Topic 6 - Inheritance, Variation and Evolution
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What is a Chromosome?
A long molecule of DNA found in the nucleus that carries genetic information.
What is a Gene?
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a particular sequence of amino acids which are put together to make a specific protein.
What is a Genome?
The complete set of genetic material, including all of an organism's chromosomes and genes.
What is the Structure of DNA?
The structure of DNA is a double helix formed by two long strands of nucleotides twisted around each other, with the strands held together by base pairs.
The Bases include A, C, G, T in which A pairs with T and C pairs with G. The order of bases in a gene determine the order of amino acids in a protein. Each amino acid is coded for by a sequence of three bases.
The backbone of DNA consists of alternating sugar and phosphate groups.
What is mRNA?
mRNA, or messenger RNA, is a type of RNA that serves as a template for protein synthesis by carrying genetic information from DNA to ribosomes.
The correct amino acids are assembled in the correct order to form proteins during translation using carrier molecules.
What are some functions of Proteins?
Enzymes - Biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in the body.
Hormones - Chemical messengers that regulate various processes in the body.
Structural Proteins - Provide support and shape to cells and tissues.
What are Mutations?
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can lead to alterations in the structure and function of proteins.
They can occur spontaneously or be induced by environmental factors and may have varying effects on an organism, from harmless to potentially harmful.
What are 3 types of Mutations?
Insertions - The addition of one or more nucleotide bases to the DNA sequence.
Deletions - The loss of one or more nucleotide bases from the DNA sequence.
Substitutions - The replacement of one nucleotide base with another in the DNA sequence.
What are the two types of Reproduction?
Asexual Reproduction - A single organism replicating itself to produce genetically identical cells.
Sexual Reproduction - The combination of genetic material from two parent organisms.
What is a Gamete?
A reproductive cell that carries half the genetic information of an organism, necessary for sexual reproduction.
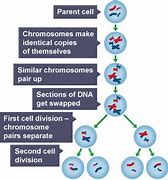
What is Meiosis?
A type of cell division where a cell divides twice to produce four genetically different gametes.
The cell duplicates its genetic information and arranges the chromosomes into pairs
In the first division, the chromosome pairs line up in the centre of the cell
The pairs are pulled apart so each new cell has one copy of each chromosome
In the second division, the chromosomes line up again in the centre of the cell and the arms of the chromosome are pulled apart
As a result, you get four gametes, each with only a single set of chromosomes that are genetically different.
Advantages of Sexual and Asexual Reproduction?
Sexual Reproduction:
Offspring have a mixture of chromosomes, producing variation
Increased adaptability to changing environments
Asexual Reproduction:
Offspring are genetically identical to the parent
Faster reproduction rate without needing a mate
What are the two types of Chromosomes?
The two types of chromosomes are X and Y Chromosomes.
A male has X an Y Chromosomes where the Y Chromosome causes male characteristics.
A female has two X Chromosomes where the XX Combinations causes female characteristics.
What is Homozygous and Heterozygous?
Homozygous - An organism with two identical alleles for a trait.
Heterozygous - An organism with two different alleles for a trait.
What are Dominant and Recessive Alleles?
Dominant - An allele that expresses its trait even in the presence of a different allele
Recessive - An allele that only expresses its trait when two copies are present
What is Cystic Fibrosis?
Cystic Fibrosis is a genetic disorder of the cell membranes. It results in the production of thick mucus that can clog lungs and lead to respiratory issues, digestive problems, and increased risk of infections. It is caused by a Recessive Allele.
What is Polydactyly?
Polydactyly is a genetic disorder characterized by the presence of extra fingers or toes. It is caused by a Dominant Allele.
What is Embryo Screening and what are the arguments For and Against it?
Embryo Screening - A procedure used to test embryos for genetic disorders before implantation during in vitro fertilization (IVF).
For - It can reduce the risk of genetic diseases, allow parents to make informed decisions, and improve the quality of life for affected individuals.
Against - It raises ethical concerns about "designer babies" potential discrimination against disabled individuals, and the social implications of selecting traits.
Who is Gregor Mendel and what did he do?
Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk and scientist known as the father of modern genetics. He conducted experiments on pea plants to establish the principles of inheritance, including dominant and recessive traits.
He reached 3 conclusions:
Characteristics in plants are determined by “Hereditary Units”
Heredity units are passed from parents to offspring unchanged from both parents
Hereditary units scan be dominated or recessive
What is Variation?
