Lab 6: Cell Division
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
what is a cell’s DNA packaged as a double-stranded DNA molecule called?
a genome
chromosomes
structures within the nucleus that are made up of DNA in the nuclei of its cells
how many chromosomes do human body or somatic cells have?
43
how many chromosomes do human sex or gametes cells have?
23
diploid
a typical body cell contains two matched or homologous sets of chromosomes (one set from each biological parent)
haploid
human cells that contain one set of chromosomes and are designated 1n
homologous chromosomes
upon fertilization, each gamete contributes one set of chromosomes, creating a diploid cell containing matched pairs of chromosomes
how many sister chromatids do eukaryotic chromosomes have?
2
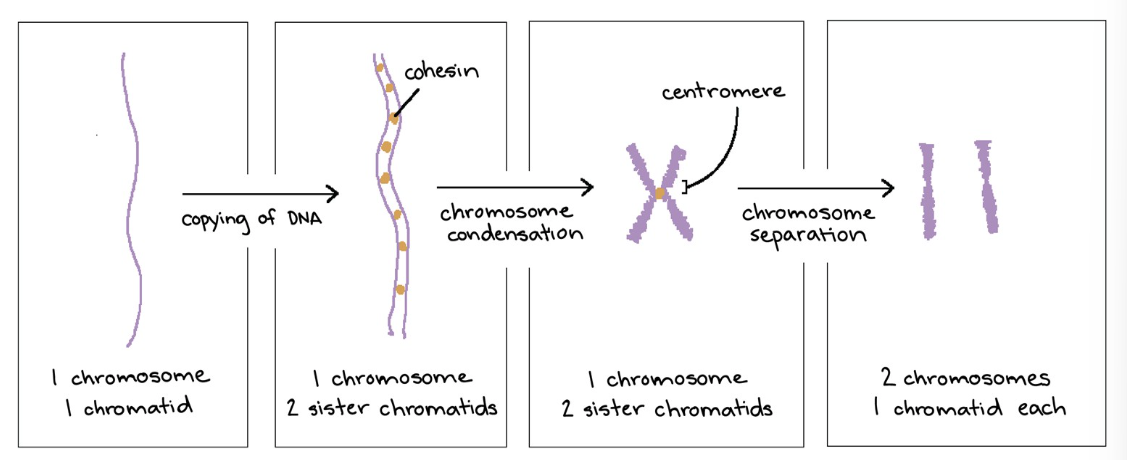
where are sister chromatids attached at?
the sister chromatids are identical to one another and attached at a compressed region called the centromere
chromatin
DNA double helix wrap around a core of eight histone proteins at regular intervals along the entire length of the chromosome
nucleosome
the beadlike, histone DNA complex. a DNA molecule in this form is about seven times shorter than the double helix without the histones
the ____________ level of compaction occurs as the nucleosomes coil into a chromatin ______. this coiling further __________ the chromosome so that it is now about 50 times shorter than the extended form.
second, fiber, condense
in the _______ level of compaction, a variety of ___________ __________ is used to “pack the chromatin”
third, fibrous proteins
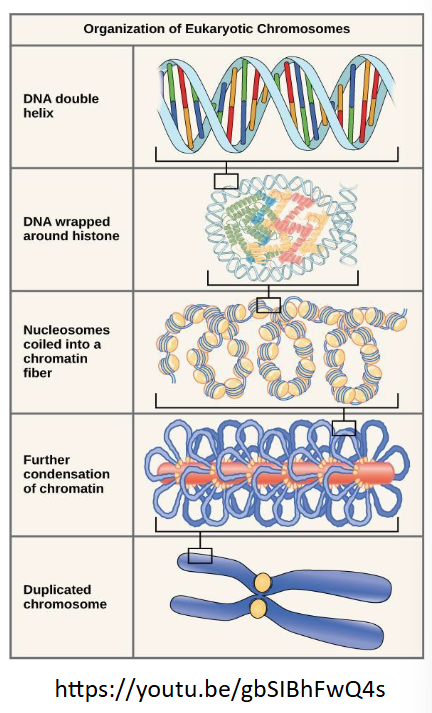
DNA replicates in the ___ phase of interphase. after replication, the chromosomes are composed of two linked sister ________. the connection between the sister chromatids is closest in a region called the ___________.
