Active and Passive Transport
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
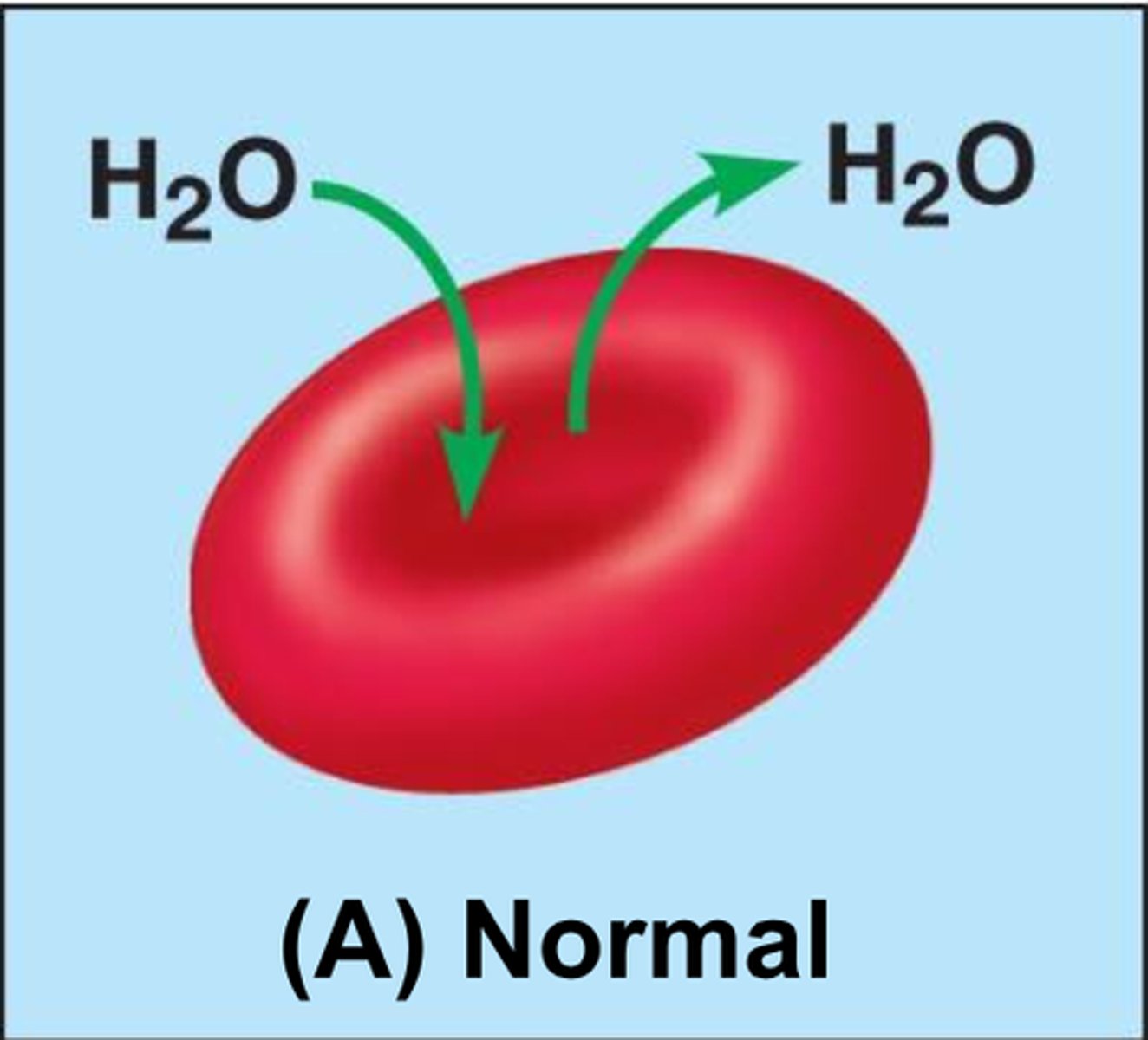
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
semipermeable
some substances can pass across and others cannot
