S1L1.1_Principles of Intervention (Part 1)
1/189
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
190 Terms
Stages of inflamm & repair
Acute
Subacute
Chronic
Acute stage aka
Reaction and inflammatory stage
Acute stage duration
Lasts 4-6 days unless insult is perpetuated
Acute stage causes
Trauma
Repetitive use
Chemical irritants to reinstate homeostasis
Acute stage signs of inflamm
Pain at rest (dolor)
Swelling (tumor)
Redness (rubor)
Heat (calor)
Loss of function
Acute stage: Pain & impaired mvmt during ROM are d/t
Irritated nerve endings
Inc tissue tension
D/t edema/joint effusion & m. guarding
The body’s way of immobilizing a painful area
Edema/joint effusion & m. guarding
Subacute stage aka
Proliferation, repair, and healing stage
Subacute stage: Duration
10 -17 days
14-21 days after onset
Subacute stage: May last up to __ in tendons (limited _)
6 wks
circulation
Subacute stage: signs of inflamm
Dec. progressively → eventually absent
Subacute stage: When is pain felt
Synch. c encountering tissue resistance @ end of avail. ROM
When newly developing / tight tissue is stressed beyond tolerance
Subacute stage: Muscle strength
Weak
Func. is limited d/t weak tissue
Subacute stage: This stage is characterized by the __ & __ of __
Synthesis & Deposition
Collagen
Subacute stage: Noxious stimuli
Noxious stimuli: Removed
Capillary beds start to grow into the area
Subacute stage: What activities inc during this stage
Fibroblastic activity
Collagen formation
Granulation tissue dev.
Chronic stage aka
Maturation and remodeling stage
Chronic stage: Duration
6 mo. → 1 yr
depends on type of tissue involved & amt of damage
Chronic stage: Inflammation
NO signs of inflamm
Chronic stage: There may be __ or __ that limit ROM + __ limiting normal func
Contractures or adhesions
M. weakness
Chronic stage: Connective tissue
Cont. to strengthen & remodel
in response to applied stresses
Chronic stage: Scar retraction is completed by __
Day 21
Chronic stage: Collagen
Fibers thicken & reorient
in response to stresses on tissue
Chronic stage: Remodeling time is influenced by __
Factors that affect density & activity lvl of the fibroblasts
Time immob.
Stress on tissue
Loc. of lesion
Vascular supply
Primary difference between the state of healing bw late subacute & chronic stages:
○ Improvement in quality (orientation and tensile strength) of collagen
○ Reduction of wound size during chronic stages
Wound healing process
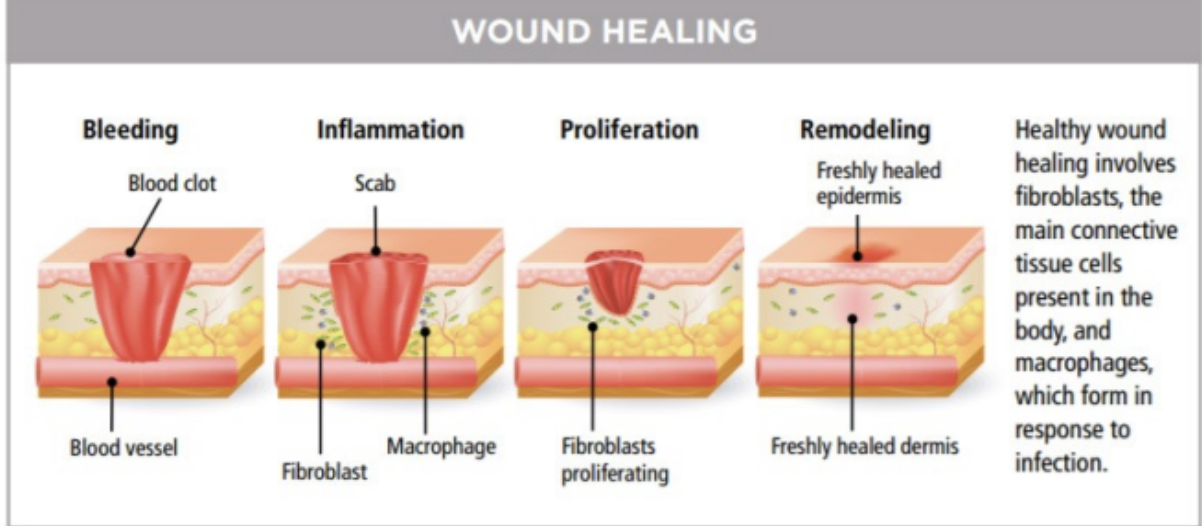
Chronic inflamm: Happens when injured tissue is __
Stressed beyond its ability to repair
Chronic inflamm: Result of excessive stress on tissues (unable to respond to repetitive or excessive nature)
Prolonged / recurring pain
Limitations in activity & function
Chronic inflamm: Precaution:
Progressive loss of ROM d/t stretching → do NOT continue to stretch
Chronic inflamm: Symptoms
Swelling
M, guarding post-act.