S, chromatids, centromere
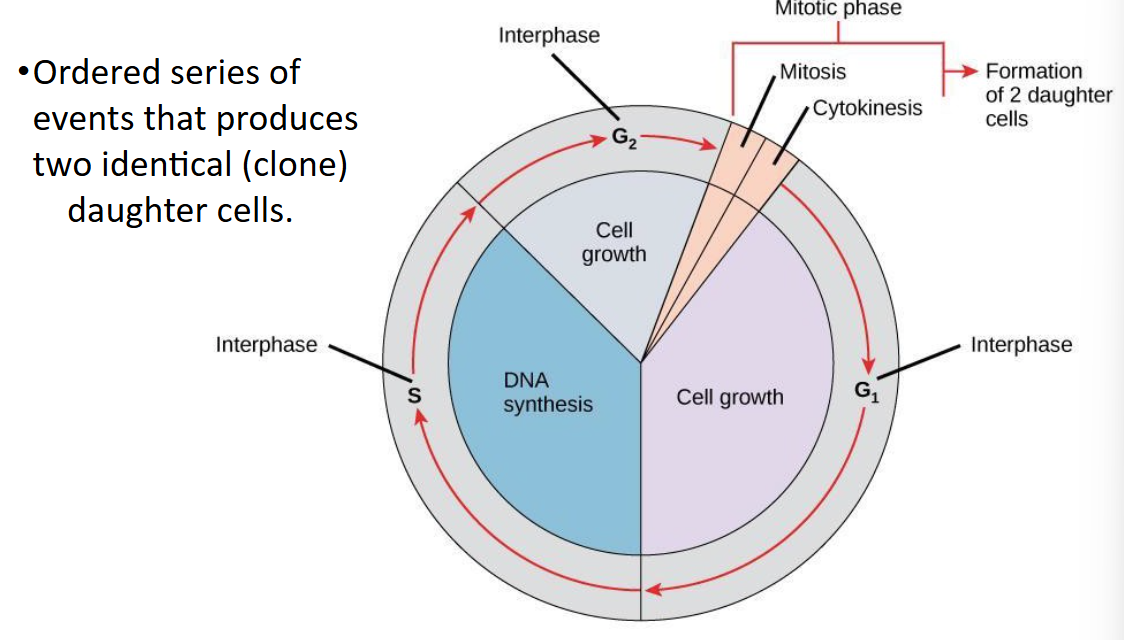
cell division cycle
G1: cell growth
S: DNA synthesis
G2: cell growth
Mitotic phase: Mitosis and Cytokinesis → formation of 2 daughter cells
G1 Phase (first gap)
getting ready by prepping for replicating each chromosome in the nucleus. includes proteins and energy reserves
S Phase (Synthesis of DNA)
results in the formation of identical pairs of DNA molecules — sister chromatids — that are firmly attached to the centromeric region. centrosomes also duplicate
G2 Phase (Second Gap)
increases energy stores and synthesizes proteins necessary for chromosomes manipulation and movement. additional growth
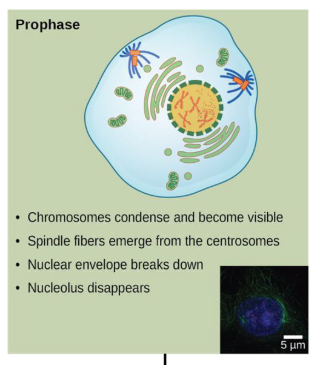
prophase
chromosomes condense and become visible
spindle fibers emerge from the centrosomes
nuclear envelope breaks down
nucleolus disappears
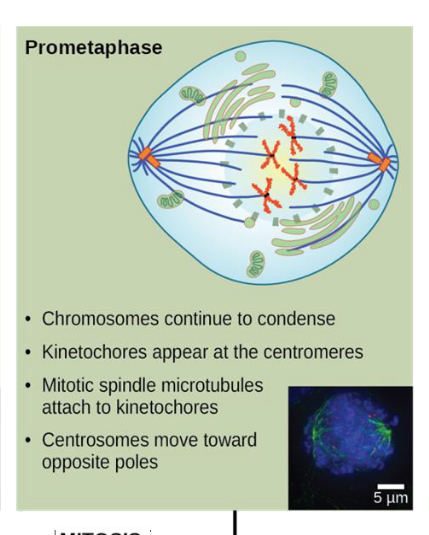
prometaphase
chromosomes continue to condense
kinetochores appear at the centromeres
mitotic spindle microtubules attach to kinetochores