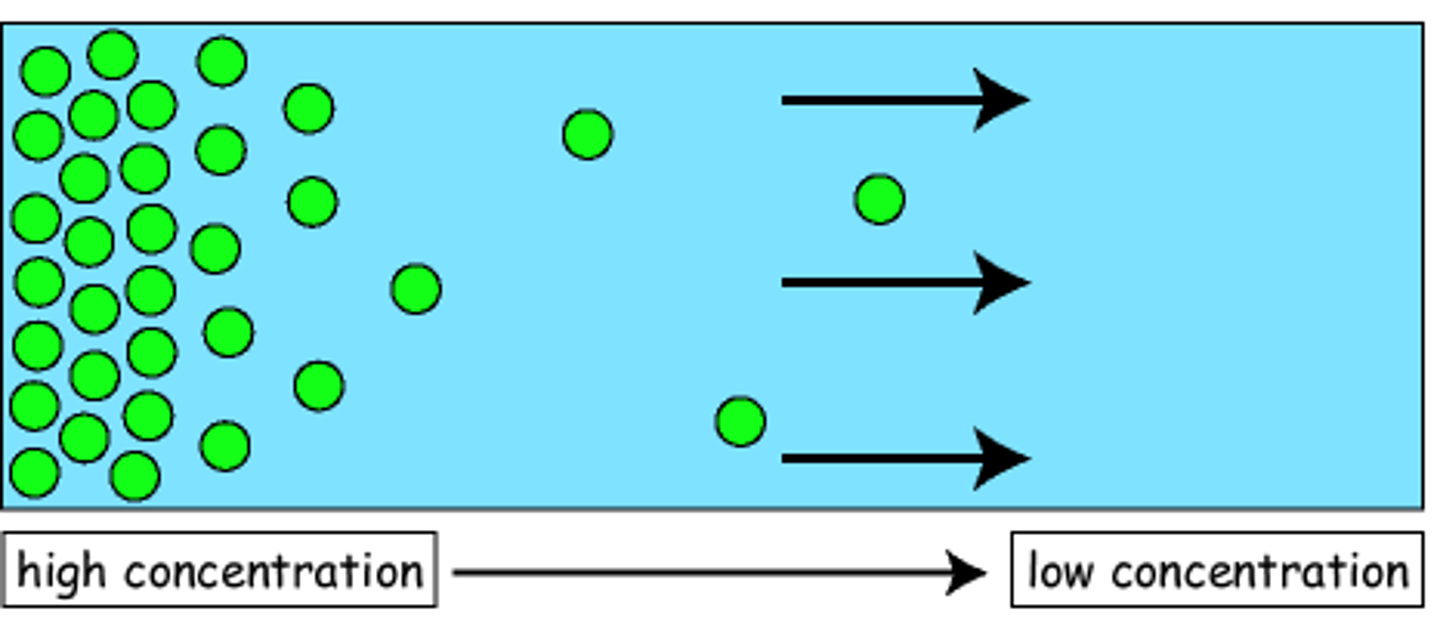
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
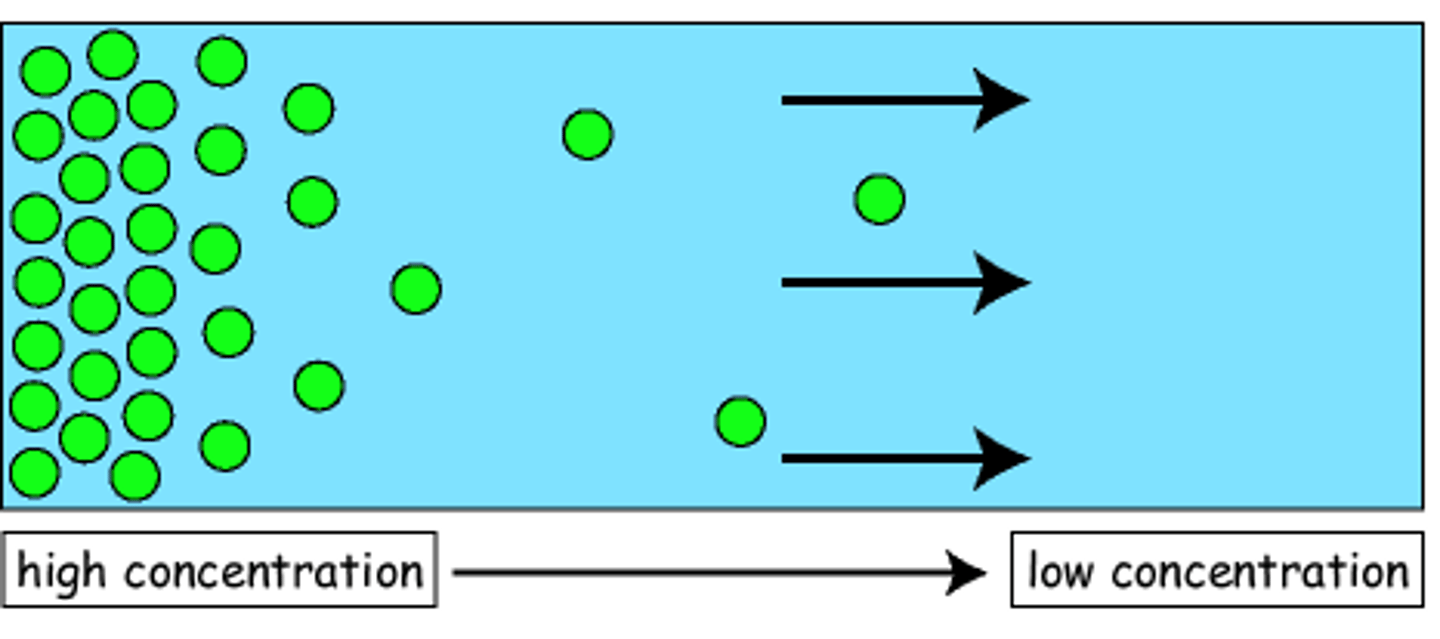
High Concentration
when molecules are more crowded in one area compared to another
low concentration
when molecules are less crowded in one area compared to another
