Pharm E4- ER
1/139
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
What is the rapid sequential process of emergent tracheal intubation?
Preparation → sedation → paralysis
What physiologic response can we expect to occur from laryngoscopy?
Inc/dec HR, inc ICP, inc BP, inc airway resistance (bronchospasm)
What 2 meds are used for pretreatment before intubation?
Lidocaine & atropine
Which drug?
antidysrhythmic with anesthetic properties
given 1-2 minutes before intubation
blunts cough//gag reflex
used to prevent rise in ICP
good for suspicion of inc ICP, TBI, cerebral swelling
Lidocaine
Which drug?
antimuscarinic given prior to intubation
prevents worsening bradycardia
also used if difficult to visualize vocal cords d/t increased secretions → helps dry
Atropine
What is the best pretreatment to give prior to intubation in a small child getting repeated doses of succinylcholine (prone to bradycardia)?
Atropine
Is a short acting sedative or long acting sedative preferred for intubation?
Short acting → need to be able to correct if things go wrong or perform neuro exam after
Which drug?
sedative/hypnotic for general anesthesia induction & prior to NMB; produces light sleep to deep coma
imidazole derivative unrelated to other agents
EEG changes similar to barbiturates
rapid onset & offset
minimal hemodynamic & respiratory effects
Etomidate
What is the MOA of etomidate?
Activate GABA-A receptors to enhance GABA → hyper polarizes neurons w/ Cl → keeps APs from occurring
What are CIs to etomidate?
Known hypersensitivity
What is the DOA of etomidate?
5-10 minutes
*rapid onset LOC & offset
What drug interactions are seen with etomidate?
Increased effect of sedatives, hypnotics, & opiates
No interaction w/ any NMB
The following SEs are seen with which drug?
Trismus
muscles lock up, more difficult for paralytic to kick in & to intubate
Muscle twitching → myoclonic jerks
pain at injection site
dec plasma cortisol
lasts ~8 hrs after injection
caution with septic patients
Etomidate
What may need to be given with etomidate if used in a septic patient d/t decreased cortisol?
Additional steroids (hydrocortisone), maybe vasopressors
What BZDs are used as induction agents before intubation & provide sedation, amnesia, & anticonvulsant properties but no analgesia?
*used as adjuncts, not deep enough sedation alone
Midazolam (faster onset 1-2 min, 20 min DOA) & Lorazepam (longer DOA)
What would be a good adjunct induction agent prior to intubation if a patient is having seizures?
BZDs (lorazepam)
When is a decreased dose of midazolam needed d/t a longer half life?
Obesity, geriatric, CHF, hepatic or renal insufficiency
Which drug?
dissociative anesthetic derived from PCP
ultrashort & rapid acting → onset: 30-40s; DOA: 5-10 min
bronchodilator & leaves resp drive intact
better for hypotensive & status asthmaticus patients
Ketamine
In what patients should ketamine be avoided?
HTN and cerebral swelling/TBI d/t catecholamine release that increases HR, BP, & ICP
What SEs are seen with ketamine?
Sialogogue (inc saliva, pretx w/ atropine), elevated ICP, dysphoric reactions, vomiting (pretx w/ zofran)
What pretreatment can be given before ketamine to prevent sialogogue?
Atropine
What pretreatment should be given before ketamine to prevent vomiting, which would increase the risk of aspiration when intubating?
Zofran
What induction agent is better for intubation in a patient with hypotension or for status asthmaticus?
Ketamine
Which induction agent?
ultrashort & rapid acting → onset: 10-50 s, DOA: 3-10 min
can cause hypotension & decreased CNS perfusion
avoid in egg & soy allergy
Propofol
Which sedative increases BP?
Ketamine
Which sedative decreases BP?
Propofol
Which sedative does not affect BP?
Etomidate
What class of drugs?
block natural transmission of nerve impulses to skeletal muscles
No effect on LOC, pain perception, seizure activity
No direct effect on: heart, digestive system, brain, pupillary response, smooth muscle, other organ systems
Neuromuscular blockers
What drugs are depolarizing NMBs?
Succinylcholine
What drugs are non-depolarizing NMBs?
Pancuronium, Cisatracurium, Rocuronium, Vecuronium
What is the MOA of succinylcholine?
