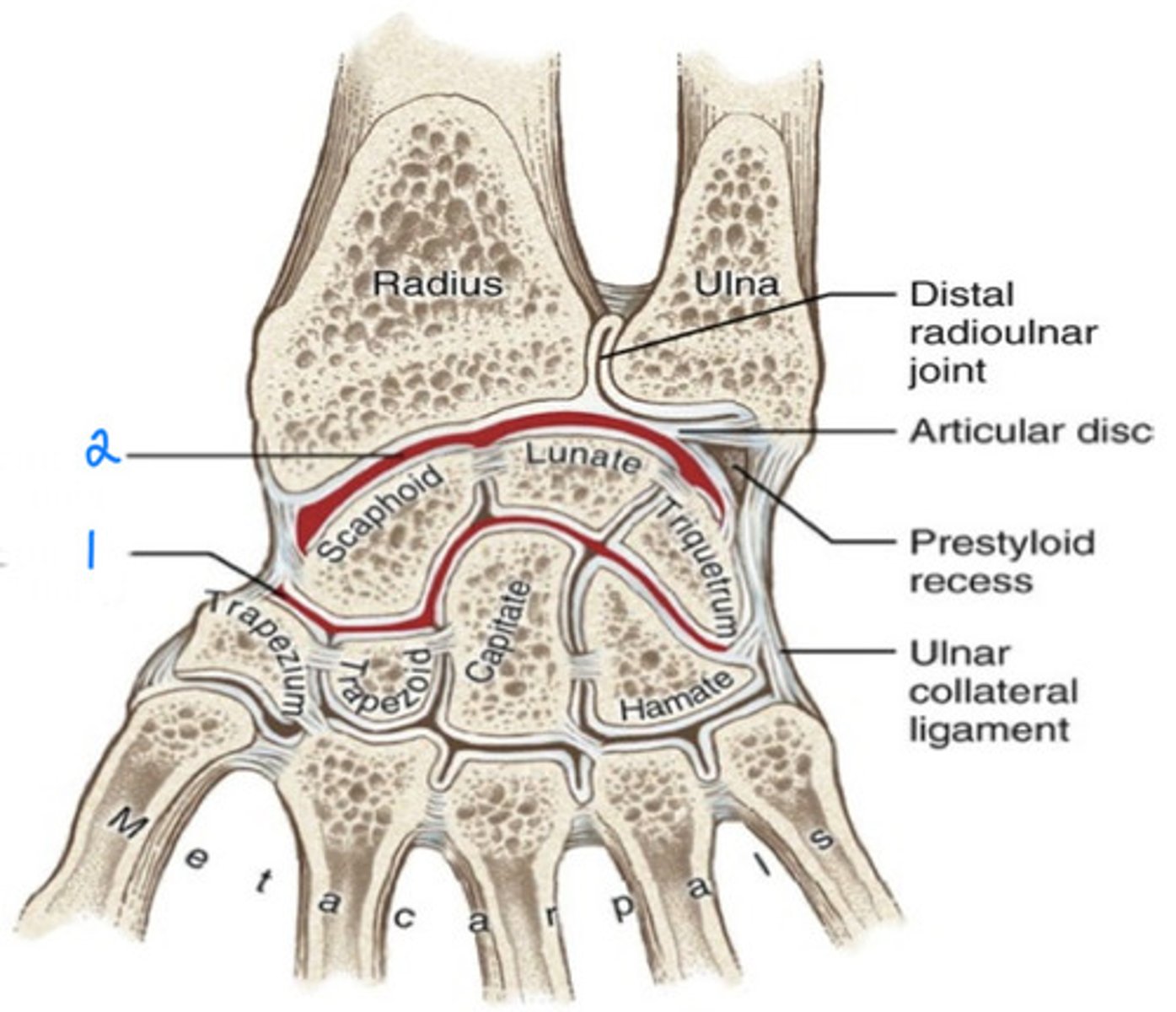
Radiocarpal joint
Most commonly thought of as the true wrist joint; distal radius and radioulnar disk articulates with proximal row of carpals (scaphoid and lunate) (2)
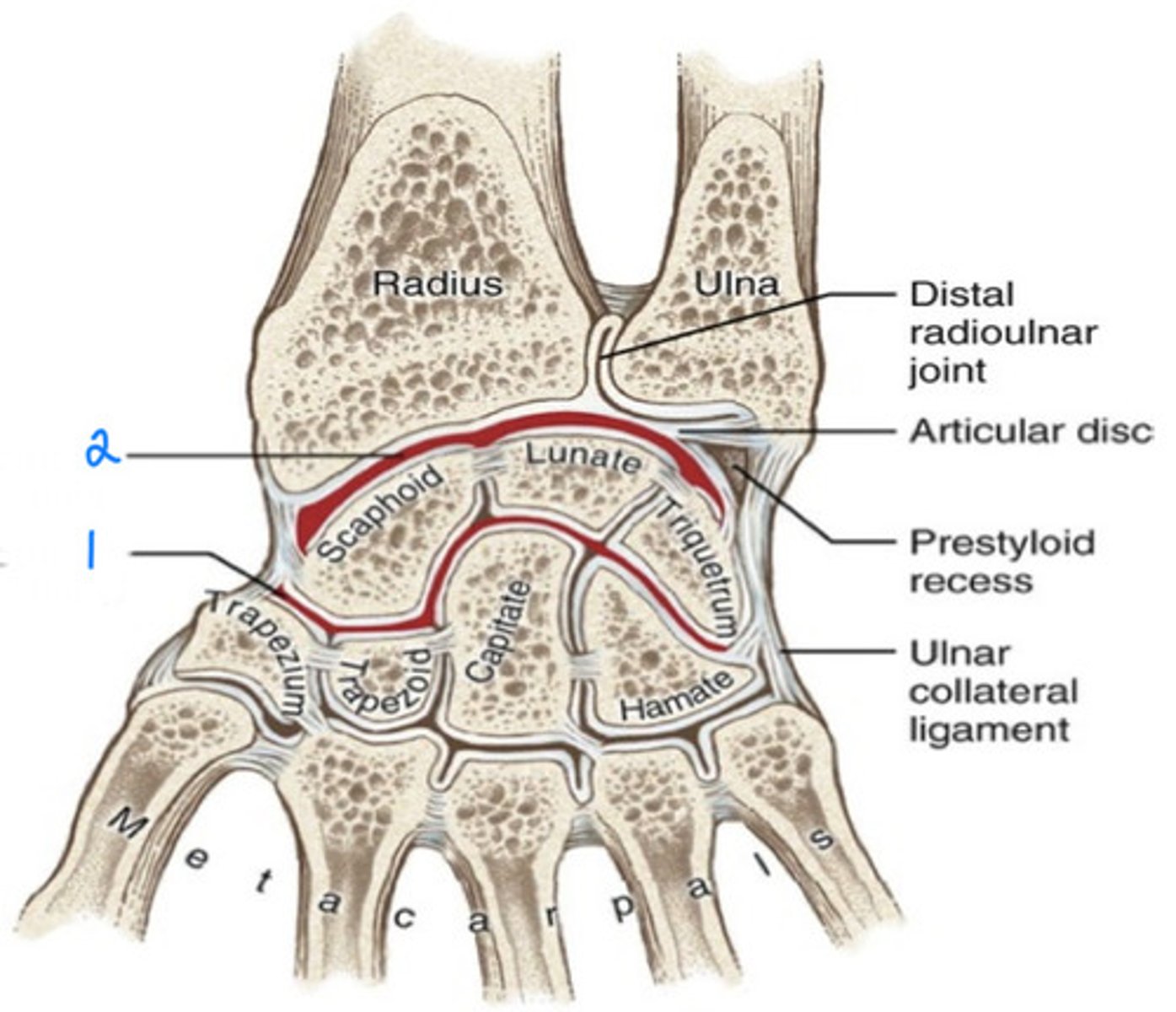
Triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC)
Cushion between distal ulna and carpals, adds to stability on ulnar side of the wrist; common injury site
False - Sagittal plane; frontal axis
T/F? Wrist extension/flexion occurs in the transverse plane around the vertical axis
Midcarpal joint
articulation between the two parallel rows of carpal bones (1)
Ulnar deviation
Occurs naturally with wrist flexion, occurs in frontal plane around sagittal axis; wrist adduction; involves flexor carpi ulnaris and extensor carpi ulnaris
Radial deviation
