IMED1002 - Chromosomes
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Chromosome abbreviation
Chr
Fundemental Roles of Chromosomes (NOT NEEDED TO KNOW DETAIL, JUST NAME)
- Faithful transmission of genetic information: this is achieved by high fidelity DNA replication, chromosome replication, correct segregation of chromosomes and histone protein code retention
- Appropriate expression of genetic information: different sections of DNA are accessed in different cell types
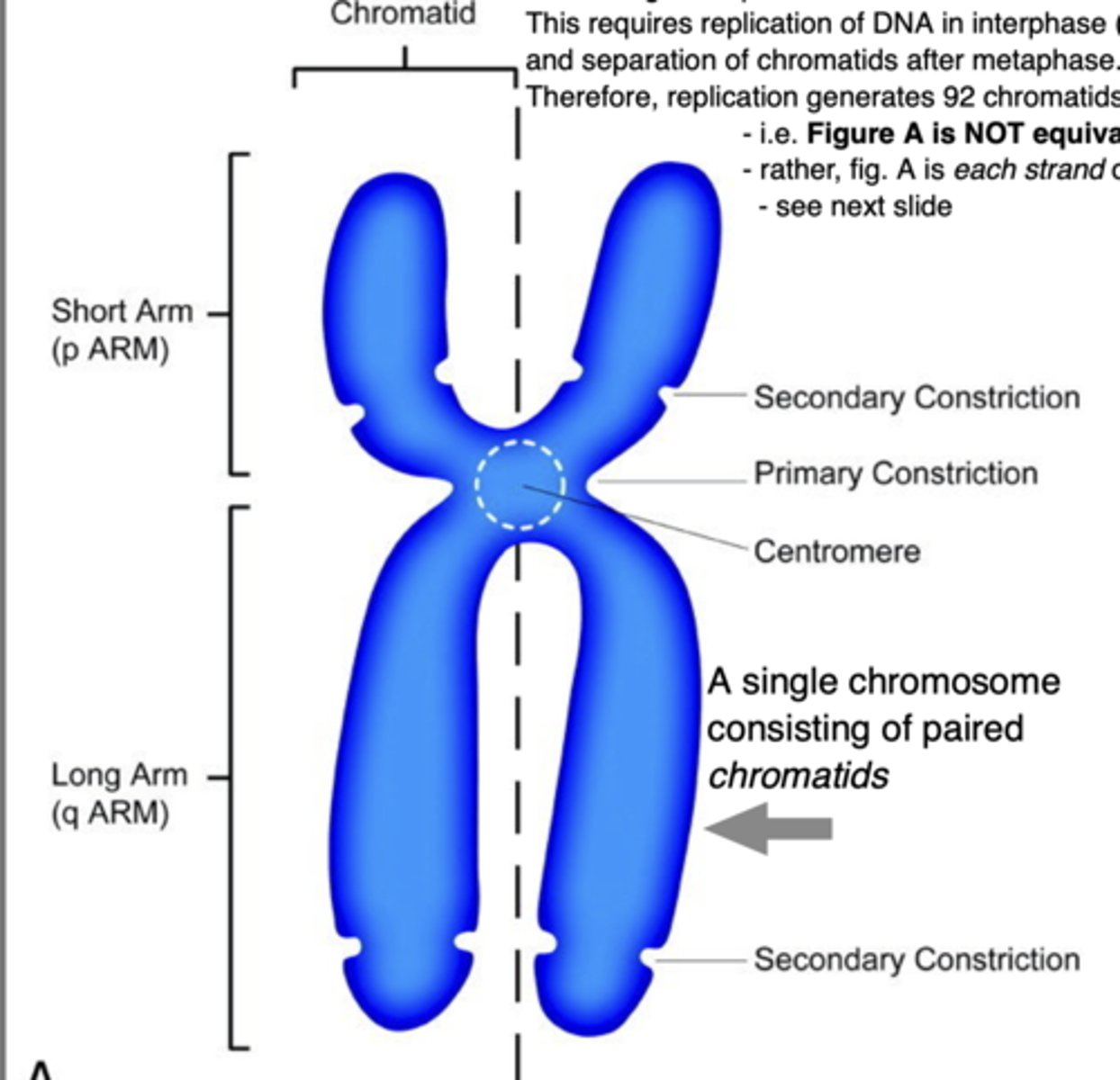
Chromosomes consist of:
- single molecule of DNA (two strands)
- various proteins that bind and package DNA into nucleus
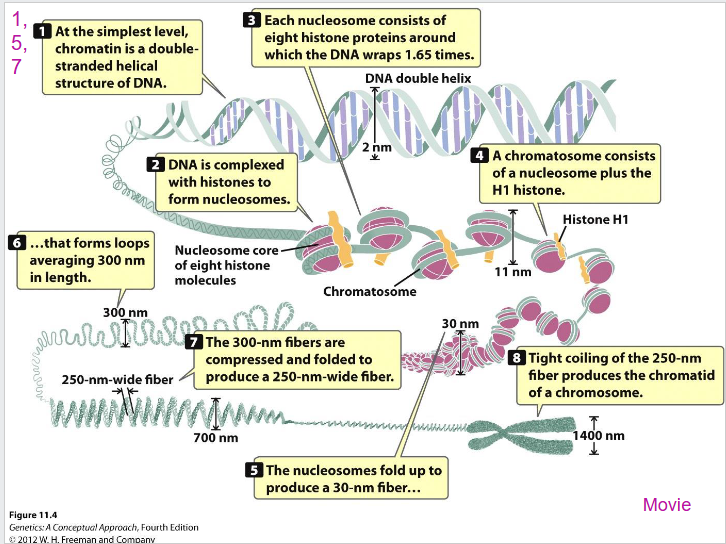
Chromatin
- combination of DNA and protein.
