Metabolism, Enzymes, and the Endocrine System Overview
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Metabolism
All chemical reactions involved in maintaining the living state of the cells and the organism.
Anabolic reactions
Reactions where energy is stored.
Catabolic reactions
Reactions where energy is released.
Enzymes
Proteins that speed up reactions that occur in living systems.
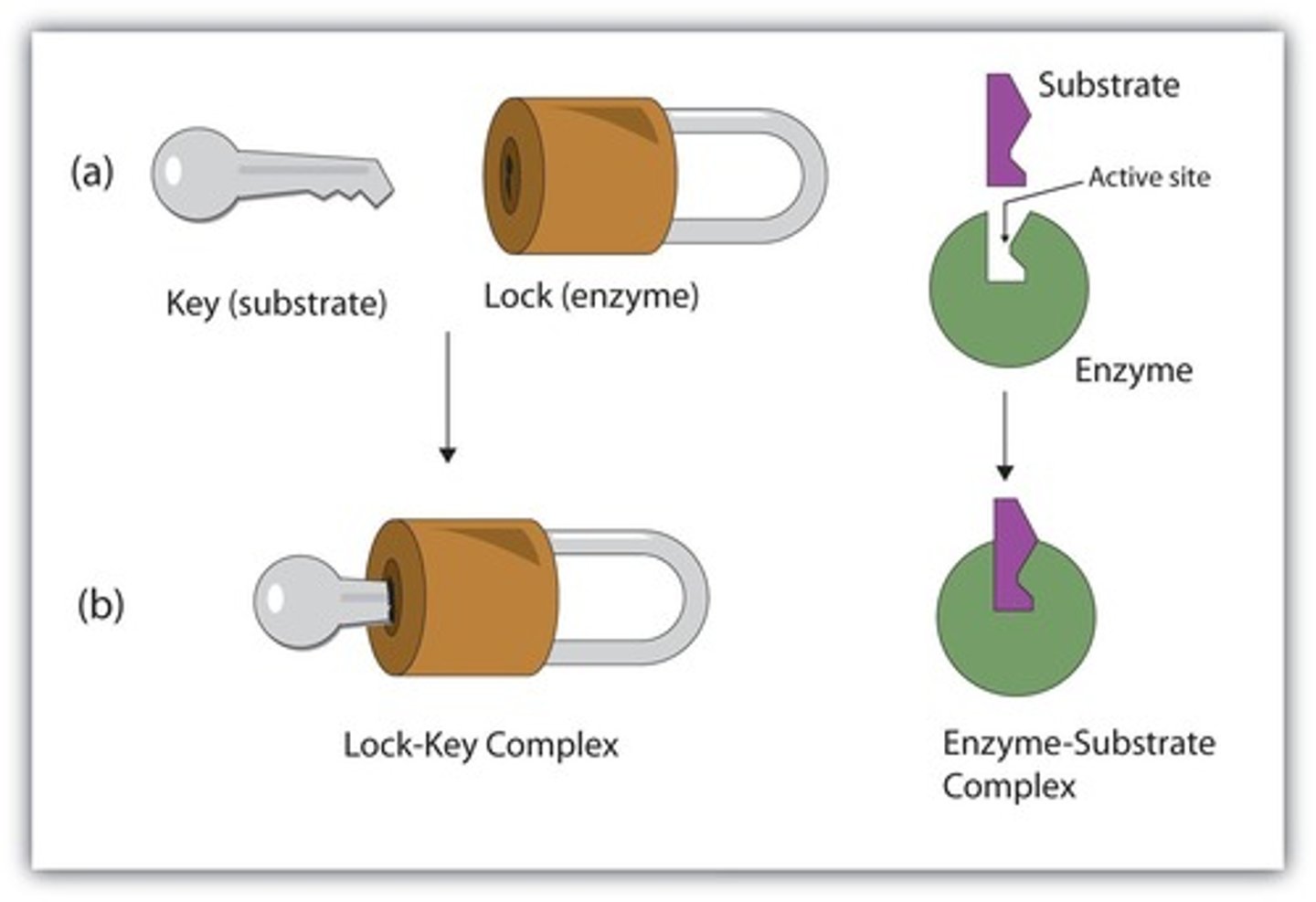
Lock and key model
Enzymes have an active site that is complementary to only one substrate.