(2 phases) Initial depolarization - activates receptor→ fasciculations (short lived) → stays on receptor, prevents from resetting/remains refractory→ continuous stimulation desensitizes receptors & close → flaccid paralysis
What paralytic agent?
rapid & short→ onset: 30-90s, DOA; 5-10 min
given 30-60s after sedative
plasma esterase metabolism
*def in enzyme → longer DOA
renal excretion
no reversal agent
Succinylcholine
What are CIs to succinylcholine?
2-5 days after injuries/ conditions regulating ACh receptors
Narrow angle glaucoma (inc IOP)
PHx or FHx of malignant hyperthermia
Pseudocholinesterase def, neuromuscular dz, hyperkalemia
What SEs are seen with succinylcholine?
Fasiculations, hyperkalemia, prolonged neuromuscular blockade (esterase def), bradycardia (give atropine), & malignant hyperthermia
What should be given with succinylcholine to prevent fasciculations if you suspect a patient has increased ICP (further increases ICP)?
Lidocaine (& defasciculating dose of rocuronium)
What conditions can cause ACh receptor up regulation (leading to hyperkalemia, which is worsened by succinylcholine)?
*avoid ≥2-5 days after condition
Burns (esp 5 days after), denervation or neuromuscular disorders, crush injuries, intra-abdominal infx, myopathies, rhabdomyolysis, renal failure
Which of the following patients is NOT CI to succinylcholine? (**Test Q)
Pt w/ pre-existing hyperkalemia
Pt w/ severe burns after house fire 4 days ago
Pt w/ longstanding muscular dystrophy
Pt w/ massive crush injury from 20 minutes ago
Pt w/ massive crush injury from 20 minutes ago
What is the treatment for malignant hyperthermia?
Dantrolene, temp reduction (ice packs in groin/axilla, evaporative cooling, cold IVFs), & bicarb for lactic acidosis
What can be given to prevent bradycardia w/ succinylcholine?
Atropine
What paralytic agents?
Onset 2-3 min, DOA 20-30 min
longer; difficult if neuro exam is needed
safer, not many CIs, may be used in CV, pulm, & neuro emergencies
hepatic & renal metabolism (failure → longer DOA)
does not cause hypotension or tachycardia (neutral)
Vecuronium
What patients need less vecuronium to maintain paralysis?
Renal or hepatic failure
Which paralytic agent?
less vagolytic properties
fastest onset of non-depolarizing NMBs → 30-60s, DOA 20-75 minutes
Rocuronium
What drug is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor that is a competitive antagonist for non-depolarizing NMBs & is the reversal agent for rocuronium & vecuronium?
Neostigmine
What should be done if giving an NMB and you are concerned about seizures?
Give anticonvulsants first & have a bedside EEG
Do NMBs treat seizure activity?
NO - stops the outward signs of a seizure but it is still occurring internally
What drug?
long acting non-depolarizing NMB
vagolytic → tachycardia
not good for CV patients
Pancuronium
What drug?
Intermediate acting non-depolarizing NMB
no hepatic/ renal metabolism/ elimination → good for organ impaired patients
no issues w/ CV effects
Cisatracurium
What agents would be used in the following situations?
ventilatory synchronization
increased ICP → need them to not move in order to reduce ICP
prevent shivering during therapeutic hypothermia
facilitating diagnostic or therapeutic procedures
Long acting NMBs
What complications are associated with long term paralytics / NMBs?
VTE (tx w/ SCDs, heparin, etc)
VAP (prevent w/ oral hygiene, chlorhexidine)
Gastric ulcers (give H2RA or PPI)
Corneal abrasions (not blinking → tape eyes, use ointments)
ICU neuropathy
What is used for paralytic monitoring?
PN stimulator / train of 4 (MC ulnar n.) → goal is 1-2 twitches
Which agent should be longer lasting, a paralytic or a sedative?
*keep track of timing; consider 2nd doses at 5-10 minutes
Sedative
What is a common sedative + paralytic combo given for intubation?
Succinylcholine (4-10 min) & Etomidate (6-10 min)
*consider 2nd dose at 5-10 min
Patient is coming in with suspected head trauma and you are worried about increased ICP. Patient is also hypotensive. What are the best agents to use and what is the correct order?
