FNH 351 - Vitamins and Energy Metabolism -#2
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
vitamin b6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
what is the active form of vitamin B6?
pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)
what forms of B6 are in meat/fish products?
PL, PLP, PM, PMP
what forms of B6 are in plant foods?
PN, PNP, PN-glycoside
what form of B6 is found in supplements?
PN hydrochloride
what are some food sources rich in B6?
liver, beef, fish, poultry, and plant-based products (thus vegetarian diet can also be adequate for B6 intake)

how is vitamin B6 digested?
phosphorylated forms are dephosphorylated by alkaline phosphatase which is located on the brush border and requires zinc, and nonspecific phosphatases located in the GI tract. Conjugated B6 (i.e., pyridoxine beta-glucoside) is hydrolyzed by mucosal glucosidase
how is B6 absorbed?
Free PN, PL and PM are absorbed (mainly in jejunum) via passive diffusion
PNP, PLP and PMP only absorbed at high intakes
Conjugated B6 (pyridoxine beta-glucoside) requires hydrolysis
In enterocyte:
Some metabolic trapping of PN/PL/PM in enterocyte as phosphorylated forms
PN, PL and PM cross basolateral membrane for entry into hepatic portal vein
Newly absorbed PL / PN / PM taken up by the liver through passive diffusion
how is the absorption efficiency of B6?
overall high
can all B6 forms be converted to the active coenzyme form?
yes, but the formation of PLP is riboflavin dependent
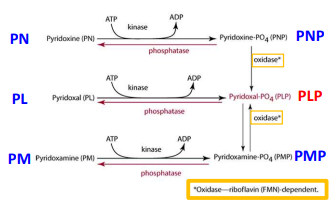
where do the conversions of different forms of B6 in the liver release into?
the bloodstream. mainly found in the form of PLP (and PL), bound to albumin (75-90% of circulating B6)
what happens to excess intracellular PLP?
its hydrolyzed; and the PL can be found in the blood but to a lesser extent
what enzyme is required for these reactions? PL / PN / PM → PLP / PNP / PMP
ATP-dependent kinase
what enzyme is required for these reactions? where is it found? PNP / PMP → PLP
FMN-dependent PNP and PMP oxidase; mainly found in liver and enterocytes
how is B6 taken up by tissues?
must be converted from the PLP form to PL by the removal of the phosphate group by phosphatase. Non-phosphorylated B6 forms are able to cross cell membranes. Rephosphorylation occurs within the cells
___% of total body vitamin B6 is in muscle, mostly in the form of ___ bound to ___. __% of total body b6 is in the _
75–80% of total body vitamin B6 in muscle, mostly in form of PLP bound to glycogen phosphorylase. 5-10% of total body vitamin B6 in liver
what is PLP metabolized/degraded to?
PLP → PL → 4-pyridoxic acid 4-PA
what enzyme degrades PLP in the tissues?
NAD-dependent aldehyde dehydrogenase
what enzyme degrades PLP in the liver/kidneys?
FAD-dependent aldehyde oxidases
how is B6 excreted?
mainly in the form of 4-PA in the urine, but also some urinary excretion of PL. At high intakes of PN (through high-dose B6 supplements), excretion of B6 occurs in the form of PN and 5-pyridoxic acid , with lower excretion of 4-PA.
what are the functions of B6?
amino acid metabolism
production of neurotransmitters, nucleic acids, heme
lipid metabolism
tryptophan catabolism → formation of niacin
glycogen catabolism → glycogen phosphorylase, formation of glucose-1-P (50% of body B6 used for this enzyme)
PLP = coenzyme in ____ reactions, ___ reactions and in ____ reactions
decarboxylation, (side-chain) cleavage reaction, and transamination
list 2 examples of PLP being a coenzyme for decarboxylation reactions
histidine decarboxylation: histidine → histamine
synthesis of neurotransmitters: Glutamate → gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), 5-HTP → serotonin, L-DOPA → dopamine
PLP is a coenzyme in the ___ pathway/ ___ metabolism
coenzyme in the tryptophan-niacin pathway/kynurenine metabolism
PLP is a coenzyme in ____ metabolism
methyl nutrient metabolism (transfer of one-carbon units from serine/glycine)
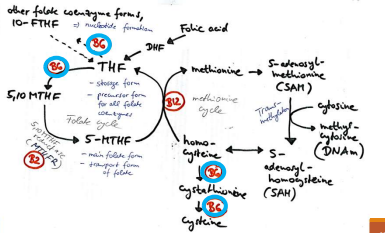
PLP is a coenzyme in the ____ pathway. What is ____?
coenzyme in the transsulfuration pathway which is the transfer of sulfur group from one aa to another. For example, from homocysteine to serine, forming cysteine
how does cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS) deficiency affect B6 intake?
this deficiency reduces the enzyme activity to 50% or less, causing homocysteine levels to increase. Therefore, to mediate this, high-dose B6 supplements are required; dosage of 100-500 mg. This high dosage improves symptoms to some extent, however, monitoring for signs of toxicity is required
what is the non-coenzyme role of PLP?
PLP effects gene expression
Which nutrient status/metabolism does vitamin B6 influence?
amino acid metabolism
folate metabolism; for folate to receive 1 carbon units from serine/amino acids
glucose metabolism → maintenance of blood glucose through gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis
lipid metabolism
niacin formation depends on B6
→ Which nutrients does vitamin B6 metabolism depend on?
zinc = cofactor for phosphatases (digestion of food-derived B6)
riboflavin (B2) for the conversion of food-derived B6 forms to the active coenzyme form of B6 (PLP)
what are the signs and symptoms of B6 deficiency?
dermatological signs and neurological symptoms
what are the dermatological signs of B6 deficiency?
Seborrheic rash on the face, neck, and shoulders
what are the neurological symptoms of B6 deficiency?
Weakness, fatigue
Confusion
Peripheral neuropathy
Seizures and convulsion
what are some other symptoms of B6 deficiency?
Reduced niacin synthesis from tryptophan
Hypochromic (reduced colour), microcytic anemia due to reduced heme synthesis
Impaired one-carbon metabolism
elevated plasma total homocysteine (hyperhomocysteinemia)
Inflammation
how prevalent are clinical symptoms of B6 deficiency?
Low prevalence of clinical symptoms of vitamin B6 deficiency in humans because of abundant occurrence of vitamin B6 in diverse food sources
what are the risk factors for developing vitamin B6 deficiency?
Alcoholism
Drug-nutrient interactions
Corticosteroids for suppressing immune system
Anticonvulsants for diminishing seizures
Oral contraceptives
Suboptimal B6 status associated with increased risk of:
Cardiovascular disease
Stroke
Dementia
Preterm birth, abortion
what are the signs of adverse health consequences of high-dose B6?
tingling in feet and hands = sensory and peripheral neuropathy
impaired motor control at intake levels of >2g/d
what is the UL of B6?
100 mg/day