Factors affecting enzyme activity
Enzymes have a specific set of conditions that will favour their action on the substrate and where they function optimally.
Denaturing
The process where the enzyme shape changes, preventing it from functioning.
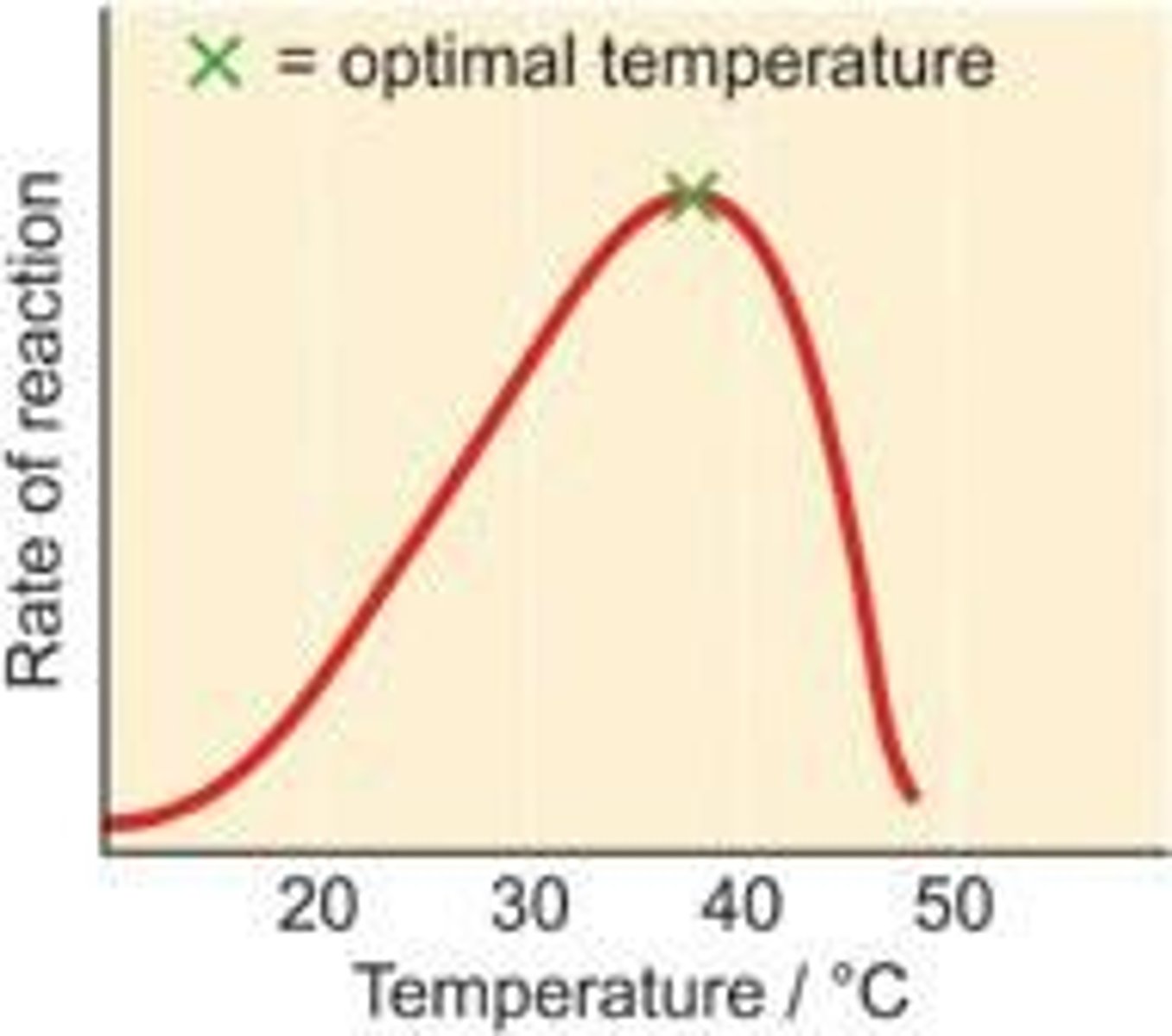
Temperature effects on enzymes
If temperatures are too high, the enzyme shape changes, preventing it from functioning. If temperatures are too low, the enzyme has not got enough kinetic (movement) energy to collide with the substrates as often and therefore action is reduced.