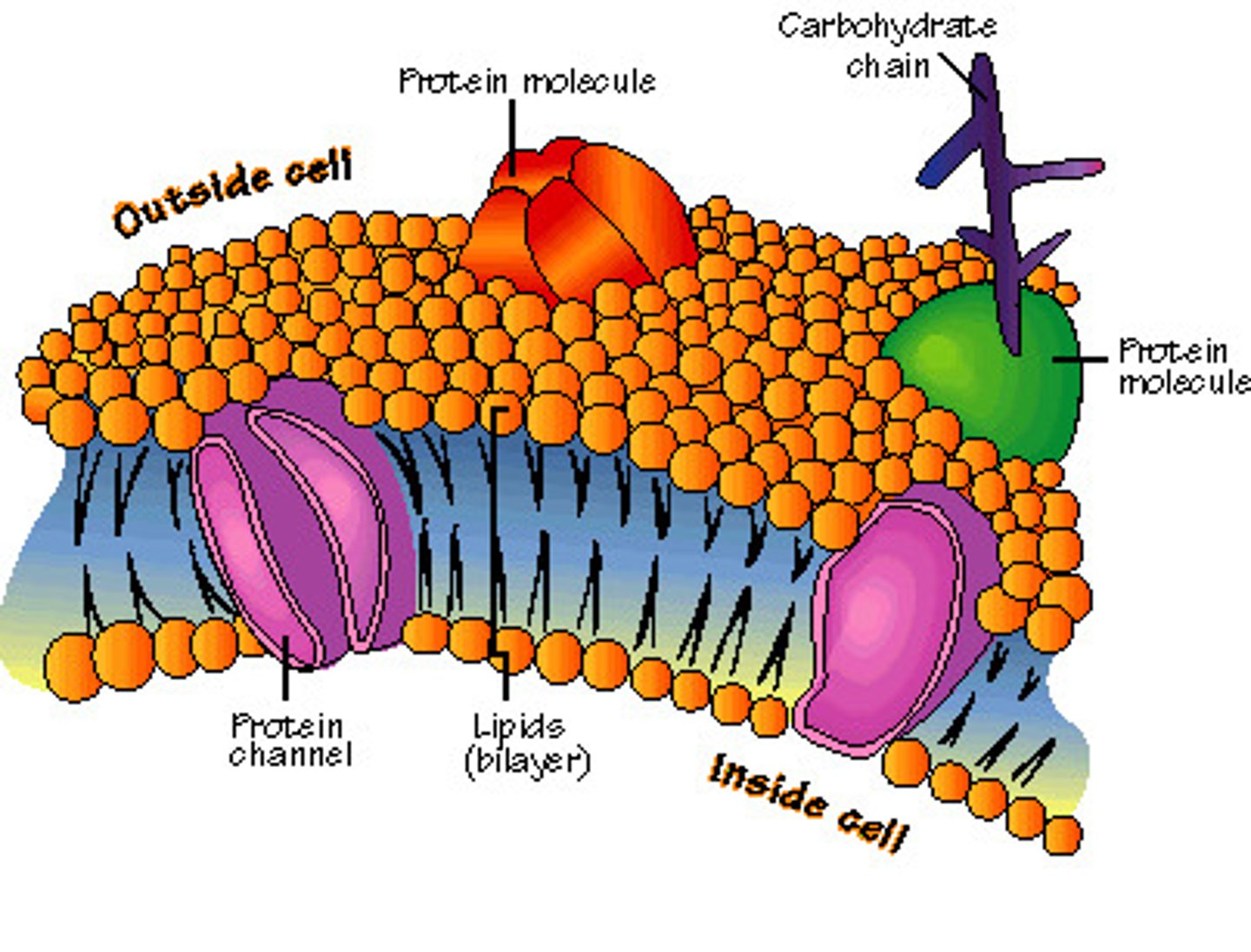
Cell Membrane
thin, flexible layer around a cell; regulates what enters and leaves the cell
Passive Transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell
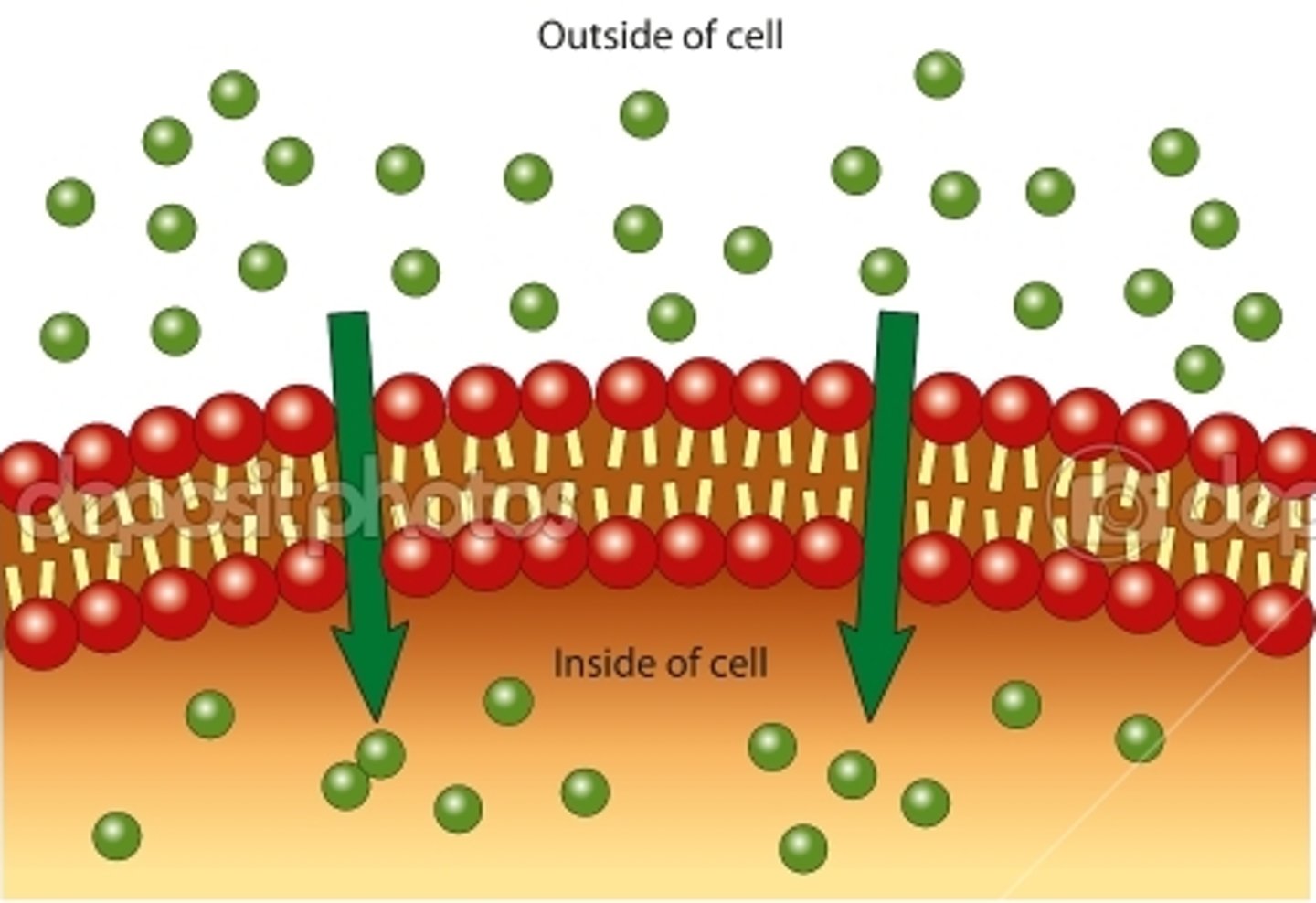