***Test Q example
Lidocaine → Etomidate → Rocaronium
What agents are used in ACLS and are typically all found in crash carts?
Adenosine, amiodarone, atropine, calcium, dextrose, epi, lidocaine, magnesium, naloxone, sodium bicarbonate
What is the MOA of epinephrine?
Endogenous catecholamine: alpha & beta stimulation → increases HR, BP, & coronary perfusion
What are ACLS indications for epinephrine?
Symptomatic bradycardia → HR < 60 & evidence of poor perfusion
Cardiac arrest → VF, VT, PEA, asystole
What is the max IV/IO epi dose?
1 mg/dose
What is the max ET epi dose?
2.5 mg/dose
What dosage routes are used when IV can’t be established?
IO > ET
Why do ET medication routes forms require higher doses?
Different bioavailability in the lungs → less absorption
Which is a higher dose of Epi; 1:1,000 or 1:10,000?
1:1,000 (1 mg in 1 mL)
What medications are available in ET dosing (although rarely used)?
Lidocaine
Epinephrine
Atropine
Naloxone
What ACLS agent?
Muscarinic receptor antagonist → blocks Ach receptors on heart
Vagloytic: dec actions of vagus nerve → inc AV conduction & HR
Indications
symptomatic bradycardia (AV block or vagal mediated)
increased secretions
*not used in cardiac arrest anymore
Atropine
What is the max IV dose of atropine?
0.5 mg
What ACLS agents are used for bradycardia?
Epinephrine & atropine
What drug is an adenosine receptor agonist that causes AV node conduction block & interrupts reentry circuits (stops & restarts heart)?
Adenosine
What are indications for adenosine?
PSVT / supraventricular tachycardia
What happens if adenosine is administered too slowly?
Degrades before it reaches the heart d/t very short half life (< 10s); ineffective
How should adenosine be administered?
2 syringes w/ T-connector or stopcock; flush w/ ≥5 mL immediately after (IDK what we’re flushing with but just do it)
What drug?
Class III anti arrhythmic → blocks K channel efflux (+ na, ca, etc)
Rhythm control; slows ventricular conduction
IV push in cardiac arrest
Given over 20-60 min w/ perfusing rhythm
bolus/ loading dose upfront, then continuous infusion if effective
Amiodarone
What should you watch for when administering amiodarone?
Hypotension & bradycardia (not worried when actively coding)
What are indications for amiodarone?
SVT unresponsive to adenosine, wide complex tachycardias, Vfib, tachycardia
What is the max single dose of amiodarone?
300 mg
Which ACLS drug?
class IB anti arrhythmic → blocks myocardial Na channels & suppresses ventricular arrhythmias
works more on dead/ dying tissue → shortens refractory period + conducts electricity
risk of increased toxicity in renal & hepatic impairment d/t dec clearance
Lidocaine
What should be done to the dose of lidocaine if using in hepatic impairment or CHF?
Use ½ dose
What are ACLS indications for lidocaine?
Vfib / tachycardia (if amiodarone not available)
What is the drug of choice for torsades de pointes?
Magnesium
What ADRs are seen with magnesium?
Flushing d/t vasodilator, hypotension if given too quickly (*give NS at same time)
What adverse reactions are seen with sodium bicarbonate?
Tetany (transient hypocalcemia)
Why might you see hypocalcemia in a patient who was given PRBCs after a massive trauma?
Citrate based anticoagulant was also given to prevent clots
Which form of calcium?
smaller molecule, contains more Ca, more potent
rough on veins → phlebitis
given in unconscious or coding patient
use deepest vein possible, central line preferred
Calcium Chloride
Which form of calcium?
bigger molecule, less room for ca, less potent
easier on veins but requires bigger dose
Calcium gluconate
What is the dosing ratio of calcium gluconate vs chloride?
3 : 1
What ADRs can be seen with calcium?
Thrombophlebitis, tissue necrosis
Why should caution be used when giving naloxone while a patient is intubated?
Reverses CNS depression, pt will wake up & start to fight tube
Monitor CO2 response; opioids turns of CO2 response; RR may look fine but CO2 is high → give narcan
What drug?
