BB lecture 2
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
the first human blood group to be identified
ABO Blood Group System
what is unique about ABO blood group?
the only blood group that has naturally occurring Abs
it doesnt require presence of foreign RBC ag to illicit the production of ABO Abs
Most significant blood group for transfusion practice!
For ABO Abs, what is the relation of specificity to the corresponding antigens that are present?
specificity is opposite to the corresponding ags that are present from RBCs
What type of antibodies are ABO antibodies?
non-red cell stimulated Abs - from environmental exposure
What are ABO Abs referred to as?
Expected antibodies
common isohemagglutinins found in ABO blood group
anti-A & anti-B
IgMs
What can be the range of the progressive results from the transfusion of incompatible RBCs?
intravascular hemolysis to renal failure to death
What is one of the primary foundations in pretransfusion testing and safe transfusion?
Detection of ABO incompatibility
Where is ABO compatibility also critical in?
transplant patients
What can occur if ABO incompatible organs are transplanted?
Acute humeral rejection that lead to graft rejection/failure (GVHD) and eventually death depending on what organ was transplanted
3 common allele system
A, B, H (O)
A & B genes are ___
O gene is ___
co-dominant
recessive & amorph
amorph
dosen’t produce transferase enzyme and results in NO detectable O ag
O ag doesn’t exist, will be H ag
ABO genes are expressed as __
where is the locus located?
co-dominant
chromosome 9
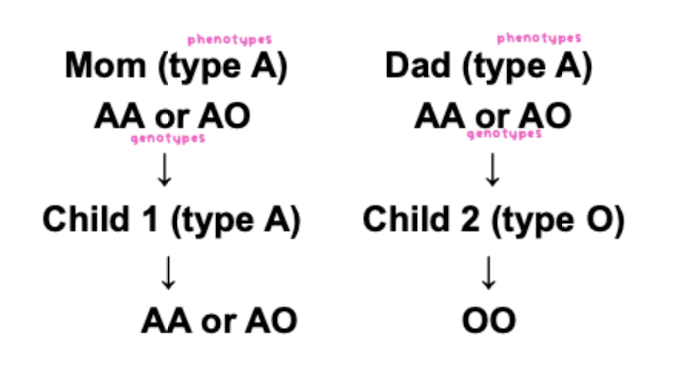
if both parents are type A, can they produce a type O baby?
yes if both parents carry the O allele
ABO Phenotype Group
O
A
B
AB
What are the possible Genotype?
Possible Genotype
HH (OO)
AA or AO*
BB or BO*
AB
when determining possible genotype, use heterozygous form * of genes
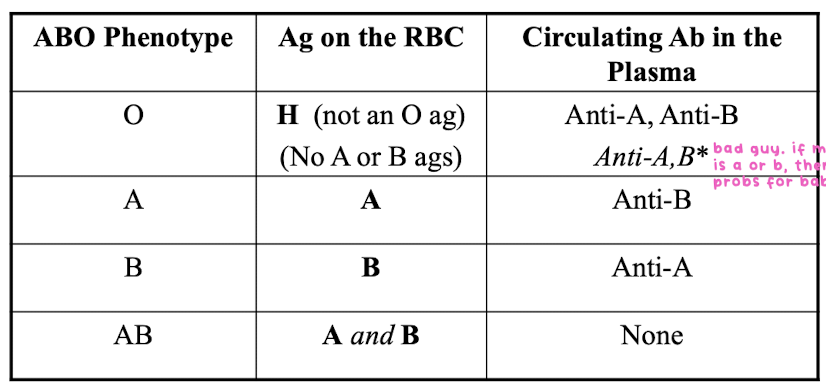
ABH =
ABO
“O” contains H ag
there is no “O” antigen
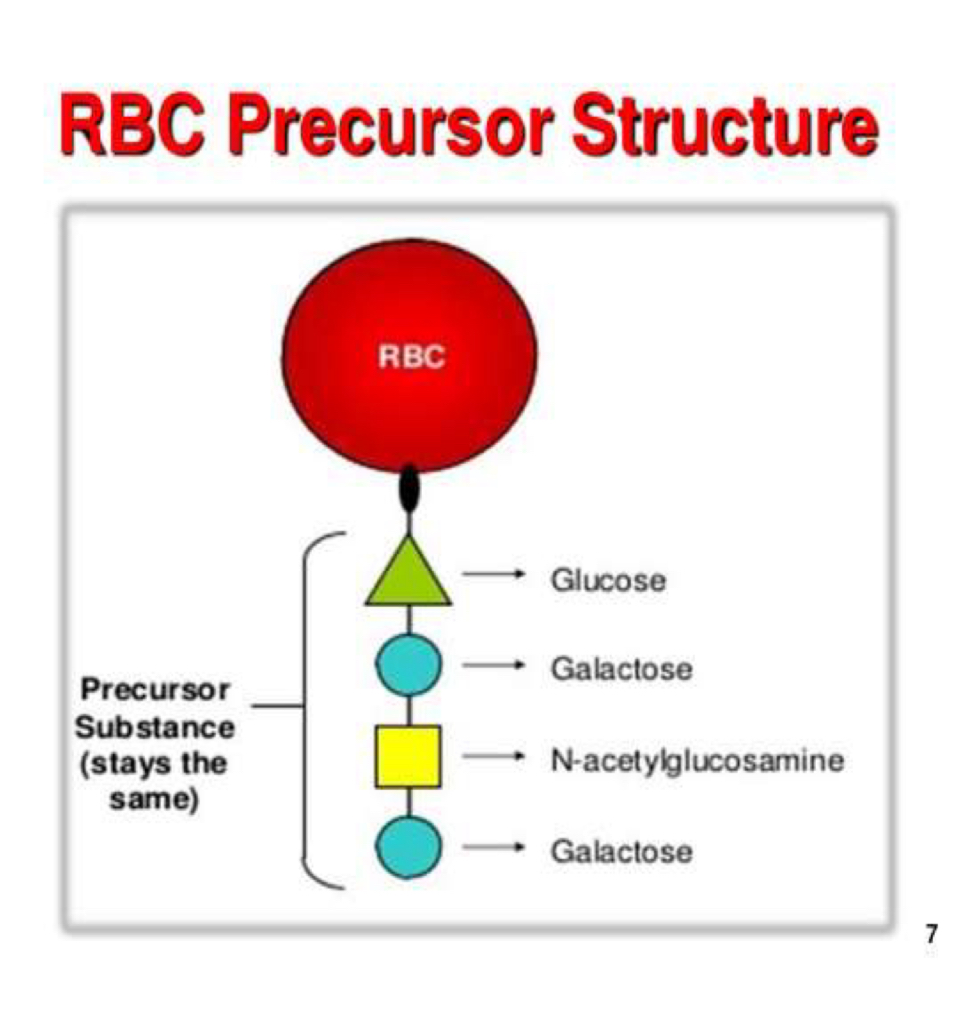
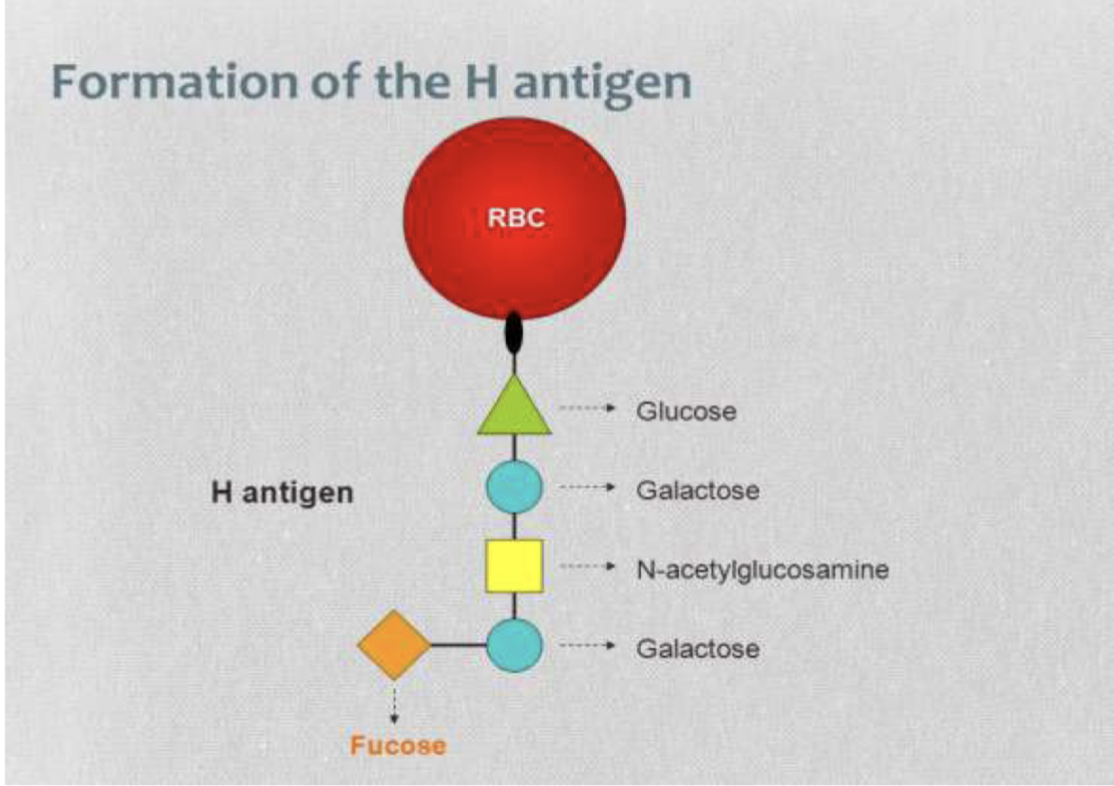