- when a cell divides ('M' phase) the chromatin is highly condensed into visible chromosomes
- following replication, each chromosome is held together as sister chromatids = two halves of a chromosome joined at the centromere
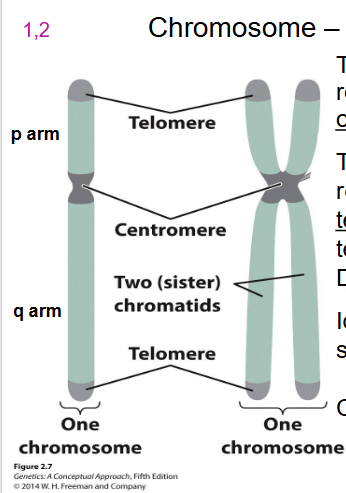
Centromere
Area where the sister chromatids of a chromosome are attached. Used to count number of chromosomes. So even if the chromatid has one chromatid its still a chromosome.
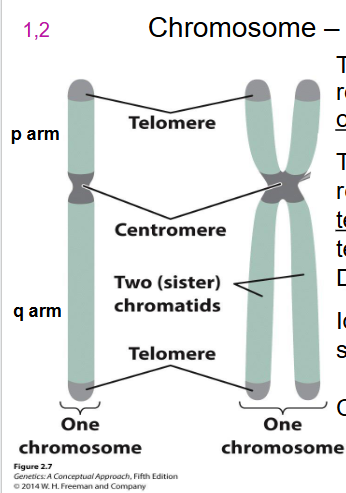
Telomeres
DNA at the tips of chromosomes. Functional chromosomes has telomeres at both ends of each DNA molecule
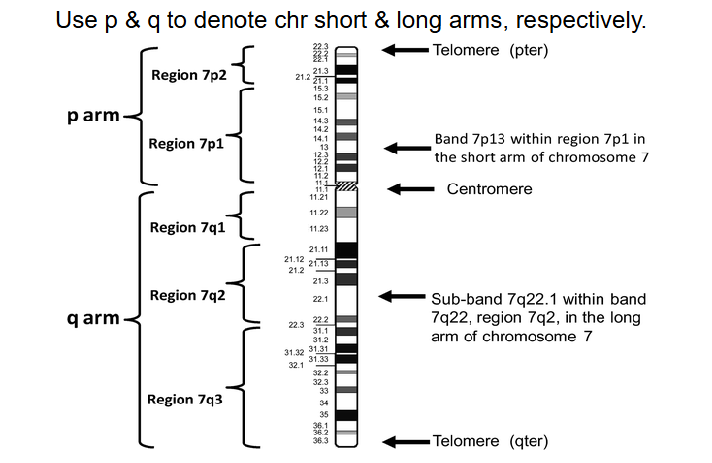
