(chap 6) SEARCH FOR IDENTITY IN ADOLESCENCE
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Psychosocial Development in Adolescence
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Identity
A coherent conception of the self,
consisting of goals, values and beliefs to which the person is firmly committed.
Theory of self
When adolescents' cognitive development allows them to construct a "theory of self".
It is part of the healthy and vital process.
what if Identity crisis in adolescence
The identity crisis is rarely entirely resolved in adolescence; problems arise again and again during adulthood.
Self-esteem
what i feel
self-concept
what i think
Erik Erikson
Theory of Psychosocial Development
James Marcia
Identity status
Erikson Identity
develops through 8 stages of life
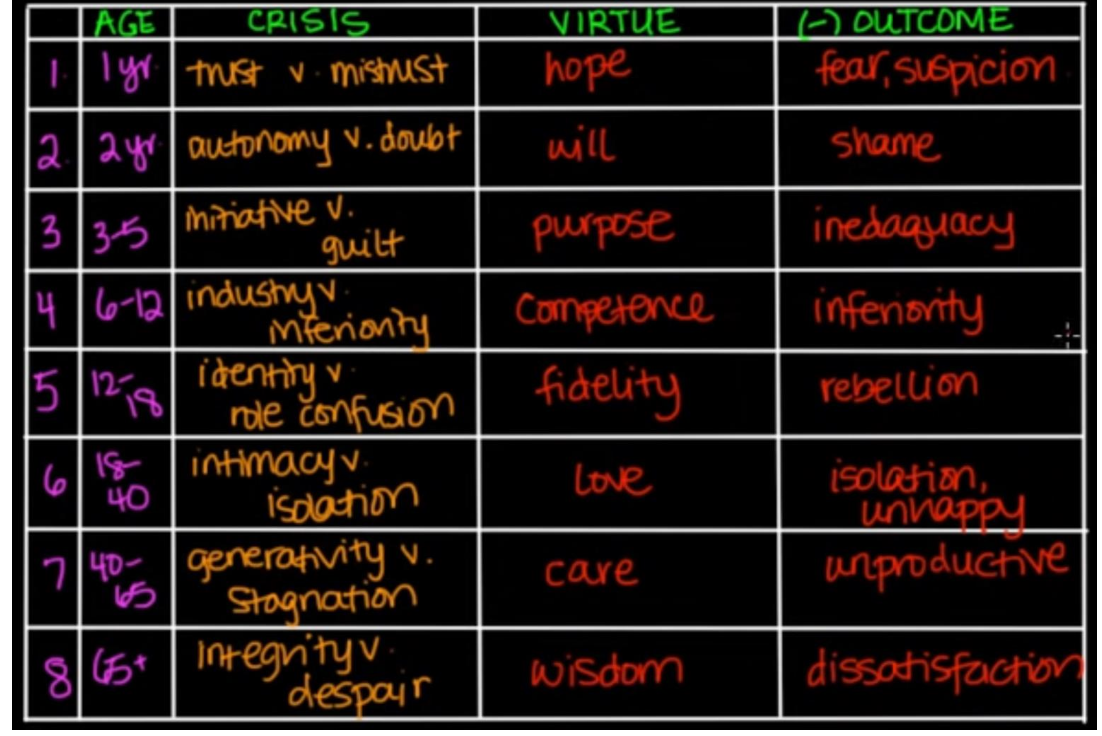
Identity vs confusion
Life stage → Puberty to early adulthood
• Type of experience → Adolescents tend to define their sense of self (Who am I?) or experience confusion about their roles.
Virtue developed: fidelity.
Unique adult with a coherent sense of self and a valued societal role.
Loyality sense of a self and valued role.
Unique adult with a coherent sense of self and a
valued societal role.
Virtue developed: fidelity.
Eriskon emphasised three fundamental problems to be solved
Choice of occupation.
Adoption of values.
Development of a satisfying sexual identity.
Choice of occupation.
Adolescence must decide important decisions in their life about their future occupation.
Adoption of values.
Adolescence goes through process of experimentation of perceptions in order to find their own value.
This will determine how they will behave in certain situations.
Development of a satisfying sexual identity.
Adolescents must explore identities, and experience their own perspective of life
this is important in order to let the identity to be mature
Psychosocial moratorium
Pause provided by adolescents, 'time out' for experimentation = period of protection needed to build a stable sense of self > allows to look for causes to engage with.
it is the time where adolescents explore without obligating them self into any identity.
Identity vs confusion - Non-resolution of the crisis
Behaviours with serious negative consequences
(e.g. criminal behaviour).
Identity vs confusion - Satisfactory-resolution of the crisis
Fidelity:
Loyalty, faith or sense of belonging to a loved one or friends.
Identification with a set of values, an ideology, religion, political movement, or ethnic group.
Fidelity
Loyalty, faith or sense of belonging to a loved one or friends.
Identification with a set of values, an ideology, religion, political movement, or ethnic group.
Identity or role confusion as the main danger
May delay the attainment of psychological maturity.
