Chemistry I Final - Second Semester (Chapter 6 - 13?)
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Topic List: Metals, Molecules (names and Lewis structures), Molecules (Shape, polarity, resonance, formal charge), Molecules (acids, comparison of ionic and molecular compounds), Chemical change (equations and types of chemical change), Chemical change (activity series & Single replacement reactions), Chemical Change (Double replacement reactions), Counting matter (the mole), counting matter (mass, moles, and particles), mole ratios in compouds, formulas of hydrates, percent compostion, empirical formulas, stoichiometry (mole ratios + mass and mole ratios in chemical change + limiting reactants + percent vs theoretical yield)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
kapeesh
atoms form covalent bonds by sharing electrons to become stable
kapeesh?
Covalent Bond
Chemcial bond formed when atoms share electrons
Molecule
formed when 2 or more atoms bond
Diatomic Molecules
exist because 2 atom molecules are more stable than one
ex. H2, F2
Dr. H BrONClIF
mnemonic to remember the diatomic molecules (7)
Hydrogen
Bromine
….
Bonding Pair
what is this called?
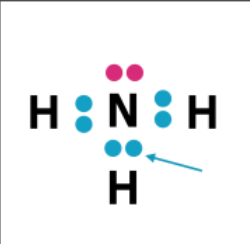
Lone Pair
now what about this?
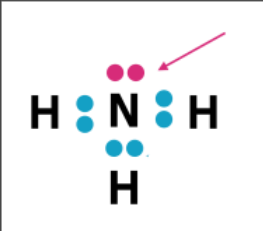
Sigma bond
single covalent bond that occurs occur when the pair of shared electrons is in an area centered between the two atoms
Single Bond
1 sigma bond
Double Bond
form when 2 pairs of electrons are shared between 2 atoms
1 sigma bond + 1 pi bond
Triple Bond
form when 3 pairs of electrons are shared
1 sigma bond + 2 pi bonds
Ich verstehe
NAMING BINARY MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS:
first element is the entire name
second element is the root + “ide”
prefixes of the elements indicate the number of atoms for each element
Verstehst du?
mono-
prefix for 1
di-
prefix for 2
tri-
prefix for 3
tetra-
prefix for 4
penta-
prefix for 5
hexa-
prefix for 6
hepta-
prefix for 7
octa-
prefix for 8
nona-
prefix for 9
deca-
prefix for 10
more; less
the strength of covalent bonds depends on the distance between the nuclei
____ distance = ____ strength
Bond dissociation energy
amount of energy required to break a bond
greater
the energy needed to break a bond is _______ when the length is shorter
Endothermic Reaction
more energy is needed to break a bond than is released
Exothermic Reaction
more energy is released breaking the bond than is needed
entiendo
HOW TO MAKE LEWIS STRUCTURES:
Find valence electron total
HCL → 1 + 7 = 8Put the least electronegative atom in the center (never H)
Put 2 electrons between the atoms to form a single bond
H : ClComplete the octet for the outside atoms
..
H : Cl :..
If center atom doesn’t have an octet, move electrons to form double or triple bonds as needed
¿lo entiendes?
je comprends
NAMING ACIDS:
first word is “hydro” - [root] - “ic”
second word is “acid”
ex. HCL → hydro | chloric | acid
comprendre?
Acids
any substance that releases hydrogen atoms in water
Binary Acids
acid with 2 elements (no oxygen)
Oxyacid
acid with hydrogen and oxyanion
!
NAMING OXYACIDS:
per-/hypo- + [root] + -ic/-ous + “acid”
if the oxyanion name ends in “ite”, the oxyacid ends with “ous”
If the oxyanion name ends in “ate”, the oxyacid ends with “ic”
ex. HClO4 → per | chloric | acid
?
Pi Bond
formed when parallel orbitals overlap and share elements
Structural Formula
letter symbols + bonds showing relative positions of atoms
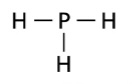
Space Filling Model
what is this picture an example of ???

Lewis Structure
dots or a line symbolizing a single covalent bond
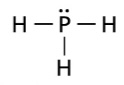
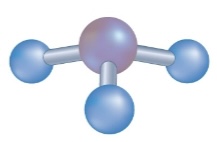
Ball and Stick Model
what is this picture an example of ??