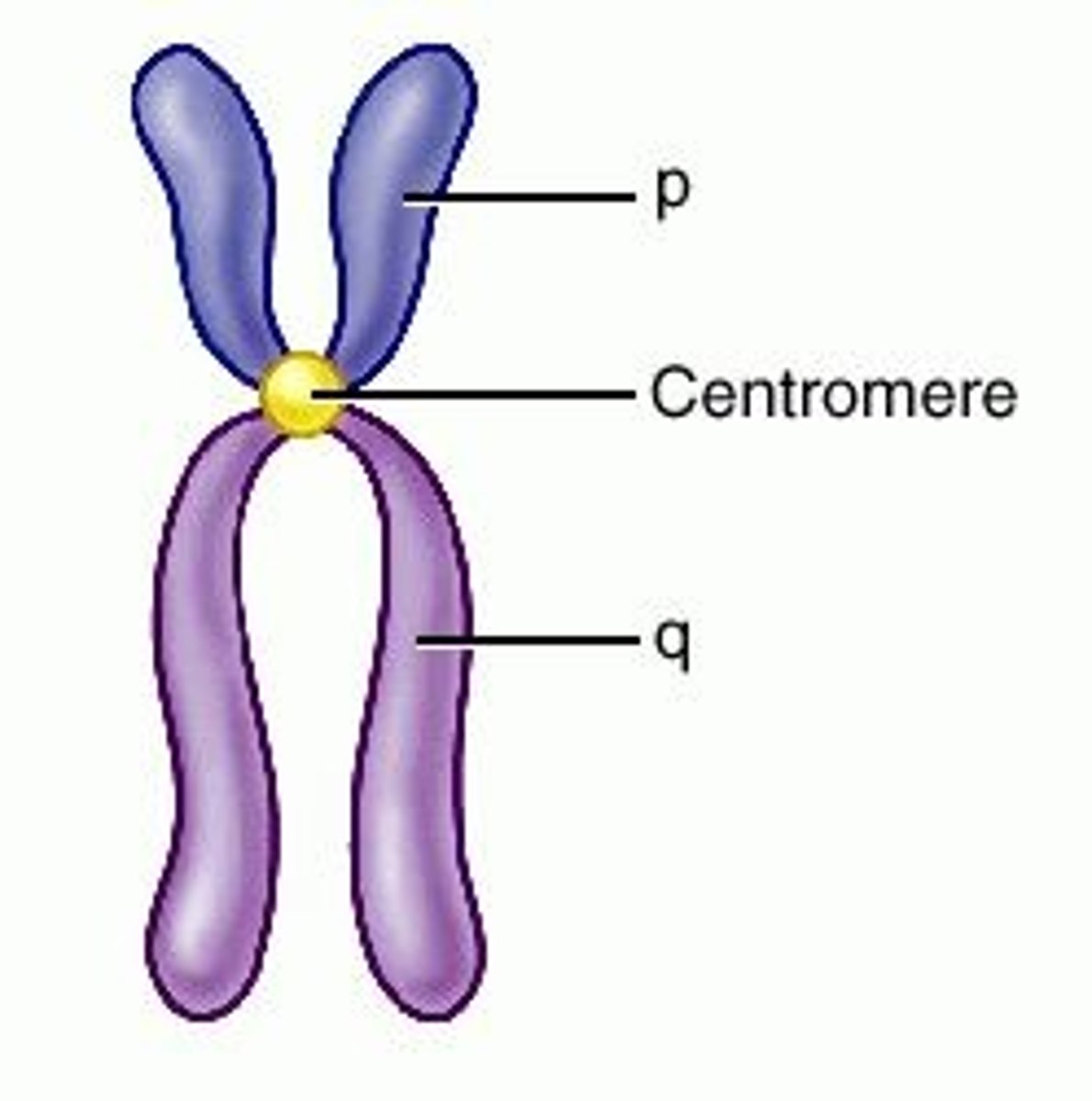
designation of chromosome arms
- p (short arm) (think of p for petit)
- q (longer arm) idk what to think for this
Chromosome Nomenclature Conventions
- Assigns numbers 1 through 22 to autosomes, according to perceived size when supercondensed.
- Sex chromosomes = X and Y
- Humans have 22 pairs of autosomes, plus 2 sex chr = 46 chr in total
- Chr differ in size as have different number of nt pairs
Why chromosomes are different
- at moelcular level:
- Each chromosome has very different nt sequence and hence different genes. Centromere position varies too
