Javascript exam study
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
What is an event loop?
it powers javascript’s async behavior
Where does javascript keep track of function calls?
Call stack
A call stack follows a ______ order
first in first out
What erro do you get from a stack being too large?
stack overflow
Where does memory allocation occur?
in the heap
where are objects, variables, and function declarations stored?
in the heap
What are not part of the Javascript API and handle network requests?
APIs
When async operations are completed, their callblacks are placed where?
in the callback/task queue
callback/task queues follow a ____ order
first in first out
where are macrotasks contained?
Callback/task queues
What higher priority queue is used for certain types of calbacks?
Microtask queue
Microtask queues follow a _____ order
first in first out
What mechanism continuously checks the call stack and queues?
event loop
What is the 1st step in executing async code?
Execution phase
What is the 2nd step in executing async code?
Delegation phase
What is the 3rd step in executing async code?
Completion phase
What is the 4th step in executing async code?
Event loop processing phase
Which has a higher priority: microtasks or macrotasks
microtasks
Macro tasks are processed after ______
all the microtasks have been processed
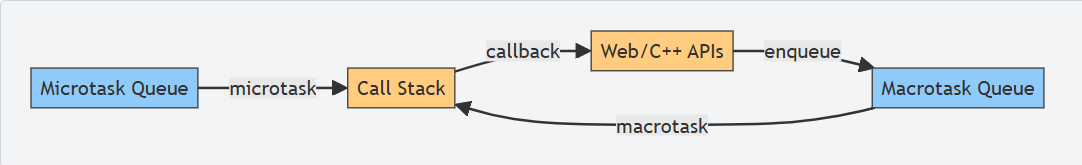
What is this a diagram of?
Event loop execution
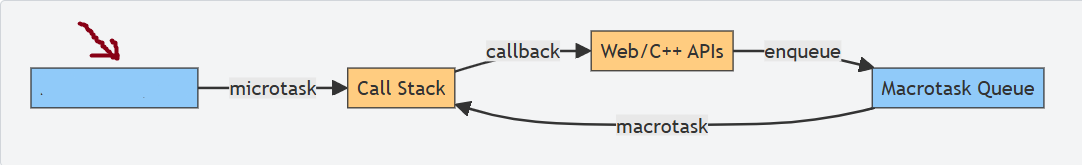
What is this box?
Microtask queue
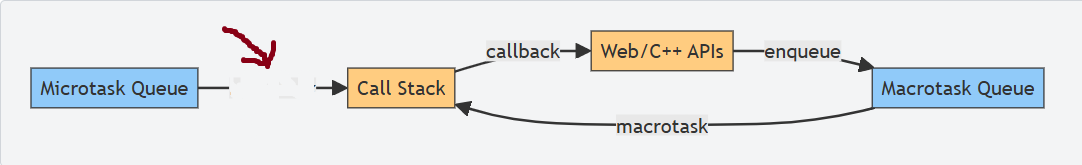
What is this?
microtask
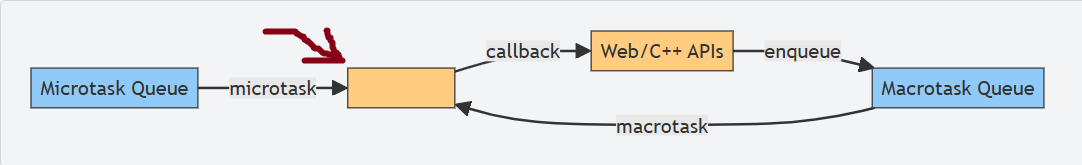
What is this box?
call stack
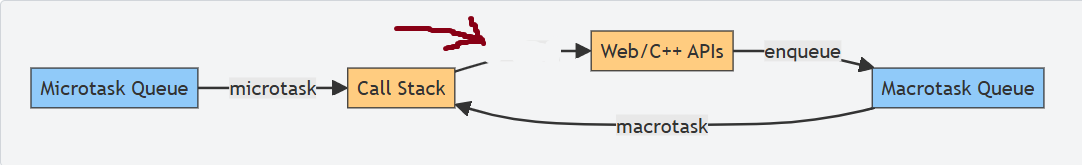
what is this?
