Proactive + Retroactive Interference
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
2 Types of Interference
What is interference
Proactive Interference
Older memory interferes with newer
Retroactive Interference
New memory prevents recall of older memory
One memory in LTM preventing retrieval of another in the LTM
Schmidt et al (2000) research supporting retroactive interference
What did he find
- Gave 211 participants aged 11 to 79 a questionnaire map and told to try name all the street names of their neighbourhood
- Gathered other info such as times moved house and how long lived there
- Amount of retroactive interference was assessed by number of times the individual had moved
Found positive association with amount of times moved and number of street names forgotten
Supports that Retroactive interference can explain forgetting in real life situations
When is interference strongest
Which research shows this
When memories are Similar
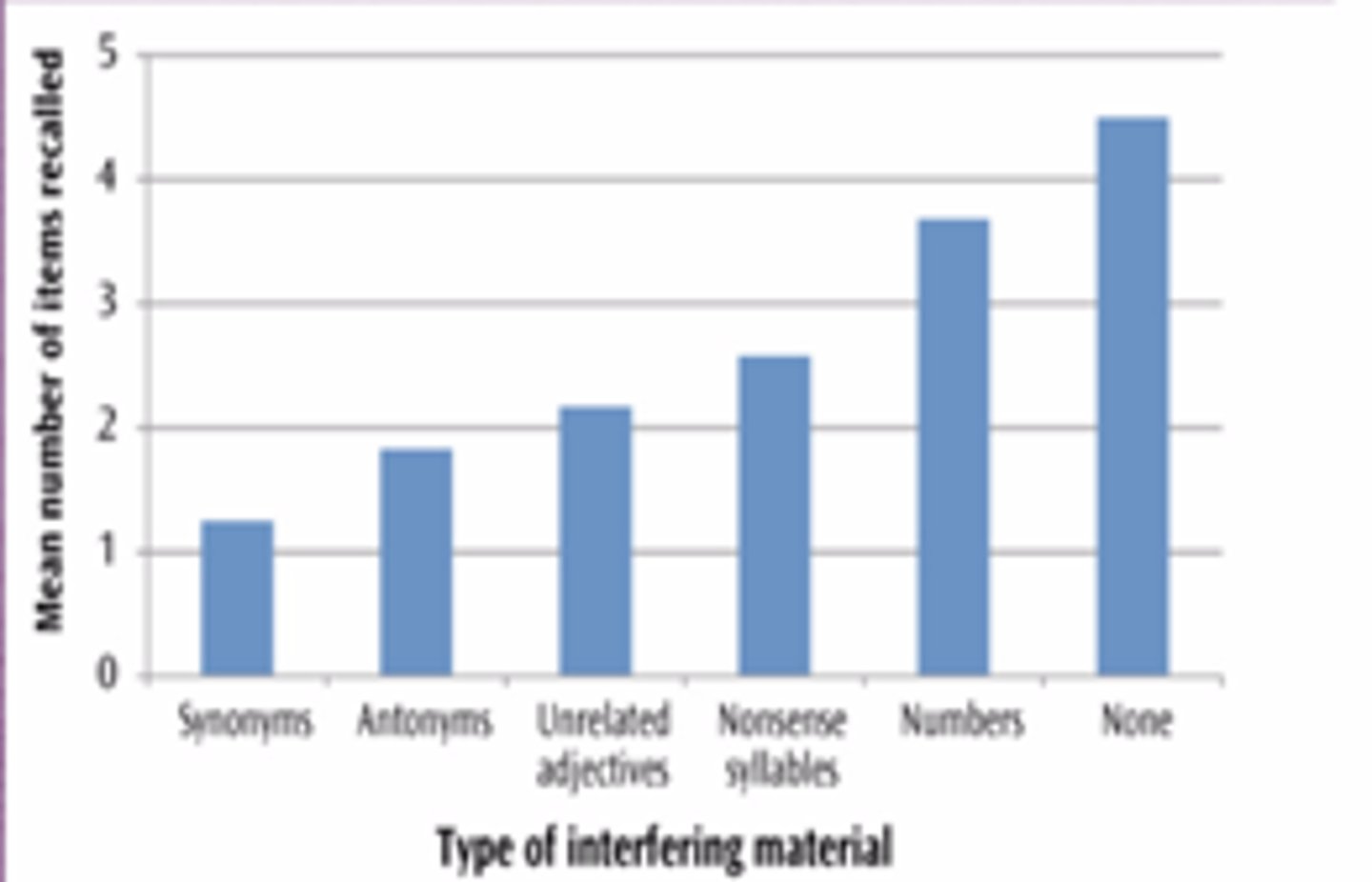
Mcgeoch and McDonald (1931)
- 6 groups of Participants learnt a list of 10 words until they could recall with 100% accuracy
- Each group then learnt a new list of words
Group 1: Synonyms
Group 2: Antonyms
Group 3: Words unrelated to the original ones
Group 4: Nonsense syllables
Group 5: Three digit numbers
Group 6: No new list learnt (Control condition)
Recall was worst where words from the new list were synonyms to the old group
Shows interference is strongest where memories are similar
Strength of interference theory
- Can explain individual differences in forgetting
- Based on amount and similarity of information learnt
- For example Schmidt et al study where he found a posistive correlation between amount of times moved and number of street names forgotten
- Likely due to those people learning alot of street names from moving in the past leading to proactive interference to new street names
- Therefore increasing its validity
Scientific strength of interference theory
- Meets Scientific Criteria
- Has been developed using the scientific process of theory construction
- Claims of the theory have been tested by gathering empirical evidence
- e.g. Schmidt's research which demonstrated Retroactive Interference in a real life situation
- Therefore having scientific credibility led to increased research in this area in the past, leading to our modern understanding of memory systems