Indication: hypoglycemia
ADR: irritating to veins
use smaller concentration on kids/ conscious pts
10% < 2 y/o
25% > 2 y/o
use higher concentrations if coding / unconscious
50% - adults
Dextrose
Besides dextrose, what else can be used to treat hypoglycemia?
PO glucose if possible or glucagon if unconscious
IDK if he’ll ask about the calories in nutrients but he mentioned it so here they are
Carbs: 4 cal/g
Protein: 4 cal/g
Fat: 9 cal/g (energy dense)
Alcohol: 7 cal/g
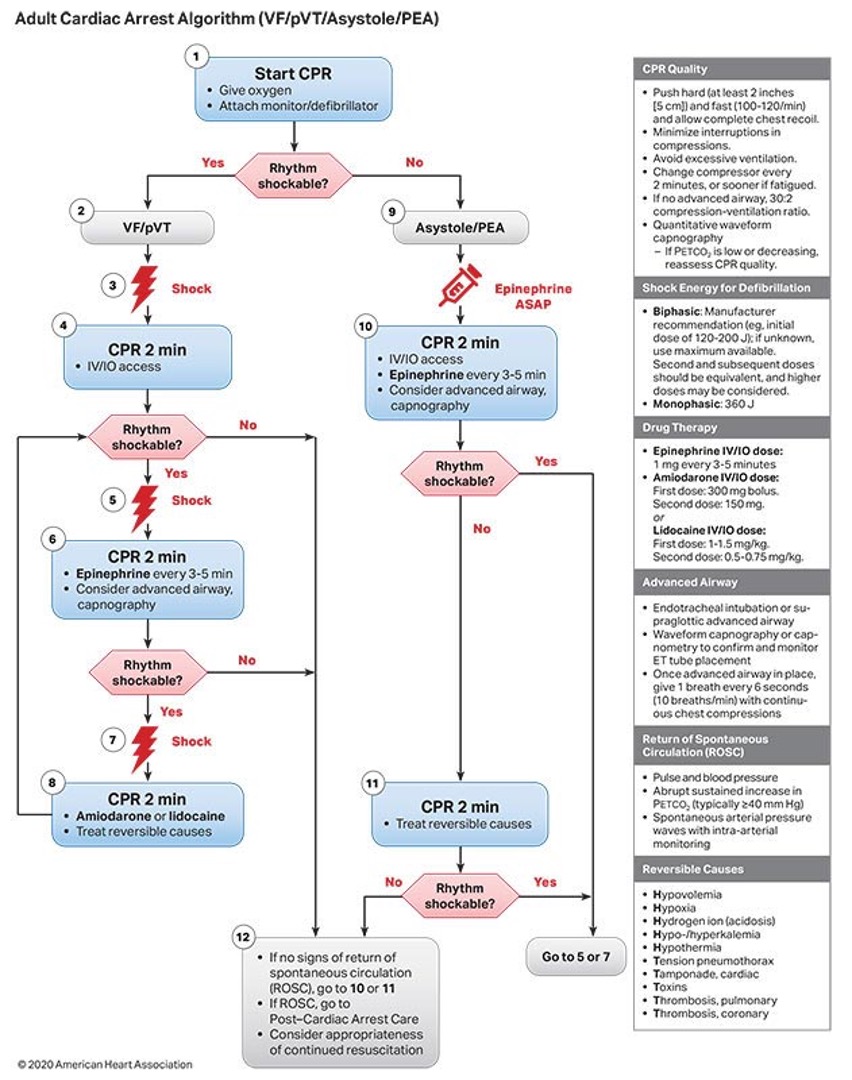
What is the treatment for a shockable rhythm (Vfib or Vtach)?
CPR & shock → epi → amiodarone (MC) or lido
What is the treatment for a non shockable rhythm (systole, PEA)?