Variation refers to the differences in genetic traits among individuals within a population. It can arise from mutations, gene inheritance and environmental factors, resulting in diverse phenotypes that can impact survival and reproduction.
What is Darwin’s Theory Of Evolution?
All of today’s species have evolved from simple life forms that first started to develop over three billion years ago.
What is Natural Selection and How does it occur?
Natural selection is a process in which organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring.
An animal will be born with a mutation
This mutation will allow the animal to survive for longer
This means that the animal can reproduce to have more offspring
The offspring will have the mutation allowing them to survive longer and have more children
Over a long time, the animals without the mutation will die out and the mutation will spread through the whole population
What is Extinction and How does it occur?
Extinction is the permanent loss of a species.
It can be caused by:
Environmental Changes
New Predators
New Diseases
Competition for Food
Catastrophic events
Who is Lamarck and what was is Theory?
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck was a French naturalist known for his early theory of evolution.
A feature is repeatedly used by an organism during its life causing it to develop
The acquired useful changes will be passed down to the offspring
This repeats leading to evolution over generations
What is Selective Breeding?
Selective breeding is the process of mating organisms with desirable traits to produce offspring that inherit those traits.
The two animals with the chosen characteristics are bred together
The offspring with the best of that characteristic are bred again
The process is repeated over several generations until all the offspring have the desired traits of the parents
What traits is Selective Breeding used for and what are the Disadvantages?
Plants/Animals that:
Have more produce
Have disease resistance
Have domestic attributes
Have ascetic features
Disadvantages:
Reduced genetic diversity
Increased susceptibility to diseases
Potential for undesirable traits to emerge
Ethical Concerns
What is Genetic Engineering?
Genetic engineering is the manipulation of an organism's DNA to alter its characteristics. This process can involve adding, removing, or modifying genes to change the trait.
Pros:
Increases the yield
Add nutrients (Golden Rice)
Enhances disease resistance and pest control
Cons:
Reduces Biodiversity
Concerns on health problems
Unethical to change life
What are two ways to clone Plants?
Tissue Culture - Where a few plant cells are put in a growth medium with hormones and they grown into new plants.
Cuttings - A section of a plant stem or leaf is cut and planted in soil or water, where it develops roots and grows into a new plant
What are two ways to clone Animals?
Embryo Transplants - A embryo is created from a sperm and a egg, then it is split in half and given to a surrogate mother.
It can create many copies quickly and for little money. It has no genetic variation and is unethical
Adult Cell Cloning - Taking an unfertilised egg cell and replacing its nucleus with one from a adult body cell. It is the stimulated by an electric shock which makes it divide to form a cloned embryo, which can then be placed in a surrogate mother.
What are 3 ways Fossils form?
Gradual Replacement - Organic matter that doesn’t decay easily are buried. They are slowly replaced by minerals as they decay forming a rock-like substance in the same shape. The surrounding sediment also turns to rock but the fossil stays distinct inside the rock
Casts and Impressions - The remains of an organism leave an impression in the sediment, which hardens into rock, creating a cast or impression of the original shape.
Preservation - Organisms can be trapped in places where no decay happens: Amber (No oxygen/moisture), Glaciers (Too cold for microbes) and Peat Bogs (Too Acidic for microbes)
What is Speciation?
The process by which new and distinct species evolve from a common ancestor, often due to geographic, behavioural, or reproductive isolation.
A population is separated by a geographical feature
A animal in the species has a mutation which allows them to survive longer in their environment
Natural Selection occurs causing all of that species to have the mutation
This creates a different species which can’t produce fertile offspring with the original population
Who was Wallace?
Alfred Russel Wallace was a naturalist and biologist who independently formulated the theory of evolution through natural selection, parallel to Charles Darwin.
He was also one of the earliest scientists to study the idea of speciation.
What is Classification?
The systematic arrangement of organisms into categories based on shared characteristics and evolutionary relationships. It was proposed by Carl Linnaeus in these groups:
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
Latin names for animals were originally made using a binomial nomenclature system, consisting of the genus and species names.
What is the Domain System?
Domain is a the top layer of classification later introduced by Carl Woese. The 3 types are:
Archaea - Organisms thought to be primitive bacteria with mixed characteristics from prokaryote and eukaryote cells, and are extremophiles
Bacteria - Single-celled prokaryotic organisms that are found in various environments
Eukaryota - Organisms with complex cells that contain a nucleus, including plants, animals, fungi, and protists