4 sugar chain for H precursor substance
which gene is amorph and very rare?
h
What gene is required for production of A or B antigens?
H gene
What does the H gene produce that adds L-fuctose (Fuc) to the precursor substance?
What is the result of of the attached L-fucose (Fuc)?
a-2-L-fucosyltransferase
H ag
H gene on precursor substance to form H antigen
Type of Oligosaccharide chain structures
Type 1: body fluids & secretions
B1-3 linkages
Type 2: rbc body fluids & secretions
B1-4 linkages
Which alleles and genes encode for glycosyl-transferases which add sugars to the H antigen?
A and B alleles / genes
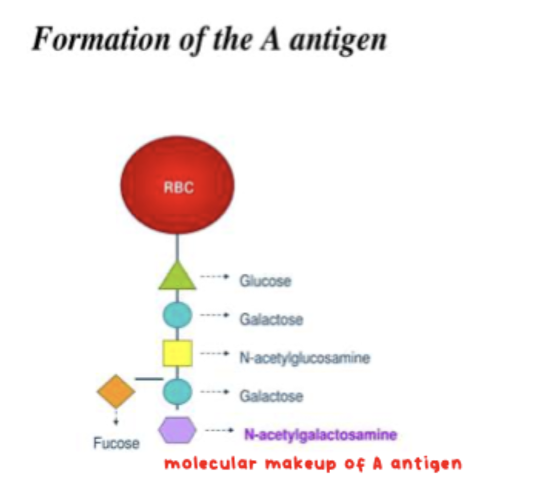
Which gene produces the α-3-N-actetylgalactosaminyltransferase? What does this do?
A gene; adds the GalNAc (N-acetyl-D-galactosamine) sugar to the H ag
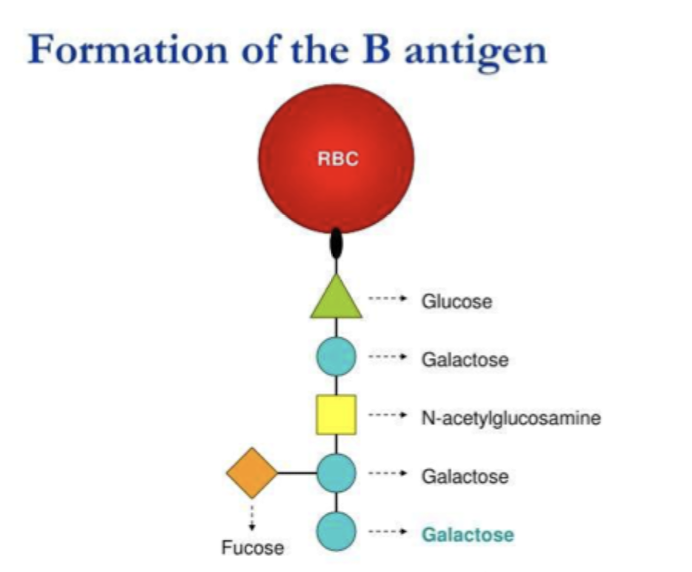
Which gene produces the α-3-D-galactosyltransferase? What does this do?
the B gene ; adds Gal (D-galactose) sugar to the H antigen
Which gene competes more efficiently for the H antigen? What is the result of this?