Three types of Passive Transport
osmosis, diffusion, facilitated diffusion
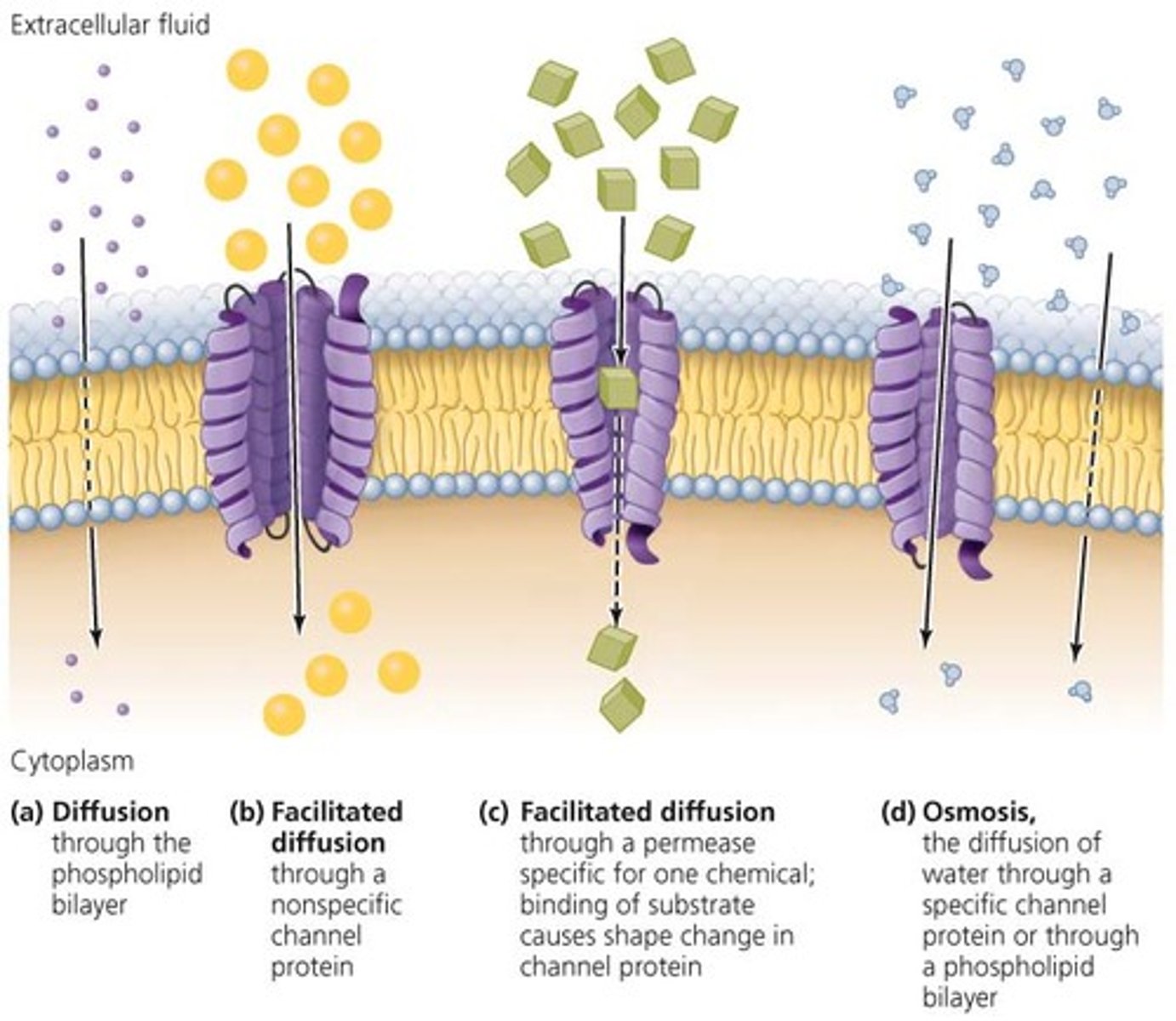
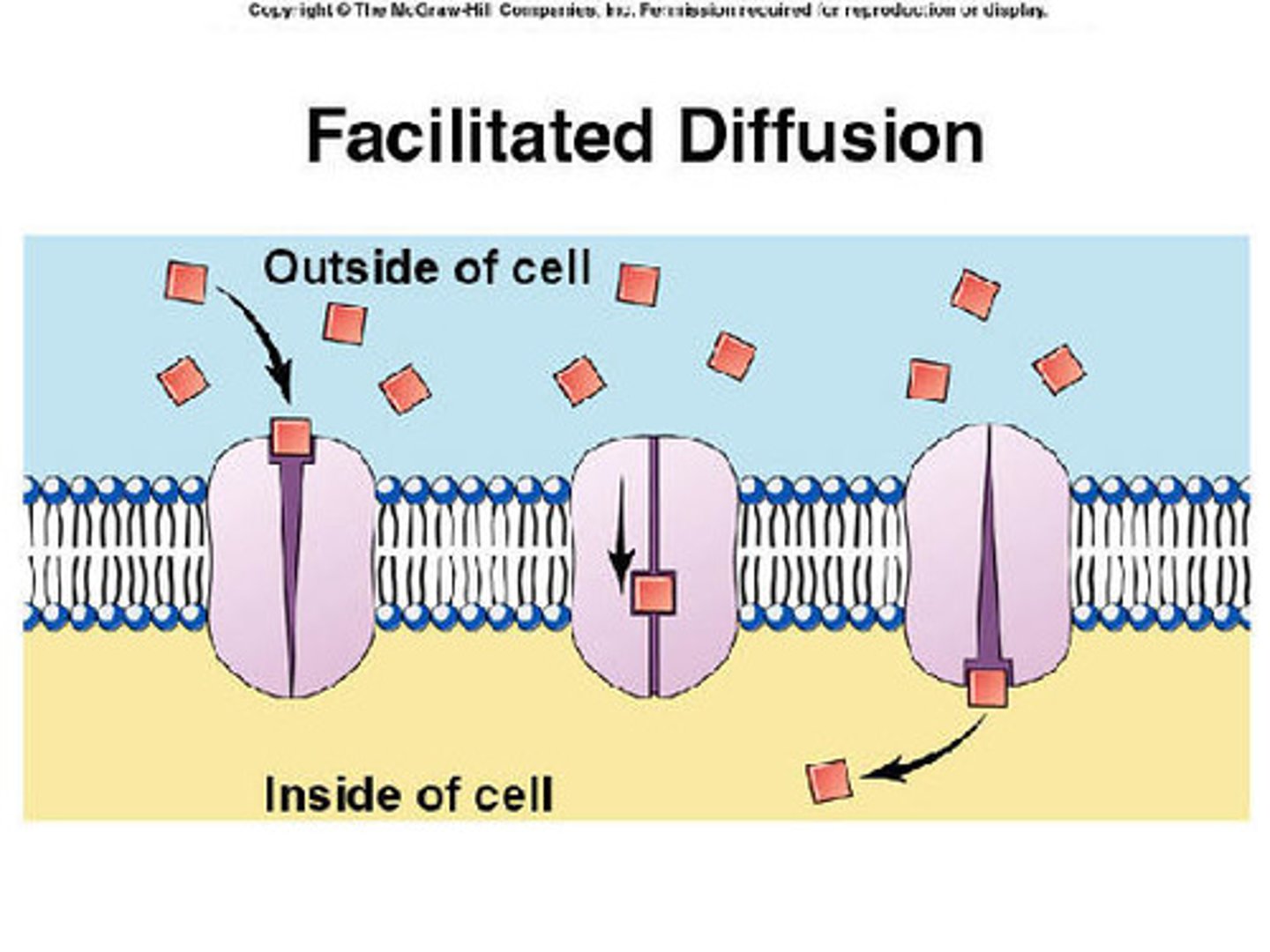
Facilitated diffusion
Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels
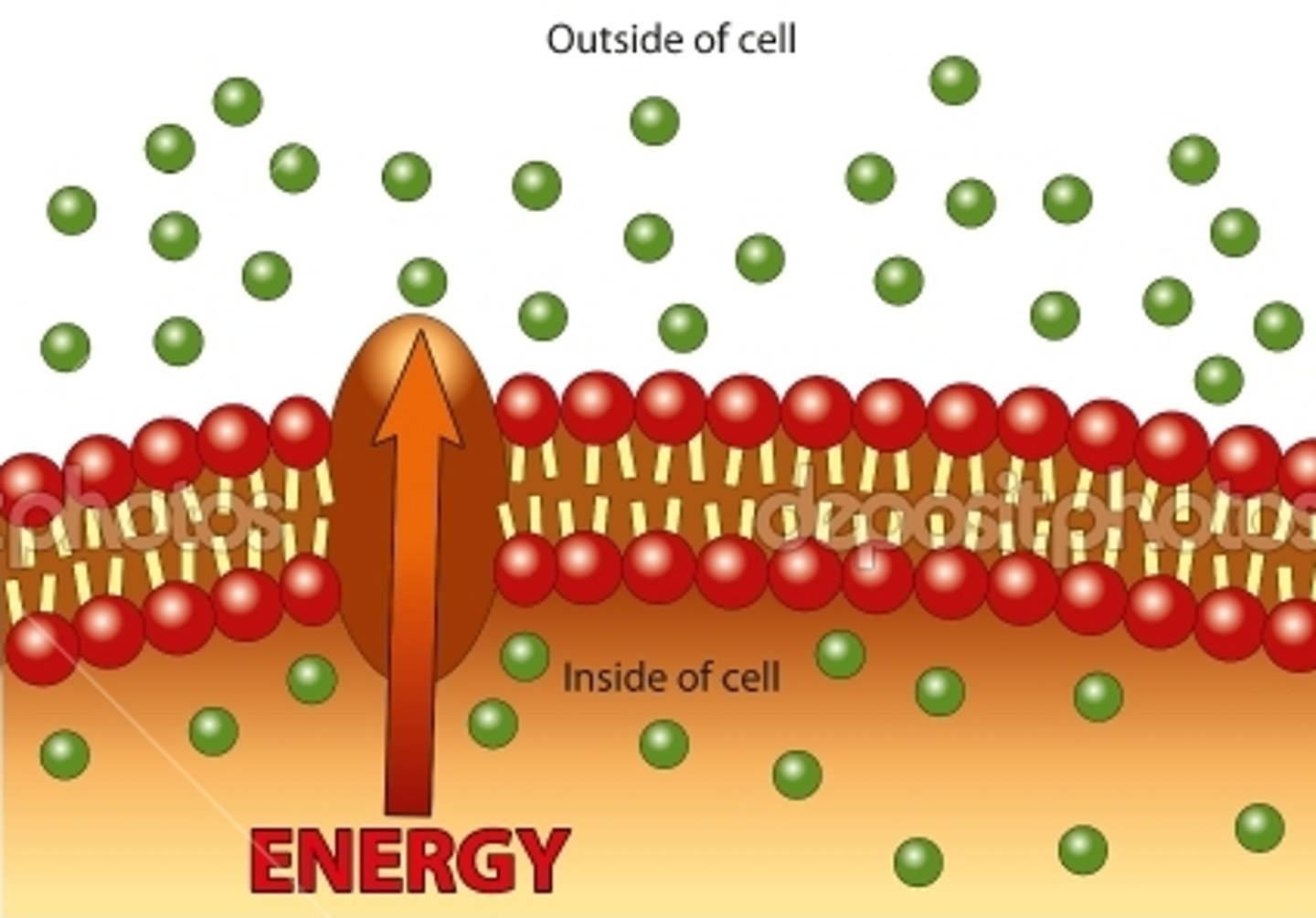