Occurs primarily at the midcarpal joint; occurs in the frontal plane along the sagittal axis; involves extensor carpi radialis longus/brevis, extensor pollicis longus/brevis, flexor carpi radialis, abductor pollicis longus
Circumduction: neutral ➡️ extension➡ radial deviation ➡ flexion ➡ ulnar deviation and repeats
Circumduction: neutral ➡️ extension➡ ______________ ➡ flexion ➡ ___________ and repeats
Median
Carpal tunnel syndrome involves compression of the ________ nerve at the carpal tunnel of the wrist
True
T/F? Smith's and Colle's fractures are both distal radius fractures
Smith's fractures involve volar displacement of the distal bone while in a distal radius fracture
___________ fractures involve volar displacement of the distal bone in a distal radius fracture
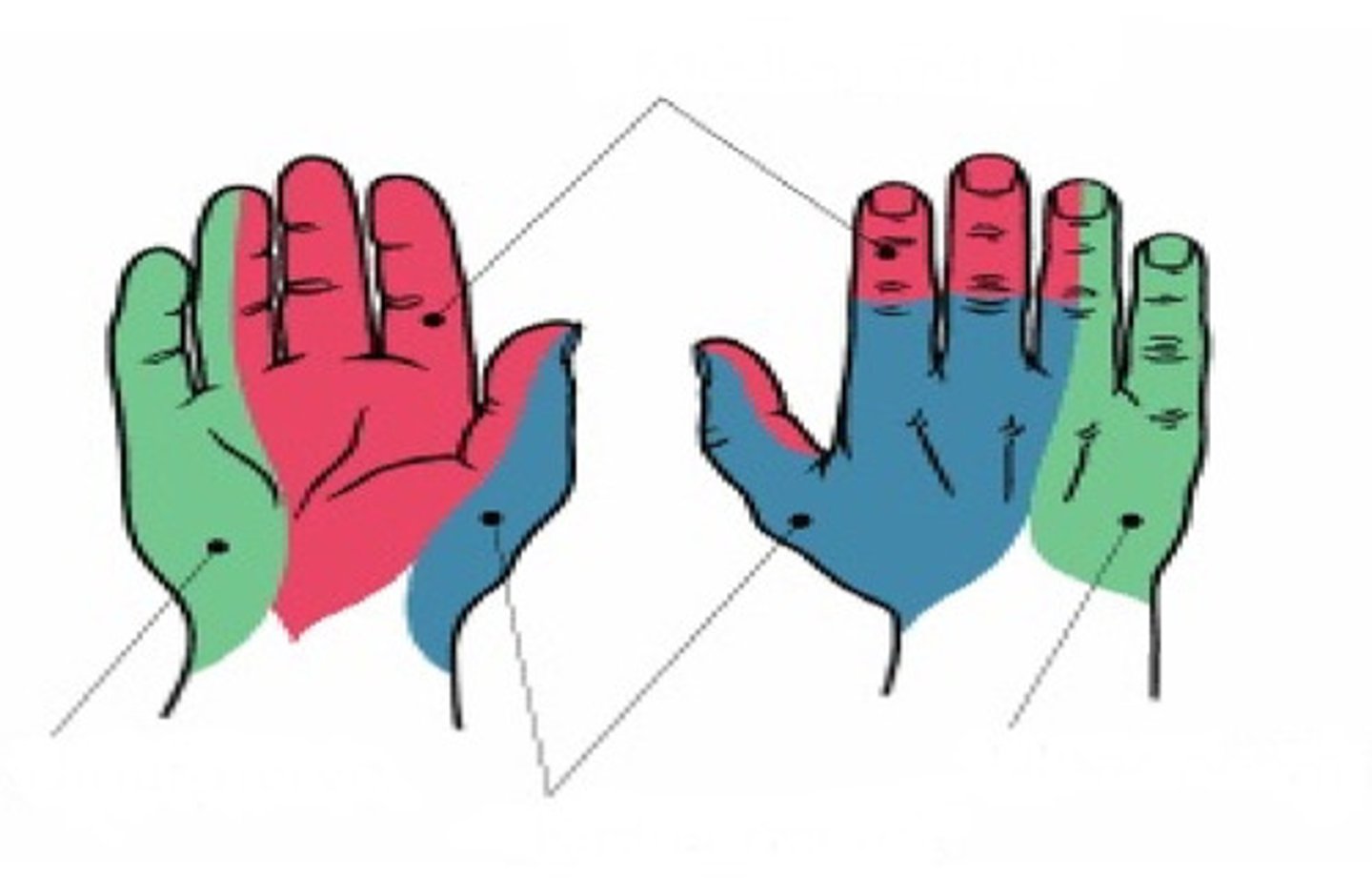
Ulnar nerve
Identify green
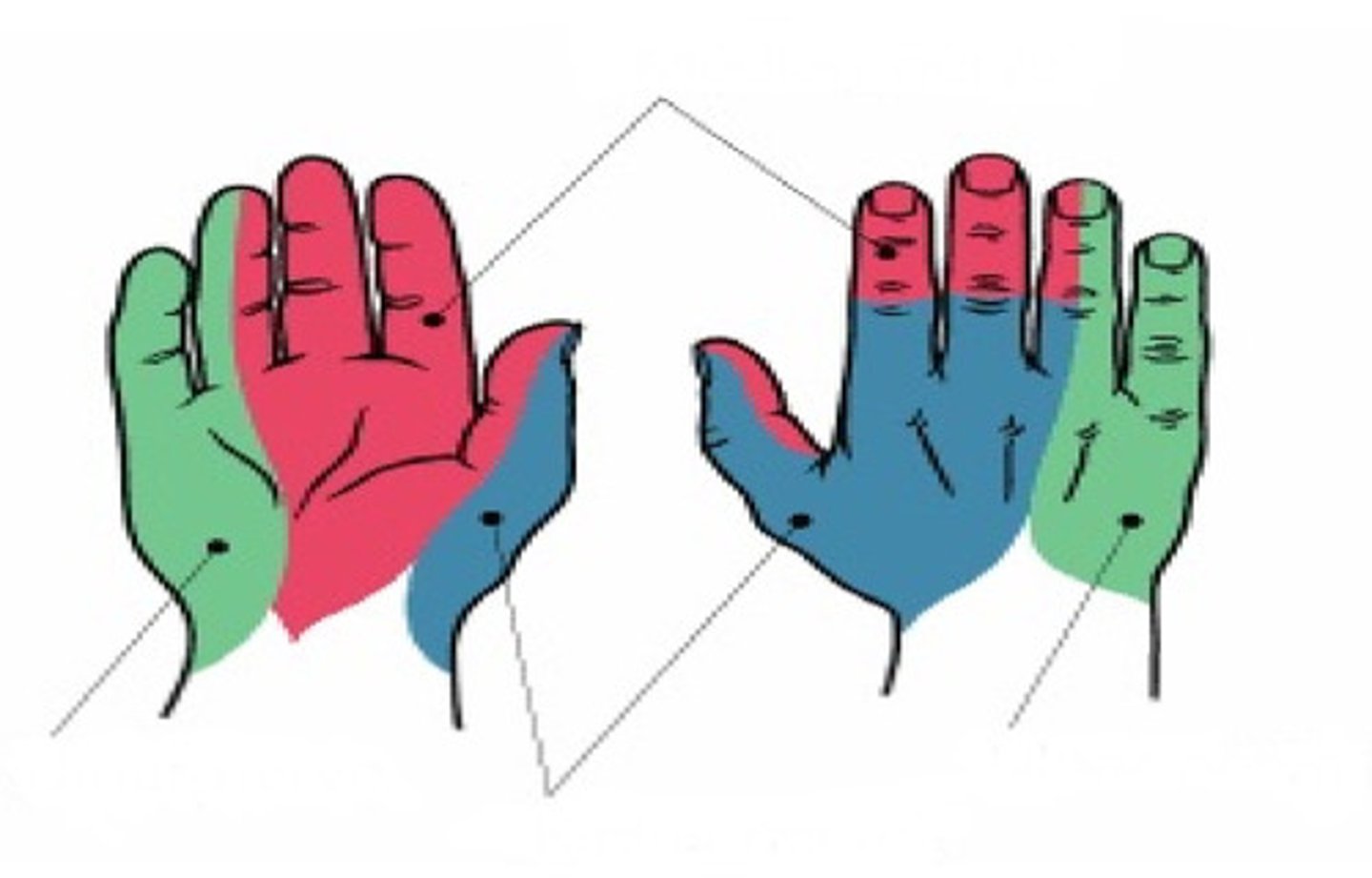
