High-Risk Pregnancy
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Identifying a High-Risk Pregnancy
Nurses should be aware of biophysical, psychosocial, sociodemographic, and environmental risk factors.
Early identification and intervention are crucial.
hyperglycemia
macrosomia
A fetus or newborn who is larger than average (4,000 to 4,500 g [9 to 10 lb]
congenital anomalies
cesarean birth
fetal demise
possible by hyperglycemia
hypoglycemia
can lead to lethargy, apnea, seizure disorders, brain damage
dizziness
polyhydramnios
Excessive amount of amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus in pregnancy.
uteroplacental insufficiency
A syndrome in which the placental vascular remodeling fails, impairing placentation and causing acidosis and fetal hypoxia.
fetal growth restriction (FGR)
Fetal weight less than the 10th percentile, as estimated via ultrasound.
asthma
increases risk of preeclampsia & need for surgical birth
chorioamnionitis
An infection within the amniotic sac.
endometritis
An infection in the lining of the uterus.
thyroid dysfunction
placental abruption→Occurs when the placenta detaches from the uterine wall.
myxedema→An extreme form of hypothyroidism.
preterm labor
hypothyroidism = related to
Obstetrical Disorders
Repeated pregnancy loss, uterine fibroids, history of surgical birth, and multifetal pregnancies increase risk for complications.
uterine fibroids→Benign tumors inside the uterus.
placenta previa→Occurs when the placenta is covering the cervical os, either partially or completely.
postpartum hemorrhage→Cumulative blood loss greater than 1,000 mL with manifestations of hypovolemia within 24 hr of birth, regardless of the route of birth.
myomectomy→Surgical removal of fibroids.
uterine rupture→A full tear in the uterus' three layers. It most frequently takes place during a trial of labor that follows a previous surgical birth.
hysterectomy→Surgical removal of all or part of the uterus.
cerebral palsy→A disorder affecting movement and coordination as a result of brain damage at or prior to birth.
Von Willebrand Disease
no clotting factors as they should
Etiology
Hereditary bleeding disorder with varying severity across three types.
Epidemiology
Affects a small percentage of the population, with Type 1 being the most common.
Comorbidities
Type 3 VWD associated with higher risk of PPH.
Clinical Manifestations
Unexplained bruising
Bleeding & heavy menstrual flow.
Nursing Interventions
Monitor for bleeding and manage intake and output.
Medical Management
Treat with antihemophilic factor, blood transfusions, and cryoprecipitate as needed
Psychosocial Factors
A person's psychological and/or social well-being can be affected by psychosocial circumstances. These elements might include social factors such as peer relationships, family circumstances, work or school colleagues, or traumatic experiences. Psychological factors may include self-esteem, emotional intelligence and temperament, and coping skills.
Psychosocial factors can significantly impact pregnancy outcomes.
These factors may be modifiable (e.g., substance use) or non-modifiable (e.g., genetic mental health disorders).
Regular prenatal care is crucial for identifying and managing these risks.
Tobacco Use
smoking = vasoconstriction = not much blood for fetus
Increases risk of SUID, birth defects, LBW, preterm birth, neonatal cleft lip.
Carbon monoxide and nicotine from tobacco can harm fetal development.
E-cigarettes also pose risks due to nicotine and other chemicals.
Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome
Caffeine Use
High intake can limit oxygenated blood to the fetus, affecting growth.
Recommended intake is 200 mg or less per day.
Energy drinks are discouraged due to variable caffeine levels and other harmful ingredients.
Caffeine in Common Foods and Drinks
Brewed regular coffee (8 oz): 80 to 200 mg
Instant coffee (8 oz): 75 mg
Decaf coffee (8 oz): 2 to 15 mg
Brewed tea (8 oz): 15 to 60 mg
Instant tea (8 oz): 26 to 36 mg
Caffeinated soft drinks (12 oz): 30 to 45 mg
Hot cocoa mix (3 tsp): 8 to 12 mg
Chocolate milk (8 oz): 5 to 8 mg
Dark chocolate (1.45 oz): 30 mg
Milk chocolate (1.55 oz): 11 mg
Semi-sweet chocolate chips (1/4 cup): 26 to 28 mg
Use of Alcohol or Drugs
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders
A spectrum of manifestations, which includes medical issues, behavioral issues, and learning difficulties, that can affect a person who was exposed to alcohol before birth.
