AP Psychology Chapter 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:46 AM on 10/11/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
1
New cards
neuron
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
2
New cards
dendrite
the bush, branching extensions of a neuron that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body
3
New cards
glial cells
cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons`
- provide structural support
- supply nourishment to neurons
- insulation to axons and other cells
- Help remove neurons’ waste products
- Play role in development of nervous system in human embryo
- May also send and receive signals
- provide structural support
- supply nourishment to neurons
- insulation to axons and other cells
- Help remove neurons’ waste products
- Play role in development of nervous system in human embryo
- May also send and receive signals
4
New cards
Glia disorders
- Dysfunction in glia cells may contribute to cognitiv impairment seen in schizo. Disorders + some forms of depressive disorders
- Degeneration of glial tissue may lead to alzheimers
- Key factor in chronic pain
- Degeneration of glial tissue may lead to alzheimers
- Key factor in chronic pain
5
New cards
axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
6
New cards
myelin sheath
a layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons; enables vastly grater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the next
7
New cards
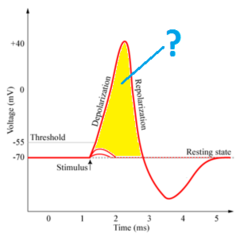
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
8
New cards
cell body (soma)
contains nucleus, DNA, RNA, info that makes that cell what it is
9
New cards
terminal branches of axon
form junctions with other cells
10
New cards
threshold
the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
11
New cards
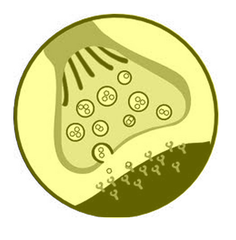
synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and he dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
12
New cards
reuptake
a neurotransmitter's re-absorption by the sending neuron
13
New cards
endorphins
natural, opiate-like neurotransmitters linked to pain control and to pleasure
- Agonist: opiate dugs (morphine + heroin)
- runner's high
- Agonist: opiate dugs (morphine + heroin)
- runner's high
14
New cards
acetylcholine (ACh)
neurotransmitter that enables inv. muscle action, learning, arousal, and memory
- excitatory
- Agonst: nicotine
- can produce excitatory + inhibitory
- excitatory
- Agonst: nicotine
- can produce excitatory + inhibitory
15
New cards
ACh producing neurons
Alzheimer's disease - associated with a deterioration of . . . ?
16
New cards
Dopamine (DA)
neurotransmitter that influences voluntary movement
- Low levels = Parkinson's Disease
- High Levels = Schizophrenia
- Low levels = Parkinson's Disease
- High Levels = Schizophrenia
17
New cards
dopamine receptor
schizophrenia is associated with an excess of this neurotransmitter's receptors
18
New cards
dopamine
under-supply associated brain produced tremors and decreased mobility associated with Parkinson's disease
19
New cards
serotonin
neurotransmitter that affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
- Abnormal levels may contribute to OCD + depression
- Agonist: LSD
- reuptake after serotonin is in synapse
- Abnormal levels may contribute to OCD + depression
- Agonist: LSD
- reuptake after serotonin is in synapse
20
New cards
serotonin
under-supply associated with depression, Prozac raises level
21
New cards
Norepinephrine
neurotransmitter that helps control alertness and arousal
22
New cards
GABA + glycine
(neurotransmitter) depress/inhibit neural firing/central nervous system
- agonist: Valium, anti-anxiety drugs + alcohol
- agonist: Valium, anti-anxiety drugs + alcohol

23
New cards
GABA agnosts
Valium, anti-anxiety drugs + alcohol
24
New cards
agonist
molecule similar enough to a neurotransmitter to bind to its receptor and mimic its effects
25
New cards
antagonist
molecule similar enough to a neurotransmitter to bind to its receptor and block the neurotransmitter's functioning
26
New cards
nervous system
the body's speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems
27
New cards
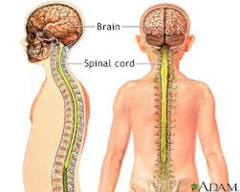
central nervous system
the brain and spinal cord
28
New cards
peripheral nervous system
