The Autonomic Nervous System
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
whats the PNS subdivided into
somatic and autonomic
what is the SNS function
includes nerves which transmit infomation
where do the nerves transmit infomation
to skeletal muscles
from sense organs and skin
under conscious control
what is the ANS
nerve pathways which connect to internal organs and glands
what does the parasympathetic output in the ANS arise
craniosacral origin
what does the sympathetic output in the ANS create
rhoracolumbar
what is dual inervation
when many organs recieve input from parasympathetic and sympathetic nerves
dual innervation in pupils
sympathetic : dilate
parasympathetics ; constricts
dual innervation in heart
=-sympathetic : increaes rate and frce of contraciton
parasympathetic- decreases only
=
dual inmervtion GI tract
sympathetic reduces ability
parasympatheirc increases activity
Autonomic neuron types
preganglionic neurons
post ganglionic neurona
what happenes to automic neurotransmiters at the ganglita
both use acetylcholine as the transmitter
what happens to autonomic neurotransmitters at the organ
the parasympathetic system uses acetylcholne
the sympatheric system uses nodrenaline
what does the adrenal medulla secrete
aldosterone
what are the major PNS reactions
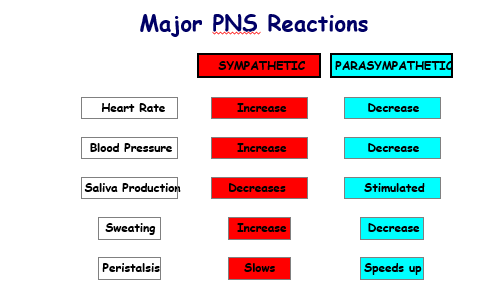
what happens to your heart rate, blood pressure and sweat in the sympathetic nervous system
they all increase
what happenes to saliva production and peristalsis in the sympathetic nervous system
saliva production decreases
peristalsis slows
what happens to heart rate,blood pressure and sweat in the parasympathetic nervous system
they decrease
what happens to saliva production and perisalis in the parasympatheirc nervous system
saliva production is stimulated
peristalsis speeds up
what is activated under conditions of stress anxiety and fear or excitment in the sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight
what happens during fight or flight (2)
increased cardiac output
blood flow away from viscera
functions of sympathetic nervous system
increase in heartrate
increase in blood sugar
functions of parasympathetic nervous system
decreased cardiac output
bladder contraction
autonomic nervous system receptors (2)
cholinergic
adrenergic
types of adenergic receptors (2)
alpha
beta
types of cholinergic receptors
nicotinic
muscarinic