Resonance Structure
more than 1 valid lewis structure for a molecule or ion
bond lengths are identical to each other
intermediate between single and double bonds
understando
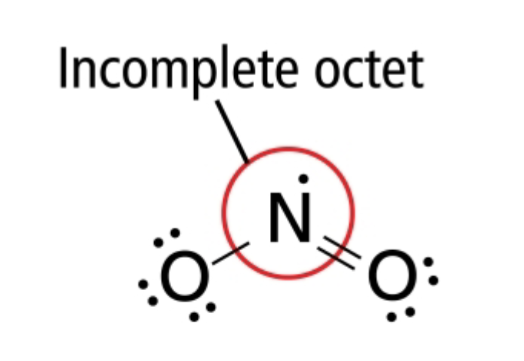
OCTET RULE EXCEPTIONS:
NO2 has 5 valence electrons from N ans 12 from 0
it can’t form an exact number of electron pairs
understando?
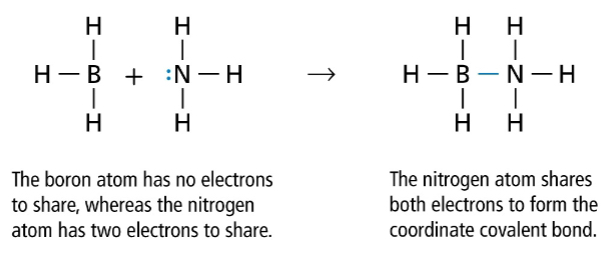
Coordinate Covalent Bonds
1 atom donates both electrons to share with an ion that needs two
expanded octet
3rd group of atoms with >8 valence electrons electrons
elements in period 3 or higher have d-orbital and can form over 4 covalent bonds
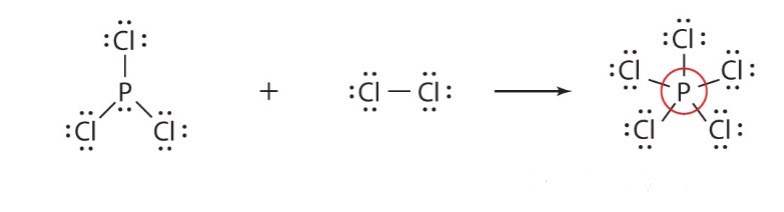
Dipole
uneven charges at the end of a polar bond
Polar Covalent Bonds
uneven sharing of electrons resulting from one element being more electronegative than the other (it attracts more of the electrons to itself)
Solubility
a substances ability to be dissolved
polar and ionic dissolve in polar
non polar dissolve in non polar
(like dissolves like)
Van der Waals forces
the weak attraction between molecules
vary in strength, but are weaker than bonds in ionic compounds
Intermolecular forces
London dispersion force (van der waals force)
dipole-dipole
hydrogen bonding
Dipole-Dipole Interaction
force between 2 oppositely charged ends of 2 polar molecules
Hydrogen Bonding
especially strong dipole-dipole force between H and either F, O, or N atoms on dipoles
O ye mi
PROPERTIES OF COVALENT BONDS:
Physical properties are usually caused by intermolecular forces
Low melting point
Low boiling point
many are soft solids
crystal lattice, but with less attraction
ṣe o ye ọ?