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body. Made up of nerves that lie outside brain + spinal cord
29
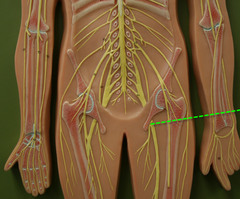
New cards
nerves
bundled axons that form neural "cables" connecting the central nervous system with muscles, glands, and sense organs
30
New cards
somatic nervous system
made up of nerves that controls the voluntary movements of skeletal muscles
- carry commands from CNS to muscles
- carry commands from CNS to muscles
31
New cards
autonomic nervous system
part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs: heart, blood vessles, smooth muscles, glands
- controlled by CNS
- Controls automatic, involuntary, visceral functions
- Two branches: sympathetic + parasympathtic
- fight or flight
- controlled by CNS
- Controls automatic, involuntary, visceral functions
- Two branches: sympathetic + parasympathtic
- fight or flight
32
New cards
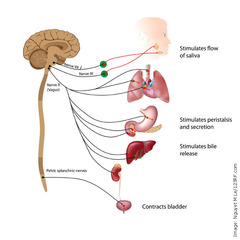
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
33
New cards
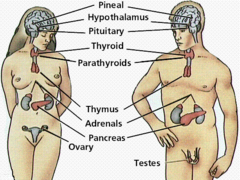
endocrine system
the body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream
34
New cards
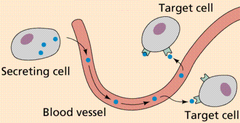
hormones
chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and affect other tissues
35
New cards
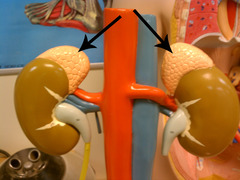
adrenal glands
a part of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) that help arouse the body in times of stress
36
New cards
pituitary glands
the endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, the pituitary regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands
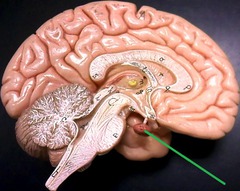
37
New cards
lesion
tissue destruction; in the brain, a naturally or experimental caused destruction of brain tissue
38
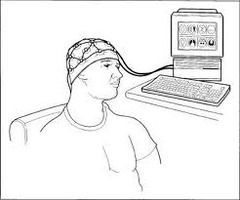
New cards
EEG
an amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity that sweep across the brain's surface. These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp
39
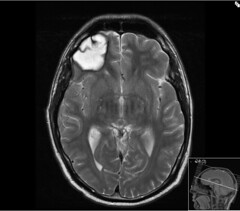
New cards
CT scan
a series of x-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by computer into a composite representation of 3d brain. Portrays only structure
Benefits:
- reasonable
- sees structure and what's phsycially wrong w/ brain
disadvantages
- exposed to a lot fo x rays
- drink contrast for scan --> some people can't tolerate that
Benefits:
- reasonable
- sees structure and what's phsycially wrong w/ brain
disadvantages
- exposed to a lot fo x rays
- drink contrast for scan --> some people can't tolerate that
40
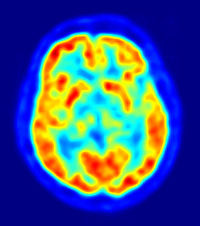
New cards
PET scan
a visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task
41
New cards
MRI
a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer generated images of soft tissues. Scans show brain structure
benefits:
- more in-depth + clearer than ct
benefits:
- more in-depth + clearer than ct
42
New cards
fMRI
measures mvmt of blood molecules (index of neural acivity). Shows structure + function
43
New cards
brainstem
the oldest part and central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull. Responsible for automatic survival functions
44
New cards
reticular formation
a nerve network in the brainstem that plays an important role in controlling arousal
45
New cards
thalamus
relay station for sensory info
- All of sensory info except smell → goes from sense organ → through thalamus
- All of sensory info except smell → goes from sense organ → through thalamus
46
New cards
cerebellum
the "little brain" at the rear of the brainstem; functions include processing sensory input and coordinating movement output and balance
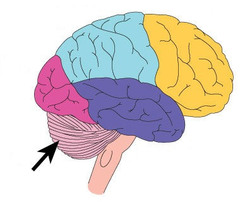
47
New cards
limbic system
the overall system of the brain that regulates emotions and controls behavior. Includes the Hippocampus, amygdala, hypothalamus, and other structures. Donut-shaped neural system located below the cerebral hemisphere; associated with emotions and drives
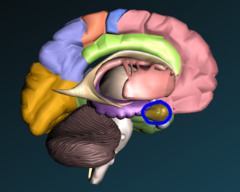
48
New cards
amygdala
two lima bean-sized neural clusters in the limbic system; linked to emotion --> specifically fear and anger but others as well
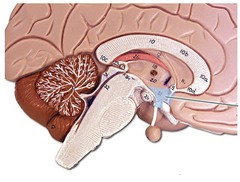
49
New cards
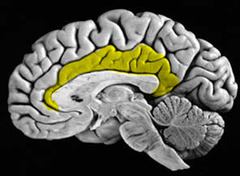
hypothalamus
a neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several body maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward (4 Fs)
50
New cards
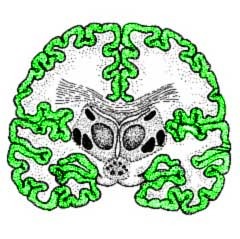
cerebral cortex
the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres; the body's ultimate control and information processing center
51
New cards
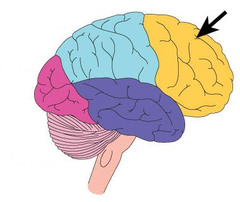
frontal lobes
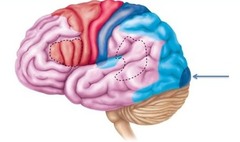
portion of the cerebral cortex lying just behind the forehead; involved in speaking and muscle movements and in making plans and judgments
- Prefrontal Cortex + Motor Cortex + Broca's Area
- Prefrontal Cortex + Motor Cortex + Broca's Area
52
New cards
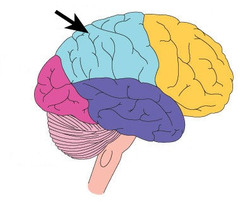
parietal lobes
portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; responsible for spacial orientation + touch
53
New cards
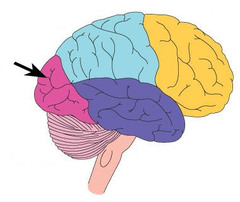
occipital lobes
portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head; responsible for visual perception, including colour, form and motion.
54
New cards
temporal lobes
portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; auditory processing + hearing
Primary Auditory Cortex + Wernicke's Area
Primary Auditory Cortex + Wernicke's Area
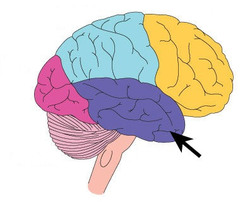
55
New cards
motor cortex
mvmt of muscles
frontal lobe
frontal lobe
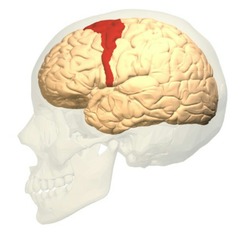
56
New cards
sensory cortex
an area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations
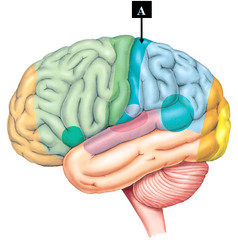
57
New cards
Wernicke's area
controls language comprehension
Temporal lobe
Temporal lobe
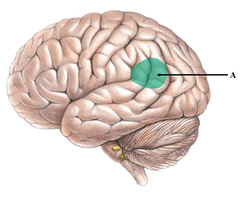
58
New cards
Broca's area
left frontal lobe
production of speech
production of speech
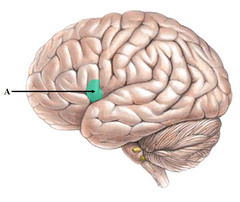
59
New cards
visual cortex
interpreting incoming visual information
60
New cards
brain plasticity
the brain's ability to change, especially during childhood, by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience --> neural reorgininzation
61
New cards
neurogenesis
the formation of new neurons
62
New cards
corpus callosum
large bind of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them
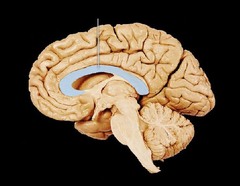
63
New cards
split brain
a condition resulting from surgery that isolates the brain's two hemispheres by cutting the fibers (mainly those of the corpus callosum) connecting them
64
New cards
chromosomes
threadlike strands of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecules that carry genetic information
65
New cards
DNA
a complex molecular containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes
66
New cards
genes
the biochemical units of heredity that make up the chromosomes and serve as the key functional units in hereditary transmission; segments of DNA capable of synthesizing a protein
67
New cards
Terminal Buttons
small knobs that secrete neurotransmitters
68
New cards
Synaptic vesicles
store various neurotransmitters
69
New cards
absolute refractory period
min length of time after an action potential, during which another action potential/ impulse can not occur. After firing Action potential --> channels close up + time is needed before they are ready to open up again
70
New cards
all or none law
a neuron either fires or it doesnt
71
New cards
Presynaptic neuron
neuron that sends a signal across the gap
72
New cards
postsynaptic neuron
neuron that recieves a signal
73
New cards
postsynaptic potential
Graded (vary in size) and inc/dec the prob of a neural impulse being fired in the receiving cell in prop. to amnt of voltage change. Do not follow all-or-none law
74
New cards
Inhibitory PSP
- stop action potentials
- negative voltage shift
- Dec likelihood that postsynaptic neuron will fire AP
- negative voltage shift
- Dec likelihood that postsynaptic neuron will fire AP
75
New cards
Excitatory PSP
- if it locks on → going to excite future cells + lots of more action potentials will happen → keep sending messages
- positive voltage shift
- Inc likelihood that postsynaptic neuron will fire AP
- positive voltage shift
- Inc likelihood that postsynaptic neuron will fire AP
76
New cards
synaptic pruning
brain eliminates extra synapses. cause neural restructuring that very likely has important consequences for normal and abnormal brain function
