AP PSYCHOLOGY - SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
Social psychology
The scientific study of how we think about, influence, and relate to one another.
Attribution theory
the theory that we explain someone’s behavior by crediting either the situation or the person’s disposition.
Fundamental Attribution error
the tendency for observers, when analyzing others’ behavior, to underestimate the impact of the situation and to overestimate the impact of personal disposition.
Attitude
feelings, often influenced by our beliefs, that predispose us to respond in a particular way to objects, people, and events.
Peripheral route persuasion
Occurs when people are influenced by incidental cues, such as speaker's attractiveness
Central route persuasion
Occurs when interested people focus on the arguments and respond with favorable thoughts
Foot-in-the-door phenomenon
The tendency for people who first agreed to a smaller request to comply with a larger request.
Role
A set of expectations about a social position, defining how those in the position ought to behave.
Cognitive dissonance theory
The theory that we act to reduce the discomfort we feel when two of our thoughts are inconsistent. For example, when we become aware that our attitudes and our actions clash, we can reduce the resulting dissonance by changing our attitudes.
Conformity
adjusting our behavior or thinking to coincide with a group standard.
Normative social influence
influence resulting from a person’s desire to gain approval or avoid disapproval.
Informational social influence
Influence resulting from one’s willingness to accept others’ opinions about reality.
Automatic mimicry (the chameleon effect)
Our tendency to unconsciously imitate others’ expressions, postures, and voice tones, is a form of conformity.
Social facilitation
improved performance on simple or well-learned tasks in the presence of others
Social loafing
the tendency for people in a group to exert less effort when pooling their efforts toward attaining a common goal than when individually accountable.
deindividuation
the loss of self-awareness and self-restraint occuring in group situations that foster arousal and anonymity.
Groupthink
When a group of people that desire harmony or conformity results in an incorrect or deviant decision-making outcome
Culture
the enduring behaviors, ideas, attitudes, values, and traditions shared by a group of people and transmitted from one generation to the next
Norm
an understood rule for accepted and expected behavior. Norms prescribe “proper” behavior.
Prejudice
an unjustifiable and usually negative attitude toward a group and it’s members. Prejudice generally involves stereotyped beliefs, negative feelings, and a predisposition to discriminatory action
Stereotype
A generalized belief about a group of people
Discrimination
unjustifiable negative behavior toward a group and its members.
Just-world phenomenon
the tendency for people to believe the world is just and that people therefore get what they deserve and deserve what they get
Ingroup
“us” people with whom we share a common identity
Outgroup
“them” those perceived as different or apart from our ingroup
Ingroup bias
the tendency to favor our own group
Scapegoat theory
the theory that prejudice offers an outlet for anger by providing someone to blame
Other-race effect
the tendency to recall faces of one’s own race more accurately than faces of others races.
Aggression
any physical or verbal behavior intended to hurt or destroy
Frustration-aggression principle
the principle that frustration- the blocking of an attempt to achieve some goal- creates anger, which can generate aggression.
Social script
culturally modeled guide for how to act in various situations
Mere exposure effect
people tend to develop a preference for things merely because they are familiar with them
Mood linkage
The tendency to absorb and participate in the prevailing mood of the other people around
Muzafer Sherif (1936)
study of how norms develop in small groups.
Compliance
An individual doing what someone else wants them to do, following his or her request or suggestion
Which branch of psychology is most directly concerned with the study of how people think about, influence, and relate to one another?
Social psychology
If a cluster of people stand gazing upward, passersby will often pause to do likewise unintentionally mimicking . This best illustrates:
the chameleon effect
Adjusting one's behavior or thinking toward a group standard is called
conformity
Research participants believed that the Asch conformity test involved a study of
conformity
Normative social influence results from people's' desire to gain
social approval
Actor-observer Bias
Tendency to attribute one’s own actions to external causes while attributing other people’s behavior to internal causes.
False consensus effect
Tendency to overestimate how much other people agree with us
Obedience
Changing one’s behavior at the direct command of an authority figure
Stanley Milgram (1963)
Designed one of the more famous experiments in the history of psychology on obedience.
Authority
Destructive obedience requires the physical presence of a prestigious authority figure
The victim
Physical separation from the victim allows for emotional distance from the consequences of actions.