Active Transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference (low to high concentration)
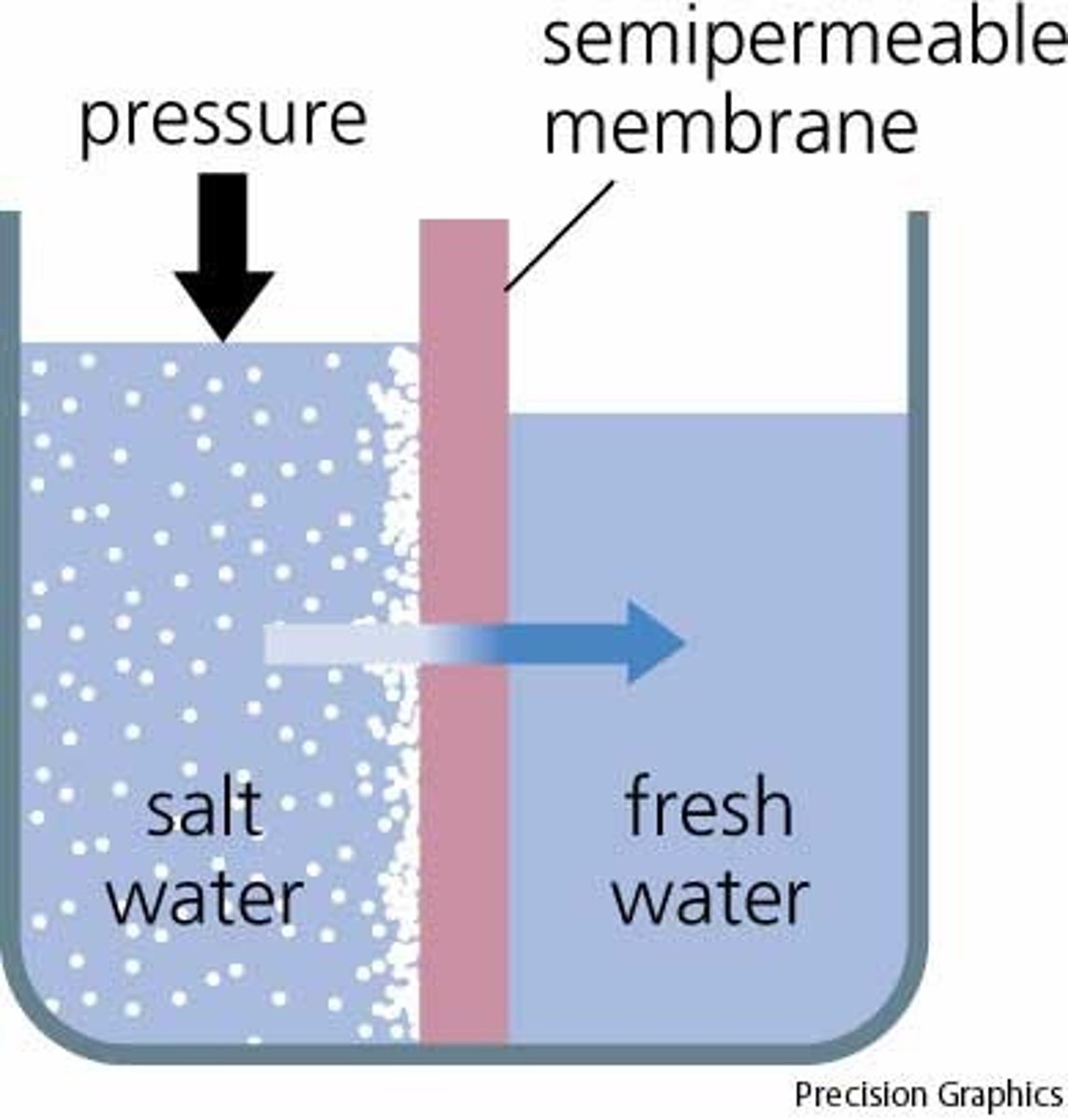
osmosis
When water molecules move across a membrane from a high concentration to a low concentration.