B enzyme compete more efficiently for the H ag than the A enzyme.
As a result of this competition, the # of B ags > # of A ags
“A” ag biochemical structure
B ag biochemical structure
The more A and B antigens are produced, the more.....
H ag is converted.
What is the density of H ag on cells from greatest to least amounts?
O > A2 > B > A2B > A1 > A1B
Which H genotype is known as Bombay?
What is the ABO phenotype?
What is the RBC antigens absent on this?
What are the expected plasma antibodies?
hh
Oh
No A, B, or H
Potent Anti-H; Anti-A and Anti-B
What genes are found and located on chromosome 19?
H (FUT 1)
Se ( FUT 2)
Which gene is found and located on chromosome 9?
ABO
Se stands for?
se stands for?
secretor; H substance found in secretions
non-secretor; silent/amorph
which gene is silent/amorph?
h, O
Se has expression over the se amorph allele
SeSe / Sese ~ 80% secretors of A, B, and / or H
most of us are secretors
sese ~ 20% nonsecretors
doesnt secrete A, B, H
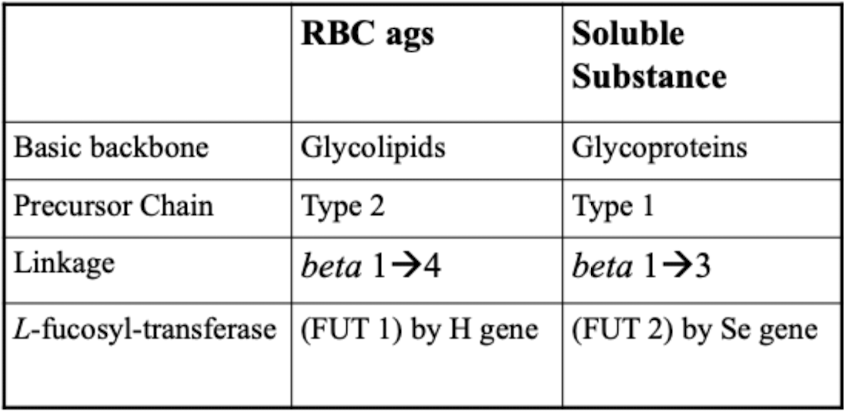
Glycolipids
imbedded in cell membranes
Glycoproteins
secreted into exocrine fluids
Fucosly-transferase adds ____ to make H antigen primarily on ____
L-fucose
Type-1 chain
distinction of ABH ags & ABH soluble substances
What is not produced in the hh genotype, aka Bombay? (Oh)
No L-fucosyl-transferase produced
No H substance / no H ag
No A or B ags present on RBCs
Only precursor substance found on RBCs
Bombay (Oh) Phenotype:
No production of L-fucosyl-transferase and no H antigen produced results in what?
RBCs with no H, A, or B ag
Bombay RBCs will NOT agglutinate with reagent Anti-A, Anti-B, Anti-A,B, or anti-H results in the patient typing as an ....?
O
What naturally occurring antibodies are found in the plasma of Bombay phenotype (Oh) individuals?
Anti-A, Anti-B, Anti-A,B, and a potent Anti-H
Agglutinating ALL ABO blood groups
What do both A1 and A2 both encode for? What does this do to the H antigen?
α-3-N-acetyl-galactose-aminyl-transferase ; puts an immunodominant sugar
N-acetyl-D-galactose on H antigen
Which A subgroup is more potent?
A1
A1A2 genotype = ?
A1 phenotype
A2A2 or A2O genotype = ?
A2 phenotype
Why do most group A infants appear to be A2 at birth?
