BIO100 Lecture #2 Nutrition
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Why is carbon special in life?
It can form many shapes like long and branching chains. These chains are the skeletons for a wide variety of atoms.
Functional Groups
Sets of atoms attached to the C skeleton. Play important roles in reactions with other compounds.
Hydroxyl group
OH
Amino Group
(—NH2) a functional group composed of nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms and to the carbon skeleton. Can act as a base in solution, accepting a hydrogen ion and acquiring a charge of +1.
Carboxylic Acid
COOH
Macromolcules
Large molecules with a complex structure. Most organic molecules.
- mostly polymers
4 Classes of Organic Molecules
Carbs (bread & candy), proteins (meat & soy), lipids (butter & oil), nucleic acids (everything except processed food)
Lipids
Fats and oils
- mostly consume triglyceride.
- hydrophobic (do not mix with water)
Uses of Lipids
- long-term energy storage
- cushion
- insulation
- membrane function
- hormonal regulation
Triglycerides
Typical dietary fats. The C/H chains in the fatty acids store energy
How do cell membranes depend on lipids?
Cell membrane isolate lipids from water by regulating the passage of material into the cell. There are simply 2 stacked layers of phospholipids.
Saturated, Unsaturated Cis Fat, Unsaturated trans Fat
saturated= saturated with hydrogen, solid
unsaturated= one or more double bonds with one fewer hydrogen on each double bond, mostly cis double bonds, liquid
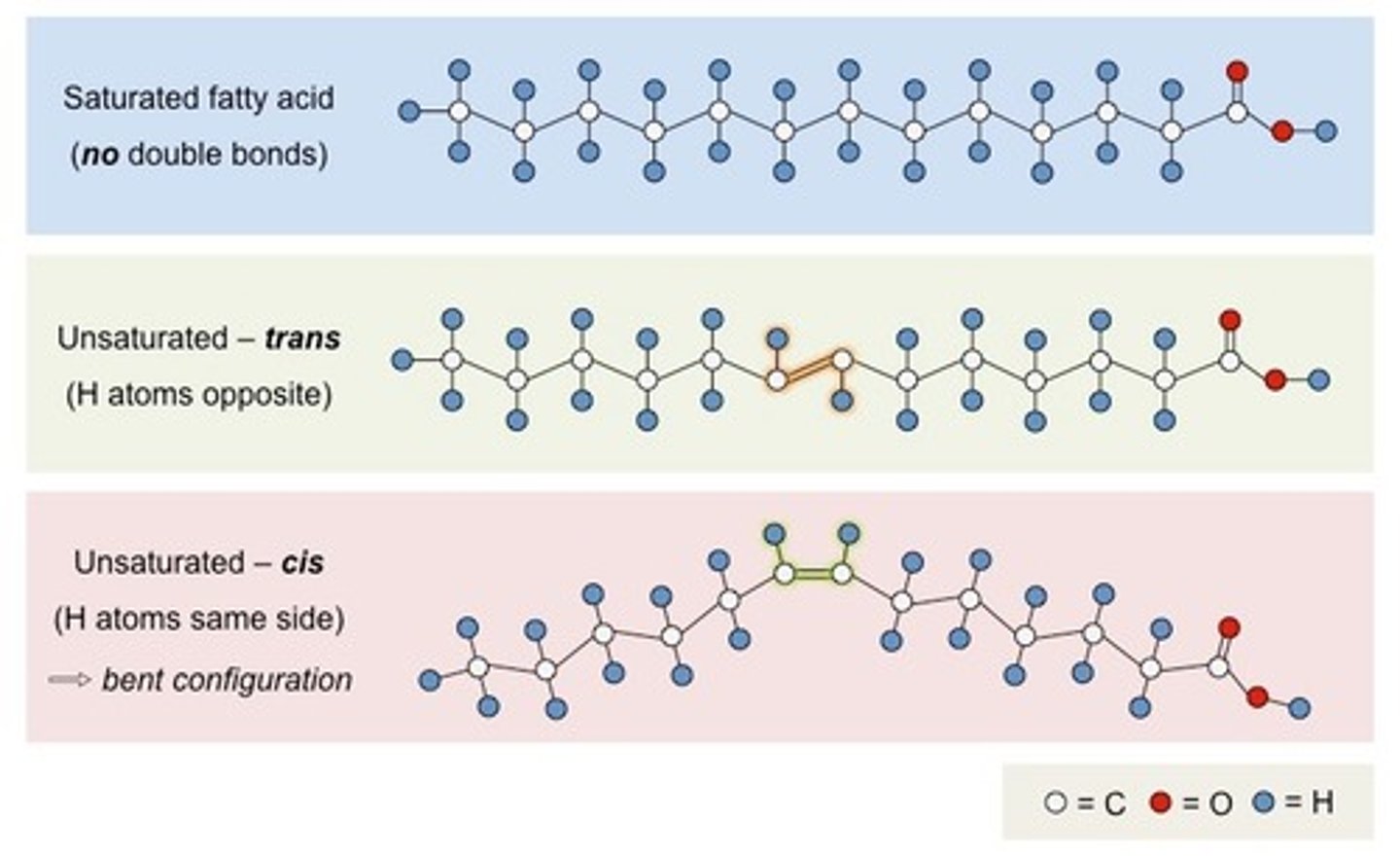
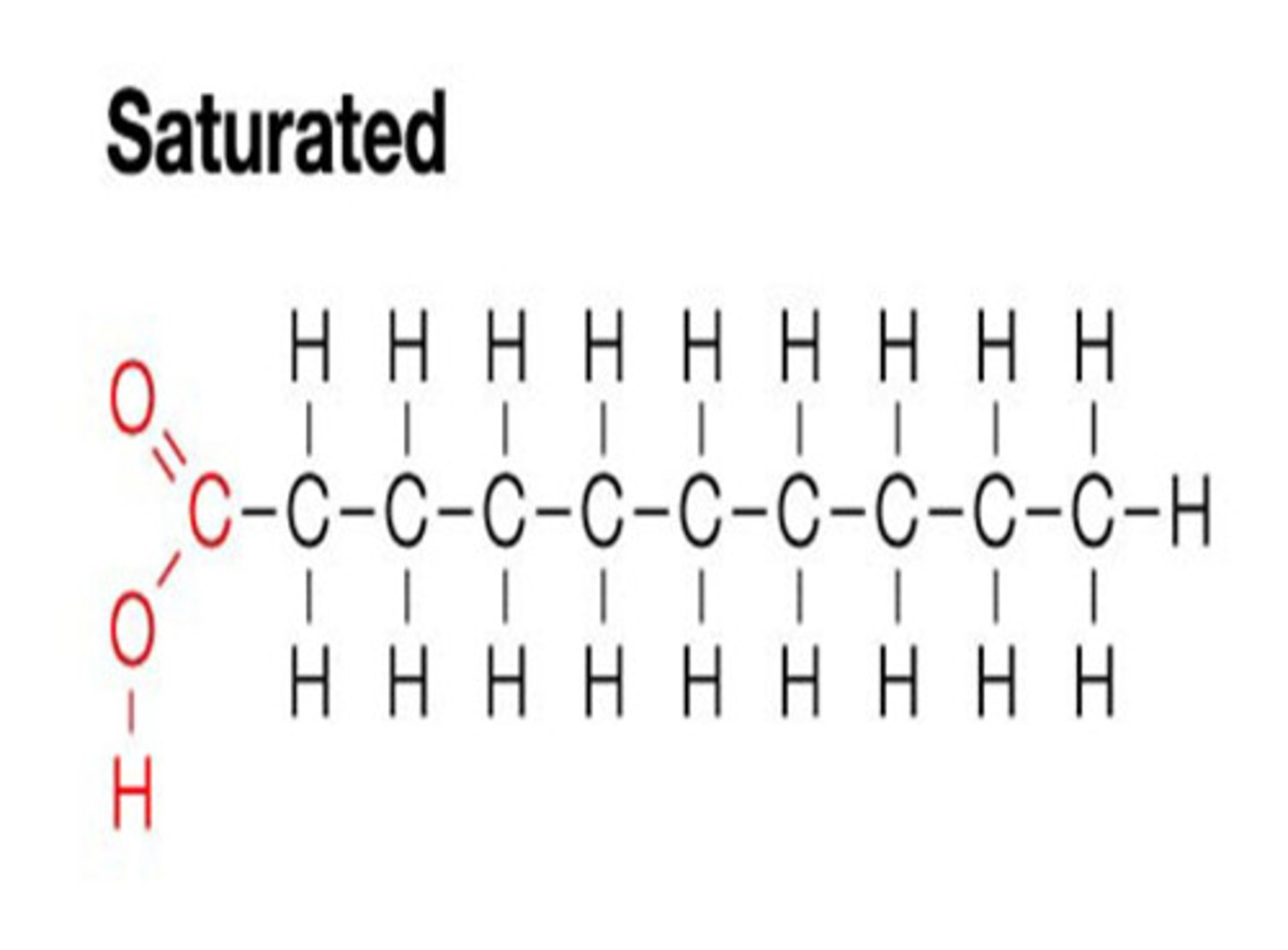
Saturated Fats
- Contain max number of H
- Solid at room temp.
- Higher amounts in animal products
- All C-C single bonds