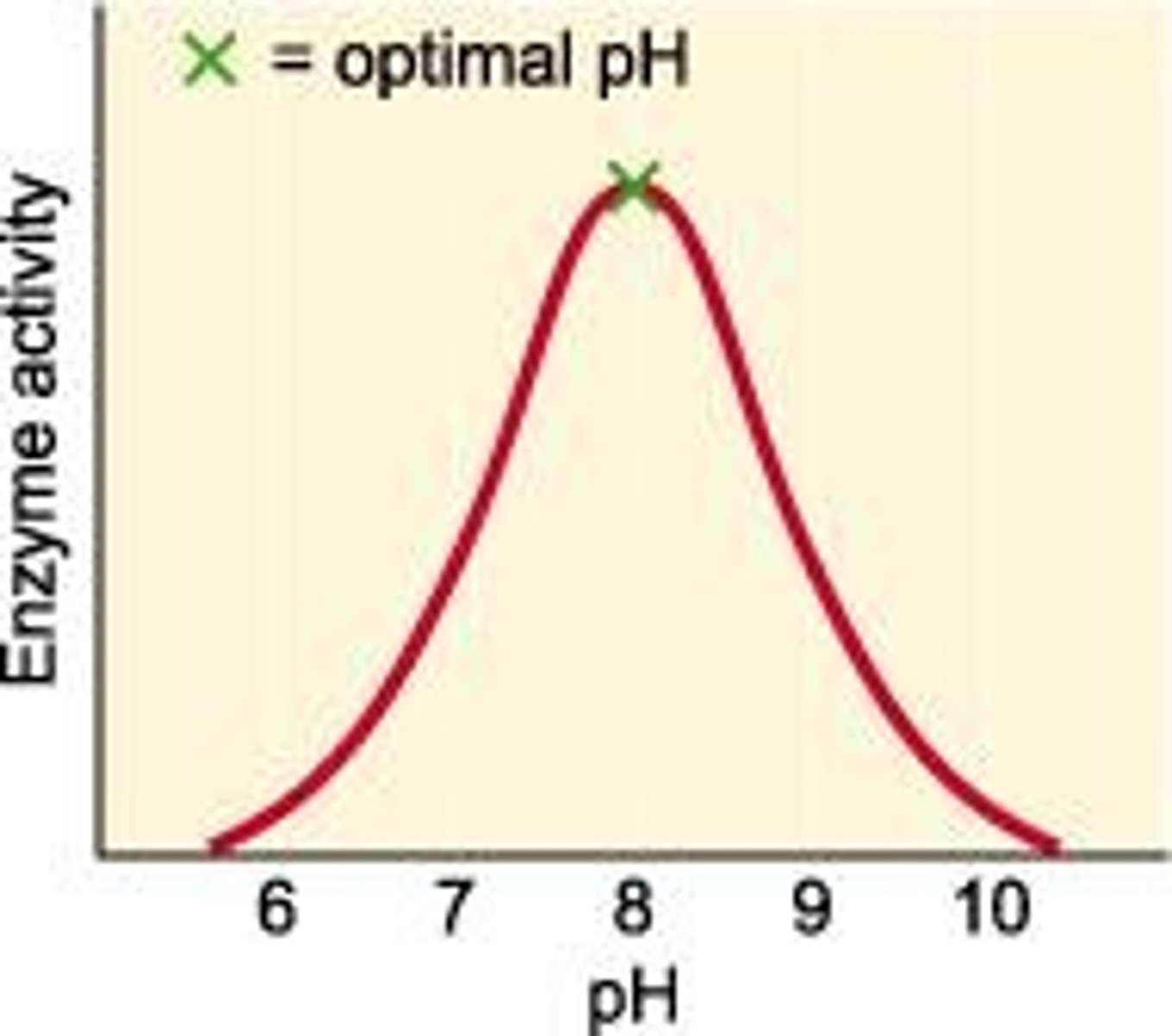
pH effects on enzymes
The rate of reaction increases to the optimum (maximum) point and then decreases either side of this.