centrosomes move toward opposite poles
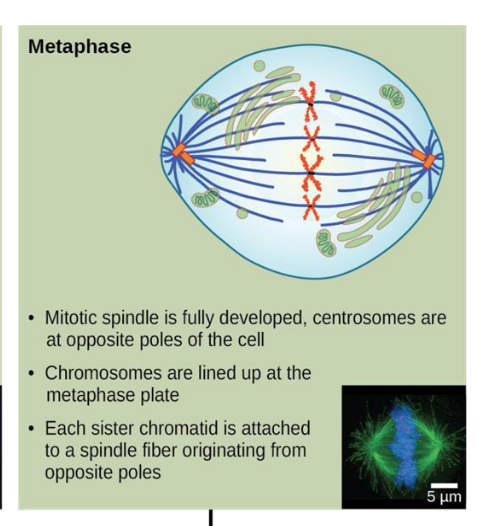
metaphase
mitotic spindle is fully developed, centrosomes are at opposite poles of the cell
chromosomes are lined up at the metaphase plate
each sister chromatid is attached to a spindle fiber originating from opposite poles
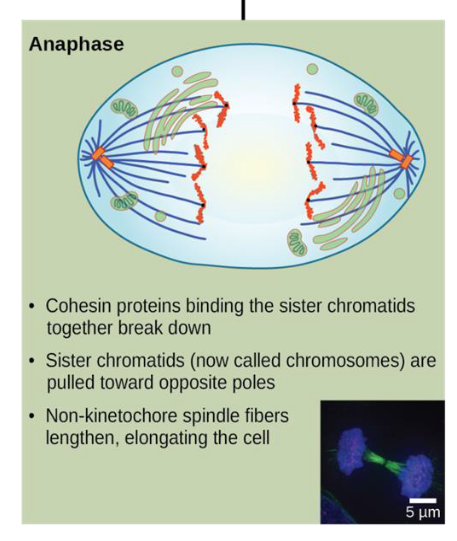
anaphase
cohesin proteins binding the sister chromatids together break down
sister chromatids (now called chromosomes) are pulled toward opposite poles
non-kinetochores spindle fibers lengthen, elongating the cell
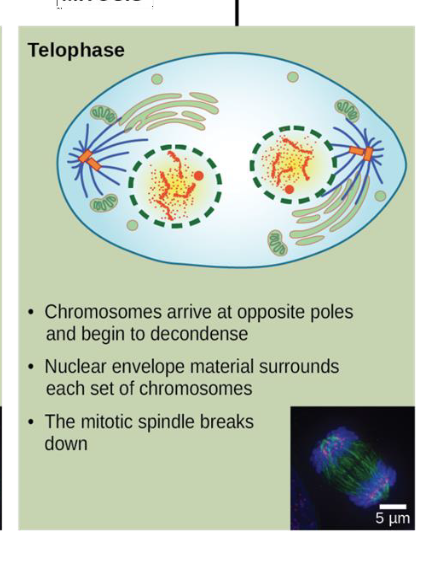
telophase
chromosomes arrive at opposite poles and begin to decondense
nuclear envelope material surrounds each set of chromosomes
the mitotic spindle breaks down8
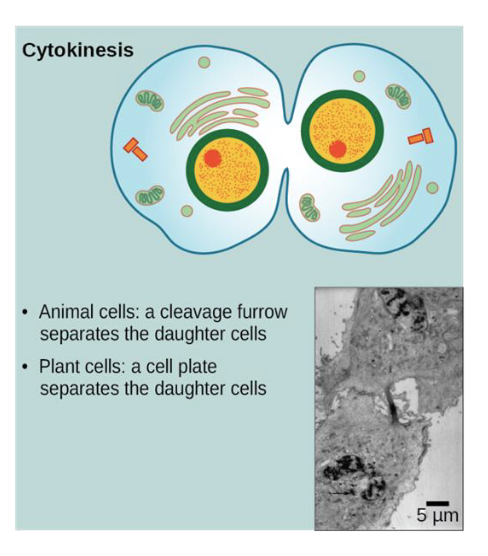
cytokinesis
animal cells: a cleavage furrow separates the daughter cells
plant cells: a cell plate separates the daughter cells
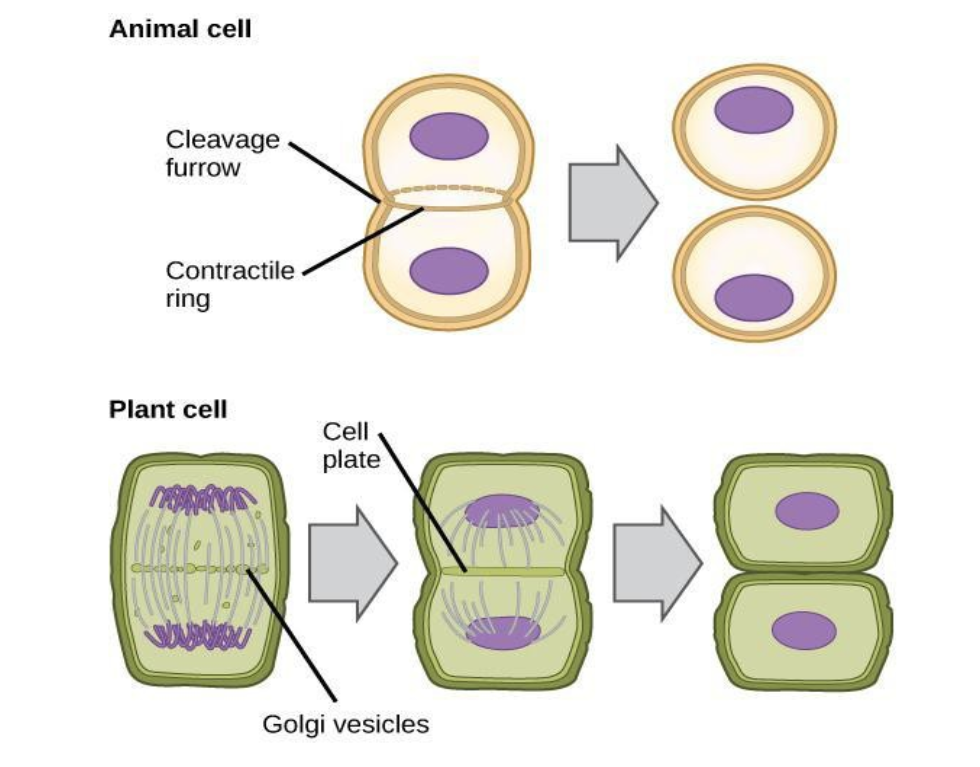
what’s the difference in cytokinesis in animals cells vs. plant cells?
