Ovaries: Embrology and Anatomy
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
How many times do women OVULATE during their REPRODUCTIVE years?
400 times
There is a _____ million follicules that are STIMULATED during a women’s reproductive years.
¼
There are over how many differenet ovarian pathologies?
100+
The tech’s PRIMARY role is determine what?
The need for surgical/medical intervention.
The ovaries are developed from what type of ducts?
Wolffian and Mesonephros
The ovaries begin in the _________ region near the _________.
Lumbar; kidneys
The ovaries gradually desends into the ______ region as it enlargens to accommodate them.
Pelvic
The ovaries consists of 2 parts, what are they?
Cortex and the medulla
What is the OUTER part of the ovaries called? What is another name for it?
Cortex; tunica
What is the INNER part of the ovaries called? What is another name for it?
Medulla; stroma
What does the CORTEX layer of the ovaries contain?
Ovarian follicles and corpus lutea
Fibrous capsule called the tunica albuginea
What does the MEDULLA layer of the ovaries contain?
Blood vessels, mainly veins and fibrous tissue
The ovaires are paired, __________-shaped structures situated on each side of the uterus close to the _________ pelvic wall.
Almond; lateral
The ovaries can vary in POSITION, due to what?
Uterus size, postion, and location
Location of ligament attachements
True or False.
Pregnancies might have huge fibroids that push the ovaries out.
True
Crainocaudad axes are parallel to _____ _______ vessels and are _________; these serve as a reference point.
Interal iliac; posterior
In the anteflexed midline uterus, the ovaries are usually ___________ and __________.
Laterally; posterolaterally
When the uterus lies on ONE side of the midline, the ipsilateral ovary often lies ________ to the uterus fundus.
Superior
In a retroverted uterus, the ovaries tend to be _________ and ___________, near the uterine fundus.
Lateral; superior
When the uterus is ENLARGED, the ovaries tend to be displaced more ________ and ________.
Superiorly; laterally
Following hysterectomy, the ovaries tend to be located more __________ and directly _________ to the vagina cuff.
Medially; superior
Why could the corpus luteum be diffcult to find?
It can appear isoechoic.
What should you find during the 1st trimester of pregnancy?
Corpus luteum
If someone has a repeated loss of pregnancy; if the __________ _________ is NOT producing enough of those hormones it could be the cause of repeated loss of pregnancy.
Corpus luteum
When you are scanning the ovaries, what are you looking for?
Correlation with the cycle
Correlation with pregnancy
Masses
Blood flow
What are the arrows pointing to?
What does it usually measure?
Is it indiciative of disease?
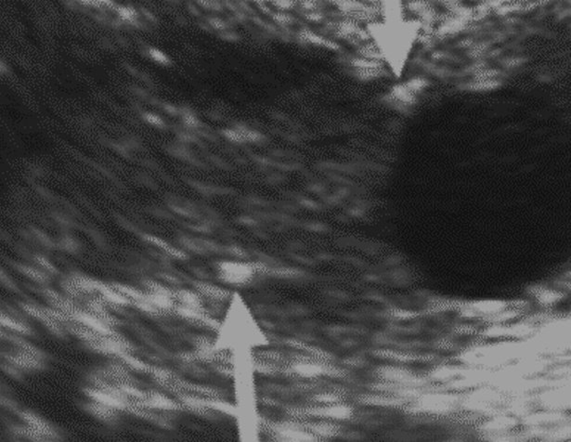
Pucture echogenic
1-2 mm; peripheral
No
How do you measure the ovaries?
The long axis of the ovaries
Because of the the variablity in ovarian shape and size what is the BEST method for determining the overall ovarian size?
Volume measurement
What is the volume measurement formula for ovaries?
L x W x H x 0.523
In a menstruating adult female, a NORMAL ovary may have a volume as large as what? What is the mean?
22 mL with a mean of 8.8 mL (cm3)
An ovarain volume of MORE than 8mL is definitely considered ABNORMAL for ____________ patients.
Postmenopausal
An ovarain volume more than DOUBLE that of the oppositie side should be considered what?
Abnormal
It is RARELY done, by what provides the MOST accurate method of ovarian volume measurement?
3D
Depending on your patient and the location of the ovaries, it should be releatively ______ resistent if this is an ACTIVE ovary (it NEEDS blood flow).
Low
The ovaries will become ________ resistent if it’s NOT active it does NOT need as much blood flow.
Higher
Following menopause, the ovary _______ and the follices ______ with _________ age. These factors make the ovaries in POSTmenopausal women _________ to visualize.
Atrophies; disappear; increasing; difficult
Stationary loop of bowel may MIMIC what? What should you look for?
Small shrunken ovary
Look for peristalsis (in bowel)
True or False
An OLDER patient with LARGER ovaries is NORMAL, it should INCREASE in size with age.
False; its abnormal and should DECREASE in size with age.
True or False
POSTmenopausal have LITTLE to no follices.
True
The NORMAL ovary has a ____________ echotexture, exhibiting a CENTRAL, more ___________ medulla.
Small ANECHOIC or CYSTIC ______ may be seen peripherally in the cortex.
Homogenous; echogenic
Follicles
The appearence of the ovary varies with what?
Age and menstrual cycle