Chapter 3: The Chemical Building Blocks of Life | D.C. Bio
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Carbon
Must contain ___ to be considered organic
Carbon can contain up to ___ covalent bonds
4
Functional Groups
Specific molecular groups that bond to carbon-hydrogen skeletons.
Purpose of Functional Groups
Influence the behavior of the entire molecule in reactions.
Isomers
Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. Isomers can have varying physical and chemical arrangements.
Dehydration Synthesis
Used to build macromolecules by removing water molecules to form bonds between monomers.
Hydrolysis
Used to break down large molecules by adding water molecules to split bonds between monomers.
Monomers are joined to form ________.
Polymers
Polymers are broken down to _______.
Monomers
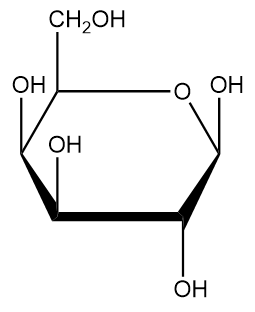
Carbohydrates
Molecules with a 1:2:1 of C, H, and O
Characteristic of carbohydrates
Good energy storage molecules.
Examples of Carbohydrates
Sugars, starch, glucose
Monosaccharides
Simplest units of carbohydrates and the simplest form of sugar. Ex. Glucose and Fructose.
Disaccharides
Two monosaccharides linked together by dehydration synthesis.
Purpose: transport sugar or for energy storage
Examples: Sucrose, lactose, maltose
Polysaccharides
Long chains of monosaccharaides linked through dehydration synthesis.
Energy Storage: Plants use starch. Animals use glycogen.
Structural Support: Plants use cellulose. Arthropods and fungi use chitin.
Nucleic Acids