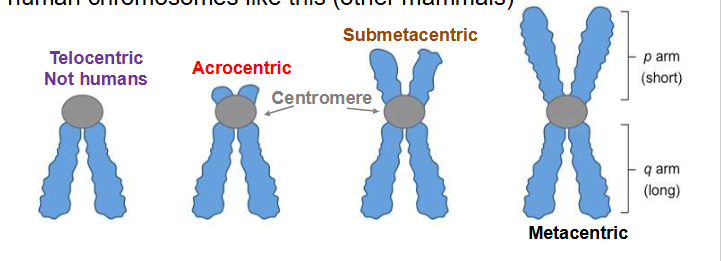
Chromosome Centromere position (NAMING ONLY)
- Metacentric
- Submetacentric
- Acrocentric
- Telocentric
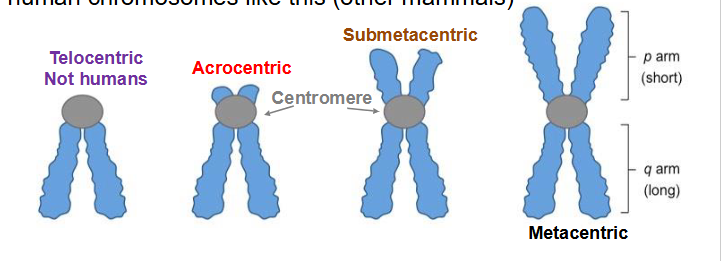
Metacentric
centromere in the centre, with both arms approximately equal length
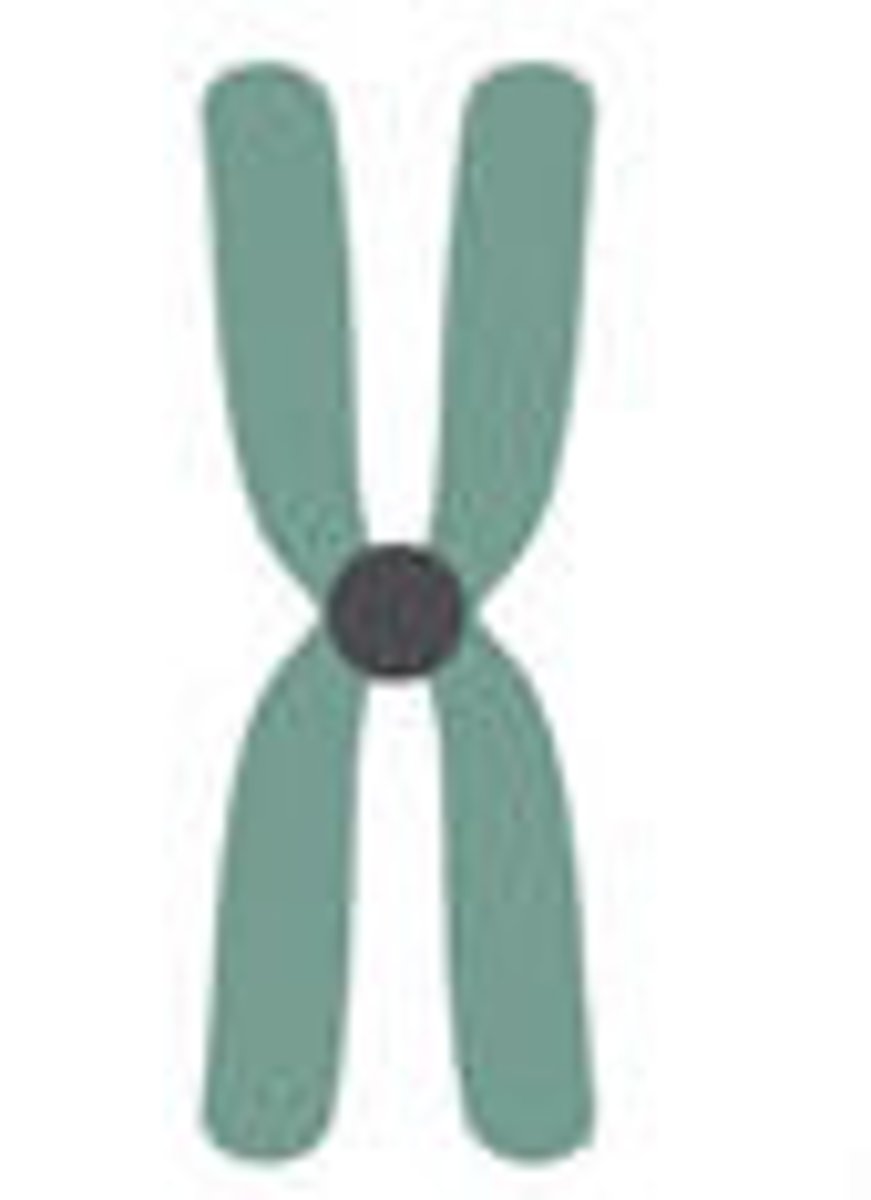

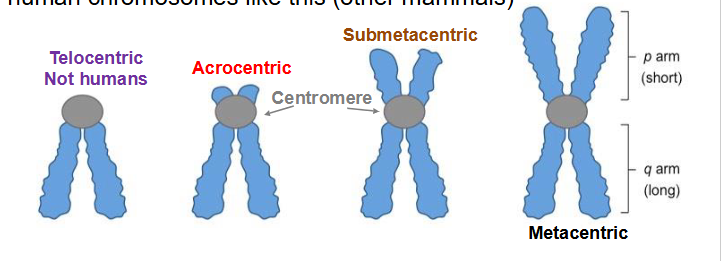
Submetacentric
centromere slightly offset from centre, leading to slight asymmetry between arms
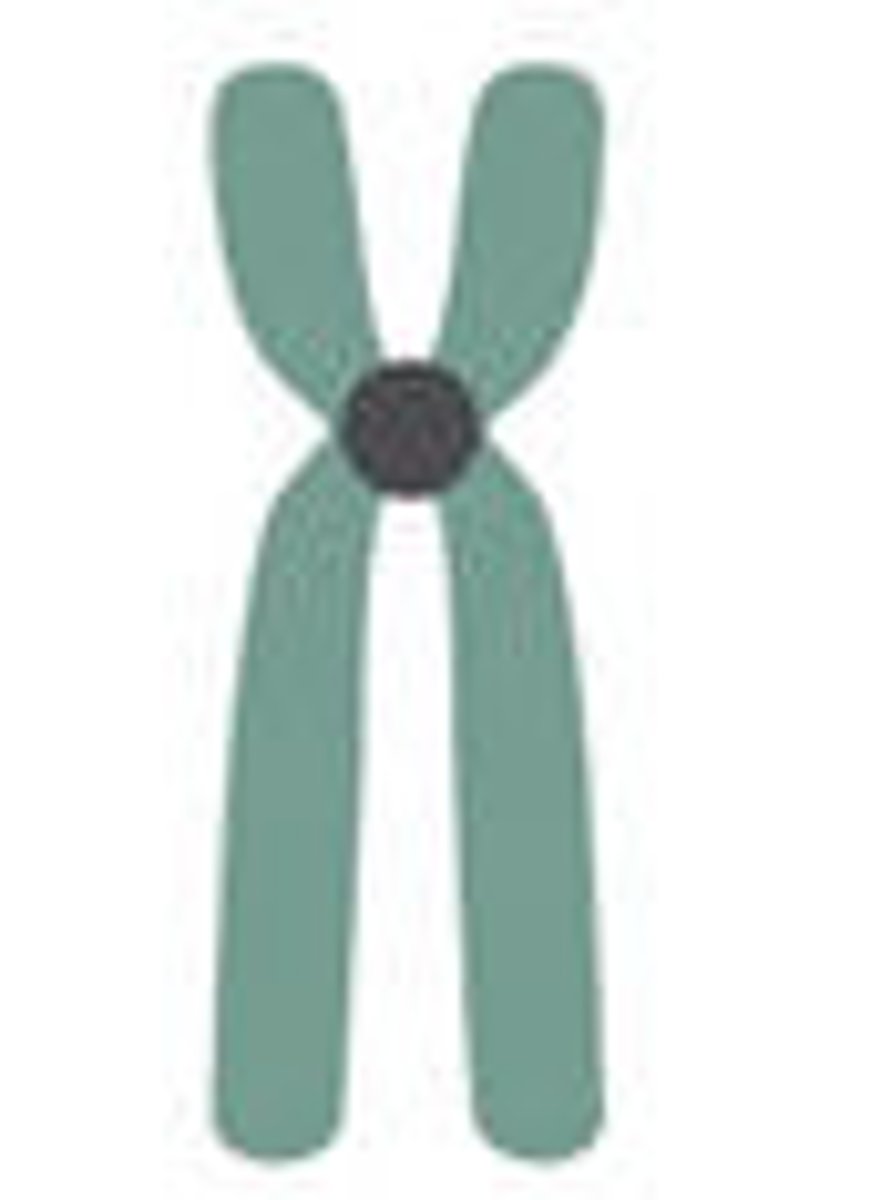

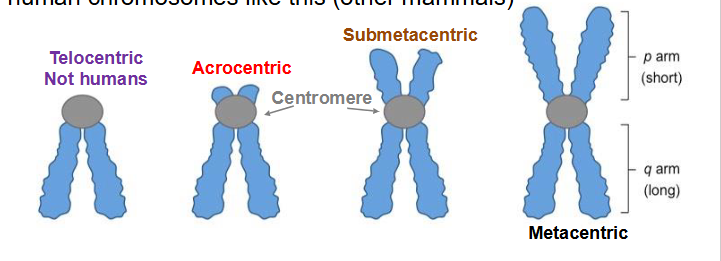
Acrocentric
centromere severely offset from centre, leading to one very long and one very short arm