Epi q 3-5 min & CPR
adult cardiac arrest algorithm
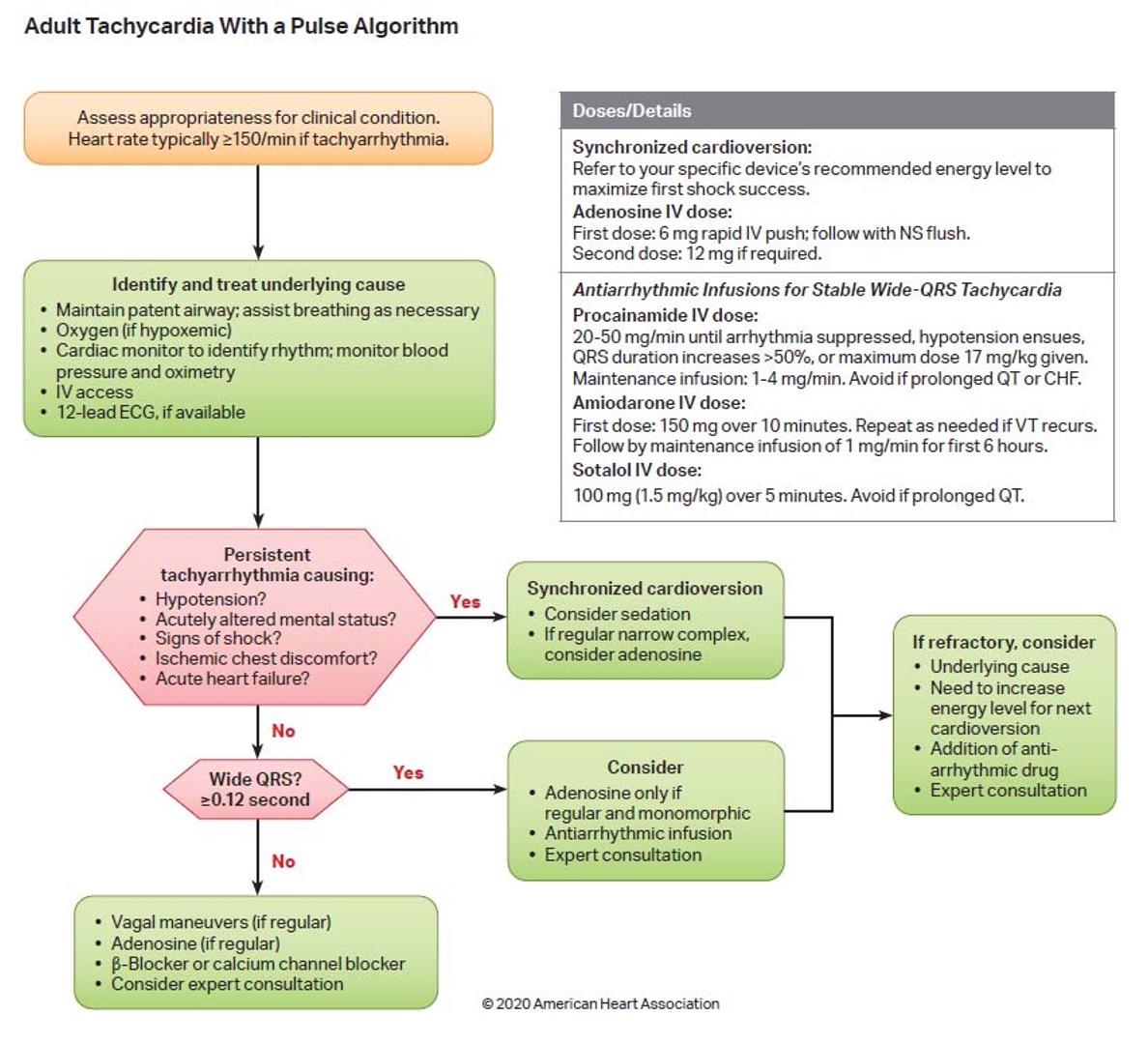
What is the treatment for adult tachy w/ a pulse (PSVT)?
