anatomy final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/142
Last updated 8:12 AM on 1/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
143 Terms
1
New cards
arteries
efferent vessels
2
New cards
veins
afferent vessels
3
New cards
artery
carry blood AWAY from heart
4
New cards
veins
carry blood TOWARDS the heart
5
New cards
capillaries
small thin vessels that connect arteries and veins
6
New cards
pulmonary circuit
carry blood to and from the heart and lungs
7
New cards
systemic circuit
carry blood to and from the heart and the rest of the body
8
New cards
aorta
where does blood leave your heart in systemic circuit
9
New cards
pulmonary trunk
where does blood leave your heart in pulmonary circuit
10
New cards
right atrium
what chamber receives deoxgenated blood from the systemic circuit and squeeze blood to the right ventricle
11
New cards
right ventricle
what chamber receives deoxgenated blood from the right atrium and pumps it to the pulmonary arteries
12
New cards
left atrium
chamber that received oxygenated blood from the pulmonary arteries and squeezes down to the left ventricle
13
New cards
left ventricle
receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium and pumps blood to the aorta and systemic arteries
14
New cards
learn learn learn
diagram
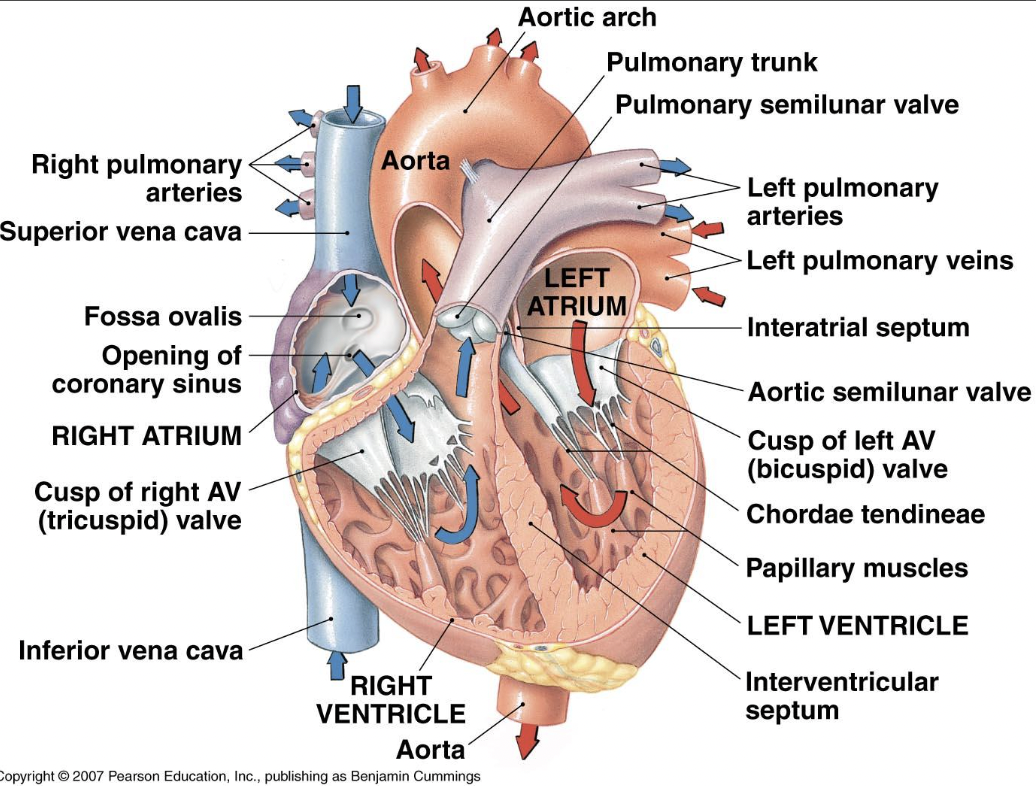
15
New cards
thoracic cavity
what cavity is the heart in
16
New cards
pericardium
serous membrane the lines the pericardial cavity
17
New cards
endocardium, myocardium, epicardium
three layers of heart (innermost → outermost)
18
New cards
epicardium
covers outer surface of heart (epithelium and loose connective tissue)
19
New cards
myocardium
muscular layer of heart
20
New cards
endocardium
innermost layer of heart
21
New cards
auricles
deflated atria
22
New cards
sulci
grooves filled w fat (coronary, anterior/posterior interventricular sulci)
23
New cards
base
superior heart - where all major blood vessels come in/leave
24
New cards
apex
anterior point of heart
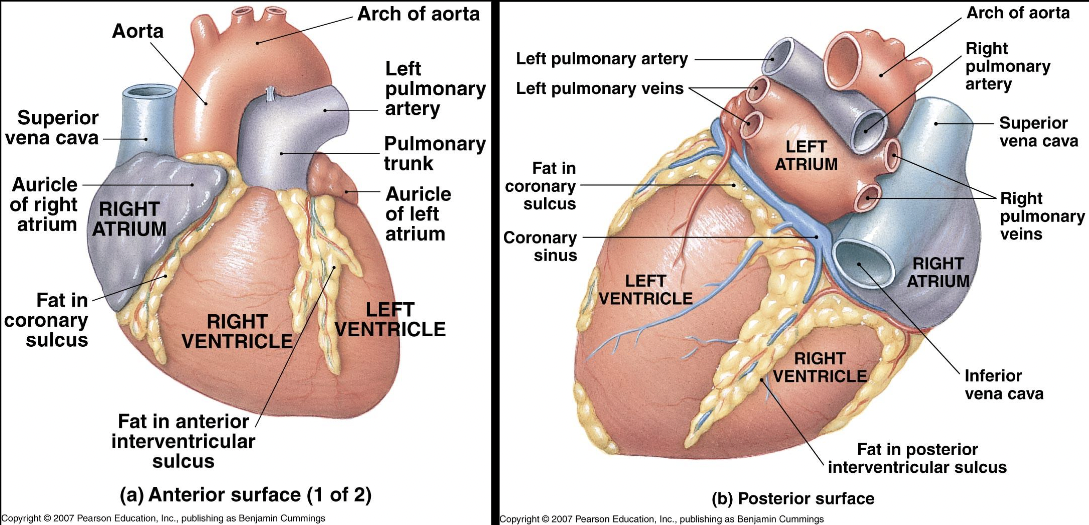
25
New cards
atrioventricular valves
prevent backflow of blood in ventricles to the atrium
26
New cards
tricuspid valve