↑ pain
↑ stiffness p rest
Loss of ROM for 24 hrs
Chronic inflamm: Causes and contributing factors:
CROP MI CREB MEAT
Cumulative trauma
Repetitive strain
Overuse
Poor mobility
M. imbalance
Intensity of activity (change in usual)
Contractures
Reinjury of old scar
Eccentric demand (rapid / excessive repeated)
Bone malalignment
M. weakness
Environmental factors
Age-related factors
Training errors
Chronic Pain Syndrome: Duration
>6 mo.s
T or F: Chronic Pain Syndrome can be linked to a source of inflamm
FALSE
Can NOT be linked
Chronic Pain Syndrome: Leads to
Activity limitations & Participation restrictions
Tissue responses & characteristics: Acute
VC PEE (Video Call PEE)
Vascular changes
Clot formation
Phagocytosis. neutralization of irritants
Early fibroblastic activity
Exudation of cells & chemicals
T or F: Vascular changes during the acute stage predominate the first 24 hrs of tissue response to inflamm
FALSE
first 48 hrs
Tissue responses & characteristics: Subacute
GC GEN (Grp Chat Generation)
Growth of capillary beds into area
Collagen formation
Granulation tissue
Easily injured tissue (very fragile)
Noxious stimuli removal
Tissue responses & characteristics: Chronic
CoCoMaR(co)
Contracture of scar tissue
Collagen aligns to stress
Maturation of connective tissue
Remodeling of scars
Clinical signs: Acute
Inflammation
Pain before tissue resistance
Clinical signs: Subacute
Dec inflamm
Pain sync. c tissue resistance
Clinical signs: Chronic
Absence of inflamm
Pain p tissue resistance
The foundation in identifying the stages of inflamm
Clinical signs
Impairments: Acute
Inflammation
Pain at rest
Edema
M. spasm
Impaired mvmt
Jt effusion
Dec use of associated parts
Accumulation of fluid in areas of the affected jt
Jt effusion
Impairments: Subacute
Pain @ end of ROM
Dec edema
Dec jt effusion
Developing contracture
Developing weakness from disuse
Dec. func. use of the part & associated parts
Developing contracture is caused by __
inability to move the injured area d/t pain
Dec. functional use is d/t __ during the period of __, which may affect associated regions
Apprehension of pt to use injured area
Recovery
Ex. Pt c elbow fx → apprehensive to move affected UE → dec. functional use of __
Shoulder, wrist, & hand
Impairments: Chronic
Contracture & adhesions
Weakness, poor endurance & neuromuscular control
Dec. functional usage of involved part
Inability to function as expected
Skeletal muscle: Muscle damage is characterized by __
Disruption of fibers & impact on contractile strength
Skeletal muscle: Area at high risk for injury
Myotendinous junction
Skeletal muscle: Common MOI
High demand / impact activities
Significant force → muscle strain / contusion
Classification of m. injuries
Grade 1: Minor
Grade 2: Moderate
Grade 3: Severe
M. injuries: Grade 1 (Minor)
Few tears
Minimal loss of strength
M. injuries: Grade 2 (Moderate)
More damage to fibers
Associated loss of contractile strength
M. injuries: Grade 3 (Severe)
Cross-sectional rupture
Complete loss of contractile strength
Healing process of m. injuries: Phases
Destruction
Repair
Remodeling
Healing process of m. injuries: Destruction phase
● Necrosis of contractile elements
● Hematoma formation & inflamm
● Fibrin & fibronectin form early linkage to provide support against contraction
Healing process of m. injuries: Repair phase
● After few days → few wks
● Phagocytosis of necrotic tissue
● Regeneration of contractile elements
● Stimulation of myofiber formation & scar formation
Healing process of m. injuries: Remodeling phase
● At least 4-6 wks
● Re-organization of tissue integrity & functional maturation
Muscle: Clinical implications for rehab: Small vs Large injuries
Small injuries → heal c muscle tissue
Large injuries → heal c scar tissue
Muscle: Clinical implications for rehab: __ is very important in the __ phase of rehab to promote healing process
Rest
Early
Muscle: Clinical implications for rehab: Modalities may be employed to control __
Inflamm
Edema
Stiffness
Muscle: Clinical implications for rehab: Cryo → (what phase), Heat → (what phase)