Digestion
Enzymes are involved in the process of digestion, breaking down food into simple chemical substances.
Carbohydrates breakdown
Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose.
Proteins breakdown
Proteins are broken down into amino acids.
Lipids breakdown
Lipids are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol.
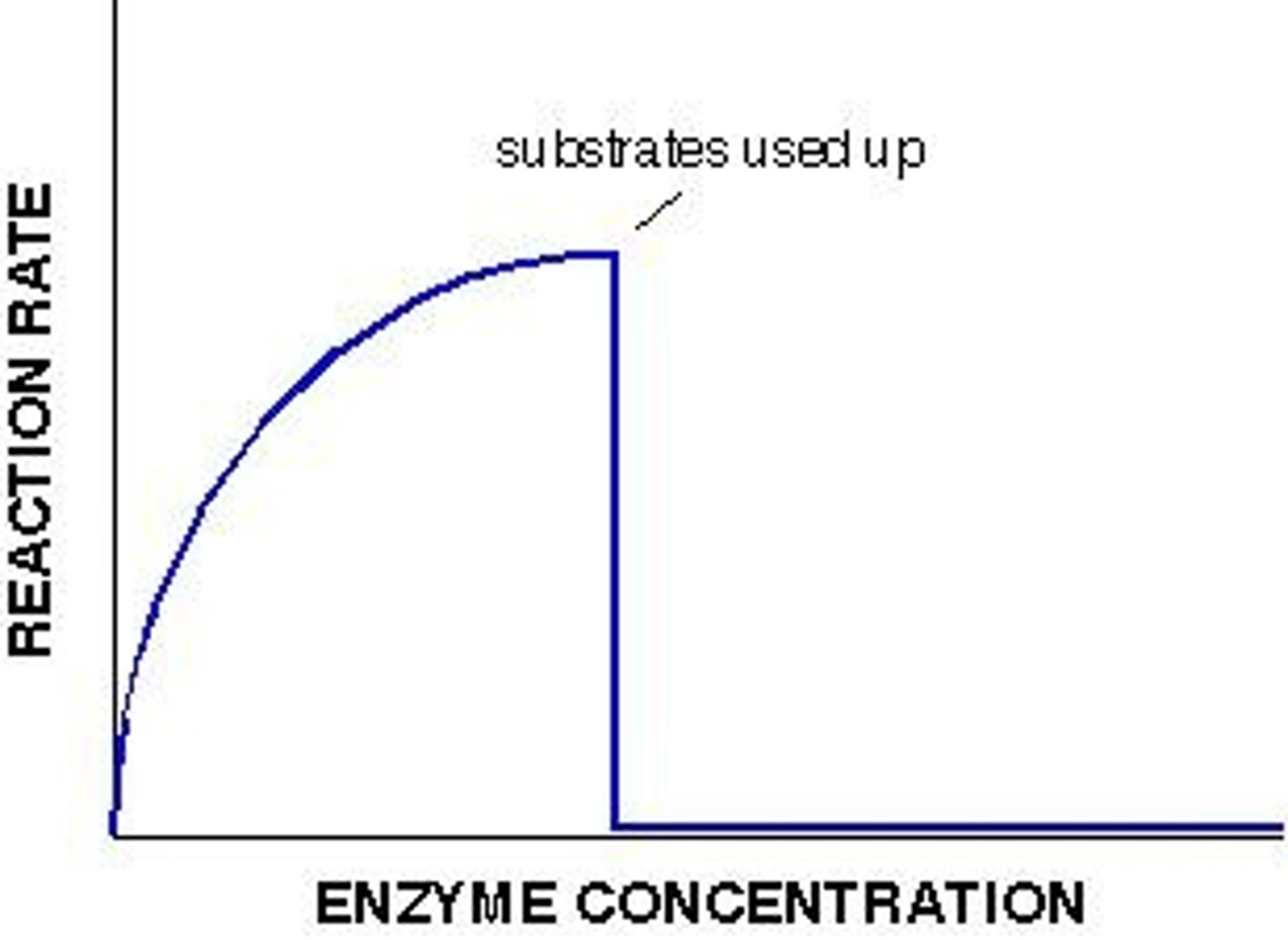
Rate of reaction with increased enzymes
The rate of reaction increases. The reaction will stop when all of the substrates have been turned into products.