Vagal maneuvers → adenosine → BBs (labetolol) or non DHP CCBs (deltiazam, verapamil)
Adult tachy w/ a pulse treatment algorithm
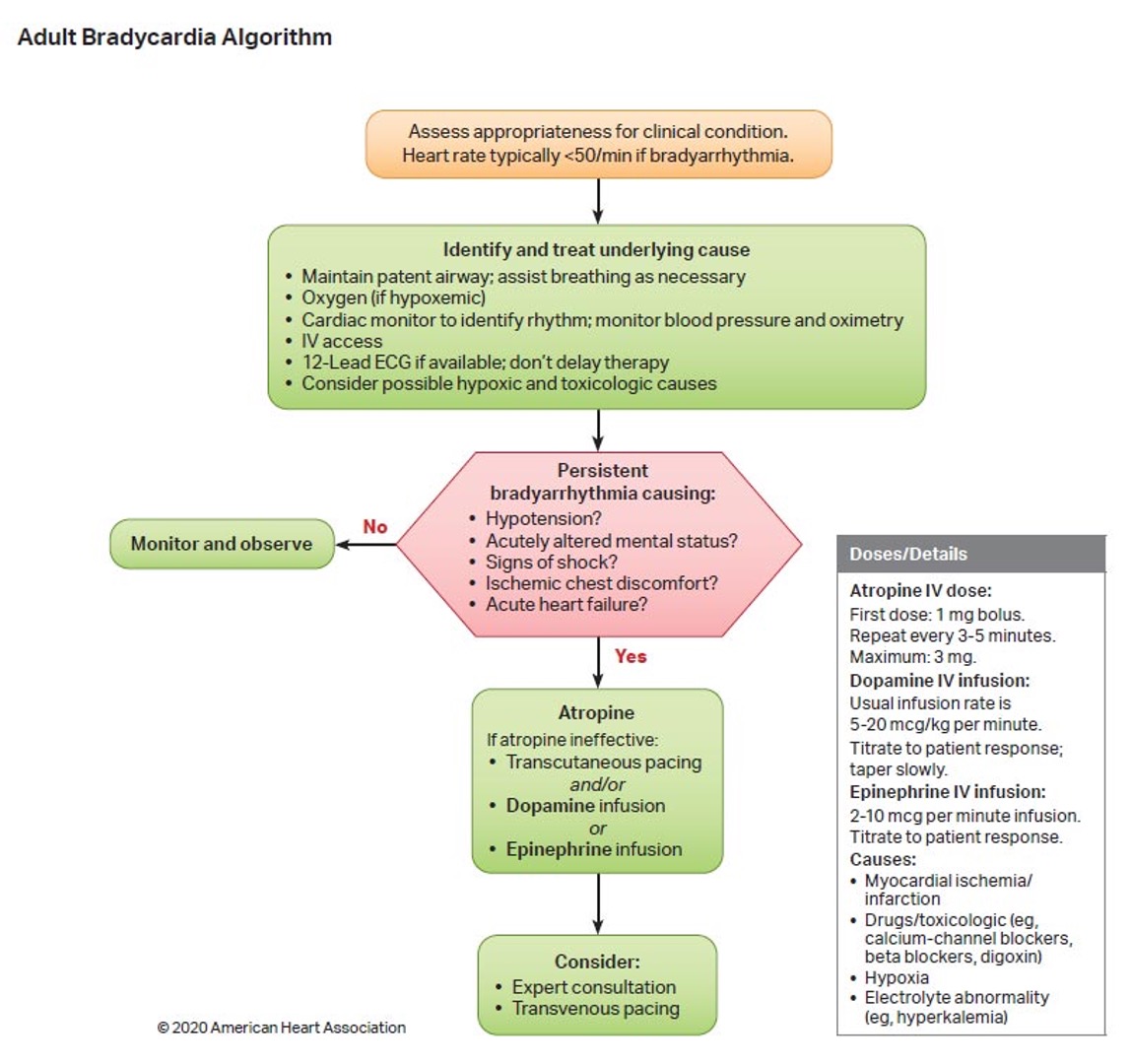
What is the treatment for adult bradycardia?
Atropine → DA infusion or EPI infusion (postive chronotrops, rate control)
Adult bradycardia algorithm
Which weight should you go with if a pediatric patient is between weights and is coding?
Round up
What are agents that increases speed of heart contractions (inc HR)?
Chronotropes
What are agents that increase contractility of heart (used if bad pump/HF)?
Inotropes
What are agents that increase peripheral vascular resistance (inc BP)?
Vasopressors
What drug is a metabolic precursor to epi & NE (converted peripherally to adrenergic agents on heart) that acts similarly to endogenous dopamine?
Dopamine (Intropin)