Cryo → subacute
Heat → chronic
Muscle: Clinical implications for rehab: Early activity is advocated to prevent __
Adhesion formation
Muscle: Clinical implications for rehab: Adhesion has great effect on
LOM, dec muscle strength & function
Muscle: Clinical implications for rehab: Active stretching should be __ for __ post-injury to __
Postponed
3-7 days
Prevent reinjury
Tendon: Causes of tendinopathy
○ Repetitive motions or load → microtears
○ Abrupt forceful contraction of muscle
T or F: Tendons have a more consistent blood supply compared to other soft tissues leading to increased ability to heal fast
FALSE
less consistent blood supply
decreased ability to heal fast
Achilles Tendon Rupture: __% of ruptures occur during recreational sports
80%
Achilles Tendon Rupture: Common complaint
Weakness c pushoff
Achilles Tendon Rupture: Confirmation tests
MRI or US
Achilles Tendon Rupture: Healing duration
6-12 wks after innjury
Achilles Tendon Rupture: Athletes return to sports after __
3-6 mo.s
Healing process of tendinous injuries: Phases
Inflammatory
Proliferative repair
Remodeling
Scar formation
Healing process of tendinous injuries: Inflamm phase
● Several days → wks
● Inflamm
Healing process of tendinous injuries: Proliferative repair phase
Few days → few wks (up to 6 wks)
Collagen synthesis
Correct faulty biomech. & compensatory posture
Healing process of tendinous injuries: Remodeling phase
● About 6 wks
● Induction of fibrous repair
● Collagen fibers align (based on direction of stress)
Healing process of tendinous injuries: Scar formation phase
● 10 wks → 1 yr
● Decline of metabolism & vascularity
● Strengthening
Tendon: Patient education is important during the __ phase to correct __
Proliferative repair
Faulty biomech. & compensatory posture
Tendon: Strengthening of tissue begins at the __ phase but intensity
given is __ to prevent __
Remodeling
Not too high
Re-injury
Tendon: Clinical implications for rehab: Avoid prolonged periods of __
Immobilization
May lead to tightness, weakness, & contractures
Tendon: Clinical implications for rehab: Identify the postural dysfunction or biomechanical fault to __
Reduce recurrent & repetitive loading to the tendon
Tendon: Clinical implications for rehab: Strengthening & stretching interventions are carefully designed particularly during the __ phase to __
Remodeling
Prevent occurrence of re-injuries
Ligament: Ligamentous sprain can result from __
Excessive lengthening of the ligament
Ligament: Most commonly injured
Ankle → then ACL
Ligament: Classification of ligamental injuries
Grade 1
Grade 2
Grade 3
Ligament: Classification of ligamental injuries: Grade 1
● Stretched
● Microfailure, few fibers in the plastic range are ruptured
● No excessive motion
● Intervention & protection ONLY → no surgery
Ligament: Classification of ligamental injuries: Grade 2
● Stretched c more fibers torn = Partial tear
● Mod jt laxity
● Surgery depends on goal & instability
Ligament: Classification of ligamental injuries: Grade 3
● Complete rupture / tissue failure
● Significant jt laxity
● Surgery
ACL Tear: Most prone to injury:
○ Football players
○ Basketball players
○ Soccer players
○ Skiers
One of the most common knee injuries sustained in sports
ACL tear
ACL tear: How it happens
Pop → severe swelling → extreme pain → difficulty walking
ACL tear: To confirm dx
Xray & MRI
ACL tear tx: Minor tear
Protective braces & PT (c strengthening exercises)
ACL tear tx: Full tear
Reconstructive surgery to rebuild ligament
Healing process of ligament injuries: Phases
Inflammatory
Regenerative
Remodeling
Healing process of ligament injuries: Inflammatory phase
● Healing w/i 72 hrs c hematoma formation
● Deposition of ground substance & disorganized collagen fibers
● (+) signs of inflamm
Healing process of ligament injuries: Regenerative phase
● Few days → 6 wks
● Fibroblast proliferation & collagen formation
Healing process of ligament injuries: Remodeling phase
6 wks post-injury → 1 yr
Remodeling of ligament
Improved collagen alignment