Alcohol use can lead to FASDs, spontaneous abortion, LBW, fetal demise, and long-term disabilities.
No alcohol consumption is recommended during pregnancy.
Substance use, including OTC and prescription medications, as well as recreational drugs, can cross the placenta and harm the fetus.
Risks include fetal demise, neonatal withdrawal, birth defects, preterm birth, and SUID.
Mental Health
Perinatal mental health conditions, including anxiety and depression, affect up to 20% of pregnant clients.
Symptoms can interfere with daily functioning and negatively impact pregnancy outcomes.
Untreated conditions increase the risk of preterm birth, LBW, fetal demise, and maternal morbidity.
Long-term effects on infants include poor attachment, behavioral issues, and delayed development.
Age
Adolescent pregnancy and advanced maternal age (AMA) are associated with increased risks.
35 years
Adolescents face higher rates of PPROM, preeclampsia, STIs, anemia, and maternal death.
AMA clients have increased risks of gestational diabetes, ectopic pregnancy, placenta previa, and fetal anomalies.
Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes (PPROM)→The rupture of the amniotic membranes before term or 37 weeks of gestation.
Apgar Score
Evaluation of neonate’s overall condition at birth by a registered nurse or provider. Scoring is based on the following parameters: activity, pulse, grimace, appearance, and respiration. The test is usually performed twice (at 1 min and 5 min of life).
Apgar Score
Evaluation of neonate’s overall condition at birth by a registered nurse or provider. Scoring is based on the following parameters: activity, pulse, grimace, appearance, and respiration. The test is usually performed twice (at 1 min and 5 min of life).
Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes (PPROM)a
The rupture of the amniotic membranes before term or 37 weeks of gestation.
Parity
Multiparous clients have higher risks of placenta previa, gestational hypertension, preterm birth, and postpartum hemorrhage.
multiparous→Two or more viable pregnancies defined as lasting at least 20 weeks.
gestational hypertension→Systolic blood pressure reading of 140 mm Hg or higher and/or diastolic blood pressure of 90 mm Hg or higher on at least two occasions, 4 hr apart, after 20 weeks of gestation, in clients who previously presented with expected blood pressure readings, with blood pressure readings returning to expected values during the postpartum period.
nulliparous→A client who has never given birth.
primiparous→A client experiencing a first pregnancy that has reached at least 20 weeks gestation.
Social Determinants of Health
Community and environmental factors can impact pregnancy outcomes.
Stress, lack of social support, and financial instability can lead to complications like preeclampsia.
Race and Ethnicity
Health disparities and inequities affect pregnancy outcomes in non-White communities.
Higher rates of pregnancy-related death, preterm birth, and LBW in Black, Indigenous, and NHOPI populations.
Cultural Beliefs and Practices
Diverse sociocultural values and practices may influence medical treatment and pregnancy outcomes.
Nurses should respect and accommodate clients' beliefs while ensuring safe care.
Access to Care
Barriers include lack of coverage, distance to services, transportation, and provider availability.
Inadequate prenatal care due to these barriers increases pregnancy risks.
Environmental Factors
A person's exposure to chemicals or industrial waste where they live or work, such as lifestyle choices (such as smoking or a poor diet) that can raise a person's risk of disease, or stressful conditions (such as racism).
Conditions or substances in the environment that can negatively impact pregnancy outcomes.
Include lead exposure, medication use, animal exposure, toxoplasmosis, food limitations, and activity restrictions.
Maternal and familial characteristics that can lead to high-risk pregnancies.
Include maternal age, number of pregnancies, social determinants of health, ethnicity, race, access to care, and cultural beliefs.
Lead Exposure
Accumulation in bones released into blood during pregnancy.