77
New cards
Norepinephrine (NE)
- excitatory
- Contributes to mood + arousal
- Cocaine elevates activity in NE synapse
- People who suffer from depression appear to have lower levels of NE
- Can produce excitatory or inhibitory effects at virtually all synapses
- Contributes to mood + arousal
- Cocaine elevates activity in NE synapse
- People who suffer from depression appear to have lower levels of NE
- Can produce excitatory or inhibitory effects at virtually all synapses
78
New cards
Sympathetic Division
mobilizes body’s resources for emergencies
- creates fight or flight
- release of hormones that ready body for exertion
- creates fight or flight
- release of hormones that ready body for exertion
79
New cards
parasympathetic Division
conserves bodily resources
- Activates processes that allow body to save + store energy
- Activates processes that allow body to save + store energy
80
New cards
Fight or flight
81
New cards
afferent nerves
axons that carry fiber info outward from body to CNS
82
New cards
efferent nerves
axons that carry info outward from CNS to periphery of body
83
New cards
spinal cord
- Connects brain to rest of body through PNS
- Houses bundles of axons that carry brain’s commands to
- Most forms of paralysis result from spinal cord damage
- Transmit signals from brain to neurons that signal body’s muscles to move
- Houses bundles of axons that carry brain’s commands to
- Most forms of paralysis result from spinal cord damage
- Transmit signals from brain to neurons that signal body’s muscles to move
84
New cards
cerebrospinal fluid
nourishes the brain + provides protective cushion for it
- To enter: substances in blood have to cross blood-brain barrier - semipermeable membrane taht stops some chemicals from leaving bloodstream to enter brain
- To enter: substances in blood have to cross blood-brain barrier - semipermeable membrane taht stops some chemicals from leaving bloodstream to enter brain
85
New cards
electrical stimulation of the brain (ESB)
sending weak electrical current into brain to stimulate/activate it
86
New cards
James Olds' research on pleasure centers
- investigating whether rats might be made uncomfortable by electrical stimulation of certain areas of their brain
- electrical current given when rats enter certain part of cage to deter them
- rats kept coming back + wanted to get shocked
- electrical current given when rats enter certain part of cage to deter them
- rats kept coming back + wanted to get shocked
87
New cards
hindbrain
cerebellum, medulla, pons
88
New cards
midbrain
reticular formation
89
New cards
forebrain
cerebrum, cerebral cortex
90
New cards
medulla
responsible for automatic functions
91
New cards
pons
responsible for controlling sleep, dreams, sleep cycle, wakefulness
92
New cards
cerebellum
responsible for balance, fine motor coordination
93
New cards
Cerebrum
largest part of the brain. It is divided into two hemispheres, or halves, called the cerebral hemispheres. Areas within the cerebrum control muscle functions and also control speech, thought, emotions, reading, writing, and learning
94
New cards
cerebral cortex
outermost layer of the brain that is associated with our highest mental capabilities
95
New cards
somatosensory cortex
controls sensory info → only touch
96
New cards
auditory cortex
Involves hearing, speaking, understanding written + verbal words
97
New cards
Prefrontal Cortex
Reasoning, planning, paying attention, getting organises, decision making, impulse control
98
New cards
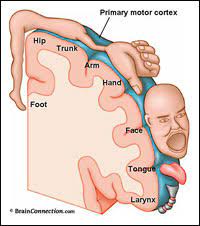
homunculus brain map
- organized map of the proportional representation of the contralateral somatosensory or motor neurons on the cortex or passing though a part of the brain
- as information comes to the brain from different parts of the body, information from the hand will all synapse in this region of the cortex
- as information comes to the brain from different parts of the body, information from the hand will all synapse in this region of the cortex
99
New cards
mirror neurons
use to incorporate info about body language, social cues, etc.
100
New cards
left hemisphere
- controls the right half of the body
- Language - written and spoken
- Simple math
- Logical + analytical
- Language - written and spoken
- Simple math
- Logical + analytical