L3 Prenatal Screening and diagnostic test
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Suggest the benefit of prenatal screening. (7)
Detection of potential genetic or chromosomal abnormalities at an early stage
Couples can decide on further diagnostic test in early pregnancy
Enable early intervention and proactive care
Reduce anxiety and uncertainty
Allow couples to prepare emotionally, gather information about their pregnancy and future care for their child
Facilitate informed decision-making
Provide an opportunity for family planning, e.g.
The option of genetic counseling
Exploring reproductive technologies
Plan for future pregnancies based on the risk factors identified
List the high risk group for prenatal diagnostic testing (9)
Maternal age ≥35
Obesity (pre-pregnancy BMI >30)
Aboriginal, African, Asian, Hispanic, South Asian ethnicity
Family history of genetic disorders / DM
Maternal health problems:
Hypertension, epilepsy, thyroid disease, heart, blood disorder
Previous pregnancy with gestational DM
Previous delivery of a baby large than 4000gm
Corticosteroid use during pregnancy
Multiple pregnancy
Suggest a test that will be do in every antenatal visit
Urinalysis for protein & glucose
Why HCG level drop gradually after the peak level at week 8 ?
HCG function is to prompts the corpus luteum to continue secrete estrogen & progesterone in order to maintain the uterine lining thickness
After week 8, the placenta is mature to take over the production of progesterone from corpus luteum
Suggest a prenatal screening that can act as an indicator of fetal life.
Fetal movement count (Kick count)
What is the normal & abnormal findings of fetal movement count ?
Normal: women counts 10 distinct kicks of her fetus per 1-2 hours
Abnormal: No fetal movement for 12 hours —> notify nurse / doctor
Suggest a prenatal screening that can use to monitor the fetal heartbeat and uterine activity over time
Cardiotocogram
Suggest a prenatal screening for fetal surveillance before the onset of labour
Nonstress test (NST)
(a form of cardiotocography (CTG))
How to interpret the result of Nonstress test (NST)
Reactive NST: ≥2 FHR accelerations within 20 mins period
Non-reactive NST: ≤2 FHR accelerations during a 40 mins period
Variable decelerations NST
No recurrent 經常性的 and < 30s → no further investigation
Recurrent: ≥ 3 episodes in 20 mins → extend monitoring
Persist for ≥ 1 minute → immediate attention
List the types of prenatal screening / diagnostic test to be performed in 1st trimester (3)
Ultrasound
Chorionic villus sampling
Maternal serum blood test / Multiple marker screening
List the types of prenatal screening / diagnostic test to be performed in 2nd trimester (6)
Ultrasound
Amniocentesis
Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling (PUBS) / Cordocentesis
Maternal serum blood test / Multiple marker screening: Triple screening / Quadruple screening
Glucose screening
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
List the types of prenatal screening / diagnostic test to be performed in 3rd trimester (2)
Ultrasound
Group B streptococcus prenatal screening
How to prepare patient for transabdominal / transvaginal ultrasound respectively
Transabdominal:
Tell the woman to drink lots of water to allow full bladder anatomically push the uterus up to the abdomen
Transvaginal:
Tell the woman to empty the bladder
What are the purpose of ultrasound assessment in 1st trimester (1-13 weeks) ? (6)
To check the embryo is developing inside the uterus
Confirm the number of embryos
Calculate the gestational age and the expected date of delivery
Determine the foetal age and growth
Guide doctors for other diagnostic test, e.g. chorionic villus sampling
Identify soft ultrasound markers: check the neck areas, aka Fetal nuchal translucency screening
Perform at ~11-13 weeks
examine the area at the back of the foetal neck for increased fluid or thickening
Extra tests should be performed when the nuchal translucency more than 3.5mm
What are the purpose of ultrasound assessment in 2nd trimester (14-26 weeks) ? (4)
Evaluate the foetus from head to toe for any developmental issues
Determine size, position and engagement of the foetus
Quantify amniotic fluid amount
Check the foetus's sex according to the parents' desire
What are the purpose of ultrasound assessment in 3rd trimester (27-40 weeks) ? (3)
(Usually perform it after 30 weeks)
Continue to monitor the baby’s growth
Identify the location of the placenta
If total placenta (completely cover the os) —> might have many blood lose during delivery
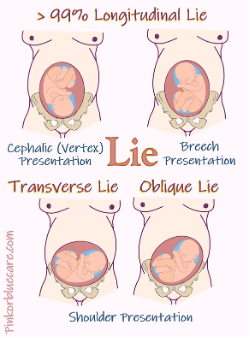
Identify the position and presentation of the foetus
Anterior (head at the os) / Vertex / Cephalic presentation —> natural passage
Breech Transverse lie —> recommend C-section
What is the indication of chorionic villus sampling ?