Can lead to spontaneous abortion, small for gestational age, preterm birth, and developmental issues in the fetus.
Effect of Lead Exposure on the Growing Fetus
Small for gestational age
Low birth weight
Preterm birth
Damage to renal system and other organs
Neurocognitive impairment
Behavioral impairment
Increased risk for ADHD
Fetal malformation
Encephalopathy
Impaired motor control
Medications During Pregnancy
Limited studies on medication use during pregnancy.
Pregnant clients should consult with their provider before taking any medications.
Animal Exposure
Pets and exotic animals can carry diseases that may affect pregnancy.
Concerns include SARS, monkeypox, salmonella, and other pathogens.
Toxoplasmosis
Infection from contact with feline feces, unwashed vegetables, or undercooked meat.
Can cause neonatal blindness, deafness, and cognitive disabilities.
Avoiding Toxoplasmosis During Pregnancy
Cook meat to recommended temperatures and use a thermometer to ensure meat is thoroughly cooked.
Have someone else change the cat litter.
Wear gloves while working in the soil.
Wash and peel all fruits and vegetables. Avoid eating any food that may have been exposed to cat feces.
Food Limitations
Certain foods contain mercury or harmful bacteria that can affect fetal development.
Avoid high-mercury seafood, raw meats, and non-pasteurized foods.
Deli meats should be heated to prevent listeria exposure.
Activity Limitations
Saunas and hot tubs are not recommended due to the risk of birth defects from increased body temperature.
Exercise is generally encouraged but with limitations for certain conditions like preterm labor, multiple gestation, or cervical insufficiency.
cervical insufficiency →Dilatation of the cervix without labor, resulting in loss of the pregnancy.
Maternal Hypertension
Regular assessment for hypertensive disorders is essential.
Includes blood pressure measurement, urine testing for protein, and monitoring for edema, headaches, or vision changes.
Preeclampsia
HELLP Syndrome
H (hemolysis, the rupture of red blood cells), EL (elevated liver enzymes), and LP (low platelet count); a life-threatening complication often associated with preeclampsia.
Risks in pregnancy: it affects the liver, eyes, peripheral vessels, lungs, kidneys
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Multi-organ disorder that can affect pregnancy outcomes.
Risks include fetal loss, preeclampsia, preterm birth, and small-for-gestational-age neonates.
Manifestations:
Fatigue, headaches, fever, dizziness
Chest pain, difficulty breathing
Anemia, increased risk of blood clots
Numb, cold fingers & toes (Raynaud's Phenomenon)
Muscle pain
Hypotension
Hypertension, myocarditis, endocarditis, pericarditis
Nephritis
Joint pain
Manifestations of Lupus:
Fatigue, headaches, fever, dizziness
Chest pain, difficulty breathing
Anemia, increased risk of blood clots
Numb, cold fingers & toes (Raynaud's Phenomenon)
Muscle pain
Hypotension
Hypertension, myocarditis, endocarditis, pericarditis
Nephritis
Joint pain
Maternal Renal Disease
Increases the risk of maternal and fetal mortality.
Monitoring includes blood pressure, urine output, and serum creatinine levels.
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)→An episode of renal injury or failure with a rapid onset.
Fetal Risks:→fetal demise, neonatal death, preterm brith, SGA neonates, low-birth-weight infants
Cholestasis of Pregnancy
Monitoring includes liver function tests, bile acid levels, and fetal biophysical profiles.
Assessing for preeclampsia & performing maternal labs (gamma-glutamyl transferase, blood chemistry, total bilirubin levels, liver function tests, prothrombin time, and bile acid levels
cholestasis→sluggish or poor flow of bile through the biliary system
biophysical profile (BPP)→An ultrasound assessment, lasting a maximum of 30 min, that assesses fetal well-being and is paired with a fetal heart rate tracing.
Previous Fetal Demise
Increases the likelihood of future fetal demise.
Early and adequate prenatal care, genetic testing, and frequent fetal surveillance are recommended.
oligohydramnios→Less-than-typical amount of amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus in pregnancy.
intrahepatic cholestasis→A disease that hinders the liver cells' ability to excrete bile.