diffusion
molecules crossing the membrane from a high concentration to a low concentration
Equilibrium
when the concentration of the solute is the same on both sides of the membrane
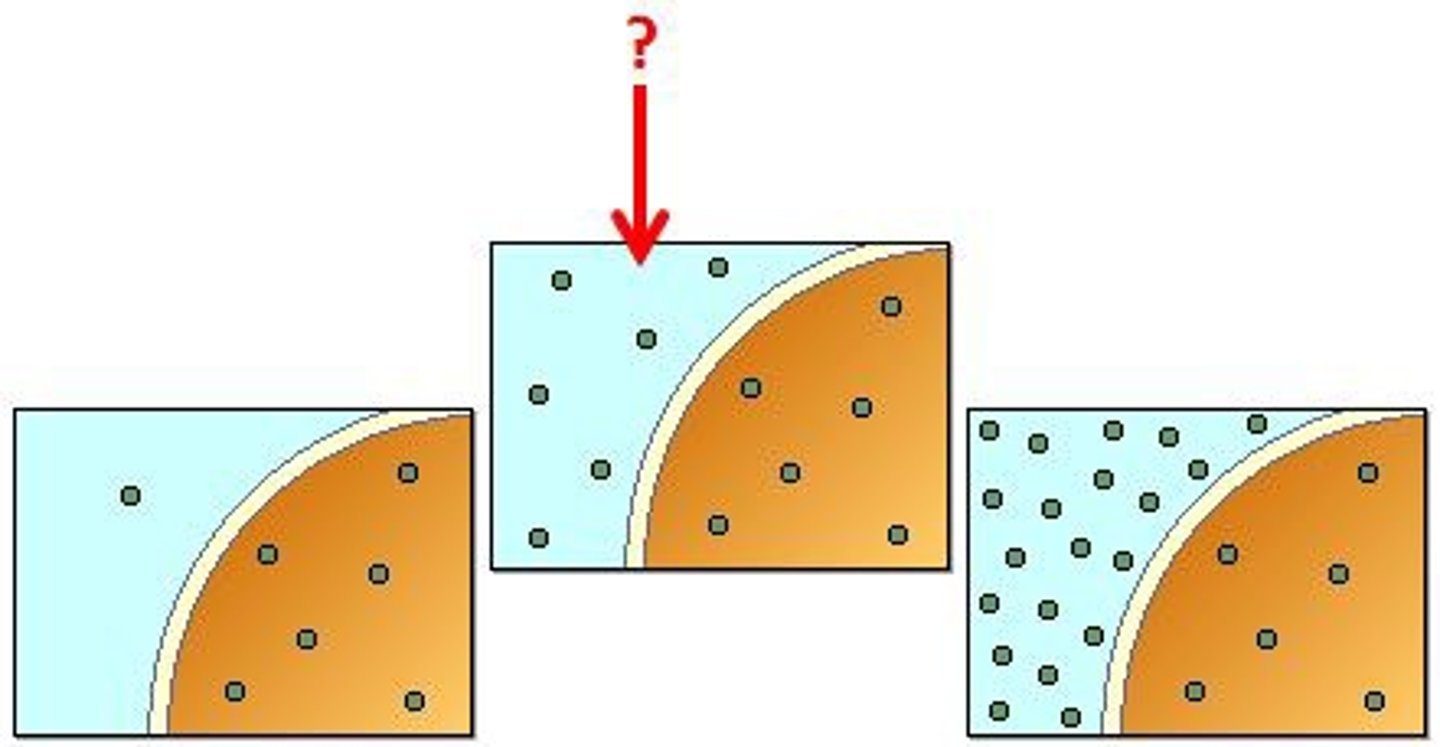
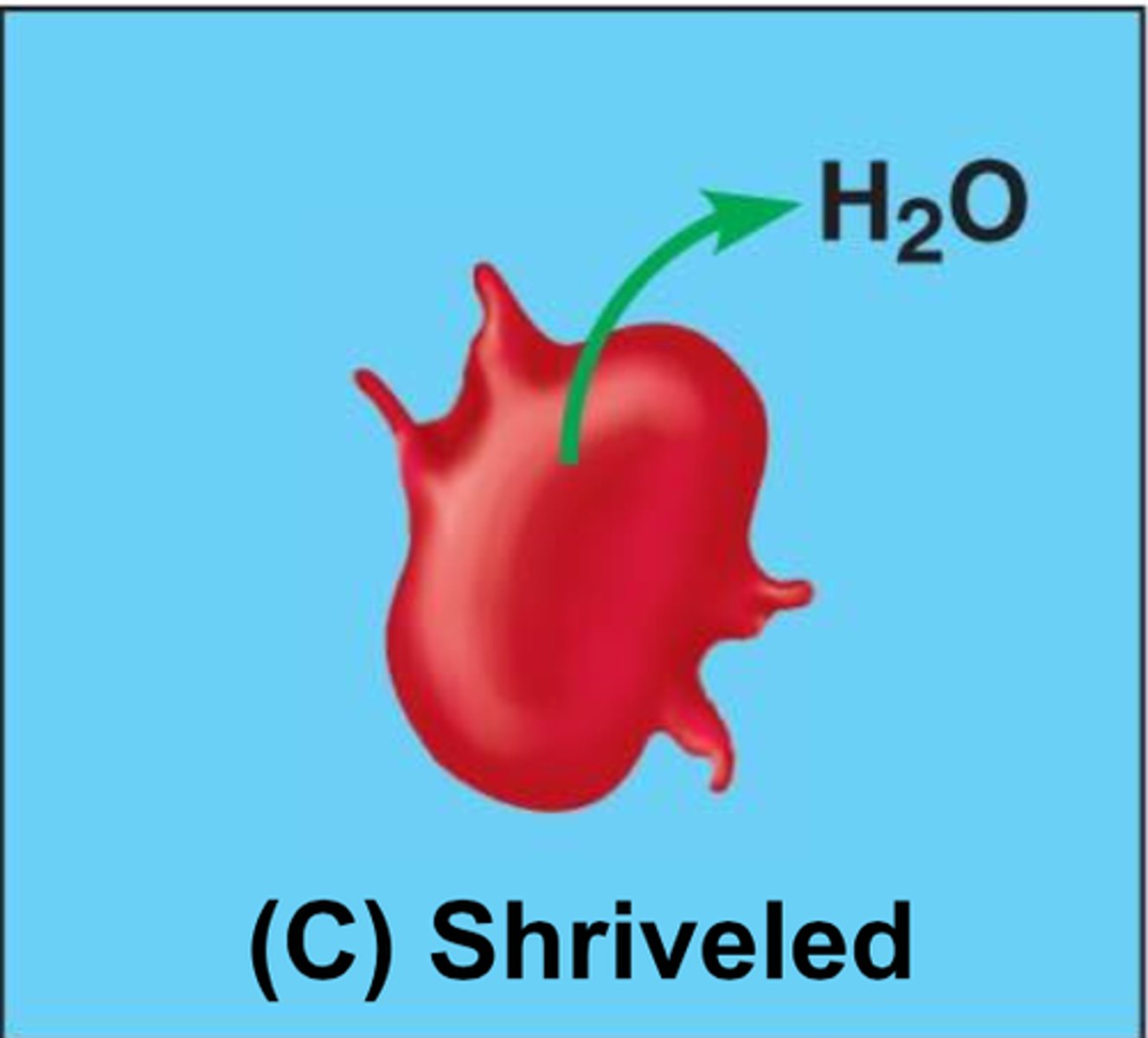
Hypertonic
Having a higher concentration of solute than another solution.