Participants in the Milgram obedience studies were ordered to:
deliver electric shocks to a learned for giving incorrect answers
Most people are likely to be surprised by the results of Milgram's initial obedience experiment because:
Teachers more obedient than predicted
The Milgram obedience experiments were controversial because the “teachers” were
Deceived and subjected to stress
According to Milgram, the most fundamental lesson to be learned from his study of obedience is that
Situations matter
In Milgram's experiments, participants were torn between whether they should respond to the pleas of the _____ or the demands of the ______
Learner and experimenter
Group
A set of individuals who interact over time and have shared fate, goals, or identity
The sucker effect
One person does all the work in a group while everyone else goofs around
Social Impairment
The tendency for an individual’s performance to decline when complex or poorly-learned tasks are performed in the presence of others.
Group polarization
the tendency for groups to make decisions that are more extreme than the initial inclination of its members
Social facilitation is most likely to occur in the performance of ________ tasks
simple
The tendency for people to exert less effort when they are pooling their efforts toward a common goal is known as __________________
social loafing
Masked bandits might be more likely than unmasked bandits to physically injure their victims due to ______________
deindividuation
The enhancement of a group's prevailing inclinations through group discussion is called
group polarization
An overwhelming desire for harmony in a decision-making group increases the probability of ________
groupthink
Pyramid of hate
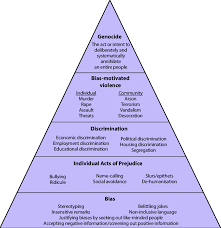
Racism
Categorization of a person or group of people based on their race or ethnicity and the systematic mistreatment of people in the targeted group
Stereotype threat
A situation in which people feel at risk of performing as their group is expected to perform
Self-fulfilling prophecy
Expectation held by a person that alters his or her behavior in a way that tends to make it true
Gordon Allport (1954)
connected scapegoating with feelings of prejudice
Ethnocentrism
tendency to use your own culture as the standard by which to judge and evaluate others
Out-group homogeneity
The tendency for us to view members of out groups as being more similar than members of ingroups
Contact hypothesis
Brining members from different groups together will reduce prejudice improve positive attitudes.
Superordinate goals
shared goals that override differences among people and require their cooperation
A store owner charges African-American customers more than Hispanic customers for the very same merchandise. The owner is most clearly engaging in ____________________
discrimination
People may unconsciously harbor negative racial associations. This best illustrate the subtle nature of ________________
prejudice
The ingroup is the set of people with whom we share a common
identity
Most children believe their school is better than the other schools in town. This best illustrates
ingroup bias
The tendency to recall faces of one's own race more accurately than faces of other races is called
other-race effect
Hostile aggression
strong emotions, particularly anger and is associated with impulsive and unplanned behavior
Instrumental aggression
Intent to harm another person but the motivation is not emotional, rather to advocate a cause or achieve something.
Genetic influences
seem to predispose people to aggressiveness or passivity
Social Learning
Our reactions are more likely to be aggressive in situations where experience has taught us that aggression pays.
Situational factors
all unpleasant events
Verbal behavior intended to hurt another person is an example of:
aggression
The frustration-aggression principle suggests that anger results when:
an attempt to achieve some goal is blocked
Parents who discipline their children with beatings are often teaching aggression through the process of _____________
modeling
The Y chromosome is the most well-known genetic marker identifying those who are most likely to
engage in aggression
Comparisons of identical and fraternal twins highlight the impact of ________ on aggression
genetic influences
Bystander effect
the greater people present, the less likely people are to help a person in distress
Diffusion of responsibility
Because there are other observers, individuals do not feel as much pressure to take action
Bystander intervention
helping an emergency despite the presence of others
Altruism
The unselfish concern for other people; doing things simply out of a desire to help, not because you feel obligated to
Social exchange theory
Argue that altruism only exists when the benefits outweigh the costs
Empathy-Altruism hypothesis
psychological altruism does exist and is evoked by the empathic desire to help someone who is suffering
Reciprocity
social expectation in which we feel pressured to help others if they have already done something for us
Social responsibility norm
Societal rule that tells people they should help others who need help even if they may not repay us
Social dilemma
a situation in which a self-interested choice by everyone will create the worst outcome for everyone
Prisoner’s dilemma
a type of dilemma in which one party must make either cooperative or competitive moves in relation to another party
Graduated & Reciprocated initiatives in Tension-reduction
This is a strategy designed to decrease international tensions. One side recognizes mutual interests and initiates a small conciliatory act that opens the door for reciprocation by the other party
The tragic murder of Kitty Genovese outside her New York apartment stimulated social psychological research on
Altruism
People are less likely to give aid if an emergency occurs in the presence of many observers. This is known as
Bystander effect
Which theory suggests that altruistic behavior is governed by calculations of rewards and costs?
Social exchange theory
Which theory suggests that altruistic behavior is governed by calculations of rewards and costs?
social responsibility norm
Which theory suggests that altruistic behavior is governed by calculations of rewards and costs?
social trap