Radial nerve
Identify blue
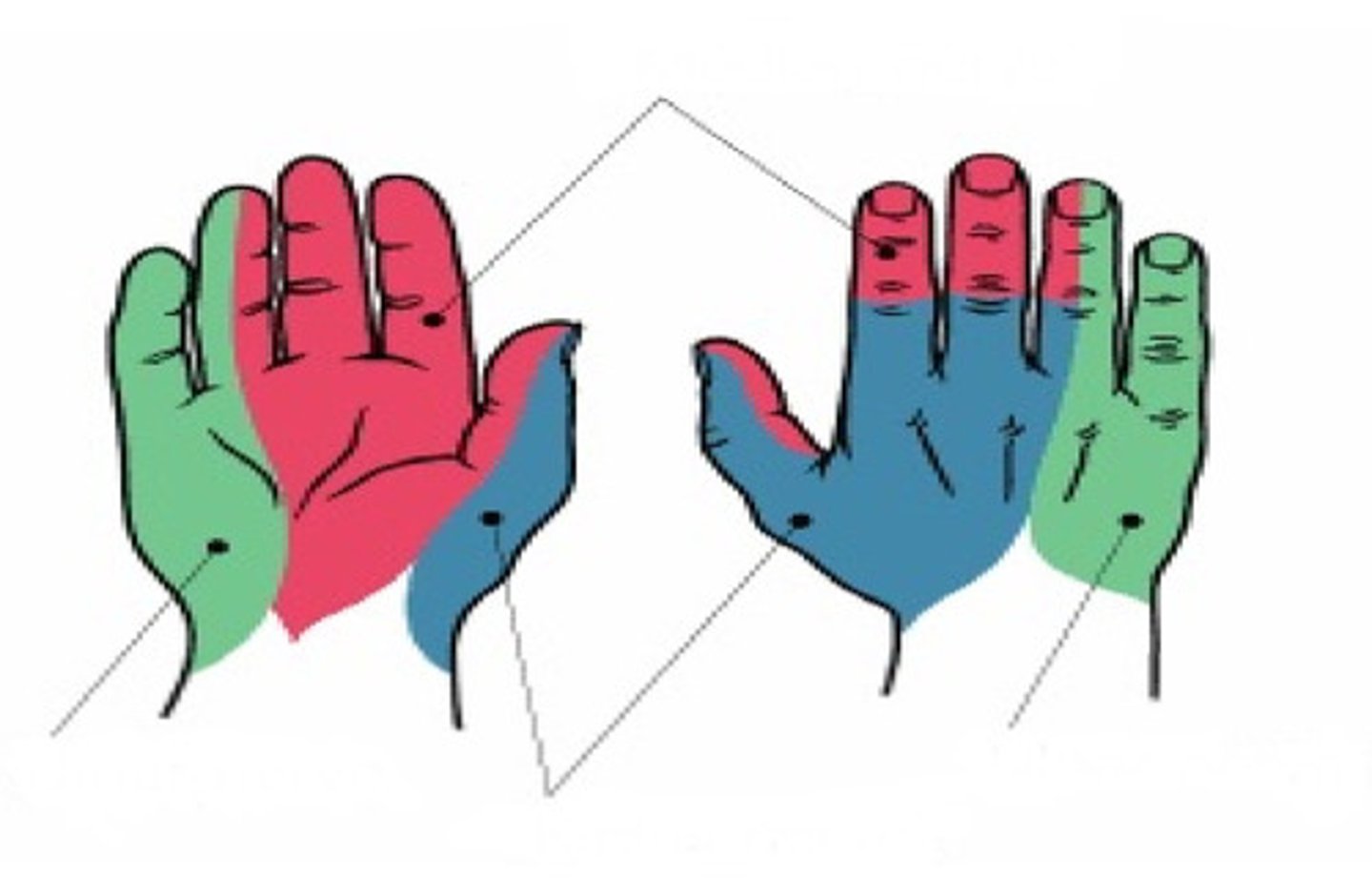
Median nerve
Identify red
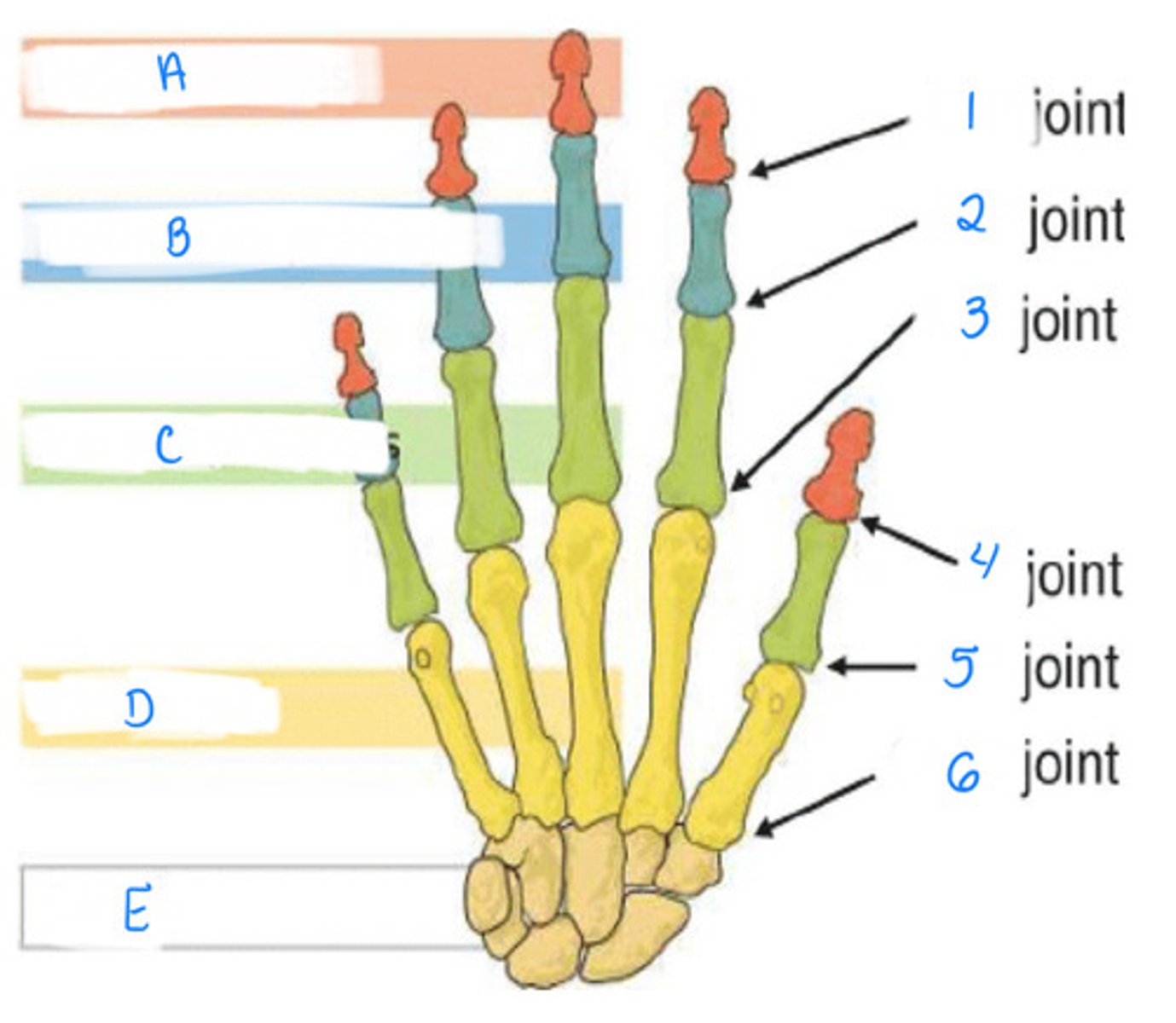
DIP joint; PIP joint; MP joint
Identify 1, 2, 3
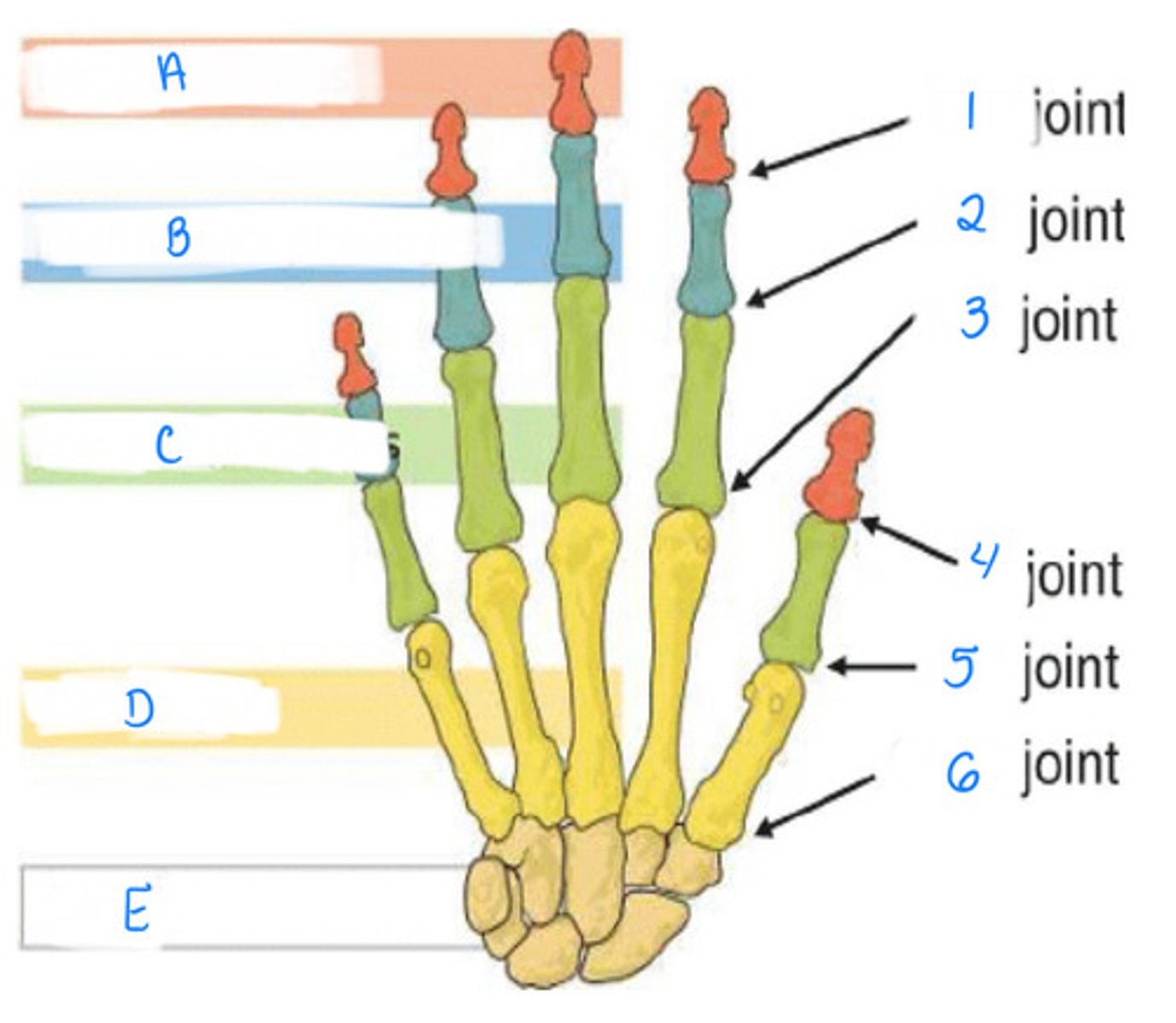
IP joint, MP joint, CMC joint
Identify 4, 5, 6
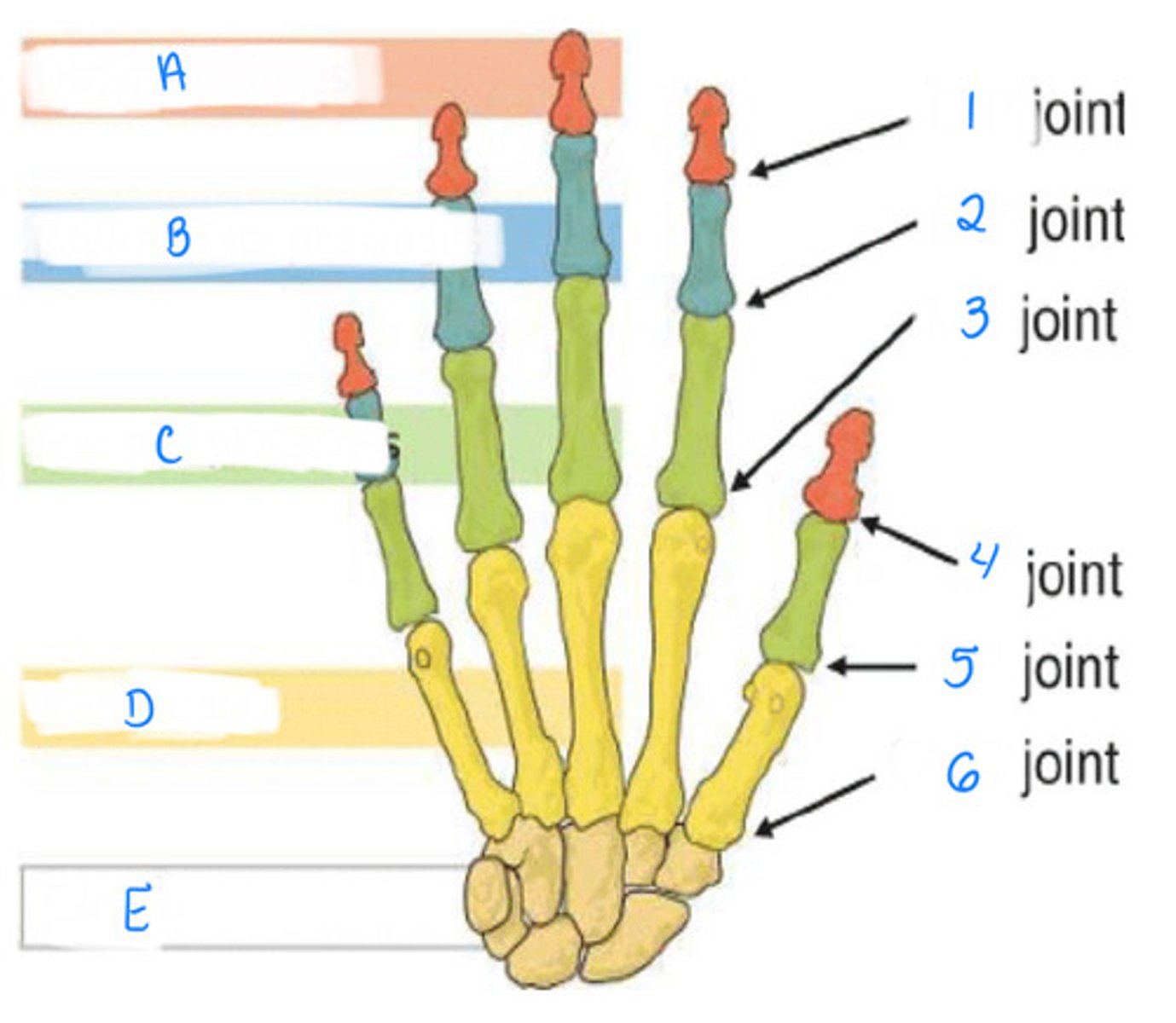
Distal phalanges, intermediate phalanges, proximal phalanges, metacarpals, carpal
Identify A, B, C, D, E
Colle's
__________ fractures involve distal displacement of the distal bone in a distal radius fracture
Ulnar; flex
A claw hand would indicate a __________ nerve injury, causing the 4th and 5th digit PIP and DIP joints to flex and in inability to fully (flex/extend) the digits
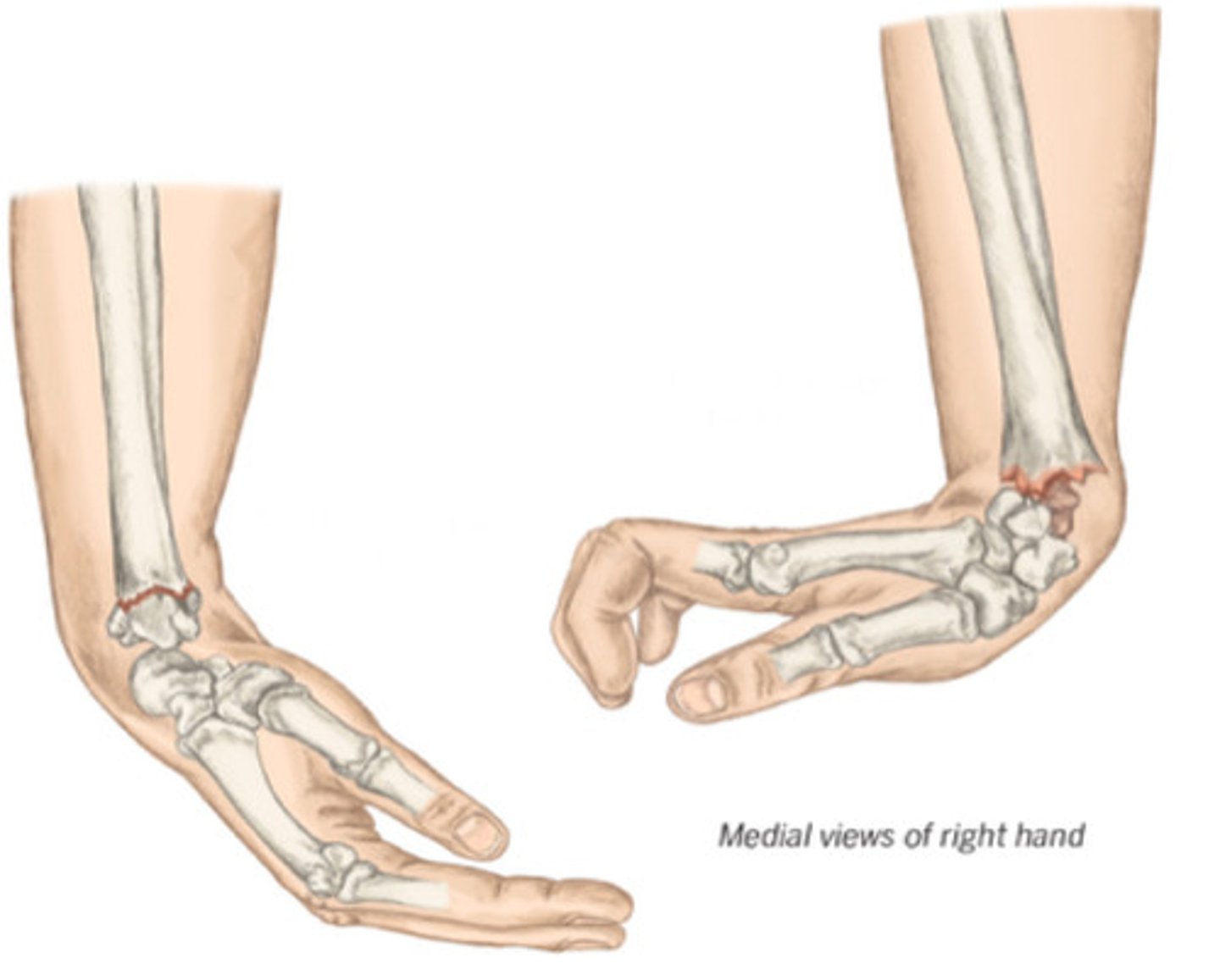
Left: Smith, Right: Colle's
Identify both of the pathologies
Median, flex