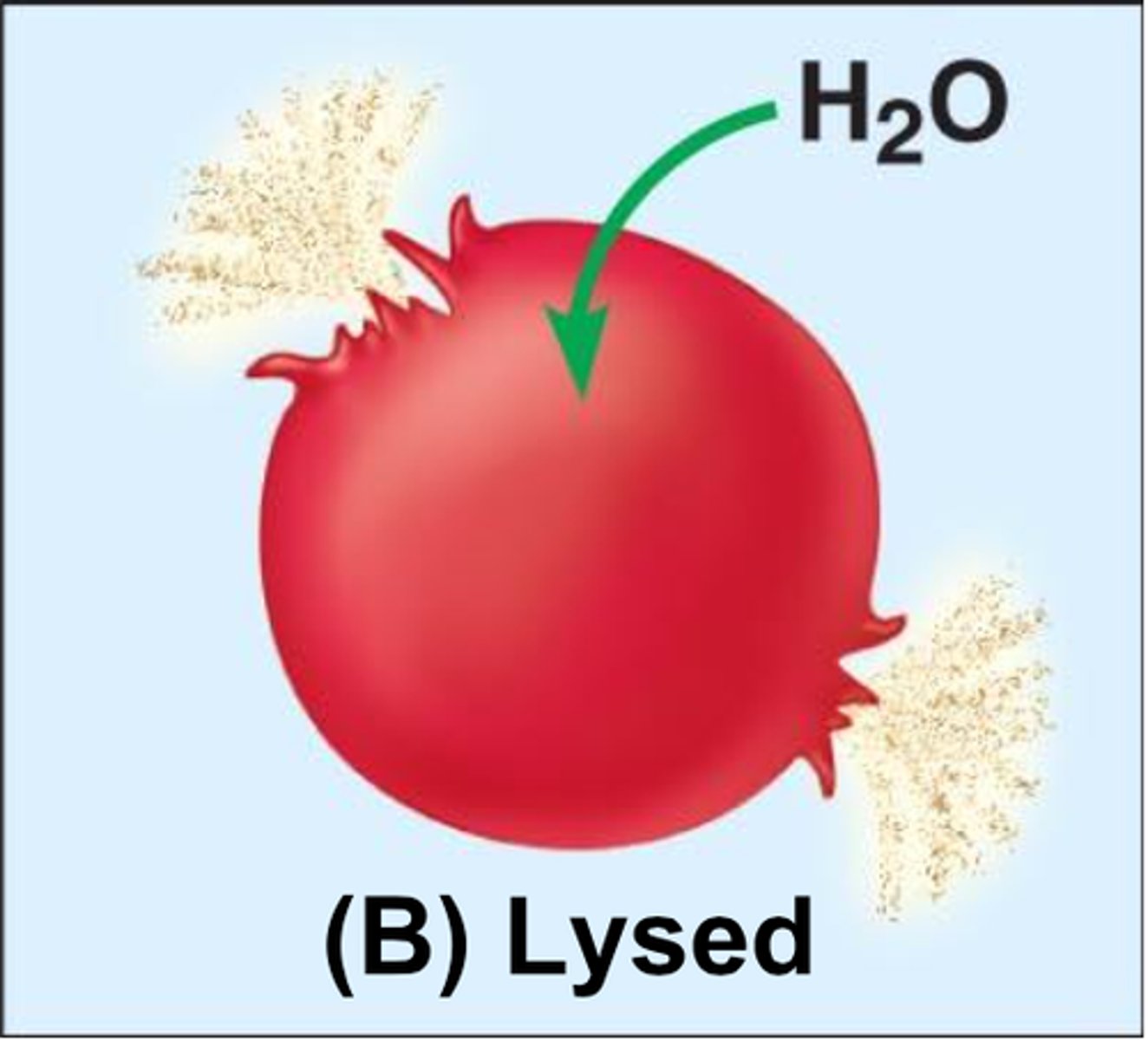
Hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute than another solution
Isotonic
when the concentration of two solutions is the same
Endocytosis
process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane
Phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which a cell engulfs large particles or whole cells
Pinocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which the cell ingests extracellular fluid (or small particles) and its dissolved solutes.
Exocytosis
a process by which the contents of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior through fusion of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane.
