Business Management 1.1 - 1.3
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What are the BM concepts?
Sustainability
Ethics
Creativity
Change
What is SWOT?
Strengths (internal)
Weaknesses (internal)
Opportunities (external)
Threats (external)
Strengths
Opportunities
- external
- market is good
- job pays good money
What is STEEPLE?
Social
Technological
Economic
Environmental
Political
Legal
Ethical
What is the Ansoff matrix?
Market penetration, market development, product development, diversification
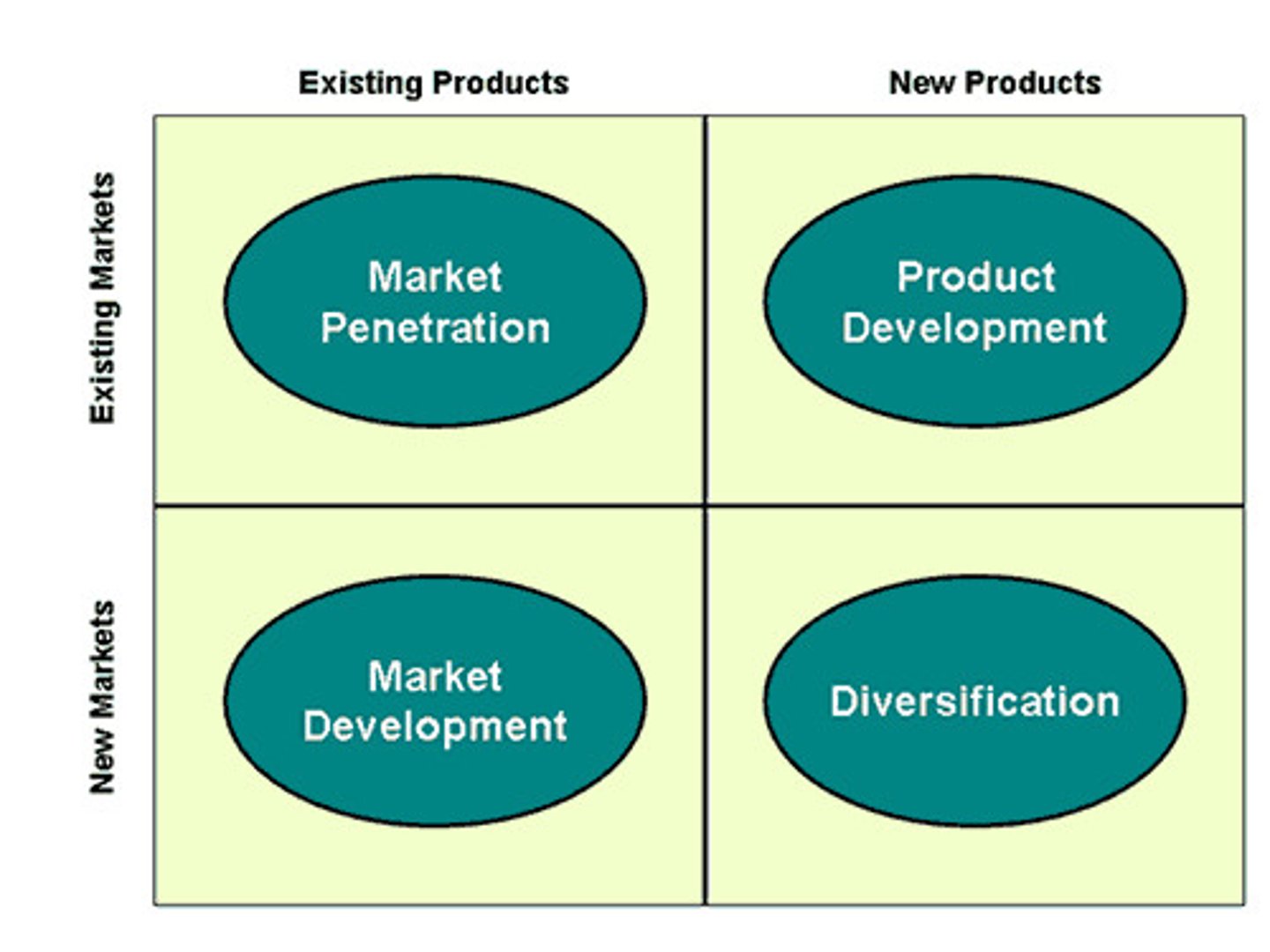
Discuss Ansoff Matrix
USE THE TERMS HIGH RISK AND LOW RISK
What is market penetration?