Made up of monomers of nucleotides that are connected by phosphodiester bonds.
Nucleotides are composed of ______+_______+_______.
Sugar, Phosphate, Nitrogen Base
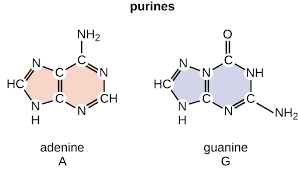
Two Families of Nitrogen Bases
Purines and Pyrimidines
Purines
Adenine and Guanine
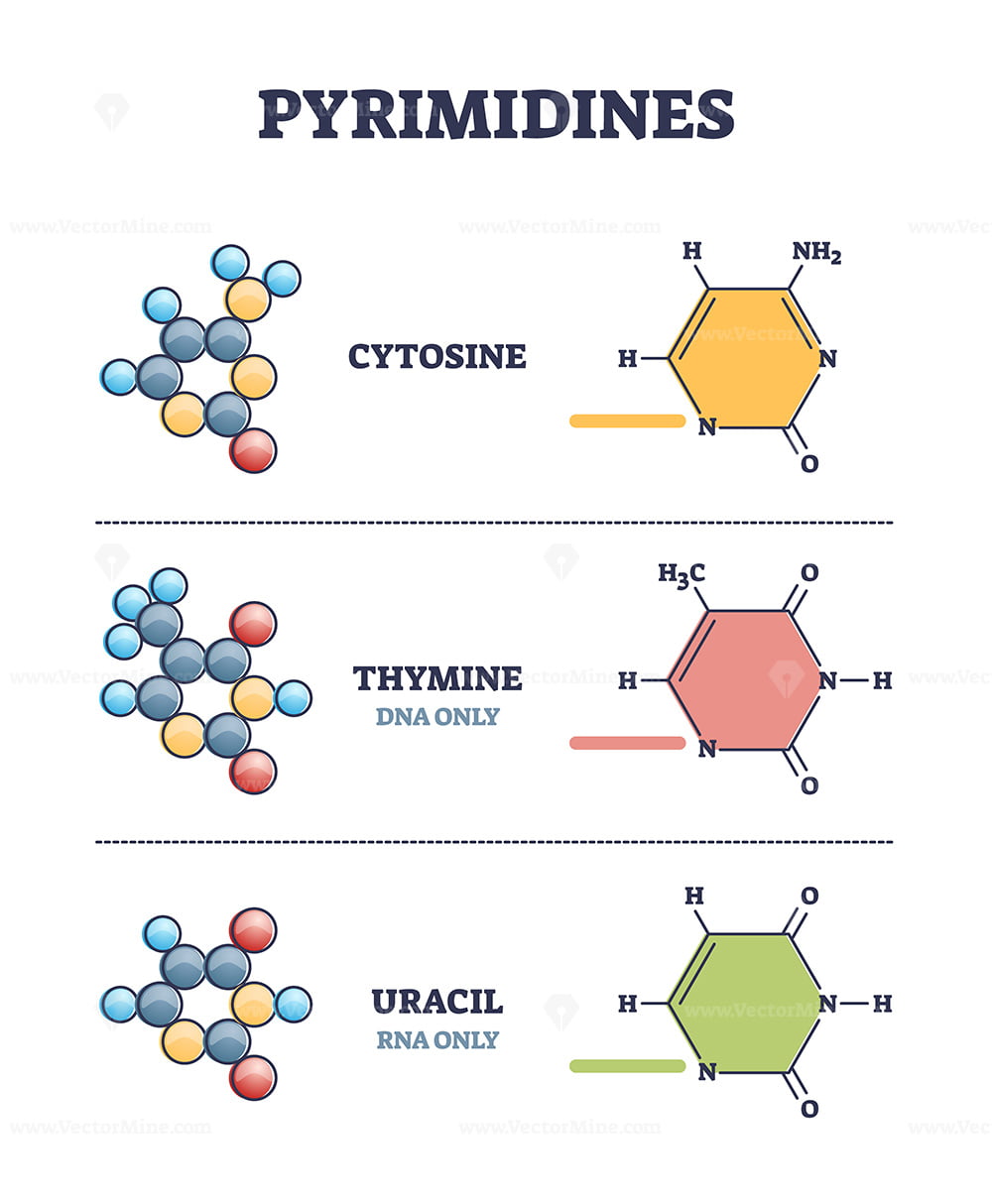
Pyrimidines
Thymine, Cytosine, Uracil
DNA
Encodes information for amino acid sequence of proteins within a sequence of bases.
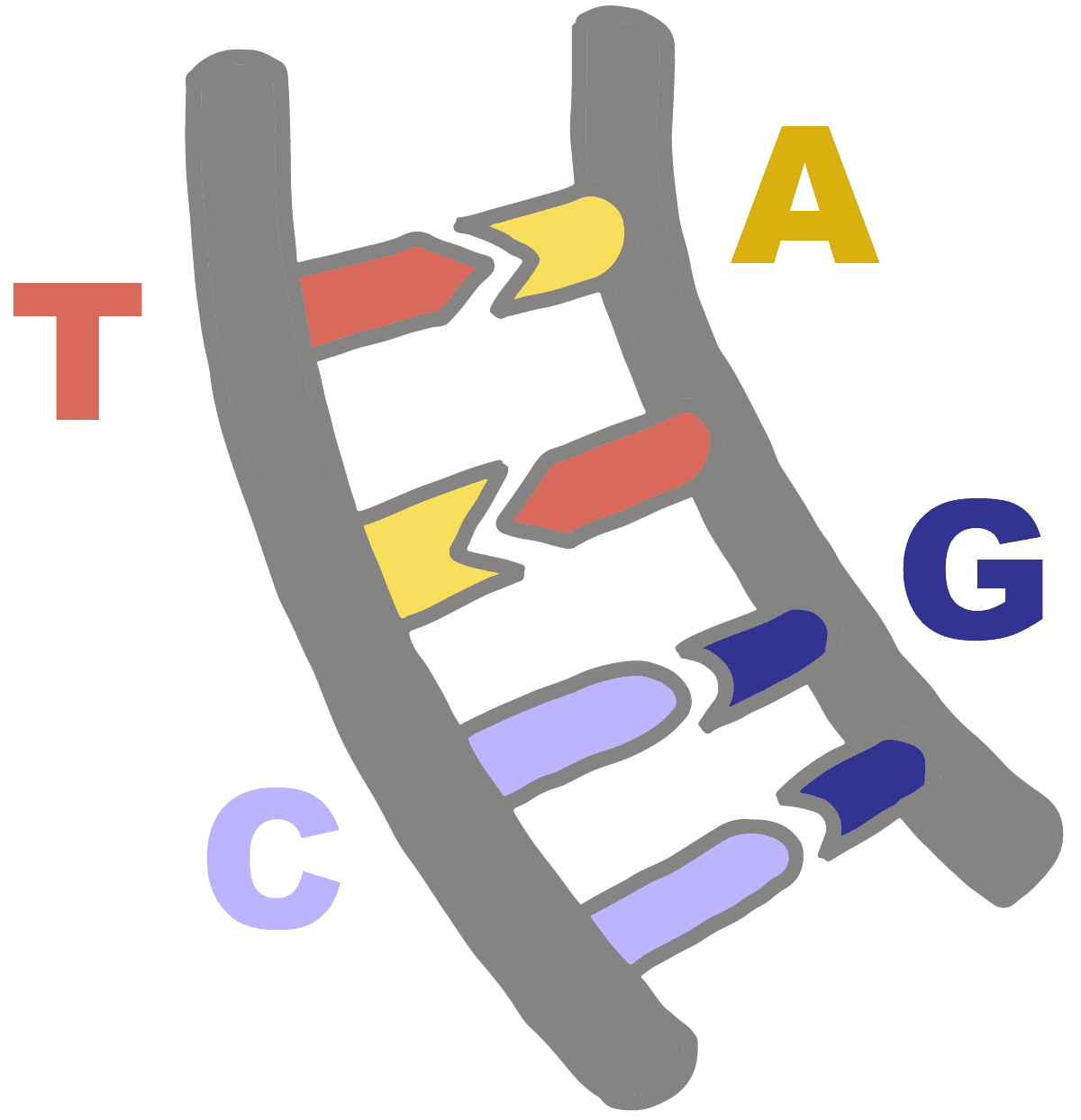
Base-Pairing Rules
A = T(or U in RNA)
C = G
RNA
Uses information in DNA to specify sequence of amino acid in proteins. Contains the sugar, ribose, and the base, uracil. Single Polynucleotide strand.
ATP
The primary energy currency of the cell.
NAD+ & FAD
