Helicopter Assembly and Rigging (Jeppesen Ch 1, section C)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is a Gyroplane
a flying craft that has no power to the main rotor. the main rotor produces lift through the autorotative force
Pros/Cons of a Dual Rotor Helicopter
Pros: Dual Rotor Helicopters do not require a anti-torque rotor, as the rotors spin in opposite directions.
Cons: More complicated drive system
3 Types of main rotor systems
Fully Articulated System
Semi-Rigid Rotor System
Rigid Rotor System
Explain the Fully Articulated Rotor system
Each rotor blade is allowed to move independently of the other blades, through the use of a flapping hinge and a drag hinge.
What is the purpose of a Flapping Hinge?
To allow each blade in a fully articulated rotor system to move up and down as needed to combat dissymmetry of lift
What is the purpose of a Drag Hinge?
To allow each blade in a fully articulated rotor system to move back and forth independently as needed to combat the Coriolis Effect
Explain the Semi-Rigid Rotor system
Two blades are rigidly mounted to the rotor hub, with the pair of blades able to freely rock and tilt on the teetering hinge
Explain the Rigid Rotor system
All blade and hub components are rigid with respect to each other.
What are the 4 forces acting on a helicopters main rotor?
Gravity
Centrifugal Force
Lift
Gyroscopic Forces
What is Drooping? What causes it?
the tendency of blades to droop with they are not turning. This drooping is limited by a droop-stop built into the hub.
What does Centrifugal Force do to a helicopter rotor?
Pulls the rotor blades out, giving them rigidity and strength to lift up the helicopter.
Why do most helicopters have a symmetrical airfoil?
so that the center of pressure does not move, which may cause vibration and rotor damage
Why are the main rotor blades of a helicopter designed with twist?
to compensate for inconsistent lift along the rotor, twist allows all parts of the rotor to produce the same lift
2 Major Forces acting during helicopter takeoff
centrifugal force acting outward
lift acting upward
Define Coning
during takeoff, rotor blades make an upward cone shape due to the lift and centrifugal forces acting on them. This bends the blades upward
List the 3 Gyroscopic Forces
Rigidity in Space
Precession
Coriolis Effect
What is “Rigidity in Space”?
The spinning rotor, or any spinning object, develops an inertial force that wants to keep the spinning object in its same place.
The spinning rotor will try to resist any force that tries to move it.
What is “Precession”?
The characteristic of a spinning rotor where the reaction to a force occurs 90 degrees later in the direction of rotation.
what is “The Coriolis Effect”?
a characteristic where, when rotor blades flap upward or downward, their center of mass moves, possibly causing vibration. This does not effect fully 2 bladed rotor systems as much as fully articulated rotor systems, and is typically compensated for by blade bending or dampeners.
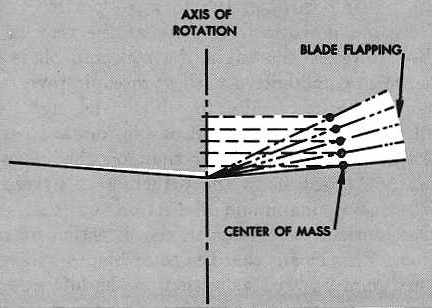
what is required for a helicopter to hover?
The thrust and lift have to equal the weight and drag of the helicopter
What is “Translating Tendency”?
During hovering, a single main rotor helicopter tends to drift opposite to the direction of the antitorque rotor thrust.
This is typically compensated for by tilting the rotor disc slightly in the opposite direction.
What is the “Ground Effect”?
Increased lift of the helicopter less than one rotor diameter from the ground due to a change in air circulation patterns
Why does the advancing blade of a main rotor make more lift than the retreating one?
The advancing blade is traveling the blade tip speed PLUS the speed of the helicopter, resulting in more lift being produced on that one side.
This effect is called Dissymmetry of Lift
Why does Retreating Blade Stall happen?
the retreating blade flaps up, causing a high angle of attack. This combined with the slow relative wind speed can stall the retreating blade.
What is “Translational Lift”?
The increase of lift as the helicopter moves forward, out of its own downwash and into undisturbed air. This additional lift is called Effective Translational Lift
Describe the process of Autorotation
Airflow enters the rotor from below as the helicopter descents, creating an aerodynamic force that drives the rotor and keeps it turning during descent.
List the 2 main parts of a Swash Plate system
Stationary Swash Plate
Rotating Swash Plate
How does the collective control the swash plates?
the collective slides the entire rotating and stationary system upward, increasing all blades pitches the same amout.
How does the cyclic control the swash plates?
Through control Rods mounted on the stationary swash plate, the stationary swash plate changes its angle, allowing the rotating swash plate to move up and down during certain points of its rotation. This allows the blade pitches to vary depending on their location in their rotational cycles.
What does the Collective Pitch Control do?
change the pitch of all blades simultaneously
Function of the throttle
To regulate engine RPM and compensate for change in collective positon if the correlator system is not functioning.
what is a correlator system?
A device that changes power automatically to meet the needs of the collective lever position.
What does the cyclic pitch control do?
Tilts the main rotor disc by tilting the swash plate assembly, thus changing the pitch angle of the rotor blades in their cycle of rotation.
List/Describe the 2 methods of controlling down load on the tail rotor
Synchronized Elevators:
Horizontal tail surfaces that are synchronized with the cyclic to create a variable down load.
Fixed horizontal stabilizer:
inverted airfoil that increases in downward load as the helicopters speed increased
Both of these systems are to keep the fuselage level at high air speeds
What are the 2 purposes of boosted controls?
To overcome high control forces
to prevent vibrations from the rotor system from being fed back into the controls
List/Describe the 3 types of tail rotor designs
Open Tail Rotor: simple tail rotor that changes in pitch to rotate about the vertical axis
Fenestron: “fan-in-tail” design, blades are safer to be around and design is similar to the regular tail rotor
NOTAR: AKA no tail rotor design, uses low pressure air forced through horizontal slots to provide antitorque and directional control
What are the 2 types of vibration?
Low Frequency Vibration: Felt as a “Beat”
High Frequency Vibration: Felt as a “Buzz”
What are the 2 directions of vibration? What does each direction indicate is wrong?
Vertical - Rotor blades are out of track
Lateral - Rotor is out of balance
What are the main components of the transmission system of a helicopter?
Main Rotor Transmission
Tail Rotor Drive System
Clutch
Free-Wheeling Unit
What is the purpose of a free-wheeling unit?
To automatically disengage the engine from the main rotor in the even of engine failure, usually for autorotation.