Achieving higher market shares in existing markets with existing products. It has the lowest risk.
What is product development?
Development and sale of new products or new developments of existing products in existing markets
What is market development?
Strategy of selling existing products in new markets
What is diversification?
Process of selling different, related/unrelated goods or services in new markets. It is a high risk growth strategy.
What is a business?
An organisation that uses resources to meet the needs of customers by providing a product or service that they demand
What are the business outputs?
Consumer goods
Consumer services
Capital goods
What are the business inputs?
Land
Labour
Capital
Enterprise
What are the four business functions?
Marketing
Human resources
Finance
Operations management
What are the economic sectors?
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Quaternary
What is the primary sector?
businesses engaged in industries that extract natural resources to be used and processed by other firms
What is the secondary sector?
businesses that manufacture and process products from natural resources
What is the tertiary sector?
businesses that provide services to consumers and other businesses
What is the quaternary sector?
information technology businesses and information service providers
What is a business plan?
A written document that describes a business, its objectives and strategies, the market it is in and its financial forecasts
Elements of business plan
1. name of business
2. type of organisation
3. details of business owners
4. business aim
5. product
6. price
7. market aimed for
8. market research undertaken and results
9. human resources plan
10. production details and business costs
11. location of business
12. main equipment required
13. forecast profit
14. cash flow forecast
15. finance
Advantages of business plan
- obtain finance for new business
- help entrepreneur gain a full and better understanding of each element of her business with a clear vision and long-term objectives, and hence the chances of success or failure
- financial and other forecasts can be business targets for employees to focus and aid motivation
- help in making strategic choices
- allows potential investors in the new business and bank to make judgment about viability of idea and chances of success
- financial forecast act as budget and control benchmark for internal stakeholders such as managers
- updated versions of the business plan can be used to apply for additional funding, attract more partners or supply data for experts if stock market flotation becomes option
- suppliers can tell from parts of business plan communicated externally whether it is worthwhile to establish a long-term trading relationship with business
What is the private sector?
Business owned and controlled by individuals or groups of individuals
What is the public sector?
Organisations accountable to and controlled by central or local government
What is a sole trader?
Business that is exclusively owned by one person who has full control of it and is entitled to all of the profit after tax
Advantages for sole traders
- easy to set up, no legal formalities
- owner has complete control, not answerable to anyone else
- owner keeps all profits
- able to choose time and pattern of working
- able to establish close personal relationships with staff and customers
Disadvantages for sole traders
- Unlimited liability, all of the owner's assets are potentially at risk
- Faces intense competition from rivalling firms
- Owners of small business may have responsibility for all aspects of management and may therefore be unable to specialise
- Difficult to raise additional capital
- Long hours necessary
- Lack of continuity
What is a partnership?
Business formed by two or more people to carry on a business together, with shared capital investment and shared responsibilities
Advantages of partnership
- Partners may specialise in different areas of business management
- Shared decision-making
- Additional capital can be injected by each partner
- Business losses are shared between partners
- Greater privacy and fewer legal formalities than corporate organisations
Disadvantages of partnership
- Unlimited liability for all partners
- Profits shared
- Lack of continuity
- All partners are bound by the decisions of any one of them
- Not possible to raise capital by selling shares
- Partners need to discuss and agree to major decisions, might take a long time
What is a privately held company?