an animal cell uses a cleavage furrow and contractile ring to separate while a plant cell uses a cell plate and golgi vesicles
onion root tip
formation of tissues begins with the root apical meristem (RAM). just below the tip of the root, there is a region of small, densely packed cells that are actively dividing
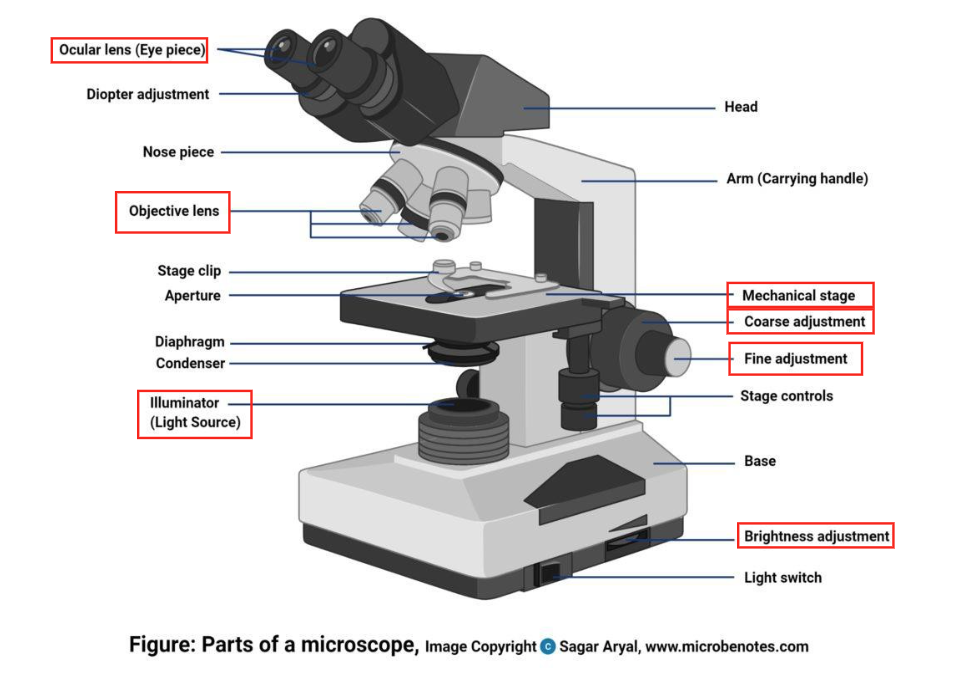
microscope parts
ocular lens (eye piece)
objective lens
illuminator (light source)
mechanical stage
coarse adjustment
fine adjustment
brightness adjustment
what are the two major phases of the cell cycle?
interphase and mitotic phase
multinucleate cells
interphase and mitosis (karyokinesis) may take places without cytokinesis, in which cells with multiple nuclei are produced
where is cell division in plants limited to?
the meristems: specialized regions of the undifferentiated cells
apical meristem in the root tip
in this region, cells are rapidly progressing through the cell cycle to increase cell number. as cells accumulate, they are pushed out of this region and exit the cell cycle. these cells then go through the process of cell elongation followed by differentiation
how is the meristem protected?
its protected from the environment by several layers of differentiated cells that form a root cap at the very tip of the root and an epidermal layer of cells along the root length. the cells in the root cap and the epidermal layer are constantly being lost and replaced by new cells arising in the meristem. other cells that leave the meristem and exit the cell cycle will differentiate into other types of cells including those specialized for starch storage and nutrient uptake