ABH antigens not yet fully developed
Unlike the A subgroup, what does not exist in reference to the B subgroups?
"anti-B1" does NOT exist
For typing a patient's ABO blood type, testing BOTH the patient's ___ & ___ is required
RBC & the plasma / serum is required
What is known as the "Forward" type/group?
RBC testing
What is known as the "Reverse" type/group?
plasma / serum testing
Which reagent is known as "group O" typing sera
What does it contain?
Anti-A,B reagent
contains anti-A,B of IgG2 subclass
Forward types give what level of reactions?
4+
What is detected in reverse typing?
circulating Abs to A, B, AB, or H
Reverse typing should not be performed on children that are younger than....
6 months
Bombay Phenotype lacks what?
lacks H antigen on RBC, so no A,B,H
needed for A or B ags
order of adding reagents
Forward
Add 1 drop of reagent antisera + 1 drop of patient cells; mix;
spin; & read
Reverse
Add 2 drop of patient serum + 1 drop of red cell reagent; mix;
spin; & read
always add clear substance first! Reagent/serum first then red cells last
ABO testing: Reverse Type/Group
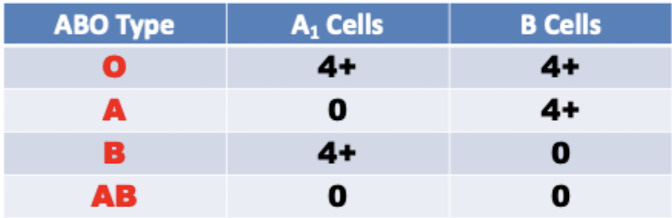
ABO antibodies are also known as
isohemagglutinins
What type of immunoglobulins are ABO antibodies (Abs)?
IgM
found in groups A & B individuals
BOTH IgM and IgG2 subclass found in group O individuals
What are the key characteristics of ABO antibodies in healthy individuals?
naturally occurring, cold to thermo-tolerant,
cause strong (4+) agglutination at immediate spin/room temp, and are present in all healthy people against the ABO antigens they lack.
Type O people have higher titers of which antibody?
Type O individuals have higher titers of anti-A than do type B people
What serious conditions can ABO antibodies cause?
Serious/fatal transfusion reactions if incompatible blood is transfused
Severe Hemolytic Disease of the Fetus and Newborn (HDFN)
Where is HDFN usually seen in?
Group O mothers giving birth to Group A neonates/babies
How does age affect ABO antibody development?
Before 3–6 months
Very low ABO antibody titers due to immature/undeveloped immune system
DONT perform reverse typing in babies <6 months old
By age 5–10: Adult levels of ABO antibodies are generally reached
After 65 years: ABO antibody titers may decrease due to aging and weakened immunity
ABO typing discrepancies
Technical / Clerical errors
RBC reactivity with antisera:
Weak or mixed field
Unexpected reaction
Plasma / serum reactivity with reagent RBCs:
Unexpected reaction
Missing or weak plasma reaction
Which group discrepancy has the following:
Reason:
weak reacting or missing antibodies
Conditions
Chimerism
New born infants
Elderly patients
Hypogammaglobulinemia (leukemia, immunodeficiency disease)
Group I Discrepancy
Which group discrepancy has the following
Reason:
weak reacting or missing antigens
Conditions:
Subgroups of A or B
Leukemia: excess amount of B
Acquired B phenomenon (in gram negative septicemia, intestinal obstruction and cancer of colon or rectum)
Group II Discrepancy
Which group discrepancy has the following:
Reason:
Protein/plasma abnormality leading to rouleaux formation
Conditions:
elevated globulin level (in multiple myeloma, Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia, plasma cell dyscrasia, Hodgkin lymphoma)
Plasma expanders like dextran, polyvinyl pyrrolidone
Wharton's Jelly (in cord blood)
Group III Discrepancy
What group discrepancy has the following reasons and conditions:
Reason:
Miscellaneous problems
Conditions:
Exposure of hidden erythrocyte T antigen (Polyagglutination)
cold and warm autoantibody (AIHA)
Transfused foreign antigen
Unexpected ABO iso-agglutinin and alloantibody
Antibody other than anti-A and anti-B
cis - AB individuals
Group IV discrepancy