- this is why these are more susceptible to genetic disorder because its unfavourable during cell division
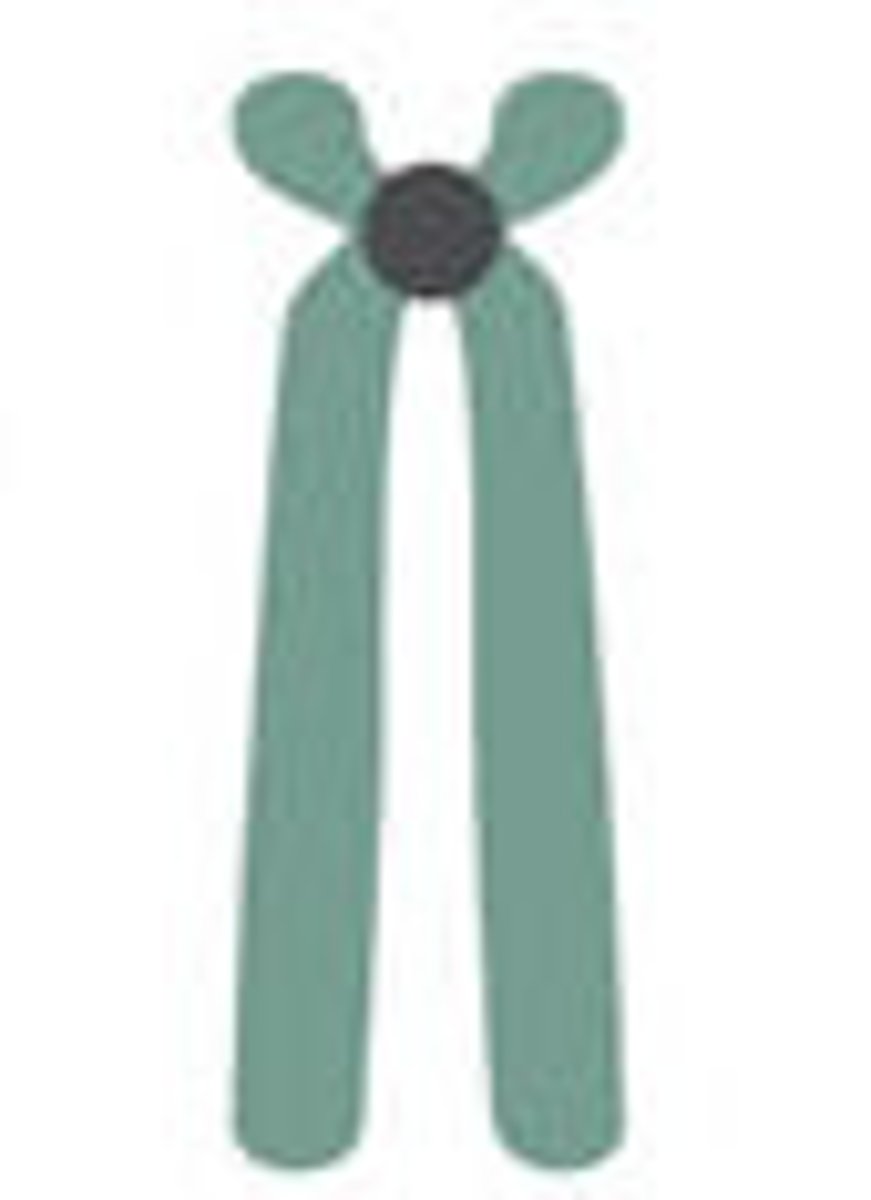

Telocentric
centromere at the very end of the chromosome. No human chromosome like this

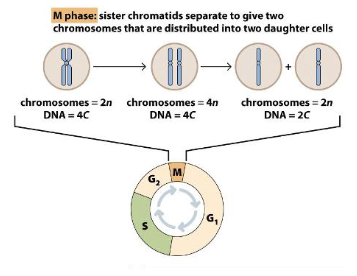
Chromosome and DNA content is defined by:
- number (n) of different chromosomes (chr set)
- associated DNA content (c)
Ploidy
number of sets of chromosomes in a cell
Haploid
An organism or cell having only one complete set of chromosomes. e.g sperm and egg cells
- e.g has n chromosomes, "c" DNA content
Diploid
2 sets of chromosomes. e.g most human cells
