Lacrimal system II: Management of DED
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What are the 4 steps in optometric management of dry eye disease?
1) Patient education and management
2) Modify risk factors
3) Basic treatment
4) Advanced therapy
how would you help patients in understanding DED?
> let them know the cause of DED + associated factors
> recognise symptoms + factors that may exacerbate symptoms ( air con, meds)
> chronic + fluctuating nature of DED
how would you educate patients and help them understand treatment options?
> let them know how and why treatment works (or don’t)
> let them know when to use different therapies
how can you ensure empathy + shared decisions making with patients?
> build trust
> informed choice
> co-operation
why does dry eye require tailored management (individual)?
> patients experience variable symptoms (burning, pain , blurriness)
> variable correlation between symptoms + signs —> sometimes poor correlation
> variable risk factors and causes —> MGD, medication , age etc
why would digital tools or apps be beneficial for patients with DED?
> can track symptoms
> support communication
Name 3 steps in modifying risk factors for DED?
Treat any underlying conditions as they could cause DED —> blepharitis, MGD , ectropion etc
Topical medications → drops may have additive effect, exacerbating symptoms so consider preservative- free options
→ ask if they’ve tried drops before + if it worked
Contact lens wear → limit CL use esp if irritation + switch to glasses when possible
what other factors could help to modify risk factors of DED?
environmental modifications → avoid dry, dusty environments + consider using humidifier to add moisture to air
screen time → take break from devices
20/20/20 rule etc
Blink awareness → be mindful of blinking frequency , esp during digital device use (reduced blink rate)
dietary changes → incorporate omega 3 as may help improve tear production
drink more water → Hydration
When and why should a multidisciplinary approach be considered in dry eye disease (DED) management?
usually in more severe cases
consider impact of associated systemic conditions as they may worsen DED e.g thyroid dysfunction, diabetes, psoriasis
can medications be implemented or modified → GP
consider impact of DED
- neuropathy + neuropathic pain
- anxiety , depression
consider if multidisciplinary approach would benefit this patient
What is the basic treatment of Dry Eye Disease?
Eyelid hygiene:
✓ warm compress
✓ massage
✓ clean
—> can help relieve symptoms esp for those with MGD
Ocular lubricants:
drops and gels
preservative free
> dietary modifications → omega 3
modify local environment → car heater etc
digital device use

what advanced therapy is available to help with tear conservation?
Punctual occlusion (plastic plug)
moisture chamber spectacles/goggles (expensive)
what are overnight treatments for DED?
ointment
moisture chamber devices

what advanced therapy is there for MGD treatment?
Meibomian gland expression
intense pulsed light therapy
what prescription drugs can be given for DED?
topical steroid course - apply to lid margin for anterior blepharitis
oral tetracycline antibiotics
what is the secondary care of management of dry eye disease?
oral secretagogues → increase tear production
autologous/allogenic serum eye drops
soft bandage CL or rigid scleral CL filled with CL fluid
surgical punctual occlusion
other surgical approaches :
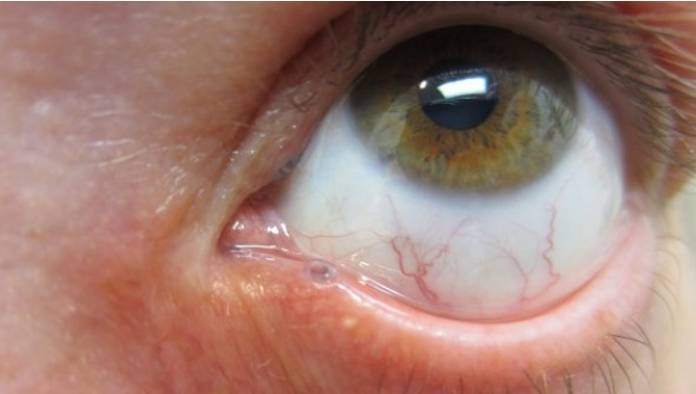
- Tarsorrhaphy
- salivary gland transplantation
what are the 3 factors in formulation for ocular lubricants?
osmolarity
viscosity
preservatives
What is tear film osmolarity and why is elevated osmolarity important in dry eye disease?
refers to particles in solution
> elevated tear film osmolarity causes morphological + biochemical changes to corneal + conjunctival epithelium and is pro inflammatory
> reduction in tear osmolarity level reduces stress of tear film
why is viscosity important when formulating ocular lubricants?
> patients compliance, comfort and convenience are important considerations
> so a range of tear substitute formulations with varying viscosities are needed
why are preservatives considered in the formulation of ocular lubricants?
> elimination of preservatives important for dry eye
How do ocular lubricants affect tear osmolarity, and what components help regulate tear pH and tonicity?
increased osmolarity factor in dry eye aetiology
normal osmolarity - mean 302.2 osmoles
HYPOTONIC products act to reduce osmolarity of tears
reduce salt levels
aid to repair conjunctiva goblet cells
hyaluronic acid —> maintained for over 2 hours , return to starting point after 3
> Buffer → regulates pH e.g Borate, Bicarbonate, phosphate
> Saline→ to regulate tonicity 0.9% NaCl
what is viscosity?
measurement of a fluids internal resistance to flow
measured using centipoise scale - cps
how sticky it is
e.g
water —> 1cps, milk→ 3 cps and motor oil→ 85-140cps
what are the benefits of more viscous ocular lubricants and give examples of agents?
increased retention time - stays longer on eye
reduce friction
sooth irritated membranes
Viscosity agents:
Carbomers
hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose , carmellose , polyvinyl alcohol , hydroxypropyl-guar
give examples of the viscosity of ocular lubricants
Blink contacts → 5.5 cps
Blink intensive Tear → 12.2 cps
Thera tears liquid gel —> 40 cps
blink intensive tears plus → 50cps

