AP Biology Chapter 3
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
How do cells communicate
Cells communicate through direct contact with other cells or ones that are close by sending chemical signals such as hormones or neurotransmitters.
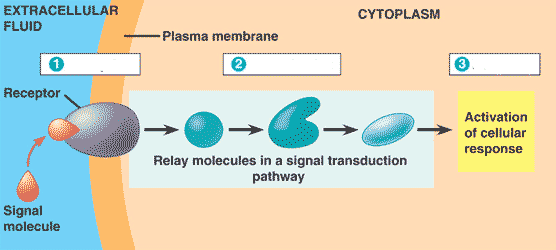
3 Stages of Cell communication
Reception- Detection of a signal molecule coming from outside the cell.
Transduction- Converts signal to a form that can bring a cellular response.
Response- The specific cellular response to the signal molecule. Ex: production of a protein
GDP
GTP
What happens if there is a mutation in the receptor protein?
Transduction can’t be activated, meaning the message can’t get to the nuclear where is may activate transcription.
Ligand (is it in transcription or translation)
The majority of signal transduction pathways involve the binding of signaling molecules, aka ligands, to receptors that trigger events inside the cell.
Signaling Cascades
Relay signals from receptors to targets, often amplifying/increasing the incoming signals. This can result in cell growth, gene expression, or release of molecules.
Why do only some cells respond to a hormone even when it’s transported throughout the body?
Not all cells have receptors for that hormone, only cells with that specific receptors are capable of responding. Cell signaling depends on the ability to detect a signaling molecule.
Homeostasis and what is used to maintain it
Homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable internal environment. Feedback are process used to maintain this balance by increasing or decreasing a cellular response to an event.
Negative Feedback
These mechanisms maintain homeostasis by returning the disrupted system back to its target set point
Positive Feedback
These mechanisms amplify responses away from a set point, often leading to a specific outcome, such as childbirth.
How many stages are in Interphase and how long do cells spend in Interphase
G1- Cell Growth
S- DNA replication
G2- Cytoplasmic components are doubled in preparation for
95%
G0 check point
Decides whether a cell enters the cell cycle and begins divide, or remains in a non-dividing, resting state(no cell division). It determines if the cell has the necessary resources and signals to proceed into the cell cycle.