History of or suspicion of a genetic disease, chromosomal abnormalities or metabolic disorders
Suggest an advantage of chorionic villus sampling
the results are available much earlier than amniocentesis
What is the purpose of chorionic villus sampling ?
To detect fetal genetic and chromosomal abnormality, perform at ~ 10-13 weeks
What are the risk of chorionic villus sampling ? (6)
· Abdominal cramping
· Bleeding
· Leaking of amniotic fluid
· Infection
· Miscarriage
· Preterm labour
What is purpose of amniocentesis ?
To diagnose certain chromosomal conditions, e.g.
Þ Down syndrome
Þ Neural tube defects
Þ Cystic fibrosis
List the nursing intervention of amniocentesis (pre-pocedure) (5)
Invasive procedure !!!
Educate the client to monitor that there will be red discharge in the first 2 days, then should transit to brown and then resolves
Uterine cramping that usually happened immediately after the procedure
Amniocentesis: a small amount of leaking of amniotic fluid may be noted on the first day
Advice resting for 24 hours
Avoid exercise, heavy lifting and sexual intercourse for several days
What is the purpose of percutaneous umbilical blood sampling (PUBS) / cordocentesis ?
Obtain a sample of blood from the foetal umbilical cord after 20 weeks of gestation:
To detect blood disorders
To deliver medication or blood transfusion to a fetus
What types of blood markers will be examinated in the 1st trimester ?
PAPP-A = Pregnancy-associated plasma protein A
hCG = Human chorionic gonadotropin
cfDNA = Cell free DNA, the fetal DNA circulate in mother’s circulation
What types of blood markers will be examinated in the 2nd trimester ?
hCG
AFP = Alpha-fetoprotein
E3 = Oestriol
Inhibin-A (Max. at 36 weeks)
Triple or Quadruple screening
If PAPP-A level drop, what might be the suspected findings ?
PAPP-A = Pregnancy-associated plasma protein A
· A lower birth weight baby
· Perterm birth
· Preeclampsia
· Mid trimester miscarriage
· Increased risk of chromosomal abnormality
PAPP-A is produced by the syncytiotrophoblast cells of the placenta. PAPP-A helps in the breakdown of insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins (IGFBPs), which control the availability of IGF to cells for growth and development.
If hCG level increase, what might be the suspected findings ?
Multiple pregnancy
Hydatidiform mole 葡萄胎
Down syndrome (Trisomy 21) [2nd trimester]
If hCG level decrease, what might be the suspected findings ?
· Fetal death / still birth [1st, 2nd trimester]
· Trisomy 18 [2nd trimester]
· Ectopic pregnancy
· Incomplete miscarriage
· Threatened spontaneous abortion
If AFP level increase, what might be the suspected findings ?
AFP = Alpha-fetoprotein
· Open neural tube defects, such as spina bifida
· Twins / multiple pregnant
· Stillbirth 死胎
If AFP level decrease, what might be the suspected findings ?
AFP = Alpha-fetoprotein
· Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)
· Trisomy 18
If E3 level drop, what might be the suspected findings ?
· Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)
· Trisomy 18
· Stillbirth 死胎
Inhibin-A findings in serum blood test might indicate what kind of suspected findings ?
· Down syndrome
· Preeclampsia
· GDM
· Macrosomia巨大兒
Describe the blood result in 2nd trimester if suspected of neural tube defect.
AFP increase
uE3 normal
hCG normal
Describe the blood result in 2nd trimester if suspected of trisomy 21 (Down syndrome).
AFP decrease
uE3 decrease
hCG increase
Describe the blood result in 2nd trimester if suspected of trisomy 18.
AFP decrease
uE3 decrease
hCG decrease
Describe the blood result in 2nd trimester if suspected of multiple pregnant.
AFP increase
uE3 normal
hCG increase
Describe the blood result in 2nd trimester if suspected of still birth.
AFP increase
uE3 decrease
hCG decrease
What is the purpose / indication of Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Do when the baby suspect of hydrocephalus
Combined with USG at or after 18 weeks of gestation
What are the indication of checking cfDNA markers in the 1st trimester (4)
1. Higher risk for a foetal chromosome disorders
2. Maternal age ≥ 35
3. Previous child with a chromosome disorders
4. Abnormal results on an ultrasound or other prenatal test
cfDNA findings in serum blood test might indicate what kind of suspected findings ?
· Down syndrome
· Trisomy 18
· Trisomy 13
Describe when and how to do group B streptococcus prenatal screening ?
Þ Perform between 35-37 weeks of gestation
Þ Taking both low vaginal & rectal swabs