right AV valve
27
New cards
bicuspid/mitral valve
left AV right
28
New cards
know this
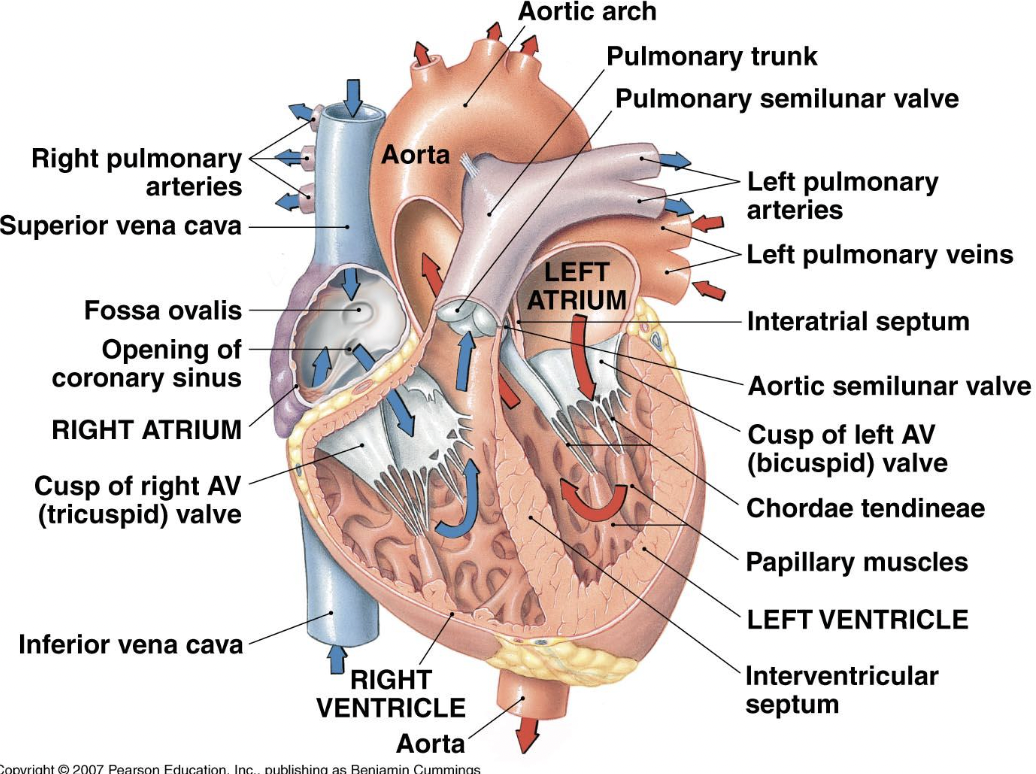
29
New cards
myocardial infarction (heart attack)
when coronary circulation gets blocked and cardiac muscle cells die
30
New cards
nodal cells
contracting cells that establish a rate of contraction aka pacemakers (ex. SA node and AV node)
31
New cards
conducting cells
relay a contractile stimulus to the myocardium (Ex. bachmann’s, left/right bundles, bundle of his)
32
New cards
bradycardia
condition where heart rate is slower than normal
33
New cards
tachycardia
condition where heart rate is faster than normal
34
New cards
ectopic pacemaker
“out of place” abnormal cells start their own action potentials and clash with SA/AV node
35
New cards
systole
contracting (squeezing blood out of) the chamber
36
New cards
diastole
relaxation (filling up with blood) of chamber
37
New cards
AV valves shutting
“Lubb” sound is “lubb dub” heart beat
38
New cards
Semilunar valves shutting
“dub” sound in “lubb dub” heart beat - aka ventricular diastole
39
New cards
cardiac output (CO)
stroke volume (SV) x heart rate (HR)
40
New cards
parasympathetic innervation
lowers HR and SV
41
New cards
sympathetic innervation
raises HR and SV
42
New cards
right atrium → tricuspid → right ventricle → pulmonary semilunar valve → pulmonary trunk → pulmonary arteries → pulmonary arterioles → pulmonary capillaries → pulmonary venules → pulmonary veins → left atrium → bicuspid → left ventricle → aortic semilunar valve → aorta → aortic arch → systemic arteries → systemic arterioles → systemic capillaries → systemic venules → systemic veins → inferior/superior vena cavas
blood flow order
43
New cards
ingestion, mechanical/chemical digestion, secretion, absorption, excretion
digestive functions
44
New cards
mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, serosa
4 layers of the alimentary canal
45
New cards
peristalsis
waves of muscular contraction to push food through canal
46
New cards
segmentation
churns material aka mechanical mixing
47
New cards
lysozome
enzyme that kills bacteria
48
New cards
3
how many salivary glands?