Serve as electron carriers for many cellular reactions.
Protein Functions:
Enzymes catalyst, defense, transport, support, motion, regulation, storage
Amino acids are ____
Monomers & composed of one or more long, unbranched chains.
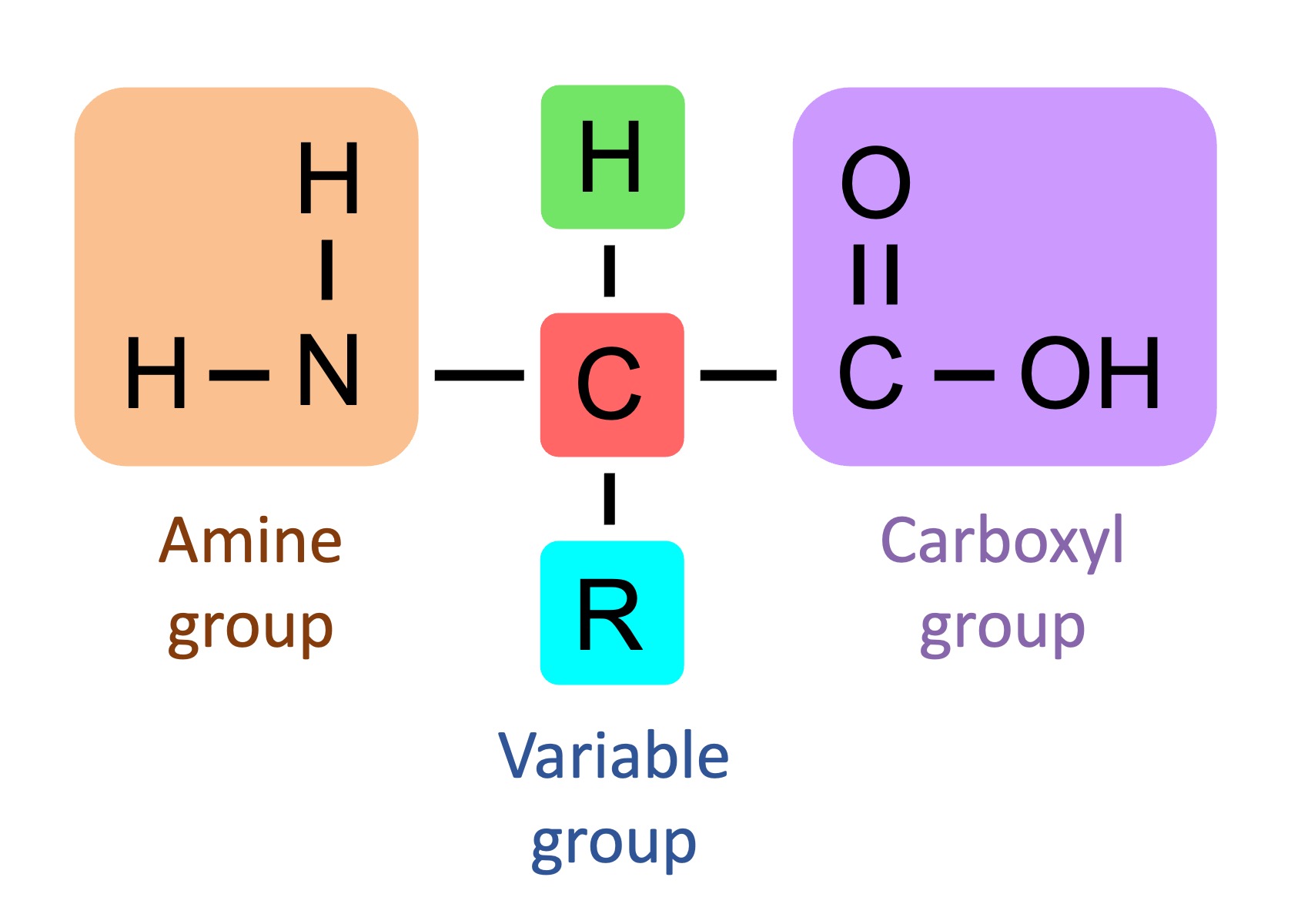
Parts of an Amino Acid
Central carbon atom, amino group, caroboxyl group, single hydrogen, variable R group.
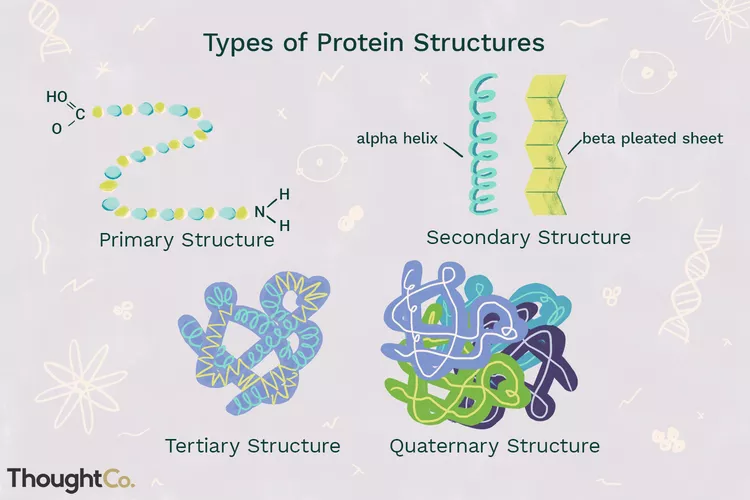
Four Levels of Protein Structure
Primary Structure: sequence of amino acids(have come straight out of ribosome.)
Secondary Structure: interaction of groups in the peptide backbone. Helps support the shape of protein. Two main shapes: helix or sheet.
Tertiary Structure: globular structure; hydrophobic inside, hydrophilic outside.