Rate of reaction with increased substrates
The rate of reaction increases until all of the available active sites are filled (substrates have to wait until an active site becomes available).
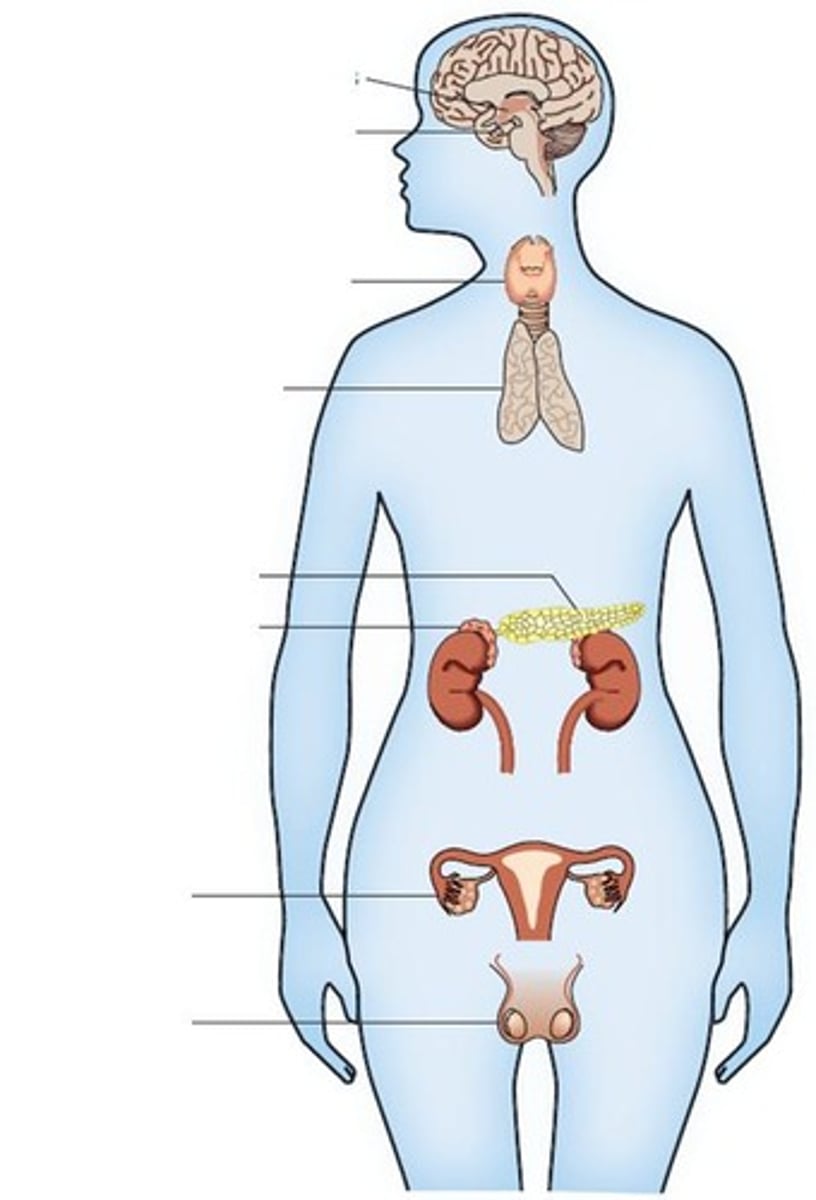
Endocrine System
Controls specific functions of the human body by the use of chemical substances called Hormones produced in various endocrine glands.