49
New cards
paritoid, submandibular, sublingual
name three salivary glands
50
New cards
clear fluid high in salivary amylase
what kind of saliva does parotid salivary gland produce?
51
New cards
more viscous cause of mucus
what kind of saliva does submandibular salivary gland produce?
52
New cards
very viscous with alot of mucus
what kind of saliva does sublingual salivary gland produce?
53
New cards
mastication
chewing - first sight of mechanical digestion
54
New cards
deglutition
swallowing
55
New cards
enzymes in salivary glands
first chemical digestion in digestive system?
56
New cards
deciduous teeth
aka baby teeth
57
New cards
chisel/cutting
incisors meant for?
58
New cards
tearing
canines (cuspids) meant for?
59
New cards
grinding
premolars/molars meant for?
60
New cards
vestibule
space between the teeth and the gums?
61
New cards
enamel
What is the tooth covered by above the gums?
62
New cards
cementum
What is the tooth covered by below the gums?
63
New cards
10 inches
length of esophagus?
64
New cards
proteins
what does the stomach mainly digest?
65
New cards
temporary storage of food, mechanical/chemical breakdown, produces intrinsic factor
functions of stomach
66
New cards
cardia, fundus, body, pylorus
4 regions of stomach
67
New cards
fundus and body of stomach
parietal cell location
68
New cards
fundus and body of stomach
chief cells location
69
New cards
produce pepsinogen
what do the chief cells produce?
70
New cards
HCl and intrinsic factor
what do the parietal cells produce?
71
New cards
mucus layer, comes from mucosal cells
how does the stomach protect itself and where does it come from?
72
New cards
nutrients
what do small intestines digest?
73
New cards
water
what do large intestines digest?
74
New cards
intestinal glands
where does intestinal hormones come from?
75
New cards
stimulates pancreas to release insulin if chyme has too much glucose
what does GIP do in intestines?
76
New cards
stimulates liver to make bile to reduce hunger feeling and digest fats/proteins
what does CCK do in intestines?
77
New cards
responds to low pH by stimulating bile and sodium bicarbonate to neutralize stomach acid.
what does secretin do in intestines?
78
New cards
stimulates enzyme and acid production if chyme has a lot of large undigested proteins
what does gastrin do?
79
New cards
breaks down fats, neutralizes stomach acid, etc.
what does bile do?
80
New cards
pancreas
where does sodium bicarbonate come from?
81
New cards
neutralize stomach acid
why does sodium bicarbonate do?
82
New cards
liver
where is bile made?
83
New cards
galbladder
where is bile stored?
84
New cards
hepatic, cystic, common
3 ducts for bile
85
New cards
cystic duct
carries bile to the gallbladder
86
New cards
common bile duct
carries bile to the duodenum
87
New cards
common bile duct
where all the bile ducts meet up
88
New cards
circular and longitudinal muscularis externa
what muscles line the alimentary canal
89
New cards
oblique
what extra muscularis externa layer is found in the stomach
90
New cards
duodenum, jejunum, ileum
3 parts of small intestine
91
New cards
10 in
how long is duodenum?
92
New cards
8 ft
how long is jejunum?
93
New cards
12 ft
how long is ileum?
94
New cards
21 ft
how long is small intestine?
95
New cards
duodenum
most enzymatic digestion?
96
New cards
jejunum
most absorption?
97
New cards
CCK
what hormone stimulates bile secretion?
98
New cards
absorption, surface area
function of villi, microvilli, and plicae is?
99
New cards
metabolic regulation, hemotologic regulation, bile production,
4 functions of liver
100
New cards
nasophyrnx, orophryrnx, hypophrynx
three areas of phyrnx