5. Sociality & Cooperation
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
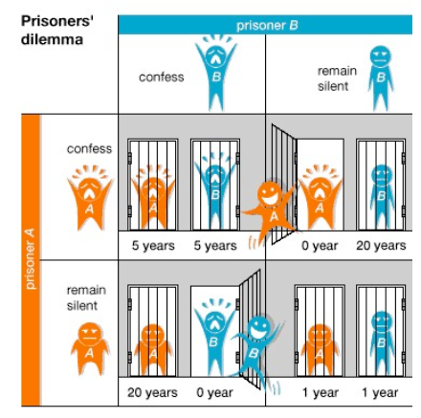
Altruism puzzle
Why help others at a cost
Kin selection
Helping relatives
Hamilton’s rule
Altruism can evolve when helping relatives is genetically “worth it” despite personal costs.
Direct reciprocity
I help you, you help me
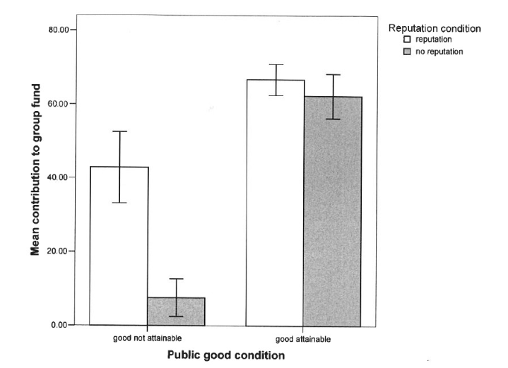
Indirect reciprocity
Reputation-based helping
Meat sharing importance
High risk, high reward, rapid decay
Foraging skill development
Long learning period requires cooperation
Human cooperation uniqueness
Scope, scale, and variation
Scope of cooperation
Helping non-kin and strangers
Scale of cooperation
Large groups and societies
Variation in cooperation
Differences across cultures
Hadza cooperation
Group norms determine behavior
Norm following
Individuals adjust to group behavior
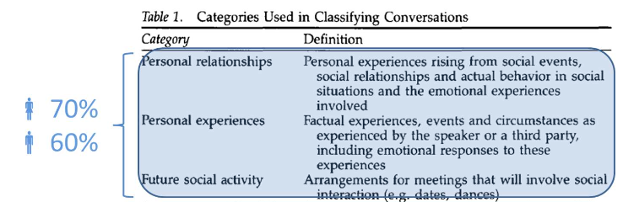
The Gossip Hypothesis (Dunbar)
Talking about others helps track behavior, share social info, and catch free riders.
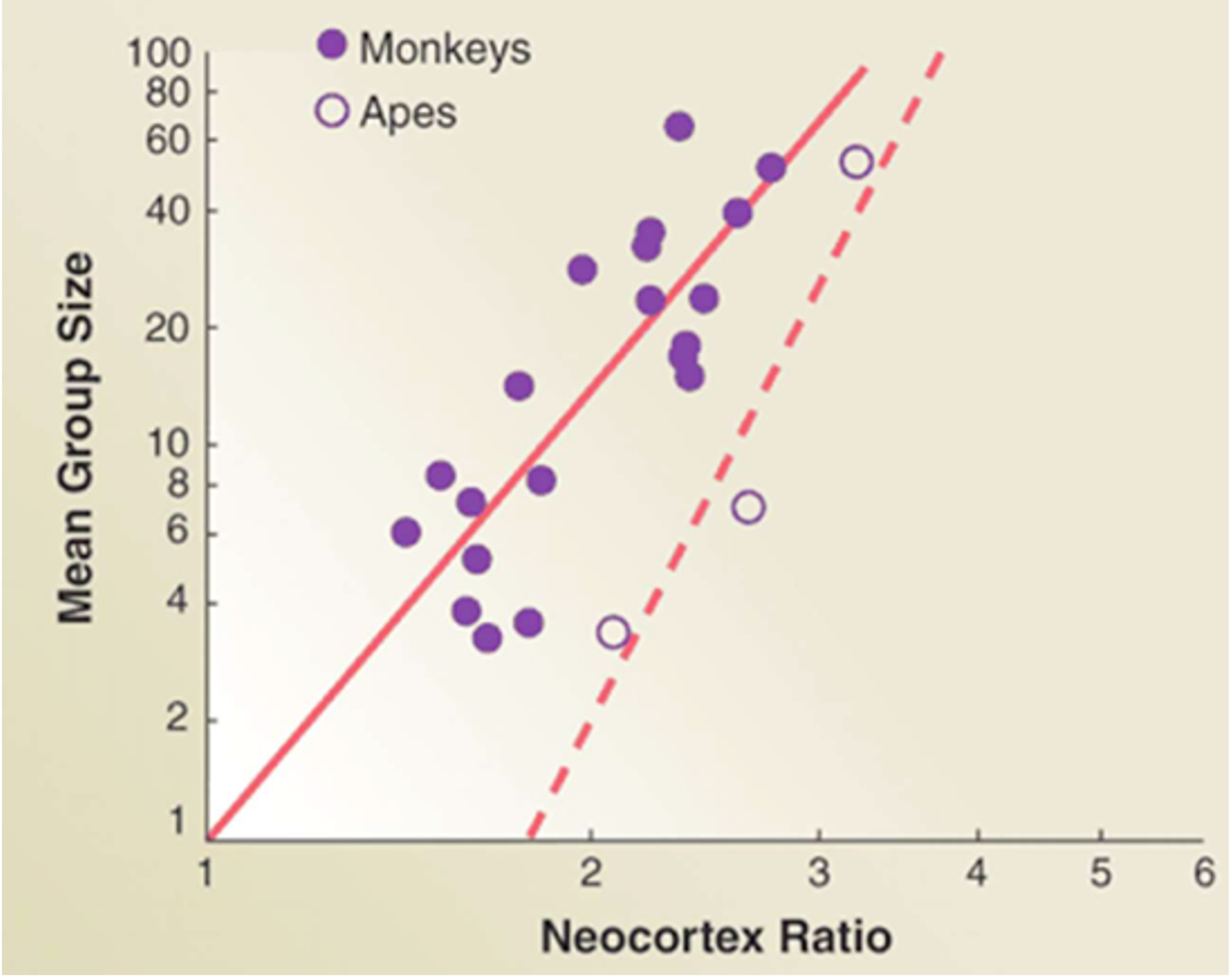
The Social Brain Hypothesis (Dunbar)
Humans evolved their large neocortices for dealing with social complexity.
Spillover Hypothesis
Cooperation in small groups spills over into large societies.