Chapter 10: Chromosomes and Mitosis
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
LIU, EENG304
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What does the term “chromosome” mean?
“Colored body,” referring to their ability to be stained by certain dyes. They are virtually colorless
How many genes does the human genome contain?
About 25,000 protein-coding genes
What is a gene?
An informational unit made of DNA, that provide instructions for specific cell functions that influence traits.
What is a genotype? phenotype?
genotype: The genetic makeup of an individual.
phenotype: The physical traits influenced by genotype and environment.
What is chromatin composed of?
DNA and protein, that form chromosomes (in eukaryotes).
What is the role of chromosomes during cell division?
They allow DNA to be sorted into daughter cells.
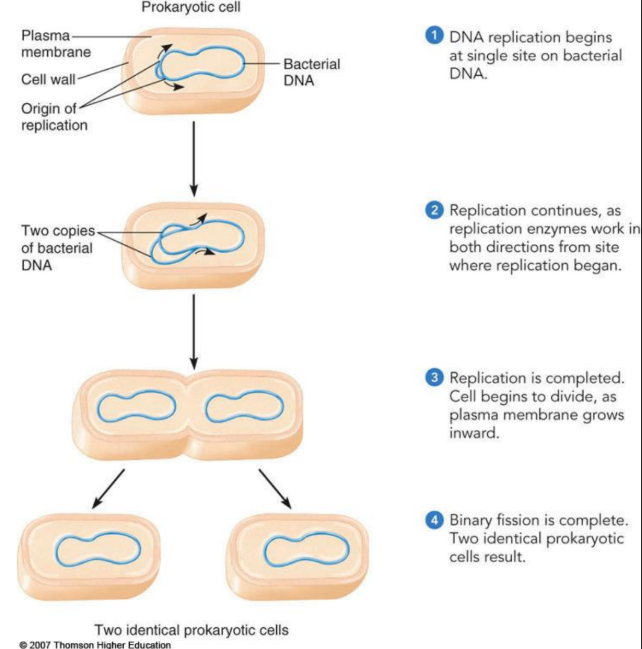
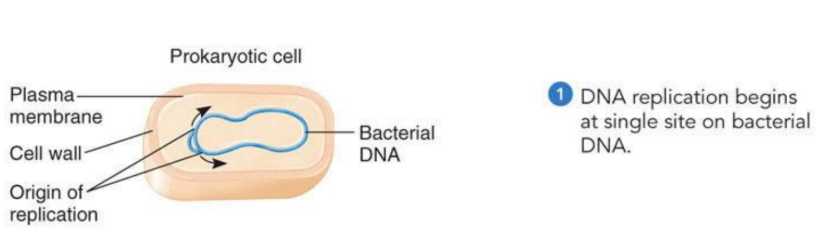
How is DNA organized in prokaryotic ?
Prokaryotic Cells contain circular DNA molecules
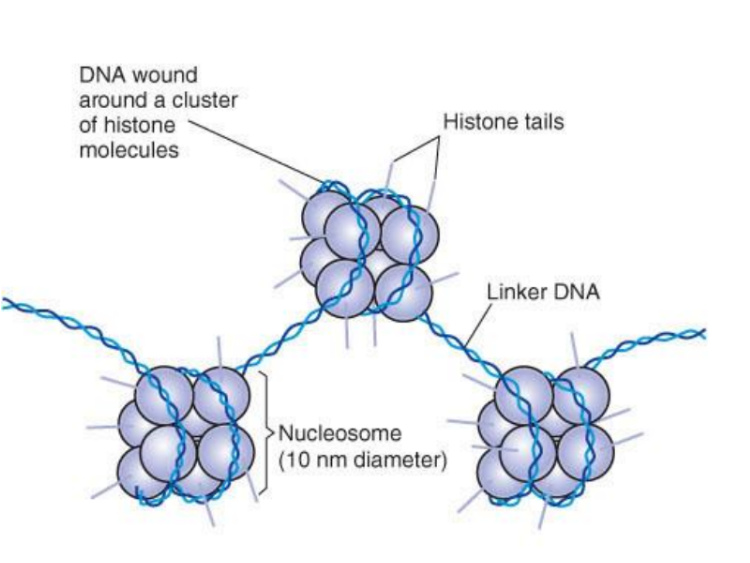
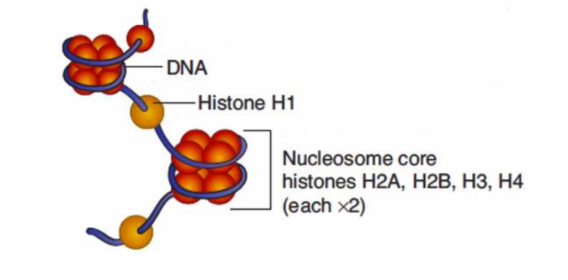
What is a nucleosome?