Decreased Fetal Movement
A change in fetal movement patterns can indicate fetal distress.
Monitoring includes nonstress tests and possibly ultrasounds and biophysical profiles.
quickening→Early fetal movements, typically felt between 16 to 20 weeks of gestation, that are often described as fluttering, small muscle spasms, gas bubbles, flickering, tapping, or pulsations.
nonstress test (NST)→A noninvasive test used during the third trimester of pregnancy to assess fetal well-being.
ultrasound→A diagnostic test that uses high-frequency sound waves to create a picture of the fetus, placenta, and cord. Also referred to as a sonogram.
quickening
Early fetal movements, typically felt between 16 to 20 weeks of gestation, that are often described as fluttering, small muscle spasms, gas bubbles, flickering, tapping, or pulsations.
nonstress test (NST)
A noninvasive test used during the third trimester of pregnancy to assess fetal well-being.
Restricted Fetal Growth
Caused by maternal, fetal, or placental issues leading to poor perfusion and nutrition.
Maternal factors: chronic/gestational HTN, substance abuse, poor maternal nutrition
Fetal issues: multiple gestation, teratogenic exposure, infectious diseases, genetic disorders
Placental diorders: stem for issues such as placental abruption, umbilical cord anomalies, placental insufficiency
Monitoring includes ultrasound measurements, Doppler blood flow assessments, and NSTs.
doppler velocimetry→A type of ultrasound used to evaluate blood supply to the umbilical cord or placenta.
Multiple Gestation
Associated with increased risks of preterm birth and preeclampsia.
postpartum depression, gestational diabetes, fetal growth restriction
Frequent ultrasounds and NSTs are used for monitoring.
Risk Factors: preterm birth
chorionicity→The count of placentas noted during a multifetal pregnancy.
amnionicity→The count of amniotic sacs noted during a multifetal pregnancy.
chorionic villus sampling (CVS)→Removal of a small section of the placenta for genetic testing.
Oligohydramnios
Low amniotic fluid levels can result from various maternal, fetal, or placental complications.
Ultrasound is used for diagnosis and monitoring.
Maternal Conditions: HTN, preeclampsia, maternal diabetes, placental insufficiency
prelabor rupture of membranes (PROM)
The rupture of amniotic membranes between weeks 37 and 40 in a term pregnancy, before labor starts; sometimes referred to as premature rupture of membranes.
It can lead to loss of amniotic fluid prior to onset labor
Primary cause of oligohydraminos
twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome→Twin gestations that share a single placenta but two amniotic sacs and in which one twin has oligohydramnios while the other twin has polyhydramnios.
prelabor rupture of membranes (PROM)
The rupture of amniotic membranes between weeks 37 and 40 in a term pregnancy, before labor starts; sometimes referred to as premature rupture of membranes.
It can lead to loss of amniotic fluid prior to onset labor
Primary cause of oligohydraminos
Polyhydramnios
High amniotic fluid levels can lead to complications such as fetal demise and preterm birth.
fetal macrosomia, PROM, cord relapse, malpresentation, surgical birth, hemorrhage
Ultrasound and laboratory testing are used for diagnosis and management.
malpresentation→When the fetus is not head-down in the birth canal.
Preterm/Pre-labor Rupture of Membranes (PROM)
Can lead to fetal and maternal infections and other complications.
Testing includes microscopic examination of amniotic fluid, pH test, ultrasound, and NST.