Pituitary Gland
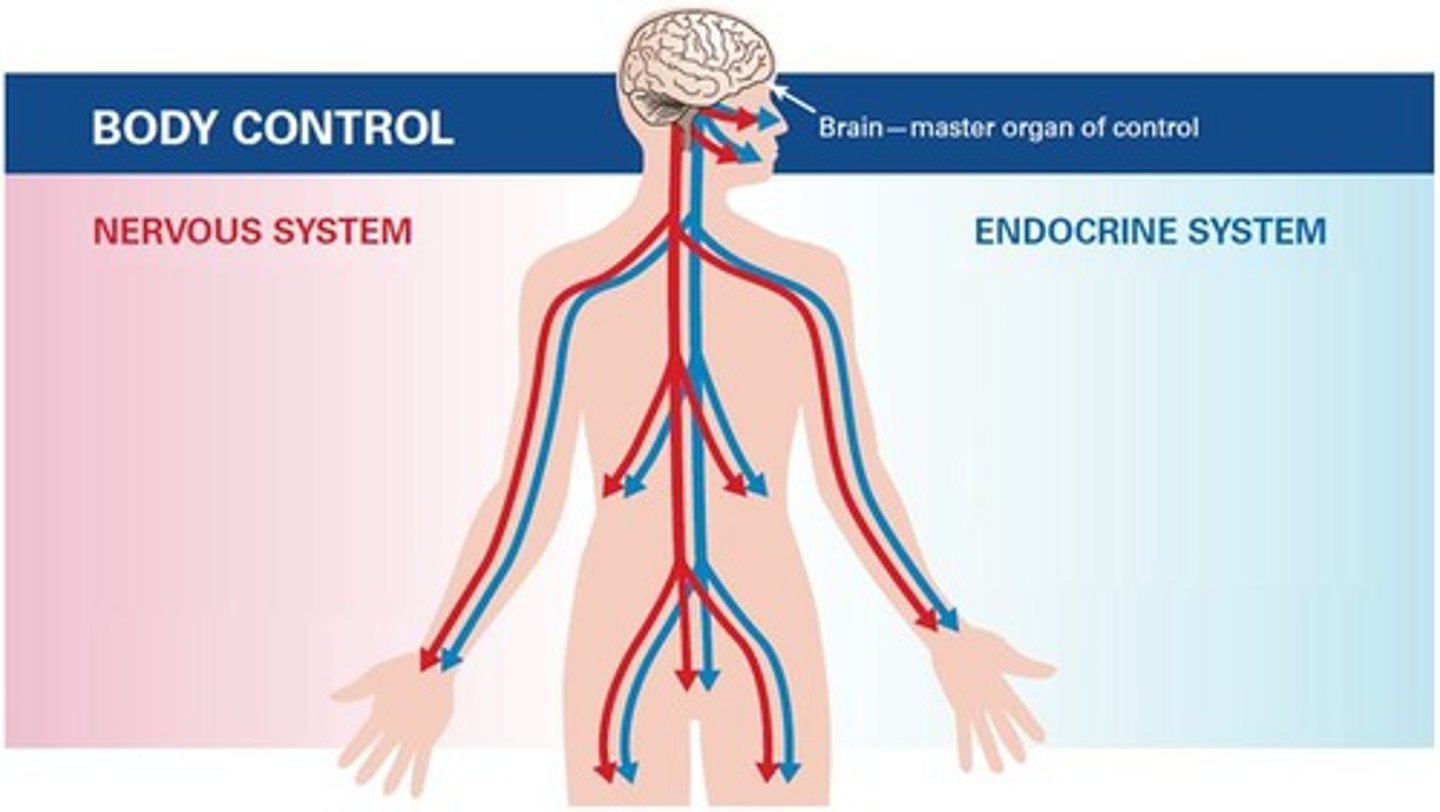
The entire Endocrine System is coordinated by the pituitary gland, which is linked with the CNS by the hypothalamus.
Role of the Hypothalamus
Checks internal environment, responds to changes, links nervous system to endocrine system by secreting hormones which act on the pituitary gland.
Processes Controlled by Hypothalamus
Controls body temperature, metabolism, water levels.
Role of the Pituitary Gland
Secretes a variety of hormones and controls other glands.
Endocrine Glands
Testis, Pancreas, Thymus, Adrenal, Hypothalamus, Thyroid & parathyroid, Pituitary, Ovary.
Hormones
Hormones instruct cells to make changes that restore the body-balance.