what is the purpose of preservatives in ocular lubricants?
preservative → maintain sterility
e.g benzalkonium chloride , cetrimide , EDTA
what are the consequences of preservatives in ocular lubricants?
ocular surface inflammation in dry eye exacerbated by preservatives
—> removing key element in managing dry eye
Benzalkonium chloride (BAK) cause epithelial toxic effects based on dose + tear film
BAK toxic to corneal epithelium , causing erosion → punctate staining
detergent properties , preservs destabilise tear film by dissolving lipid layer
increase of evaporation leads to ocular dryness
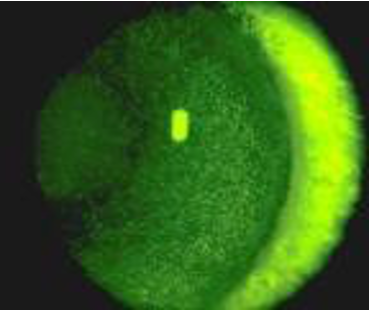
what symptoms could patients with punctate corneal staining experience ?
> feels uncomfortable
> blurs vision
> makes eye more prone to infections
What are minims?
single or unit dose
1 of them and then throw away
preservative free (as only use once)

what are multidose drops?
multidose → bottles
preserved
preservative -free

what are smart preservatives?
oxidative preservatives
break down into natural tear components when exposed to LIGHT

give examples of eye drops?
sodium Hyaluronate
Hypermellose
Carbomers
Carmellose
Polyvinyl alcholol
hydroxypropyl guar
Blink intensive tears
Thera tears
examples of ointments?
Liquid paraffin
Xailin night
VitA-POS
Mild aqueous insufficiency aims?
increase vol of tears
maintain lubrication
Hycosan , Blink
Moderate aqueous isnufficiency aims?
Maintain lubrication
increase contact time → higher viscosity
Thera Tears
Evaporative → lipid instability aims
recreate or rebuild
stabilise lipid layer
lipid containing eye drops → NOT with CL
Liposamal spray
spray on closed eye
OK with makeup + CLs
Evaporative → mucin deficiency aims?
stabilise mucin layer
bind to epithelial cells to protect them as a mucomimetic
improve electrolyte balance
promote healing of goblet cells
e.g systane
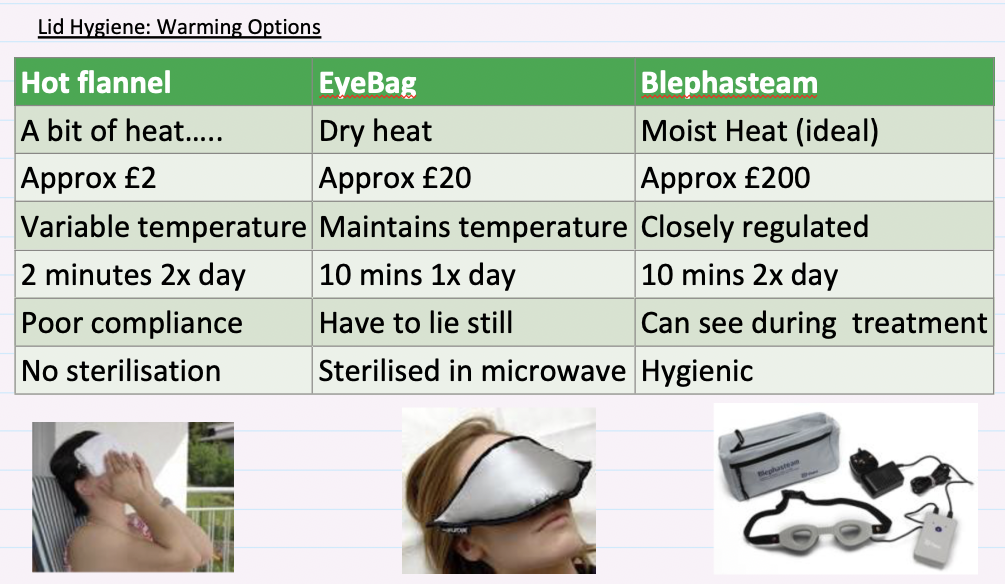
What are the warming options for lid hygiene?
when to do a lid hygiene massage?
after warm compress
use index finger and apply gentle downward pressure along eyelid moving from inner corner to outer corner then towards lashes
what are the benefits of nutritional supplements?
Stimulate tear secretion
encourage thinner more fluid lipid to be secreted
decrease apoptosis goblet cells
decrease inflammation
help suppress meibomitis
When should you refer a person with suspected DED?
Same day if red flag symptoms → sudden vision loss, pain or diplopia
urgent if → Steven-johnsosn syndrome , dry mouth , adhesions between conjunctiva
referral → abnormal lid anatomy or function, suspected underlying condition esp if child