- has 2n chromosomes (46), has a DNA content of 2C
Chromosome Availability
- during metaphase chromatids are connected and condensed, can be seen under light microscope as tightly packed = DNA inaccessible so no gene expression
- hence for most of the cell cycle (interphase), chromosomes are highly extended and accessible chromatin
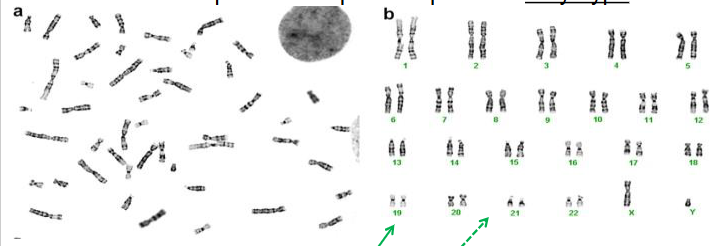
Karyotype
the number and visual appearance of the chromosomes in the cell nuclei of an organism or species.
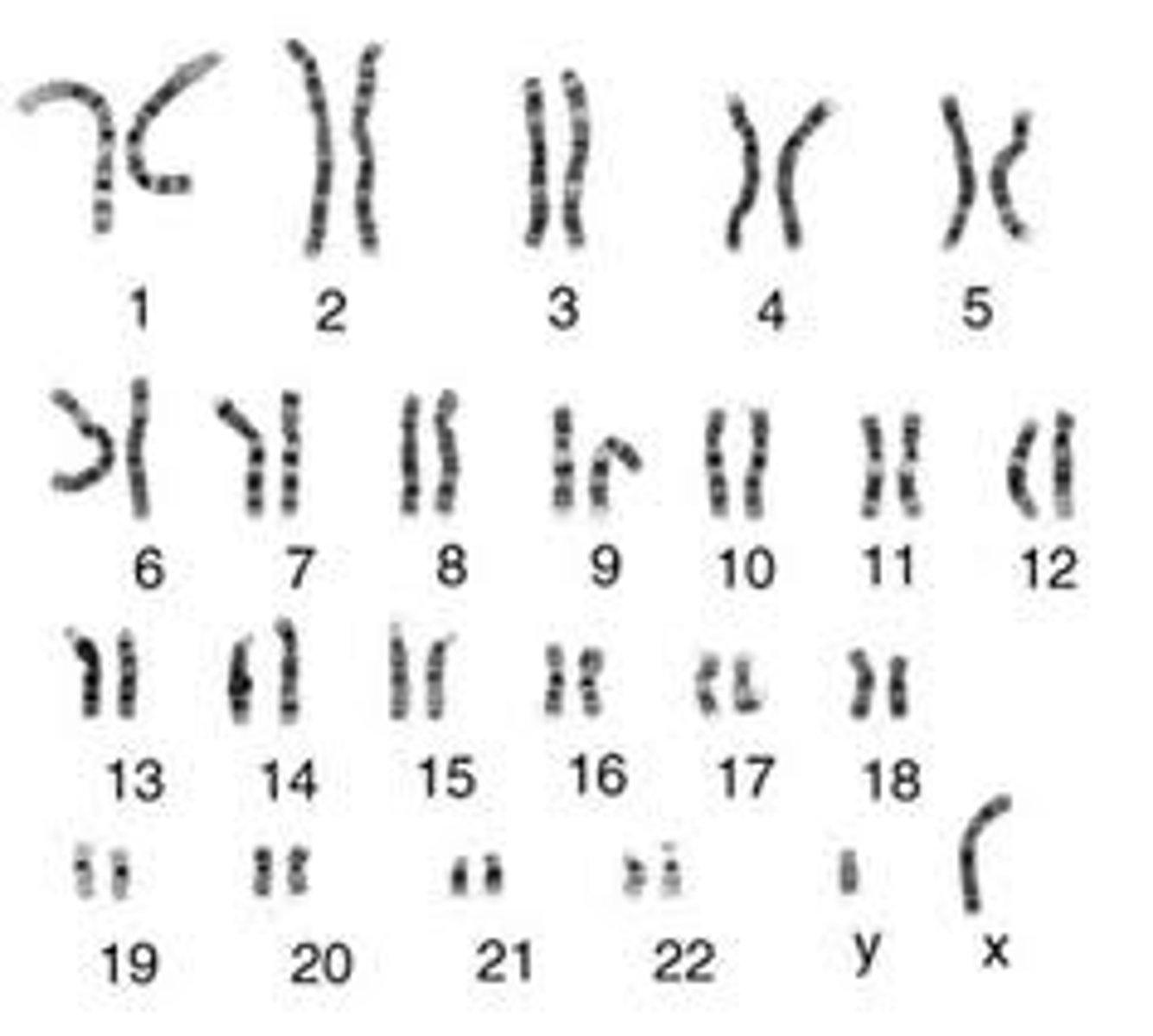
Karyogram
shows the chromosomes of an organism in homologous pairs of decreasing length.