callback
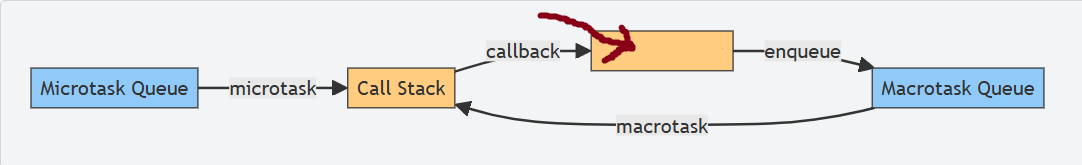
What is this box?
Web APIs
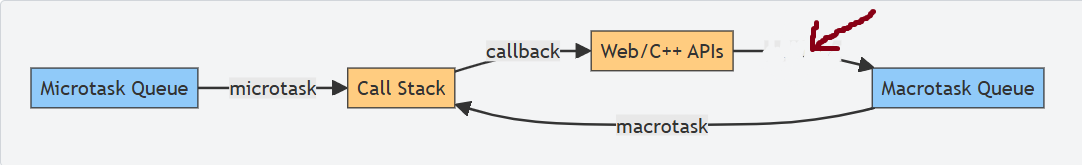
What is this?
enqueue
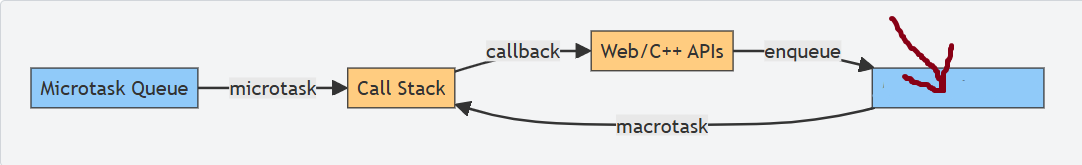
What is this box?
Macrotask queue
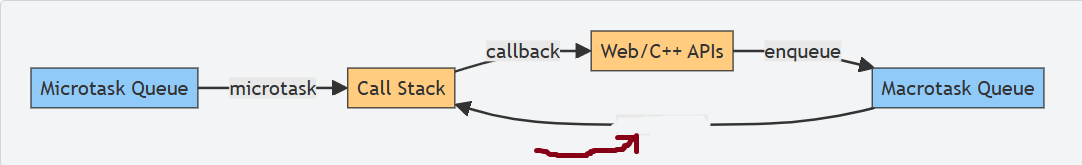
what is this?
macrotask
What are callbacks?
functions passed as arguments to another function
What is a synchronous callback?
callback functions that are executed immediately
What is an asynchronous callback?
A callback function that is executed later
What is an error-first callback?
a callback function function reserved for errors
What is a promise?
objects representing completion/failure of async operations
What is a pending promise?
the initial state of a promise when the operation is in progress
What is a fulfilled promise?
when the operation is successful and the promise has a resulting value
What is a rejected promise?
When the operation has failed and the promise has the cause of that failure
What does the following code do?
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (/* operation successful */) {
resolve(value);
} else {
reject(reason);
}
});Creates a promise
What does this method do?
promise.then(
(value) => { /* fulfillment handler */ },
(reason) => { /* rejection handler (optional) */ }
);registers callbacks for fulfillment and/or rejection
What does this method do?
promise.catch((reason) => { /* rejection handler */ });registers a callback for rejection
What does this method do?
promise.finally(() => { /* cleanup code */ });registers a callback to be fulfilled regardless of promise value
What does promise.resolve(value) do?
returns the resolved promise with the given value
What does promise.reject(reason) do?
returns the rejected promsie with the given reason
What does the promise.all(iterable) do?
returns a promise that is resolved when all the promises within the iterable are resolved
What does the promise.race(iterable) do?
returns a promise that resolves or rejects as soon as one of the promises within the iterable resolves or rejects
What does the promise.allSettled(iterable) do?
returns a promise that resolves when all promsies within the iterable have settled
What does the promise.any(iterable) do?
returns a promise that resolves as soon as any of the promises in the iterable resolves
What does async mean?
an async function that return a promise
What does await mean?
paues the executions of a async function until a promise is settled
What does the following code do?
async function myAsyncFunction() {
return 'Hello World';
}Creates an async function
What does the following code do?
async function fetchUserData() {
try {
const response = await fetch('/api/user');
const userData = await response.json();
return userData;
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error fetching user data:', error);
throw error; // Re-throw to propagate the error
}
}Creates an async function with await
Always wrap await expression in a ______
try-catch block
What is data serialization?
converting structured data to a format that allows sharing or storage
What step 1 in data serialization?
