IB biology B4.2 ecological niches
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
define ecology
the study of the relationships between living organisms and their physical environment
define ecological niche
the role of a species in an ecosystem
what are biotic factors
the living parts of an ecosystem
what are abiotic factors
the non-living parts of the ecosystem
the interaction between biotic and abiotic factors influences the
growth, survival, reproduction, and how an organism obtains food
what obligate anaerobes
microorganisms that only respire when there is no oxygen and instead they use other compounds as electron accepters such as mercury. Oxygen is toxic to them because they do not have the right enzymes to deal with it
what are obligate aerobes
they require oxygen as a final electron acceptor to carry out respiration and release energy
how can you test for the kind of respiration used by a microorganism
place them in a culture containing thioglycolate, which has a low amount of sugar and removes oxygen. the top is exposed to air, but the bottom is devoid of oxygen, so obligate aerobes will migrate to the top, obligate anaerobes will migrate to the bottom, and facultative anaerobes will be in the middle
what are facultative anaerobes
capable of carrying out both aerobic and anaerobic respiration without being hurt or killed in the presence of oxygen
what are autotrophs
organisms that can generate their own source of nutrition usually from the sun through photosynthesis like plants, algae and some prokaryotes
what are heterotrophs
organisms that need to take in their nutrition from external sources like most anmals
what are mixotrophs
organisms that have evolved a combination of ways to gain energy
what do photosynthetic prokaryotes lack
membrane bound chloroplasts, and instead they have infoldings on their plasma membrane where photosynthesis takes place
what is holozoic nutrition
it refers to organisms that take in solid or liquid food internally. after it is brought inside, it is digested and broken down into smaller organic compounds that act as building blocks
what are examples of mixotrophic nutrition
euglena- facultative mixotroph
and some oceanic plankton
what are the two types of mixotrophs
obligate mixotrophs
facultative mixotrophs
what are obligate mixotrophs
they must use both autotrophic and heterotrophic modes of nutrition
what are facultative mixotrophs
they can use either heterotrophic or autotrophic modes of nutrition, switching between the two
what is saprotrophic nutrition
it is a method in which the organism secretes digestive enzymes that break down dead organic material into simpler molecules which are absorbed by the organism
what is a type of saprotrophic nutrition
decomposers, which obtain nutrients from dead organic matter like fungi and bacteria
what are the two types of heterotrophic nutrition
holozoic and saprotrophic
what are the two types of autotrophic nutrients
photoautotrophs
chemoautotrophs
what are detritivores
they break down dead organic matter by direct consumption
what are the three main domains
bacteria
eukarya with archea branching from it
what makes archea special
they have evolved enzymes which allow them to survive in extreme conditions such as high salt concentrations, very low pH, etc.
which energy source do archeas use
some use oxidation of inorganic chemicals such as sulfur (chemoautotrophs)
some use light (photoautotrophs)
some use energy from organic compounds (heterotrophs)
there is a relationship between —— and ——-
dentition and diet
hominins vs hominids
hominins are all modern and extinct humans and their immediate ancestors.
hominids include hominins and include the great apes
describe the dentition of Paranthropus robustus
large teeth with thick enamel
large chewing muscles and a wide face (strong jaw muscles)\
could grind tough fibrous foods and are believed to be herbivores that ate tough grasses
describe the dentition of homo floreniesis
they were short and had small brains but large teeth comparatively
it is believed they were omnivores and ate plants and uncooked meat because of the markings on their teeth which show they ate fibrous stuff that needed a lot of chewing
describe the dentition of homo sapiens
they evolved in africa and gathered food and hunted. they were adaptable and their jaws are less heavily developed and their teeth are smaller
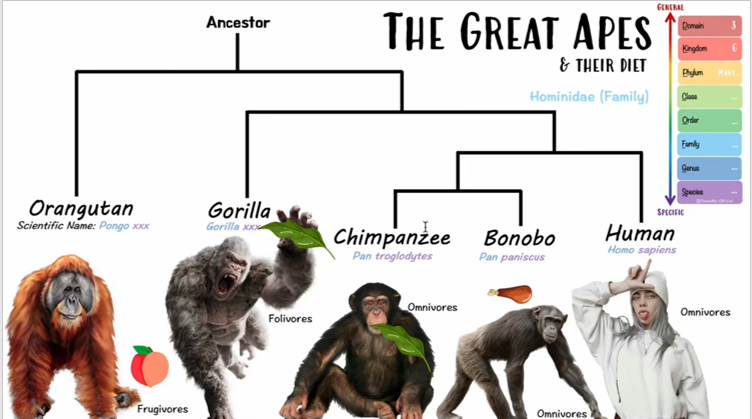
Hominidae family includes
humans-homo, orangutans-pongo, gorillas-gorilla, and chimpanzees-pan
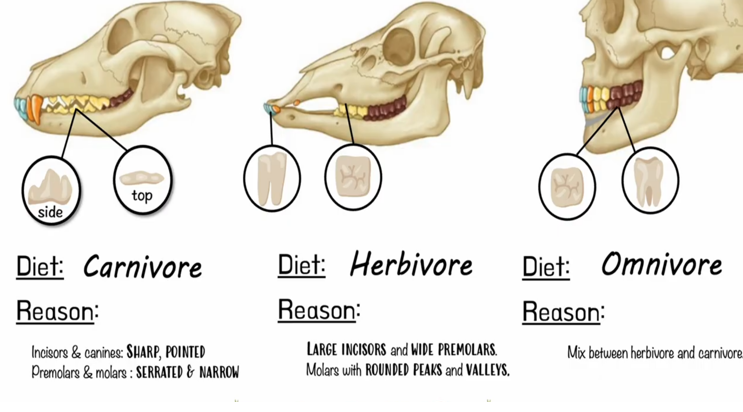
what are the teeth of herbivores
large and flat to grind down the plant tissues
large incisors with wide premolars
molars with rounded peaks and valleys
what are the teeth of omnivores
a mix of different types to break down both meat and plant
what are the teeth of carnivores
incisors and canines that are sharp and pointed
premolars and molars that are serrated and narrow
what is a molar used for
grinding and reducing food into a paste
what is a premolar used for
crushing or slicing up food
what are canines used for
ripping and tearing materials such as meat