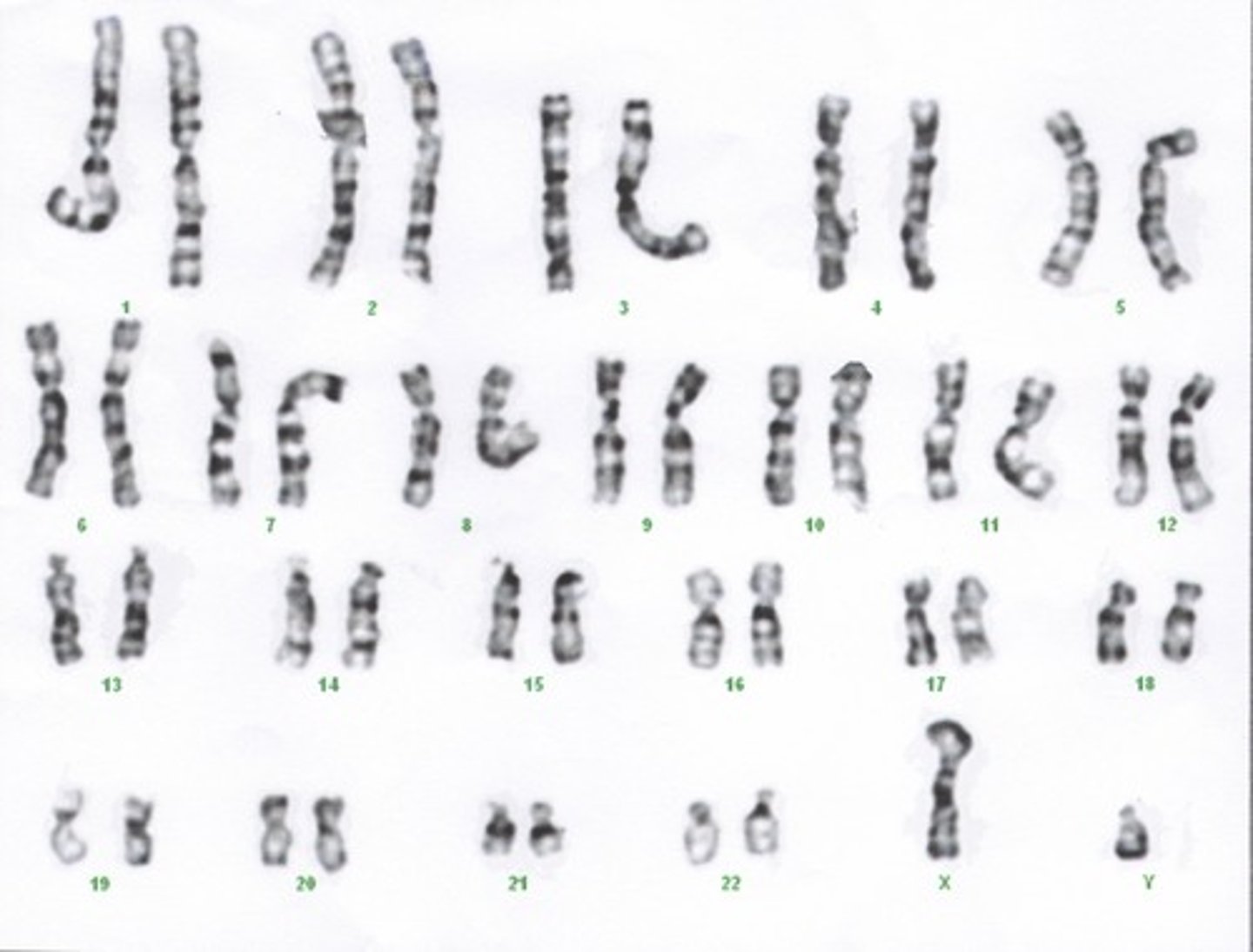
Homologous Chromosomes
Chromosomes that have the same sequence of genes and the same structure
Chromosome Banding
alternating light and dark regions along the length of a chromosome, produced after staining with a dye that binds to DNA. allows us to identify large scale abnormality
Types of Chromatin
- Euchromatin: less densely packed (more accessible) (think euchromatin is "used"
- Heterochromatin: highly condensed state (less accessible) has implications for gene expression