Data collection
What step 2 in data serialization?
Conversion
What step 3 in data serialization?
Transmission
What step 4 in data serialization?
Storage or processing
What does the following code do?
const person = {
name: "John Doe",
age: 30,
isStudent: false,
courses: ["Web Development", "Database Design"]
};
const serializedData = JSON.stringify(person);
console.log(serializedData);serializes an object literal into a JSON string
What is the output of the following code?
const person = {
name: "John Doe",
age: 30,
isStudent: false,
courses: ["Web Development", "Database Design"]
};
const serializedData = JSON.stringify(person);
console.log(serializedData);{"name":"John Doe","age":30,"isStudent":false,"courses":["Web Development","Database Design"]}What is deserializing?
converting serialized data back into it;s OG structure like an object or array
What is step 1 in deserialization?
data reception
What is step 2 in deserialization?
Validation
What is step 3 in deserialization?
Conversion
What is step 4 in deserialization?
utilization
What does this code do?
const serializedData = '{"name":"John Doe","age":30,"isStudent":false,"courses":["Web Development","Database Design"]}';
try {
const person = JSON.parse(serializedData);
console.log(person.name);
console.log(person.courses[0]);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Deserialization error:", error);
}Deserializes a JSON string back into an object
What is the output of
const serializedData = '{"name":"John Doe","age":30,"isStudent":false,"courses":["Web Development","Database Design"]}';
try {
const person = JSON.parse(serializedData);
console.log(person.name);
console.log(person.courses[0]);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Deserialization error:", error);
}John Doe
Web DevelopmentWhat are CSV files?
Comma seperated values with rows and columns
What data format is the following:
name,age,email,role
John Doe,30,john@example.com,Developer
Jane Smith,28,jane@example.com,Designer
Mike Johnson,35,mike@example.com,ManagerCSV
What does the following code do?
function parseCSV(csv) {
const lines = csv.split('\n');
const result = [];
const headers = lines[0].split(',');
for (let i = 1; i < lines.length; i++) {
const obj = {};
const currentLine = lines[i].split(',');
for (let j = 0; j < headers.length; j++) {
obj[headers[j]] = currentLine[j];
}
result.push(obj);
}
return result;
}
const csvData = `name,age,email,role
John Doe,30,john@example.com,Developer
Jane Smith,28,jane@example.com,Designer`;
const parsedData = parseCSV(csvData);
console.log(parsedData);parses CSV data
What is XML?
eXtensible Markup Language that has a hierarchal structure and looks a but liek HTML
What data format is the following:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<employees>
<employee id="1">
<name>John Doe</name>
<age>30</age>
<email>john@example.com</email>
<role>Developer</role>
</employee>
<employee id="2">
<name>Jane Smith</name>
<age>28</age>
<email>jane@example.com</email>
<role>Designer</role>
</employee>
</employees>XML
What does the following code do?
import { JSDOM } from 'jsdom';
function parseXML(xmlString) {
const dom = new JSDOM(xmlString, { contentType: 'text/xml' });
return dom.window.document;
}
const xmlString = `<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<employees>
<employee id="1">
<name>John Doe</name>
<age>30</age>
</employee>
<employee id="2">
<name>Jane Smith</name>
<age>28</age>
</employee>
</employees>`;
const xmlDoc = parseXML(xmlString);
const employees = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("employee");
console.log("Employee Information:");
for (let i = 0; i < employees.length; i++) {
const name = employees[i].getElementsByTagName("name")[0].textContent;
const age = employees[i].getElementsByTagName("age")[0].textContent;
const id = employees[i].getAttribute("id");
console.logID: ${id}, Name: ${name}, Age: ${age});
}
Parses an XML file
What is JSON?