Most common with Black Americans
Risk Factors:
nutritional deficits (low copper or vitamin C)
underweight BMI
Complications:
fetal or maternal infection
neonatal respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)
fetal lung hypoplasia
fetal intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH)
cesarean birth
perinatal mortality
prelabor rupture of membranes (PROM)
The rupture of amniotic membranes between weeks 37 and 40 in a term pregnancy, before labor starts; sometimes referred to as premature rupture of membranes.
preterm prelabor rupture of membranes (PPROM)
The rupture of the amniotic membranes before term or 37 weeks of gestation. ROM may or may not be associated with preterm labor.
neonatal respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)
Neonate who lacks adequate surfactant production, causing respiratory distress. Commonly seen in preterm infants.
fetal lung hypoplasia
Inadequate lung development that may have an impact on a child's overall development. It usually results in the fetus having significant respiratory insufficiency and can either be primary (idiopathic) or due to other congenital anomalies.
intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH)
Bleeding inside or around the ventricles in the brain that contain the cerebrospinal fluid.
ferning
A fern-like pattern when examined under a microscope, such as with dried amniotic fluid.
Daily Fetal Movement Count
Prenatal testing is essential for monitoring fetal health and identifying potential complications.
Tests are performed based on maternal health conditions, pregnancy complications, and risk factors.
Ways to Count:
They may count the number of times the fetus moves or kicks over 1 hour, or they may calculate how long it takes the fetus to move or kick 10 times.
Clients are instructed to call their provider if the fetal movement does not meet the given criteria, such as 10 movements felt within 1 hour.
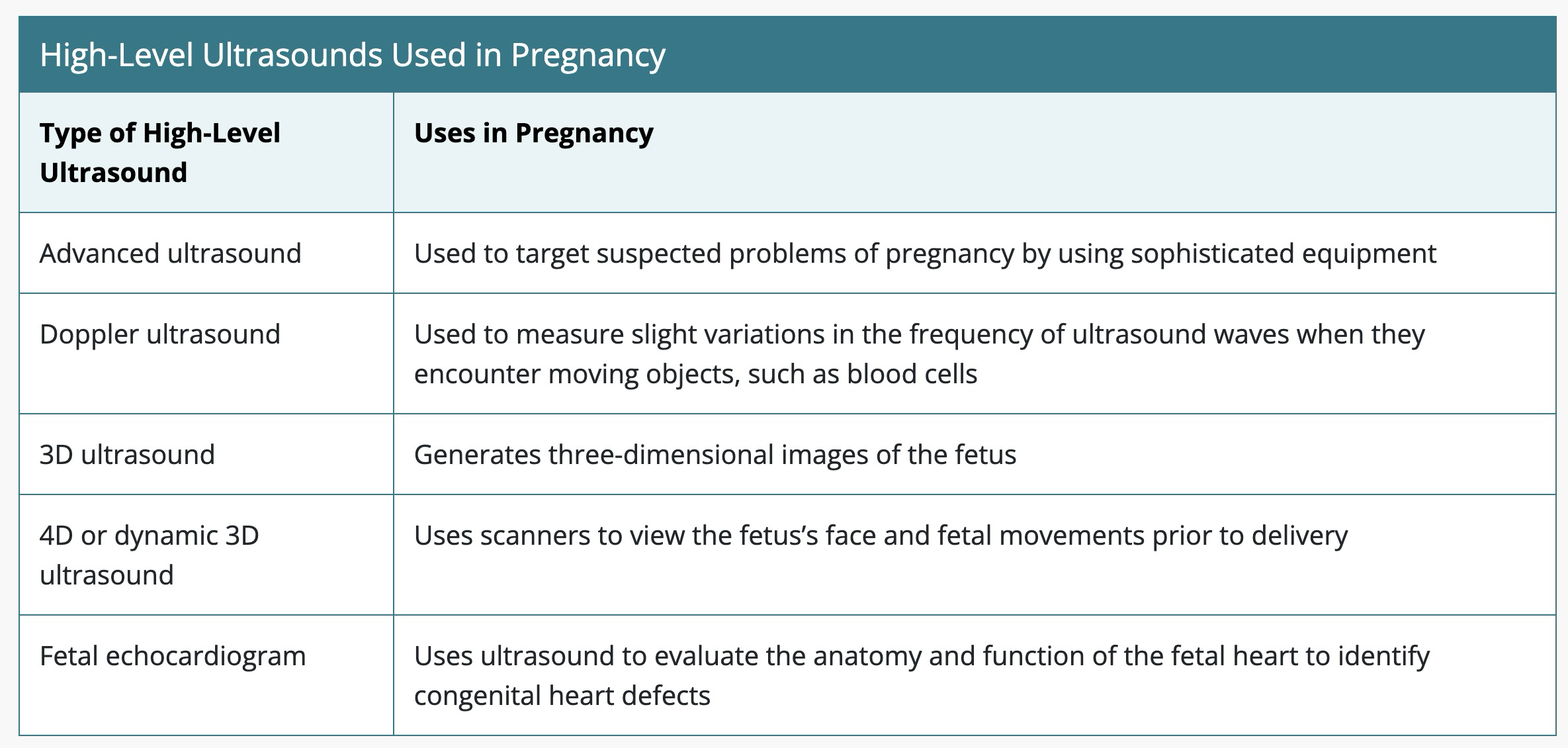
Ultrasound
Used to confirm pregnancy, monitor fetal development, and diagnose complications.