- Straight F.A chains
- Less healthful.
Unsaturated Fat
- less than max number of H
- liquid at room temp
- higher amounts in plant products
- some C=C bonds in F.A. chains
- bends in fatty acid chains.
- healthfuler
Healthful Lipids
Some lipids are essential to a heathy diet
- Fats containing w-3 fatty acids reduce risk of heart disease.
- Foods rich in essential fats are part of a balanced diet.
Cholesterol
A lipid that maintains fluidity in animal cell membranes.
- not a Triglyceride
- steroid hormone synthesis
- produced by the organism or obtained from food.
- transported by lipoproteins
Lipids and Heart-vascular diease
Excess cholesterol may be stored into the arteries and build up plaque. This can cause fat to rupture into the bloodstream or cause a heart attack.
What does high cholesterol mean?
LDL "Bad" = can be increased through poor diet
HDL "Good" - can be increased through exercise
NOT DIFFERENT KINDS OF CHOLESTEROL
What are some tasks proteins perform?
Defense (antibodies), Structure (keratin), enzymes, movement (muscle contraction)
Proteins
Polymers of amino-acids. Function and structure is determined by a precise amino-acid sequence.
Polypeptide
A chain of amino acids. Twists and folds to form a unique 3-D shape. Chains may be joined together into a large complex.
How do you recognize an animo acid?
Transmembrane Proteins
Three ion pumps highly specific to an ion. A protein can bind at the ion binding site and block the bump, like venom.
Apamin
Bee venom. Smallest proteic venom.
9 Essential Amino-acids
Valine, leucine, isleucine, methione, trytophan, phenlatimine, threoine, lysine, hisitidine.
- essential because we cannot make them
Dehydration Synthesis Reaction
Dense Irregular