Electronegativity, pKa, and the Inductive Effect
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Definition of Electronegativity
A chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom to attract a shared pair of electrons (or electron density) towards itself
Electronegativity is determined by what?
Nuclear charge (more protons = more pull)
Number and location of electrons in atomic shells
How does electronegativity change across a periodic table?
Increases from left to right of the periodic table, and from bottom to top
F is the most electronegative
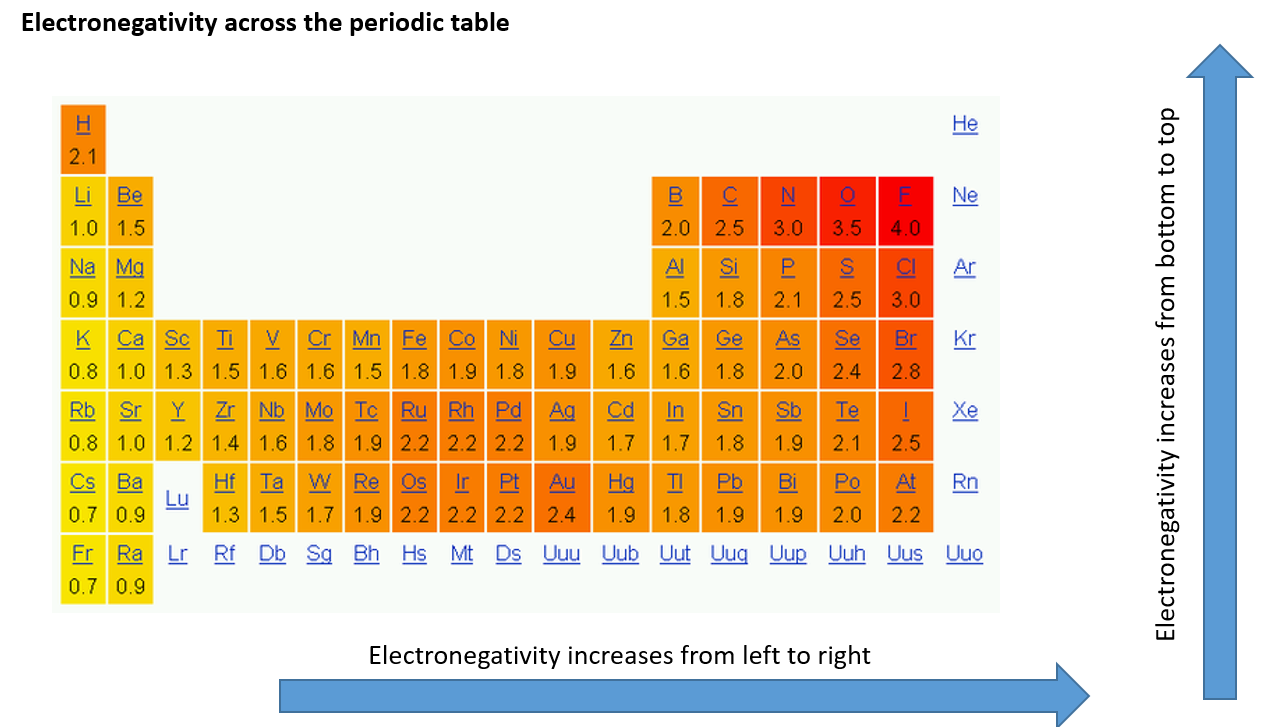
What explains the reduction in electronegativity when you descend a group?
There is extra shielding of the shells of electrons
What effect does electronegativity have on charge distribution of a molecule?
When there are difference in electronegativity, atoms will become slightly positive (δ+) and slightly negative (δ-)
This leads to induction and inductive effect
The stronger the electronegativity….
….the stronger the inductive effect
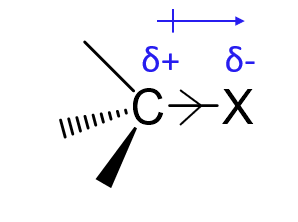
What is the inductive effect?
The permanent shifting of electron density along σ-bonds due to electronegativity differences.
What is a -I group?
An electron-withdrawing group that pulls electron density away through σ-bonds
X =
Br
Cl
NO2
OH
SH
SR
NH2
NHR
NR2
CN
COOH
CHO
C(O)R
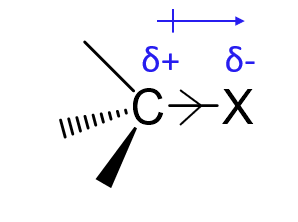
What is a +I group?
An electron-donating group that pushes electron density through σ-bonds (e.g. alkyl groups, metals).
X =
R (alkyl or aryl)
Metals (e.g. Li, Mg)
How does distance affect the inductive effect?
The inductive effect decreases rapidly as distance from the substituent increases.
What does pKa measure?
Acid strength.
Lower pKa = stronger acid = more willing to donate H⁺.
How do electron-withdrawing groups affect pKa of acids?
They stabilise the conjugate base → lower the pKa → increase acidity.
How do electron-donating groups (EDG) affect pKa of acids?
They destabilise the conjugate base
Raise the pKa
Decrease acidity.
What’s the pKa of carboxylic acid?