Double stranded DNA (146 nucleotide pairs) wrapped around 8 histone proteins, organized into coiled loops, and held together by nonhistone scaffolding proteins.
60 nucleotide pairs segment of DNA links nucleosome beads.
Diameter =10nm
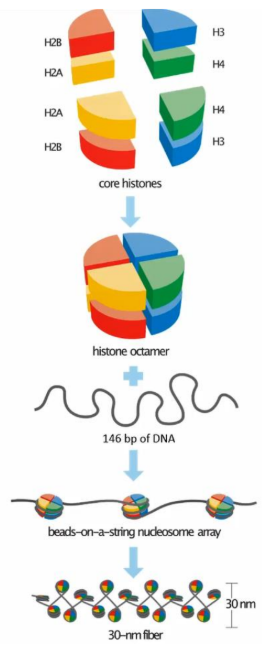
Histones.
-Facilitate chromosome packaging in eukaryotic cells
-Positively charged since they contain many amino acids with basic side chains.
-Has 5 types: H1, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4, by which the histone octamer has 2 (except H1) of each.
How and why do histones associate with DNA?
DNA is negatively charged due to phosphate groups, allowing electrostatic interaction with histones.
They associate to form nucleosomes.
What is the hierarchical sequence of DNA packaging in a chromosome? diameter of each?
DNA 2nm → Nucleosomes 10nm → Chromatin fiber (Packed nucleosomes) 30nm → Extended chromatin 300nm → Condensed chromatin 700nm → Condensed chromosome 1400nm
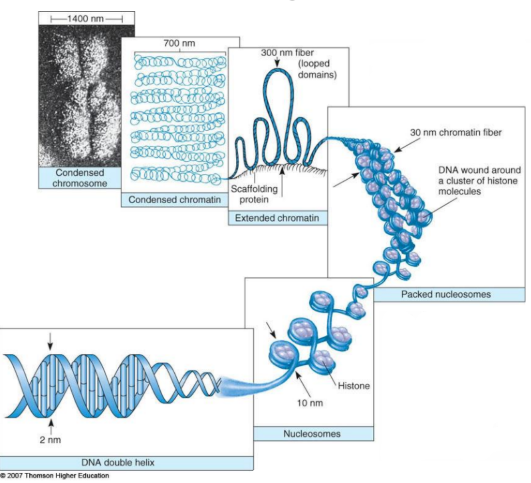
What enables nucleosomes to pack into a 30-nm chromatin fiber?
Histone H1 binds to linker DNA, compacting adjacent nucleosomes.
What protein group is required for chromosome compaction?
Condensin, Binds DNA and wraps it into coiled loops for mitotic/meiotic chromosomes.
What defines species uniqueness: chromosome number or genetic information?
Genetic information specified by genes, not chromosome count. other species have the same chromosome number as humans (ex olive trees).
What is the typical chromosome range for most animal and plant species?
Between 8 and 50 chromosomes per body cell.
Eukaryotic Cell Cycle
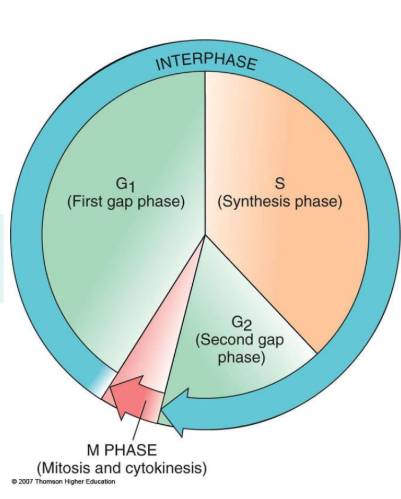
Interphase
-G1 Phase: (Longest phase)The cell grows and prepares for S phase, and toward the end of G1, the enzymes required for DNA synthesis become more active.
-S Phase: DNA replicates and histone proteins are synthesized to duplicate chromosomes.
-G2 Phase: (Shortest phase) Protein synthesis increases and the cell prepares for division.
note: during interphase, the cell carries out normal life activities.
M Phase
-Mitosis: Begins at the end of the G2 phase ;Nuclear division producing two nuclei identical to the parent nucleus.
-Cytokinesis: begins before mitosis is complete ; cytoplasm divides to form two daughter cells.
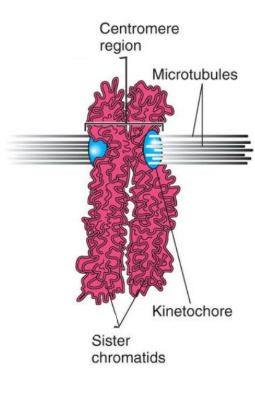
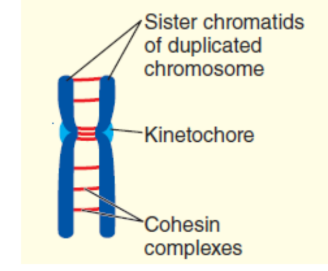
What is the structure of a duplicated chromosome?