Business that is owned by shareholders who are often members of the same family. This company cannot sell shares to the general public.
Advantages of privately held company
Shareholders have limited liability
Separate legal personality
Continuity in the event of death of a shareholder
Original owner is still able to retain control
Ability to raise capital from sale of shares to family, friends and employees
Greater status than non-company or unincorporated business
Disadvantages of privately held company
Legal formalities in establishing business
Capital cannot be raised by sale of shares to general public
Difficult to shareholders to sell shares
Less secrecy over financial affairs
What is a publicly held company?
Limited company with the legal right to sell shares to financial institutions and the general public. Its share price is quoted on the national stock exchange.
Advantages of publicly held company
Limited liability
Separate legal identity
Continuity
Ease of buying and selling shares for shareholders, encourages investment
Access to substantial capital sources as can offer shares for sale to public
Disadvantages of publicly held company
Legal formalities
Cost of business consultants and financial advisers
Share prices subject to fluctuation for reasons beyond business's control
Legal requirements to disclose information to shareholders and public
Risk of takeover due to availability of shares on stock exchange
Directors influenced by short-term objectives of major investors
What is a social enterprise?
Business with social and/or environmental objectives that reinvests most of its profits into benefitting society rather than maximising returns to owners
Why would you choose to change a partnership to a privately limited company?
- limited liability
- management control
Why would you choose to become a sole trader?
- Full control
- Confidentiality
Compare the four types of businesses
x
Compare for-profit business vs social enterprise
x
What is a charity?
Organisation set up to raise money to help people in need or support causes that require funding
What is the triple bottom line?
The three objectives of social enterprises: economic, social and environmental
What is a public corporation?
Business enterprise owned and controlled by the state
What is a cooperative?
Group of people acting together to meet the common needs and aspirations of the members, sharing ownership and making decisions democratically
What is a non-profit organisation?
Organisation that has aims other than making and distributing profit, usually governed by a voluntary board
What is a non-governmental organisation (NGO)?
Legally constituted body that functions independently of any government and has a specific humanitarian or social aim
Compare for-profit business vs NGO
What is a mission statement?
Statement of the business's core aims to motivate employees and stimulate interest from outside groups
What is a vision statement?
Statement of what the organisation would like to achieve or accomplish in the long term
Advantages of mission and vision
- gives a sense of purpose and direction
- quickly informs groups outside the business what the central aim and vision are
- motivate employees
- guide and direct individual employee behaviour
- help other groups establish what the business is about
Disadvantages of vision and mission
- too vague, unquantifiable
- too similar
- PR exercise
- virtually impossible to really analyse or disagree with, so may be ignored or not taken seriously
What is a corporate aim?
Long-term goals which a business hopes to achieve
What is a business objective?
Short- or medium- term goals that are specific and must be achieved so as to achieve overall corporate aim
What are the advantages of corporate aim and business objectives?
- gives genuine sense of direction and purpose
- motivates employees and raises labour productivity
- promotes greater sense of belonging and team spirit
- enables organisations to measure progress
What are common business objectives?
- profit objective
- growth objective
- protecting shareholder value
- ethical objectives
- limitations
What are strategic objectives?
Long-term target for the whole organisation to achieve corporate aim (broad ways and means)
What are tactical objectives?
Short-term target at specific problem or goal for longer-term objective (detailed day-to-day ways and means)
What is corporate social responsibility?
The concept that the activities of businesses have an impact on society, so businesses should act responsibly and ethically towards all stakeholders, such as customers, employees, communities and the environment.
What are benefits to CSR?
- enhance/maintain PR, goodwill of community and suppliers
- enhance employee morale, motivation and cohesion
- enhance/maintain brand image, create niche position
- improve long-term profitability of business
Disadvantages of CSR
- Increase costs (raw materials, wages, technology)
- Limitations in working partners
What are SMART goals?
Specific
Measurable
Achievable
Realistic
Time specific