Cell Structure and Function: Organelles, Protein Synthesis, and Energy Production
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Cells
the basic structure and functional units of every organism
Prokaryotic cells
Domains in bacteria and archaea; DNA is in nucleoid region; generally smaller in size than eukaryotes
Eukaryotic cells
Cells that contain membrane-bound organelles and DNA in the nucleus
Organelles
membrane bound structures found in eukaryotic cells
Endomembrane organelles
Includes nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi complex, lysosomes, vesicles/vacuoles, and plasma membranes
Energy organelles
Includes mitochondria and chloroplasts
Compartmentalization
Allows for different metabolic reactions to occur in different locations, increases surface area for reactions, and prevents interfering reactions from occurring in the same location
Unique Cell Components in Plants
Chloroplasts, central vacuole, cell wall, plasmodesmata
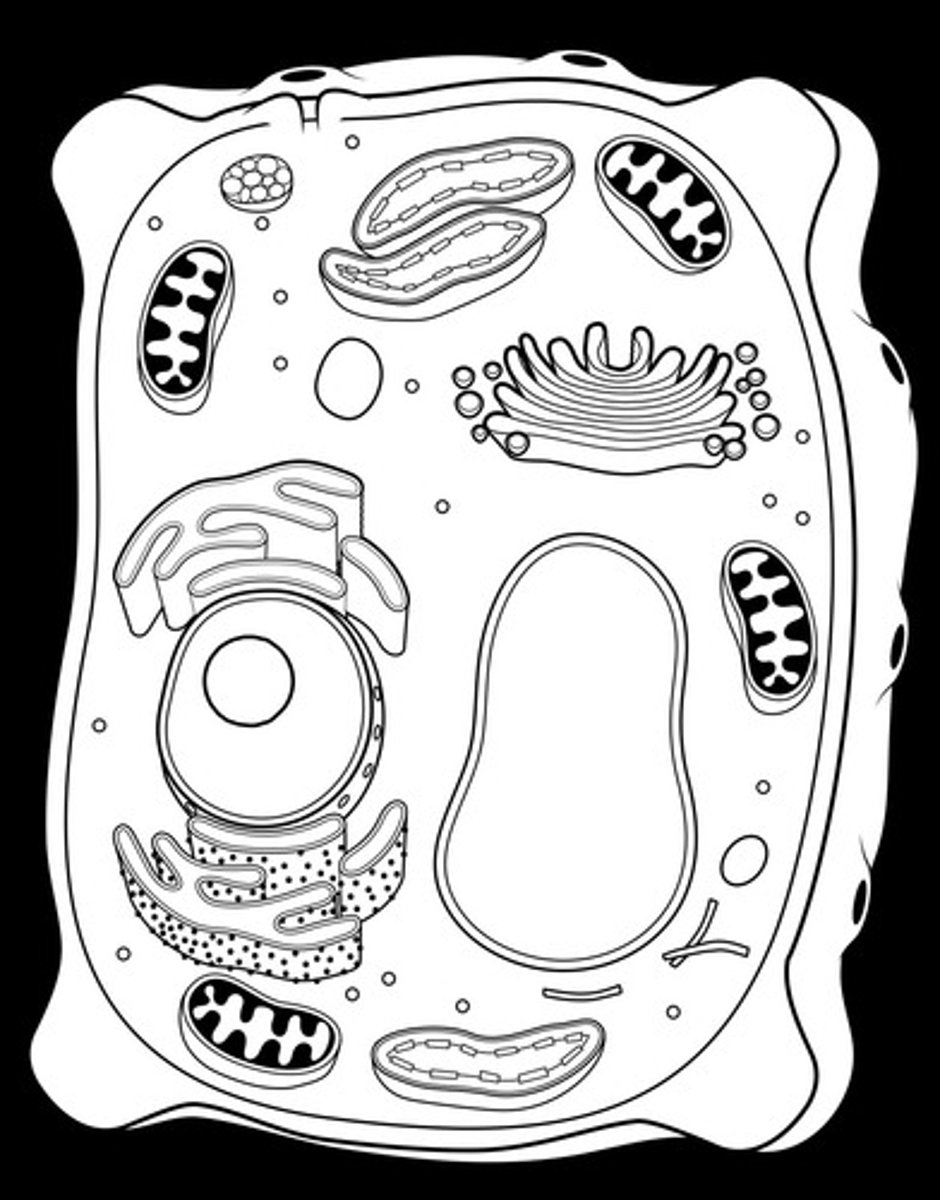
Unique Cell Components in Animals
Lacks chloroplasts, central vacuole, cell wall, and plasmodesmata
Nucleus
Contains chromosomes (genetic information), enclosed by nuclear envelope, double membrane, has pores that regulate entry and exit of materials from cell
Nucleolus
Dense region of the nucleus where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is synthesized
Ribosomes
Translate messages found on mRNA into primary structure of polypeptides
Transcription
The process of DNA being transcribed by RNA polymerase into messenger RNA (mRNA)
Translation
The process where ribosomes decode the information in mRNA and form continuous chains of amino acids, thus forming a protein
Monomers of Proteins
Amino acids, which contain a carboxyl and amino group
Structural Levels of a Protein
Primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure, and quaternary structure
DNA
Deoxyribose, double stranded with anti-parallel connections, contains thymine
RNA
Ribose nucleic acid, single strand, contains uracil
Free Ribosomes
Ribosomes found in the cytosol; Proteins produced here generally function only within the cytosol (I.e. enzymes).