Quaternary Structure: Subunits(polypeptide chains) come together give this structure.
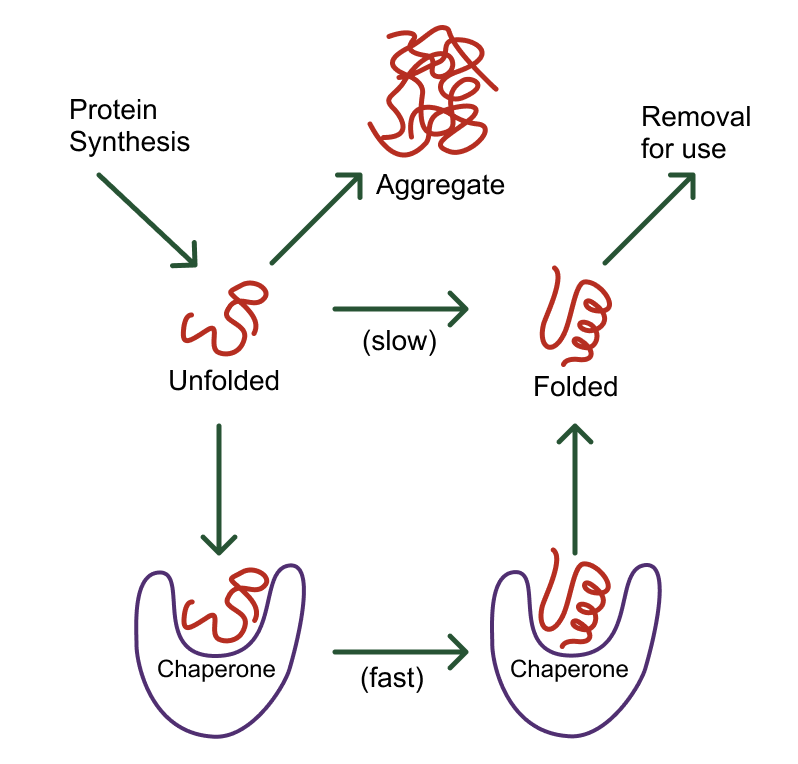
Chaperones
Help proteins fold correctly
Denaturation
Protein loses its structure by unfolding, promptly losing its function. Due to environmental conditions: pH, temperature, ionic concentration of solution.
Dissociation
Subunits of protein with a quaternary structure separate but do not lose their function.
Lipids
Insoluble in water
High proportion of nonpolar C—H bonds cause the molecule to be hydrophobic.
Ex. Fats, oils, waxes, terpenes, steroids, and some vitamins
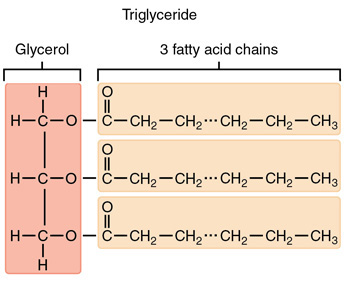
Fat Molecules
Triglycerides : composed of one(1) glycerol and three(3) fatty acids.
Fatty Acids: need not to be identical; the chain length varies.