JavaScript Object Notation that uses key-value pairs
What data format is the following:
{
"employees": [
{
"id": 1,
"name": "John Doe",
"age": 30,
"email": "john@example.com",
"role": "Developer"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Jane Smith",
"age": 28,
"email": "jane@example.com",
"role": "Designer"
}
],
"company": "Example Corp",
"established": 2010
}JSON
What does the following code do?
const jsonString = '{"name":"John","age":30,"city":"New York"}';
const person = JSON.parse(jsonString);
console.log(person.name);
const team = {
name: "Development Team",
members: ["John", "Jane", "Mike"],
lead: {
name: "John Doe",
yearsExperience: 5
}
};
const teamJSON = JSON.stringify(team);
console.log(teamJSON);Parses JSON data
What data format is tabular and godo for spreadsheets, data exports?
CSV
What data format is good for complex data with metadata, document based apps, and enterprise systems?
XML
What data format is good for web APIS, configuration files?
JSON
In JSON, data is represented using _______
key value pairs
What does JSON.Stringify() do?
converts JavaScript objects into JSON strings
What does the following code do?
const person = {
name: "John Doe",
age: 30,
isStudent: false
};
const jsonString = JSON.stringify(person);
console.log(jsonString);Converts the object into a JSON string
What is the output of
const person = {
name: "John Doe",
age: 30,
isStudent: false
};
const jsonString = JSON.stringify(person);
console.log(jsonString);{"name":"John Doe","age":30,"isStudent":false}What does JSON.parse() do?
converts a JSON string into a JavaScript object
What does the following code do?
const jsonString = '{"name":"John Doe","age":30,"isStudent":false}';
const person = JSON.parse(jsonString);
console.log(person.name);
console.log(person.age);
console.log(typeof person.isStudent);converts a JSON string into an object
What is the output of the following
const jsonString = '{"name":"John Doe","age":30,"isStudent":false}';
const person = JSON.parse(jsonString);
console.log(person.name);
console.log(person.age);
console.log(typeof person.isStudent);John Doe
30
booleanWhat is the difference between JSON and dictionaries?
JSON is a file format that uses key value pairs while dictionaries are data types
What does the following code do?
const user = {
name: "Alice",
password: "secret123",
email: "alice@example.com",
loginAttempts: 5
};
function replacer(key, value) {
if (key === "password") {
return undefined;
}
return value;
}
const safeUserJson = JSON.stringify(user, replacer);
console.log(safeUserJson);Uses a replacer function to exclude the password value
What is the output of the following?
const user = {
name: "Alice",
password: "secret123",
email: "alice@example.com",
loginAttempts: 5
};
function replacer(key, value) {
if (key === "password") {
return undefined;
}
return value;
}
const safeUserJson = JSON.stringify(user, replacer);
console.log(safeUserJson);{"name":"Alice","email":"alice@example.com","loginAttempts":5}What does the following code do?
const user = {
name: "Bob",
age: 25,
email: "bob@example.com",
phone: "555-1234",
address: "123 Main St"
};
const properties = ["name", "email"];
const filteredJson = JSON.stringify(user, properties, 2);
console.log(filteredJson);uses a replacer function to only include the name and email
What is the output for
const user = {
name: "Bob",
age: 25,
email: "bob@example.com",
phone: "555-1234",
address: "123 Main St"
};
const properties = ["name", "email"];
const filteredJson = JSON.stringify(user, properties, 2);
console.log(filteredJson);{
"name": "Bob",
"email": "bob@example.com"
}What are the unsupported data types in JSON?
functions, date objects, circular references, and symbols
What does the following code do?
const jsonWithDate = '{"name":"Meeting","date":"2025-07-11T09:00:00.000Z"}';
function dateReviver(key, value) {
if (key === "date" && typeof value === "string") {
return new Date(value);
}
return value;
}
const meeting = JSON.parse(jsonWithDate, dateReviver);
console.log(meeting.date instanceof Date);
console.log(meeting.date.toLocaleString());uses a reviver function to convert date strings into date objects