≈ 5
What’s the pKa of phenol?
≈ 10
What’s the pKa of alcohol?
≈ 15
Why does phenol have a lower pKa than alcohol?
Phenol is more acidic than alcohols because its conjugate base (phenoxide) is resonance stabilised, whereas alkoxides have a localised negative charge and are destabilised by +I alkyl groups.
What is resonance?
The delocalisation of electrons over several atoms, represented by multiple canonical forms.
Why does resonance stabilise molecules/ions?
Because charge is spread over a larger area, lowering energy and increasing stability.
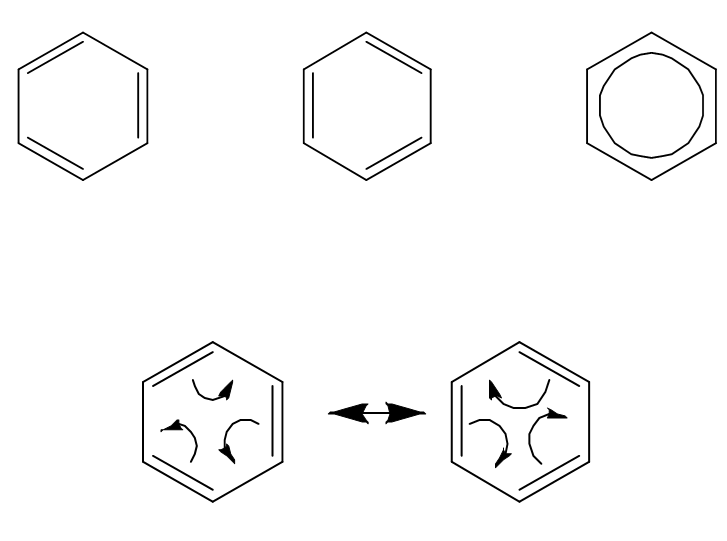
Why are benzene bonds all the same length?
Because π electrons are delocalised over the ring (true structure is a resonance hybrid).
Carboxylate resonance forms
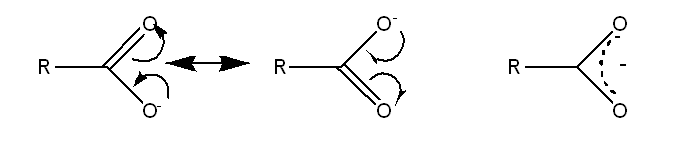
Why are resonance forms useful?
Resonance forms are useful for showing electron movement and reactivity, even though none is fully correct.
Curly arrows are used to show the movement of bond electrons between resonance forms.
Definition of the Mesomeric effect
Electron donation or withdrawal through resonance involving π systems and lone pairs.
Double bond adjacent to a lone pair of electrons
+M
When electron density is pushed into the π-bond (orbital).
-M
Where a π-orbital overlaps with an adjacent p-orbital that is low in electron density.
How do +M groups affect phenol acidity?
They destabilise the phenoxide ion → increase pKa → make phenol less acidic.
How do –M groups affect phenol acidity?
They stabilise the phenoxide ion → decrease pKa → make phenol more acidic.
What does pKa mean for bases?
It refers to the protonated form of the base; higher pKa = stronger base.
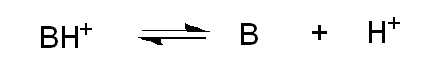
What happens when pH = pKa for a base?
About 50% of the base is protonated.
Why are alkyl amines more basic than ammonia?
Alkyl groups donate electron density (+I), making nitrogen more able to accept H⁺.

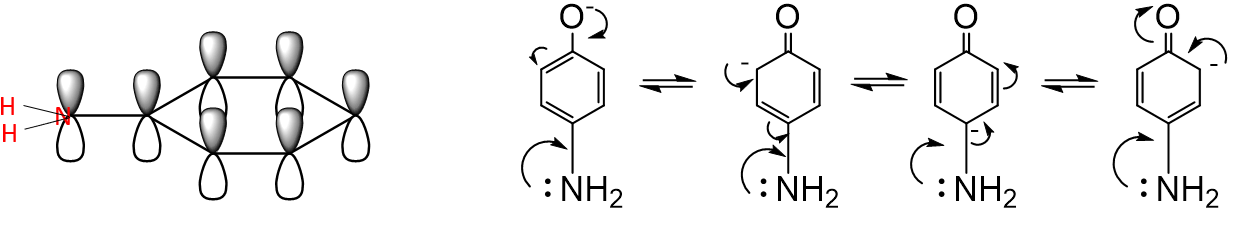
Why is phenylamine much less basic than cyclohexylamine?
The lone pair in phenylamine is delocalised into the aromatic ring, reducing availability to bind H⁺.
Why is pyrrole very weakly basic?
Its lone pair is part of the aromatic system and cannot accept a proton.
Why are amides extremely weak bases?
The lone pair on nitrogen is delocalised into the carbonyl group by resonance.
Why are carbonyl groups polar?
Oxygen is more electronegative than carbon, giving O δ⁻ and C δ⁺.
How do substituents affect carbonyl reactivity?
Electron-withdrawing groups increase δ⁺ on carbon → more reactive
Electron-donating groups decrease δ⁺ → less reactive