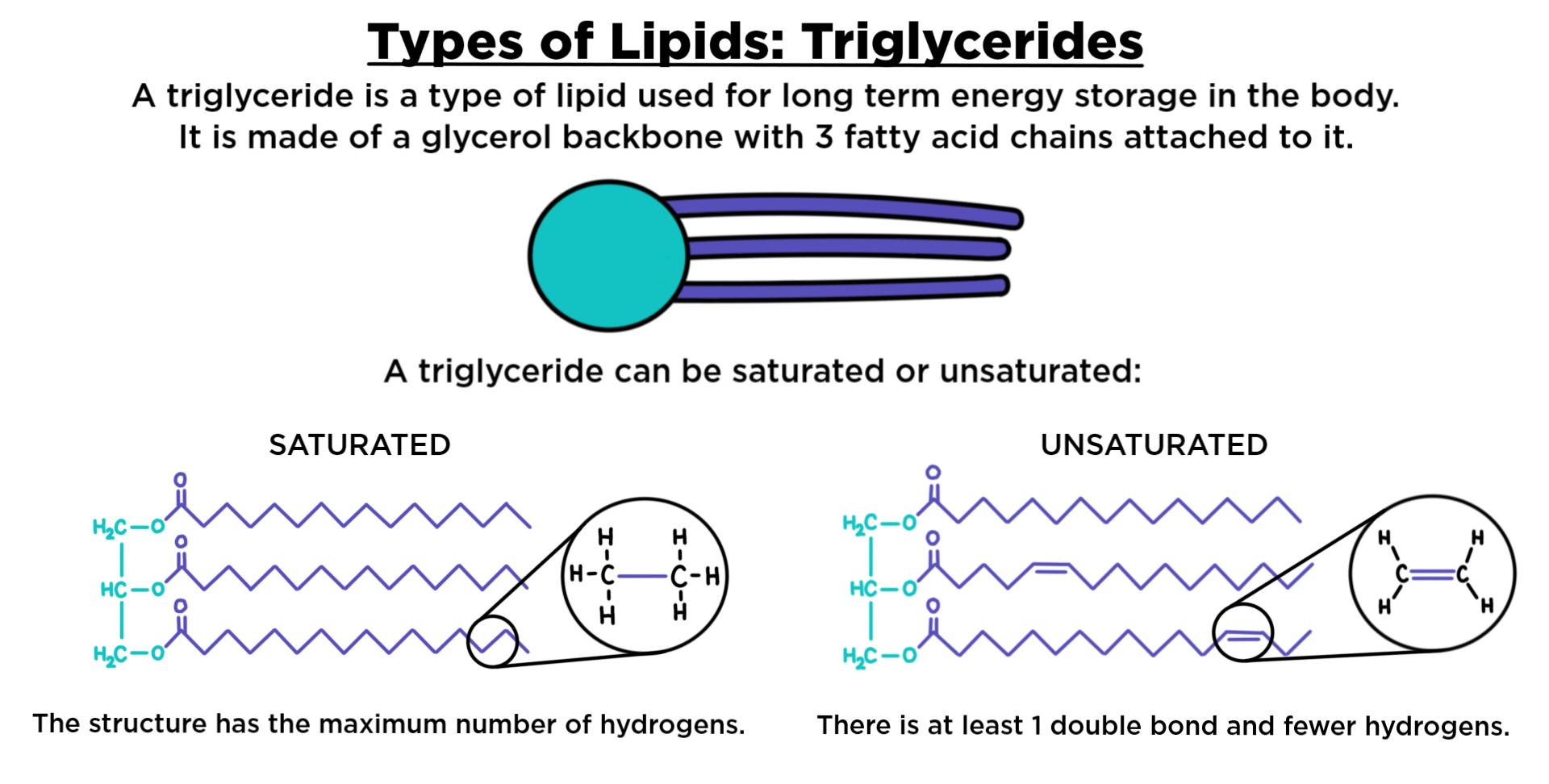
Saturated Fat
No double bonds between carbon atoms.
Higher melting point
Animal origin.