Covalent Network solids
solids composed of only atoms interconnected by a network of covalent bonds
Quartz
Diamond
Chemical Reaction
the rearrangement of atoms to form a new substance
change in temp
change in color
odor/gas
bubbles forming
Reactants
starting substance
Products
substances formed
Reversible
⇋
precipitate formed
↓
gas formed
↑
aqueous solution
(aq)
has 1 or more dissolved substances in water
solid
(s)
liquid
(l)
gas
(g)
Word Equation
what is this?:
aluminum (s) + bromine (l) → aluminum bromine (s)
Skeleton Equations
chemical equations are also called
chemical equation
statements using chemical formulas to show identities and relative amounts of the substance
Coefficient
chemical equation number written in front of a reactant or product to show the lowest whole number ratio of the amounts
Synthesis
2 or more substances react to form a more complex main substance
Decomposition
complex substances breaks down into simple substances
Requires heat, light, or electricity
Single replacement
atoms of one element replaces another element’s atom in a compound
strong metals displace weak metals
Double Replacement
When ions exchange between 2 compounds
acid-base reactions
produce water, precipitates, or gas
Precipitate
solid product in a reaction
Combustion
Oxygen reacts with a substance and releases heat and light energy
also technically a synthesis reaction
Solute
dissolved substance
solvent
the most plentiful substance; what the solute is dissolved into
Complete Ionic equations
show all the particles in a solution as they exist
only written for double displacement reactions
Mole
SI unit to measure the amount of a substance
equal to 12g of pure C12 (in terms of how many atoms are in it)
6.022 × 1023
Avogadro’s number
6.022 × 1023
Molar mass
mass (g) of one mole of any pure substance
found by adding up the atomic mass of all the elements in the substance
Molar Volume (gas)
volume 1 mol occupies at 0 degrees C and 1.00 atm (pressure)
1 mol of gas occupies 22.4 L
Percent Composition
percent by mass of an element in a compound (can be determined by chemical formula)
(Mass of element in 1 mol of a compound / molar mass of compound) * 100
Empirical Formula
compounds smallest whole number mole ratio of the elements
ex. H2O2 → HO
can be the same as the molecular formula
Molecular Formula
specifies actual number of atoms of each element in the formula unit of the substance
whole number multiple of the empirical formula
Hydrate
compound that has a specific number of water molecules bound to its atoms
ex: Na2CO3 ‧ 10H2O
Anhydrous
hydrous compounds after heating
Stoichiometry
study of quantitative relationship between amount of reactants and products
chemical reactions stop when a reactant runs out
based on the law of conservation of mass
relationships derived from balanced chemical equation
Mole ratio
ratio between the number of moles of any substance in a balanced equation
Number of mole ratios written
n(n - 1)
n = number of species in a chemical reaction
Limiting Reactants
limits the extent of the reaction and determines the amount of product formed
Excess Reactants
unused reactants
rozumim
HOW TO FIND THE LIMITING REACTANT:
Problem: The reaction of chlorine gas with solid phosphorus (P4) produces solid phosphorus pentachloride. When 22.5 g chlorine reacts with 29.0 g P4, which reactant is limiting?
Balance the equation
10Cl2(g) + P4(s) → 4PCl5(s)Convert the gram amounts of both elements into moles
22.5 × 1 / 70.892 = 0.317
29 × 1 / 123.7512 = 0.234Divide the mol amounts you just found (0.317, 0.234) by the respective coefficients from the balanced equation
0.317 / 10 = 0.0317
0.234 / 1 = 0.234The lowest number from step 3 is the limiting reactant
0.0317 < 0.235
chlorine is the limiting reactant
Rozumíte?
Ymmaerraen
HOW TO FIND THE MASS OF THE EXCESS REACTANT:
Equation: 10Cl2(g) + P4(s) → 4PCl5(s)
Limiting Reactant: Chlorine (22.5g = 0.317 mol)
Excess Reactant: Phosphorus (29.0g = 0.234 mol)
Since we know that chlorine is the limiting reactant, use mole ratios to find out how many moles phosphorus will actually be used
0.317 mol Cl × 1 mol P4 / 10 mol Cl2 = 0.0317 mol P4convert mol to g
0.0317 mol P4 × 123.7512 = 3.93subtract the amount used with the amount given in total
29.0 - 3.922 = 25.078
Ymmärrätkö?
Theoretical yeld
maximum amount of a product that can be produced from a given amount of reactant
if two reactant amounts are given, find the limiting reactant, and then solve
Actual Yield
The amount of a substance actually produced
Percent Yield
actual yield / theoretical yield × 100
Suspension
mixtures containing particles that settle if undisturbed
Colloids
heterogenous mixtures with particles sized 1-100nm (intermediate)
do not settle out
Brownian movmenet
jerky, random movements of particles in a liquid colloid (from particle collisions)
Tyndall Effect
when dispersed colloid particles scatter light
miscible
two liquids that are soluble in each other are ________
Insoluble
substance that does not dissolve
Immiscible
liquids that can be mixed but then separate are __________