Different types of ultrasounds are available for various purposes throughout pregnancy.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Provides detailed images of the fetal brain, airway, lungs, abdomen, and placenta.
Safe for use during pregnancy, but not commonly performed.
Amniocentesis
Diagnostic test to assess for genetic conditions.
Involves withdrawing amniotic fluid for laboratory examination.
Chorionic Villas Sampling (CVS)
Performed to conduct genetic testing early in pregnancy.
Involves taking a placental biopsy for analysis.
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)
Screening test for neural tube defects and chromosomal abnormalities.
Performed by drawing maternal blood.
Pregnancy-Associated Plasma Protein A (PAPP-A)
Low levels are associated with poor pregnancy outcomes.
Measured alongside hCG in the first trimester.
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)/Free Beta-Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Subunit
Commonly used to confirm pregnancy and monitor for complications.
Measured in urine or blood.
Fetal Nuchal Translucency (NT)
Ultrasound measurement to screen for chromosomal, cardiac, and genetic anomalies.
Performed in the first trimester.
Quad Screen
Maternal blood test that screens for various conditions.
Includes measurements of AFP, hCG, estriol, and inhibin A.
Coombs Test
Coombs Test
Identifies antibodies against red blood cells that can lead to hemolytic anemia in the neonate.
Performed on maternal blood.
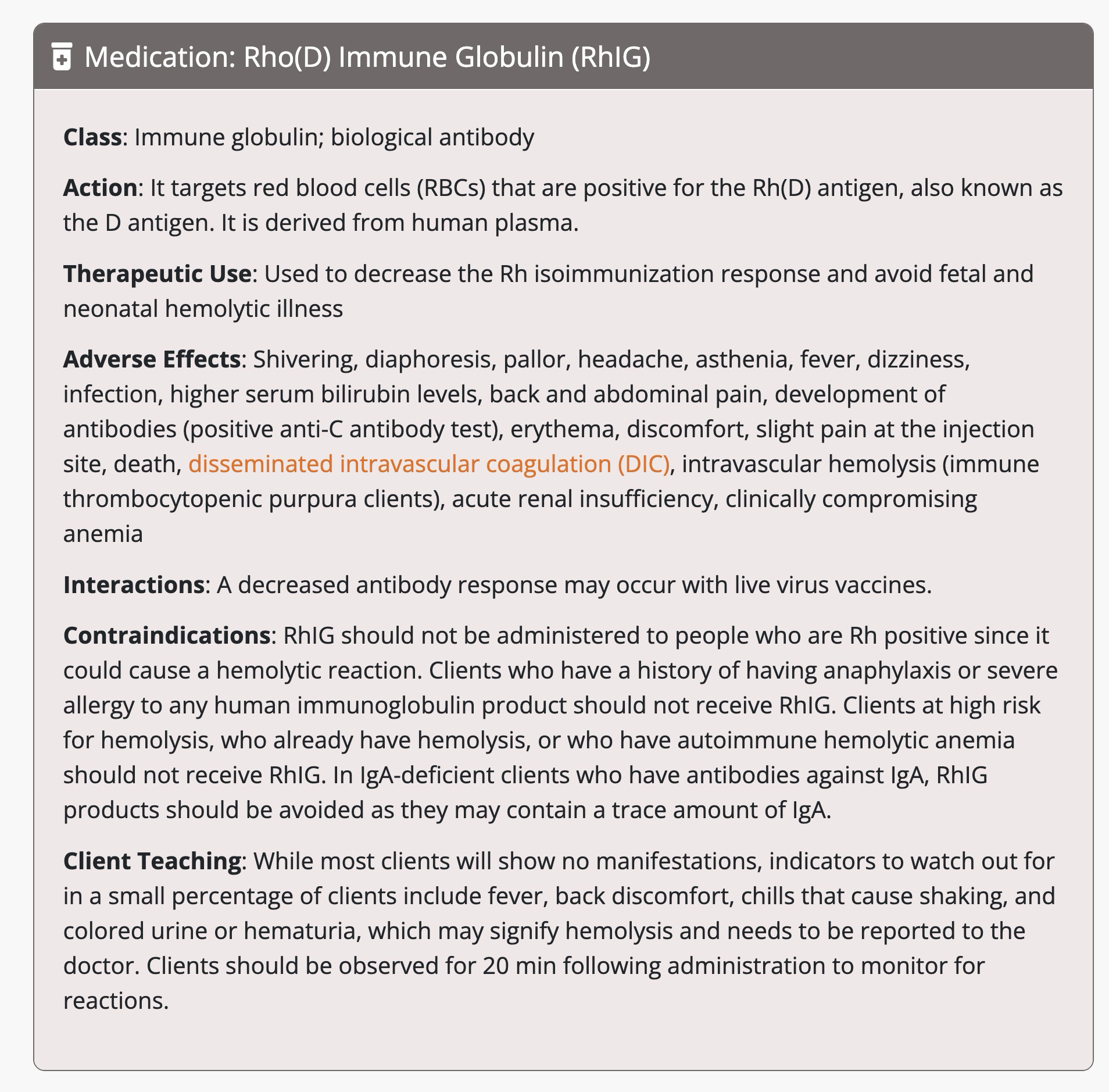
RhoGam
Cell-free DNA
Screens for chromosomal disorders using maternal blood.
Can be performed as early as 10 weeks of gestation.
Fetal Testing
Fetal testing or surveillance is conducted to monitor well-being in at-risk or high-risk pregnancies.
Begins in the third trimester, typically around 32 weeks of gestation.
