Basic Structure of Human Eye - VORBV (Week 4)
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
radius of curvature of front corneal surface
r1= +7.7mm
radius of curvature of back corneal surface
r2= +6.8mm
corneal thickness
0.5mm
corneal diameter
12mm
refractive index of cornea
1.376
refractive index of aqueous
1.336
as light travels through the system, it is refracted by the back surface of the cornea into?
the anterior chamber
what is the anterior chamber made up of
aqueous humour
what is the depth of anterior chamber
3mm
power of front surface of cornea
1.376 take away 1
power of back surface cornea
1.336 take away 1.376
diameter of pupil can vary in sizes between
1-8mm
what is the purpose of the pupil
control the amount of brightness and the optical quality of light entering eye
pupil size in dark
5-8mmp
pupil size in light
2-5mm
consensual pupil response
shining a light in one eye causes the other eye to have a response
when is pupil size also reduced
looking at something close up
name 2 clinical conditions that may affect pupil size
ocular drugs (mydriatic and miotic eye drops) and emotions
what does the crystalline lens provide a mechanism for
focusing at different distances
presbyopia
lens no longer able to produce accommodation
diameter of crystalline lens
9mm
radius of anterior surface of crystalline lens
+10mm
radius of posterior surface of crystalline lens
-6mm
thickness of crystalline lens
3.6mm
refractive media of crystalline lens
1.416
definition of accomodation
increase in power of crystalline lens that occurs to allow focus of the eye to change
what age does accommodation become less flexible
40
what does accommodates mean
when the eye alters its power
what is an increase in power known as
positive accomodation
what is a decrease in power known as
negative accommodation
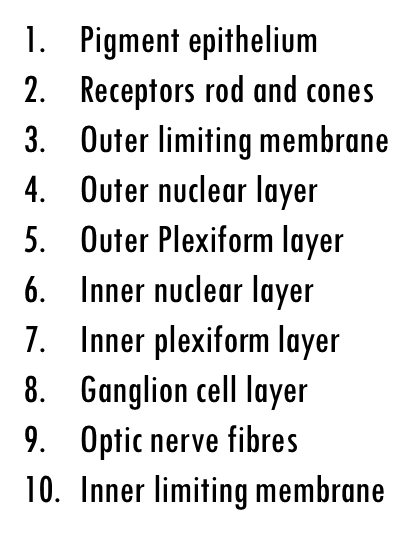
how many layers is the retina divided into
10
name the retina layers
1.Pigment epithelium
2.Receptors rod and cones
3.Outer limiting membrane
4.Outer nuclear layer
5.Outer Plexiform layer
6.Inner nuclear layer
7.Inner plexiform layer
8.Ganglion cell layer
9.Optic nerve fibres
10.Inner limiting membrane
what does the energy contained in light that is incident on the retina intitiate?
chemical reaction in the retinal receptors (rods and cones) generating a neural discharge which is then passed to the brain
name the 2 photoreceptors on the retina
rods and cones
are rods and cones evenly distributed
no
central retina (fovea)
high retinal resolution densely packed cones
surrounding retina
larger more spread out cones and rods; lower retina resolution
what pattern does the central retina have
honeycomb, hexagonal shape
what are cones responsible for
vision in high ranges of luminance and for colour vision
what is the fovea
centre of macula
describe the distribution of cones in the fovea
higher
does the fovea contain rods
no, rod free
the foveolar is entirely ?
rod free (blind spot)
what do rods provide
achromatic vision in low levels of illimitation (scotopic vision)
how many types of colour sensitive photopigments are there in cones
3
how do cones respond
respond with maximum sensitivities in the blue, green and red regions
what are cones most sensitive do
yellow to green (555nm)
what are rods most sensitive to
blue/green (500nm)
what is dark adaptation
coming from a brightly lit environment to a dark environment
describe pupils change when there is a small change of light levels in eye
adjust quickly
what adaptations occur gradually for larger changes in brightness
biochemical and neural
how long does it take for cones to adapt in dark adaptations
7-10 min
how long does it take for rods to adapt in dark adaptations
20-30 min
what is the photopigment that rods contain called
rhodopsin
describe the colour change that rhodopsin gives
purple, orange, yellow, colourlessa
absorption of light causes rhodopsin (purple) to become?
bleached (transparent)
a bleached molecule will spontaneously revert back to?
unbleached state
is cone or rods dark adaptation faster?
cone
what do cones have outer segments of
3 classes of photopigments that bleach when exposed to light (blue, red, green)
refractive index of cornea
1.376
power of reduced eye formula
(n’-n)/r