Bound Ribosomes
Ribosomes that are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum or nuclear envelope; Proteins produced here can be secreted from the cell.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
A network of membranous sacs and tubes; Functions: Synthesized membranes, Compartmentalize the cell to keep proteins formed in the ER separate from those free ribosomes.
Rough ER
Type of endoplasmic reticulum that contains ribosomes bound to the ER membrane.
Smooth ER
Type of endoplasmic reticulum that contains no ribosomes; Synthesizes lipids, metabolizes carbs, and detoxifies cell.
Golgi Complex
Contains flattened membranous sacs called cisternae; Functions: Receives transport vesicles with materials from ER, Modifies the materials, Sorts the materials, Add molecular tags, Packages materials into new transport vesicles that exit the membrane via exocytosis.
Cisternae
Separate sacs in the Golgi complex that are not connected.
Lysosomes
Membranous sac with hydrolytic enzymes; Function: Hydrolyzes macromolecules in animal cells.
Autophagy
Process by which lysosomes recycle their own cell's organic materials, allowing the cell to renew itself.
Peroxisomes
Similar to lysosomes; Membrane bound metabolic compartment that catalyze reactions producing H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide) and then break it down to water.
Vacuoles
Large vesicles that stem from the ER and Golgi; Selective in transport.
Food Vacuole
Formed via phagocytosis (cell eating) and then digested by lysosomes.
Contractile Vacuole
Maintains water levels in the cell.
Central Vacuole
Found in plants; Contains inorganic ions and water; Important for turgor pressure.
Albumin
An important protein in humans that functions primarily to regulate oncotic pressure of blood, important for the regulation of fluids in vessels of the body and tissue repair.
Hepatitis C
A virus that attacks the liver and can cause liver disease, linked to a reduction in albumin levels.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Organelle in liver cells most likely affected by hepatitis C, responsible for holding ribosomes that create proteins.
Insulin
A hormone synthesized by pancreatic cells in the endoplasmic reticulum; Patients with type 1 diabetes cannot produce insulin.
Insulin Production
Insulin would be produced after ribosomes attach to the rough endoplasmic reticulum and get processed as insulin, then sent to the golgi body in order to sort and package the insulin and ship it inside of vesicles to the plasma membrane via exocytosis.
Endosymbiont Theory
The theory that explains the similarities mitochondria and chloroplasts have to a prokaryote.
Prokaryotic Cell
A cell that became an endosymbiont (cell that lives in another cell) after being engulfed by an early eukaryotic cell.
Evidence of Endosymbiont Theory
Double membrane, ribosomes, circular DNA, capable of function on their own.
Mitochondria
Site of cellular respiration.
Outer Membrane of Mitochondria
Smooth.
Inner Membrane of Mitochondria
Has folds called cristae.
Intermembrane Space
Space between inner and outer membrane of mitochondria.
Mitochondrial Matrix
Enclosed by inner membrane; location for the Krebs cycle; contains enzymes that catalyze cellular respiration and produce ATP, mitochondrial DNA, and ribosomes.
Mitochondria and Metabolic Activity
The number of mitochondria in a cell correlates with metabolic activity; cells with high metabolic activity have more mitochondria.
Chloroplast
Specialized organelles in photosynthetic organisms; site of photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll
The green pigment contained in chloroplasts.
Thylakoids
Membranous sacs inside chloroplasts that can organize into stacks called grana; light dependent reactions occur in grana.
Stroma
Location for the Calvin cycle in chloroplasts; contains chloroplast DNA, ribosomes, and enzymes.
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers throughout the cytoplasm that gives structural support (especially for animal cells) and mechanical movement.
Functions of Cytoskeleton
Anchor organelles, allow for movement of vesicles and organelles and/or whole cell; movement occurs when the cytoskeleton interacts with motor proteins.
Microtubules
Grow from tubulin; assist in centrosome assembly; serve as structural support like train tracks for the movement of organelles interacting with motor proteins.
Functions of Microtubules
Assist in the separation of chromosomes during cell division; cell motility like cilia and flagella.
Microfilaments
Thin solid rods made of the protein actin.
Functions of Microfilaments
Maintain cell shape, bear tension, assist in muscle contraction and cell motility; actin works with myosin to cause contraction.
Intermediate Filaments
Fibrous proteins made up of varying subunits; permanent structural elements of the cell.
Functions of Intermediate Filaments
Maintain cell shape, anchor nucleus and organelles, form nuclear lamina, line nuclear envelope.