Hand of benediction would indicate a ________ nerve injury, causing the 2nd and 3rd digits to extend and in inability to fully (flex/extend) the digits
Radial; extension
Wrist drop would indicate a ________ nerve injury resulting in loss of wrist, digit, and thumb (flexion/extension)
False
T/F? The thumb has a middle phalange
3rd metacarpal
Location of transverse arches peaks
The proximal transverse arches is along the CMC joints, the distal transverse arch is along the MCP/MP joints
The proximal transverse arches is along the _____ joints, the distal transverse arch is along the ______ joints
Proximal transverse arch
(Proximal/Distal) transverse arch: capitate is centrally located along this arch, fairly rigid, produces concave appearance of palm
Distal transverse arch
(Proximal/Distal) transverse arch: important for "cupping" or "flattening palm" which involves metacarpals 1, 4, and 5 rotating around stable 2 and 3
Metacarpal heads (knuckles)
Peak of longitudinal arch which allows for us to hold and manipulate objects
CMC joints
Articulation between distal carpal bones and adjacent metacarpals
2nd and 3rd CMC joints
Primary stabilizers of the hand (2 joints), allows us to hold tools
4th and 5th CMC joints
2 joints: Most mobility in the hand; allows hands to cup or curve
False - gliding/sliding occurs at these joints but not movement occurs specific to this joint
T/F? The CMC joint is responsible for flexion/extension
MCP joint of fingers
Articulation of metacarpal joint with adjacent proximal phalanx
Flexion/extension and abduction/adduction
Movements that occur at the MCP joints of the fingers
True
T/F? MCP flexion of fingers is not tested on its own unless testing for flexor digiti minimi