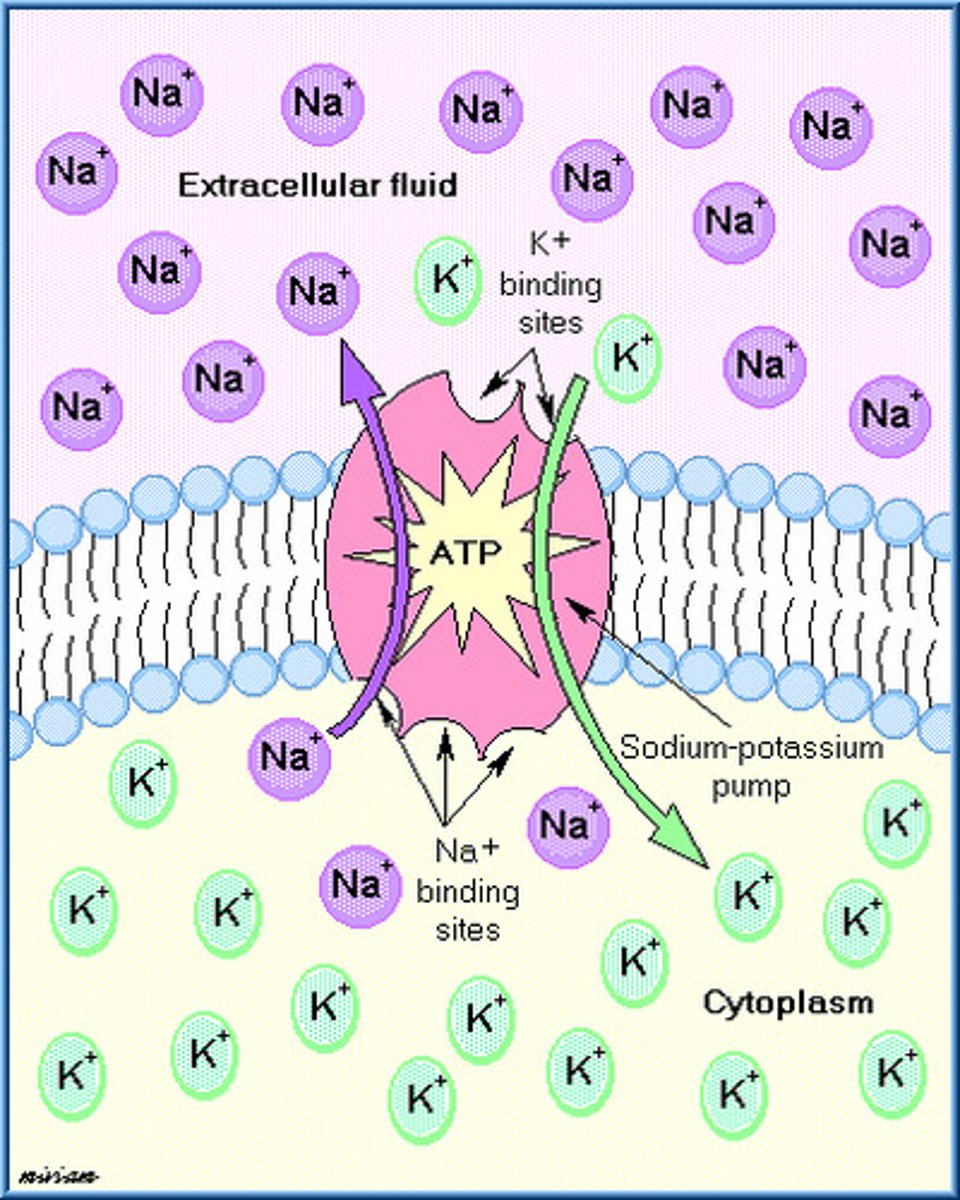
sodium-potassium pump
a carrier protein that uses ATP to actively transport sodium ions out of a cell and potassium ions into the cell
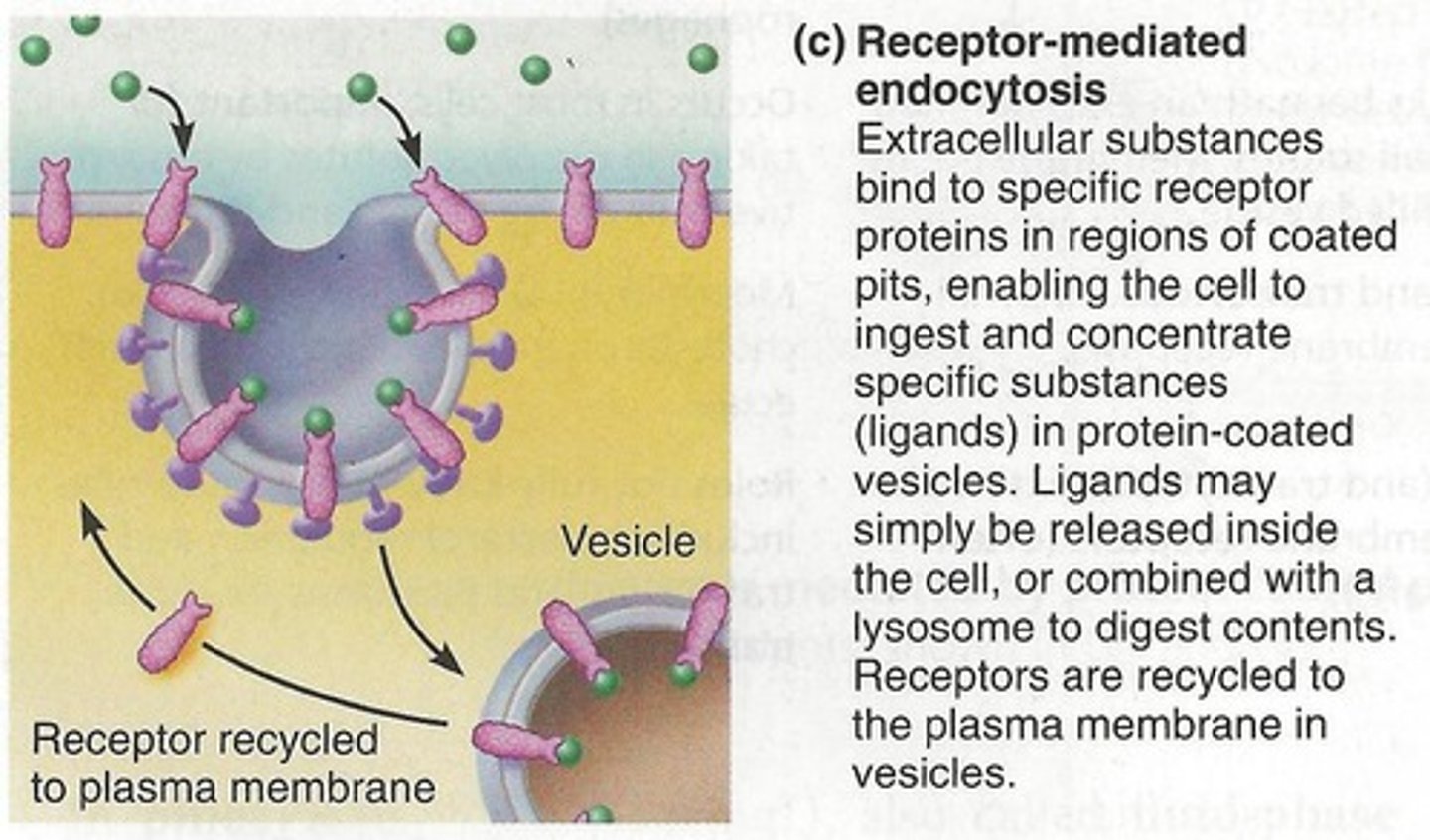
receptor-mediated endocytosis
The bulk transport of substances into a cell, that are only allowed into the cell if the substance can fit into the cell's receptors.