Includes nonstress test (NST), biophysical profile (BPP), and contraction stress test (CST).
Nonstress Test (NST)
Noninvasive method to assess fetal well-being through external fetal monitoring.
A reactive NST indicates positive fetal health.
Nurses play a role in explaining the procedure, positioning the client, and applying monitors.
Biophysical Profile (BPP)
Combines NST with ultrasound assessment of amniotic fluid, fetal breathing, movements, and limb tone.
Scores range from 0 to 10, with higher scores indicating better fetal health.
Nurses ensure client comfort and assist with the procedure.
Contraction Stress Test (CST)
Evaluates fetal response to contractions and placental function.
Performed after a nonreactive NST or concerning BPP.
Nurses prepare the client, monitor vital signs, and assist with the procedure.
Role of the Nurse
Nurses provide multidimensional care to minimize complications and protect both the pregnant client and fetus.
They offer support, education, and individualized care based on each client's unique needs.
Caring for the Client and Fetus
Optimal care involves communication between the nurse, provider, client, and support persons.
Nurses provide honesty, sensitivity, and are often the primary source of information and support.
Delayed Prenatal Care
Delayed care can lead to increased NICU admissions and neonatal mortality.
Nurses can advocate for clients through telehealth to overcome barriers to care access.
Nursing Role in Prenatal Care
Nurses influence the client's prenatal care experience and satisfaction.
Providing dignified, respectful, and nonjudgmental care is crucial.
Quality information and positive experiences encourage continued care.
cerclage
A medical procedure in which a stitch is placed around the cervix to prevent dilation.