True - occurs parallel to the palm
T/F? Radial adduction/abduction is the same movement as flexion/extension of the CMC joint of the thumb
False - palmar abduction/adduction is the same movement (occurs perpendicular to the palm)
T/F? Radial abduction/adduction is the same movement as abduction/adduction of the thumb
Opposition
Movement of the thumb to touch the fingertips
Radial adduction/abduction (flexion/extension), Palmar abduction/adduction (abduction/adduction), opposition
Identify all of the movements occurring at the CMC joints of the thumb
True - it is an accessory movement
T/F? Rotation occurs at the CMC joint of the thumb
Flexion/extension
What movement(s) does that MCP joint of the thumb participate in?
Flexion/extension
What movement(s) does that IP joint of the thumb participate in?
Abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis, Opponens pollicis, adductor pollicis
What muscles make up the thenar eminence? (4)
Abductor digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi, Opponens digiti minimi
What muscles make up the hypothenar eminence? (3)
Prehension
Grasp, holding/manipulating objects; can be power grip or precision grip
Power grips; decreased
In the ______ grip digits position objects against palm forcefully while being moved by a more proximal joint, the thumb has (increased/decreased) function as it wraps around in the opposite direction of the digits flexing in one direction
Cylindrical Grip:
Fingers: flexed and adducted
Thumb: opposition
Cylindrical Grip:
Fingers: _________ and ________
Thumb: _____________
Spherical grip:
Fingers: flexed and abducted
Thumb: opposition
Spherical grip:
Fingers: _________ and __________
Thumb: __________
PIPs/DIPs flexed, MCPs neutral/extended
A hook grip can sustain force for a long time and involves the 2nd-5th __________/_________ flexed in a hooklike manner while the _______ are neutral and extended
Composite grip
Maximal flexion of all digits
Ex. wringing out towel
Precision grips
Used for holding objects between tips of fingers and the thumb, provide more fine movement and accuracy, proximal joints do not move as much
Lateral pinch
Pad of thumb presses object against lateral index finger, strong grip but has less fine movement; such as when holding a key
Tip pinch
Tip of finger with tip of thumb to pick up small objects, forms a circle, important for fine motor coordination not for power
Palmar pinch
Palmar surface of distal phalange in contact with palmar surface of thumb; forms an oval; used when holding a pencil or pinching tweezers