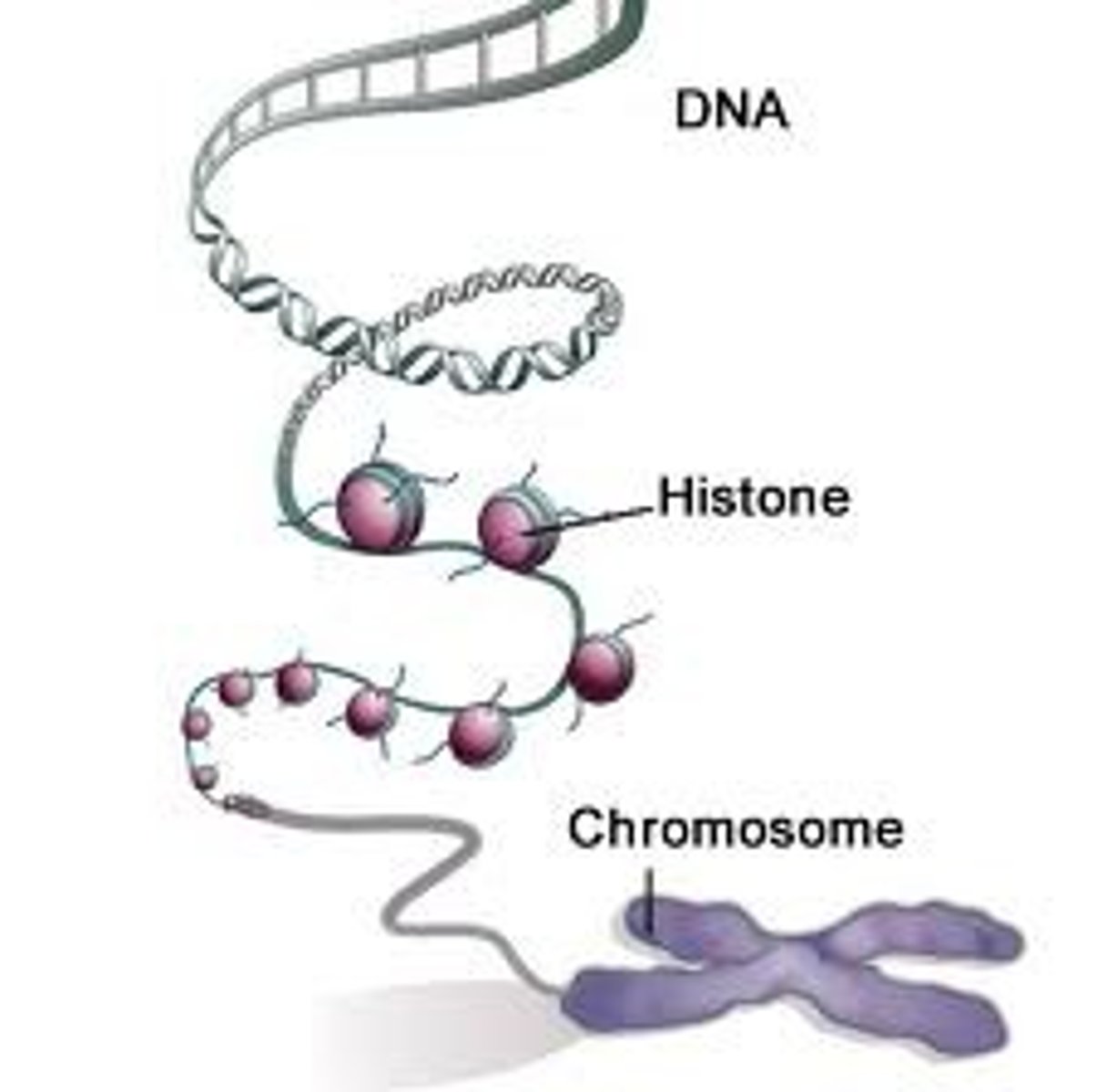
Histones
protein molecules around which DNA is tightly coiled in chromatin. Carry net positive charge because of high % of arginine and lysine residues (+ve charged AA)
Genes
the biochemical units of heredity that make up the chromosomes; a segment of DNA capable of synthesizing a protein
- functional parts of chromosomes (double stranded DNA)
SUMMARY
Slide
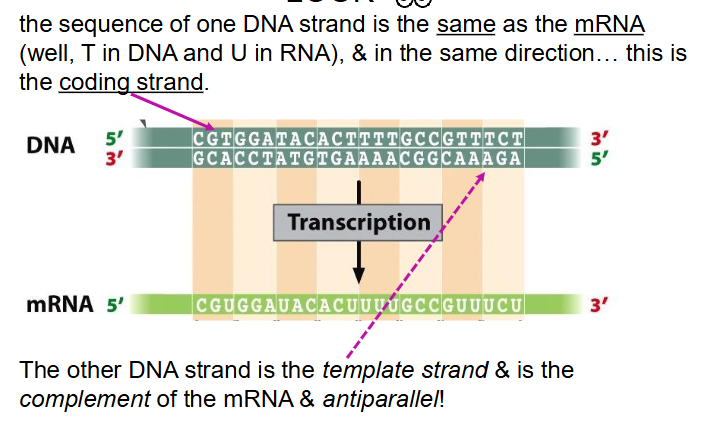
DNA strands naming
DIAGRAM