• Consists of a pair of sister chromatids containing identical DNA sequences.
• Centromere is a constricted region that joins sister chromatids.
• Kinetochore is a protein attached to centromere, to which microtubules bind.
What protein complex links sister chromatids?
Cohesin — a ring-shaped complex, that extend along the length of the sister chromatid arms and are particularly concentrated at the
centromere.
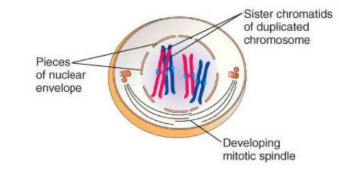
Prophase of Mitosis
-Chromatin condenses into duplicated chromosomes.
-Nuclear envelope begins to disappear, its components are stored in vesicles for reuse in daughter cells.
-Mitotic spindle begins to form, and cytoskeleton is disassembled.
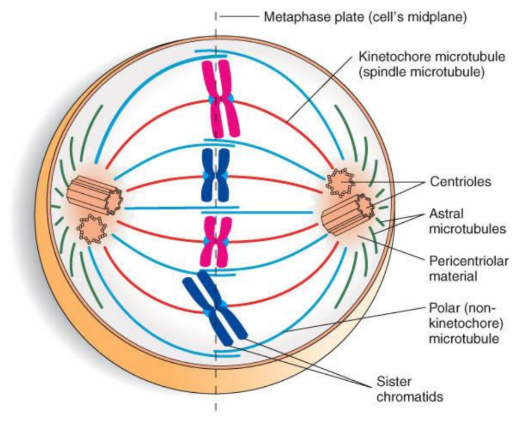
What are the three types of microtubules in the mitotic spindle?
• Kinetochore (spindle) microtubules: connect chromosomes to spindle poles.
• Polar microtubules: overlap at the midplane to aid in the separation.
• Astral microtubules: radiate outward from centrioles forming the aster
Prometaphase of Mitosis
• Spindle microtubules attach to kinetochores of chromosomes.u
• Chromosomes begin to move toward cell’s midplane.
Metaphase of Mitosis
• Chromosomes align on cell’s midplane (metaphase plate).
• Mitotic spindle is complete.
• Microtubules attach kinetochores of sister chromatids to opposite poles of cell.
Anaphase of Mitosis
Sister chromatids separate, move to opposite poles.
Each former chromatid is now a chromosome.
Telophase of Mitosis
• Nuclear envelope re-forms
• Nucleoli appear
• Chromosomes uncoil
• Spindle disappears
• Cytokinesis begins
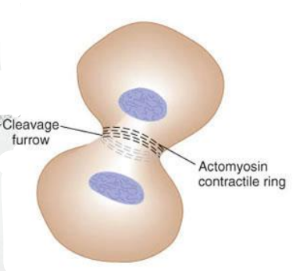
Cytokinesis
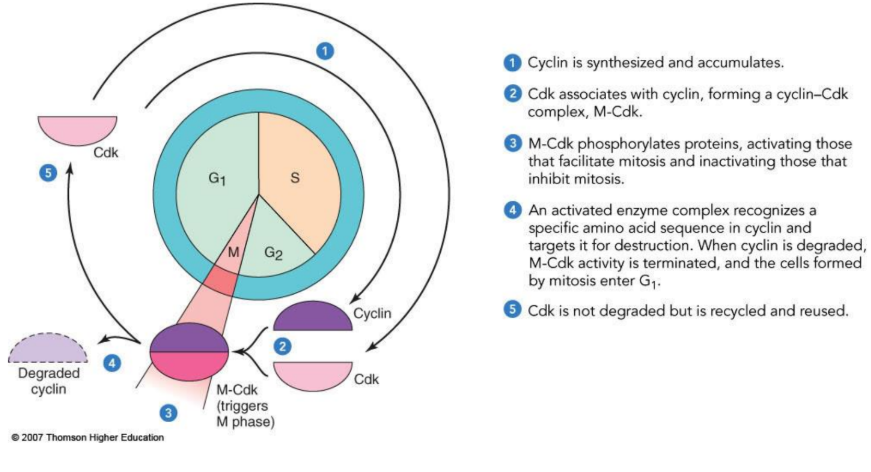
What are Cdks?
Cyclin-dependent kinases: Protein kinases that control the cell cycle; active only when bound to cyclins.
What are cyclins?
Regulatory proteins whose levels fluctuate during the cell cycle.
Cyclin-Cdk Regulation
Asexual reproduction
It involves a single parent and produces offspring with identical hereditary traits.
Eukaryotes by mitosis.
Prokaryotes by binary fission.
Binary Fission