Some degree of confusion is standard → chaotic adolescent nature.
Exclusivism & intolerance of difference as defences against identity confusion.
James Marcia identity status
He proposed four identity statuses that depend on the combination of two dimensions:
whether or not they have undergone an identity crisis
whether or not they have adopted vocational, ideological or personal commitments
Two dimensions
Whether or not they have undergone an identity crisis
Whether or not they have adopted vocational, ideological or personal commitments
Identity levels or status
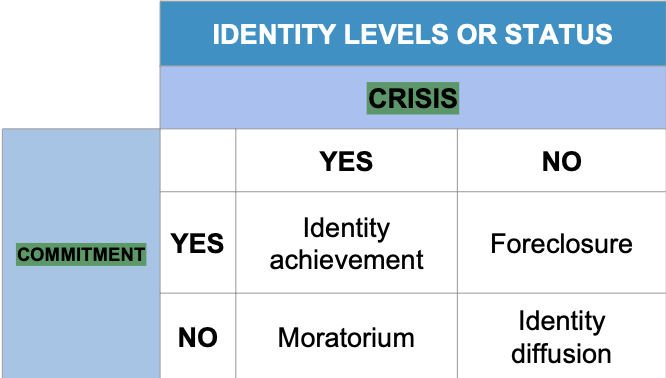
Identity achievement
Commitment yes
Crisis yes
Foreclosure
Commitment yes
Crisis no
Moratorium
Commitment no
Crisis yes
Identity diffusion
Commitment no
Crisis no
Exploration - crisis
Behaviour aimed at obtaining information about oneself or one's environment in order to make a decision of some importance
(internal behaviour, such as thinking about a subject, or external behaviour, such as changing one's clothes or appearance)
Commitment
Adherence to a set of goals, values and beliefs and their consolidation as likely guides for future action: a sense of loyalty.
Identity is expressed in our commitments objectively what is seen from the outside, which are the activities or areas in which he/she is involved, and subjectively what is most important to him/her.
Marcia: Identity, crisis and commitment.
Research-based on 30-minute semi-structured interviews on identity
status.
Identity-seeking theories
Distinction of 4 identity states →
■ identity achievement,
■ exclusion,
■ moratorium,
■ identity diffusion.
Key elements of Marcia´s theory
Presence or absence of crisis and commitment
Crisis/exploration
period of conscious exploration.
Commitment
Personal investment in an occupation or belief system, in the choice made.
decision or choice
crisis leads to compromise
Identity achievement
commitment without crisis
Foreclosure
crisis without compromise
Moratorium
without compromise or crisis
Identity diffusion
Identity-seeking theories.
They are not stages but changing states of identity depending on the particular moment.
CASE Olivia has considered her interests and talents and plans to become an engineer. She narrowed her college choices to 3 schools that offer good programmes in that field.
Identity achievement → crisis leads to compromise.
- It relates to:
✔ Greater maturity.
✔ Better performance in establishing social relations.
✔ High self-esteem and self-confidence.
✔ Democratic parents.
CASE Isabella knows exactly what she will do with her life. Her mother, a union leader in a plastics factory, arranged for her to enter the factory's apprenticeship programme. Isabella has never considered doing anything else.
Foreclosure → commitment without crisis.
- It relates to:
✔ Very close family ties.
✔ Tendency to follow a "powerful leader".
✔ Low levels of anxiety.
✔ High self-esteem and emotional well-being.
✔ Authoritarian parents.
CASE Josh can't decide about his future - should he attend community college or join the army? He can't decide what to do now or what he wants to do in the future.
Moratorium → crisis without compromise.
- It relates to:
✔ Seeking and resisting intimacy.
✔ High levels of anxiety.
CASE Jayden still has no idea what he wants to do, but that doesn't worry him. He thinks he can get some work and decide his future when he is ready.
Identity diffusion → without compromise or crisis.
- It relates to:
✔ Loneliness and unhappiness.
✔ Increased levels of anxiety and depression.
✔ Lower self-esteem.
✔ Permissive parents.
Almost half of adolescents
Exclusion or diffusion
From late adolescence onwards
more people are in moratorium or attainment.
Influencing factors affecting the search of identity
Ethnic and intercultural factors
Cultural socialisation
Refers to parental practices that teach children about their racial or ethnic heritage, promote cultural customs and traditions, and foster pride in one's culture.
Young people who have experienced cultural socialisation tend to have stronger and more positive ethnic identities.
Marcia's model applied
to ethnic identity
Case
Juanita has done little or no exploration of her ethnicity and needs to understand the issues involved clearly.
Identity diffusion → No commitment, no crisis.
Case:
Caleb has done little or no exploration of his ethnicity, but he feels about it. These feelings can be positive or negative, depending on the attitudes he assimilates at home.
Foreclosure → commitment without crisis.
Case
Emiko has begun to explore her ethnicity but needs clarification about what it means to her.
Moratorium → crisis without commitment.
Case
Diego has explored his identity and understands and accepts his ethnicity.
Identity achievement → Crisis and commitment.