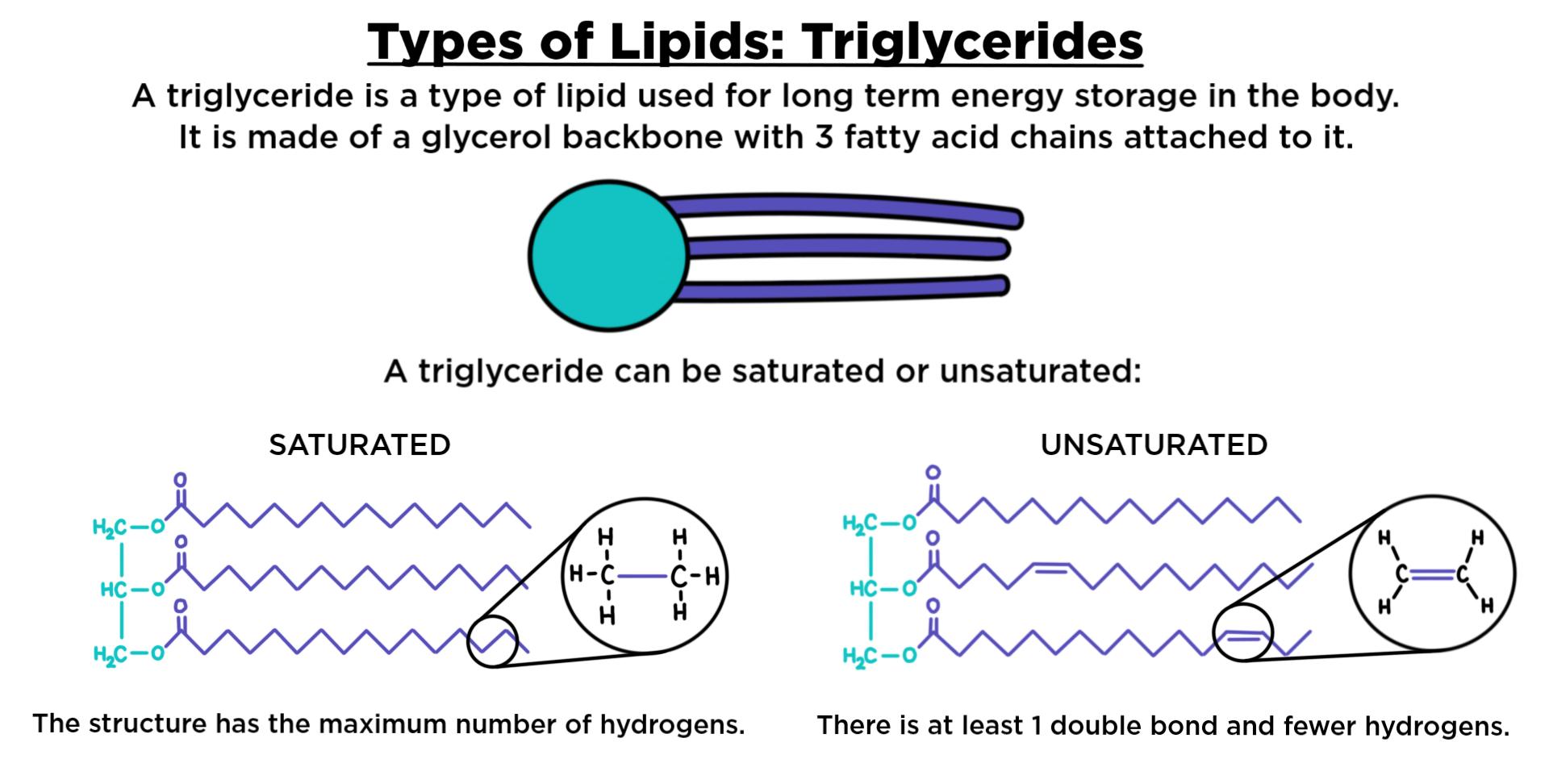
Unsaturated Fat
One or more double bonds.
Low melting point
Plant origin
Trans Fat
Produced industrially
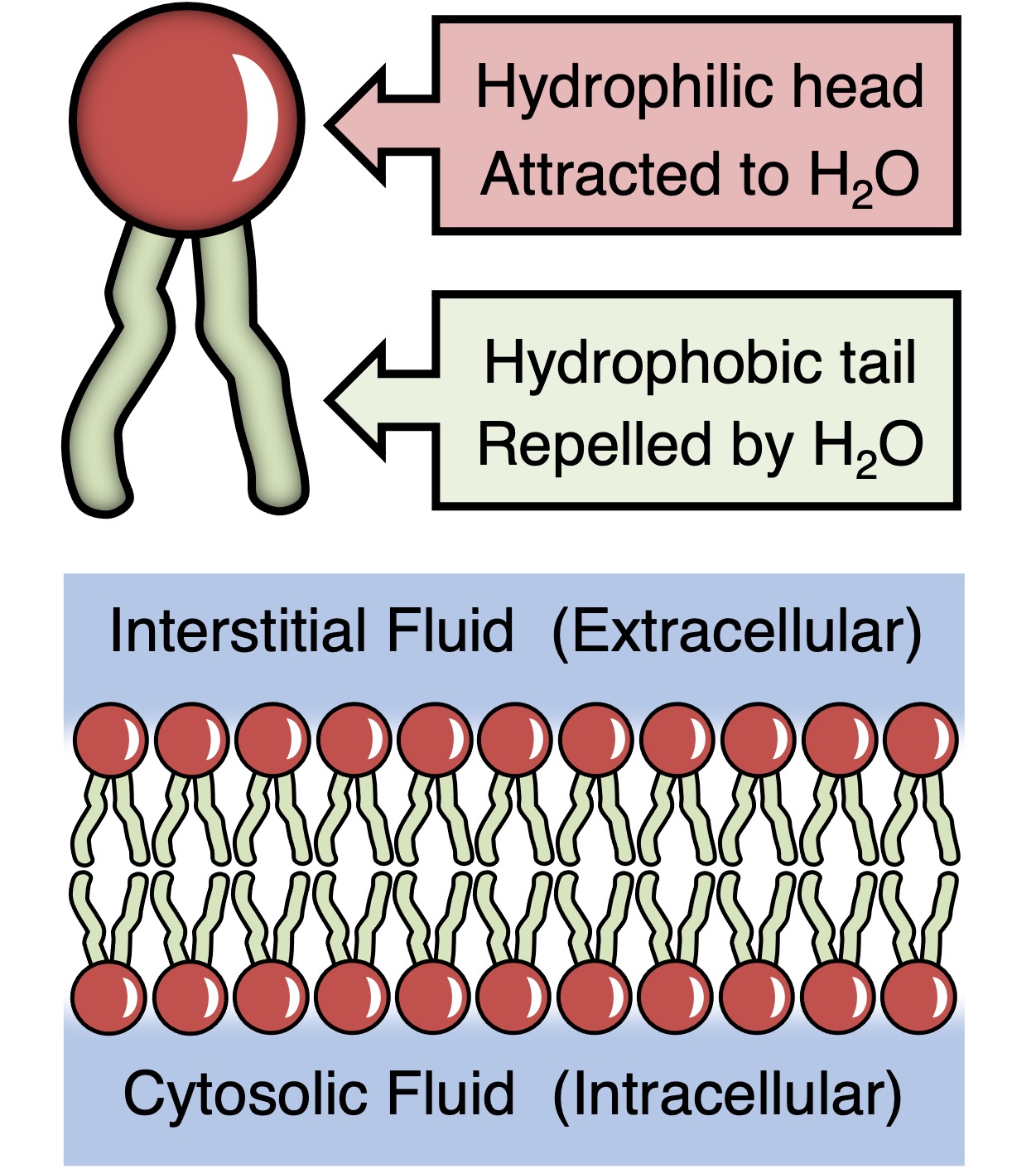
Phospholipids
Composed of glycerol, two(2) fatty acids — nonpolar “tails” and a phosphate “head”. Form all biological membranes.
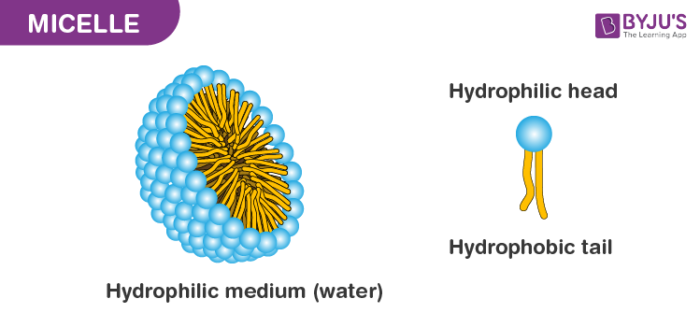
Micelles
Lipid molecules orient with polar(hydrophilic) head toward water and nonpolar tails away from water.
phospholipid bilayer