what are incisors used for
cutting up bite sized pieces of food
look at this
look at this
what are some adaptations of insect herbivores
some insects have mandibles to cut and tear and chew their food
some insects feed off fluids internal using a stylet
what are some adaptations of herbivorous mammals (4)
they have long and flat incisors that can cut the plant material and back molars that can soften plant tissues by grinding them to increase the surface area for digestive enzymes to break the food down.
because they are always grinding, they can wear their teeth down and so they have constant teeth growth
they also have space between the premolars and incisors called diastema
giraffes have long necks and tough tongues to reach trees and protect themselves from thorns
how do herbivores protect themselves from being eaten
their eyes are on opposite sides of their head so they can increase their visual field
how do plants prevent herbivory (2)
they secrete toxic secondary compounds which are toxic to those that eat them but dont affect the plants
evolved non-toxic chemicals that only become toxic when ingested
how did animals respond to the selective pressures that were set by plants that did not want to be eaten for some reason
they developed special enzymes that enable them to metabolize those compounds and not be affected by them
they can also use them to protect themselves from predators sometimes
what are the plant compounds made for protection called and what are the 4 groups
phytochemicals
the four groups are:
terpenes
phenolics
polyketides
alkaloids
what is the benefit of phytochemicals other than for plants and give an example
they helped in the derivation of some medicine
artemisinin is a drug that has been used against malaria
paclitaxel is a chemical used for cancer
both came from trepene group
what are some physical adaptations of plants that help them avoid herbivory
having thick rigid leaves that are hard to chew
spiny thorns or microscopic thorns called trichomes
microscopic thorns have chemicals that can cause irritation
they sometimes hide by growing small
what are some physical adaptations of predators to help them kill prey
they have strong speed and agility and sharp claws and teeth
their digestive system can break down the prey
they have strong sensory systems that are finely tuned like the eagle
what are some chemical adaptations of predator to kill their prey
some release venom that paralyzes or poisons their victim by interfering with normal biological processes like the Brazilian fire ant and the cone snail
what are some behavioral adaptations of predators to catch their prey
ambushing the prey where they wait for them to come and then eat them like spiders
hunting in a pack like wolves
luring them like the margay and anglerfish
trapping them like dolphins
what are some physical adaptations of prey to resist predation
they use camouflage to blend into the background
they have some defensive mechanisms like porcupines
what are some chemical adaptations that help prey avoid predation
they sometimes release chemicals that are toxic into the air or water like skunks
what are some behavioral adaptations that help prey resist predation
they work together to deter the predator and look larger, like the mackerel
what are some adaptations of plants to harvest more light
some are epiphytes and grow on other plants
some are shade tolerant and have larger thinner leaves for maximum sunlight
some herbs grow on the bottom of the forest floor and can withstand low light conditions
lianas are climbing plants and grow on the plant away from light
some trees are really tall and can reach the canopy
what are epiphytes and what is one type of epiphyte and example for both
epiphytes grow on entirely separate plants
strangler epicpytes that climb on trees and shade them out, leading to the tree dying
what is a fundamental niche
the niche of an ecosystem in which an organism can live and reproduce, so it is their potential niche based on their adaptations and tolerance limits
what is a realized niche
it is formed when the species within a fundamental niche has to deal with pressure from having to co-exist with other species in the environment so now it is forced to live in a smaller niche
what is the competitive exclusion principle/ Gause’s law
it states that when there is more than one species competing for the same resuorce there will be competition, so it is not possible for two species to occupy the same niche because eventually one will outcompete the other one
what is niche partitioning
due to natural selection, different competing species can still occupy close areas or niches
what are the two types of niche partitioning
spatial partitioning
temporal partitioning
what is spatial partitioning
animals like warblers may have very small differences between requirements, so they may be found to occupy different parts of the same tree, so they have different nesting times
what is temporal partitioning
it is based on the way animals have evolved to cope with existing in the same habitat, like being active at night or in the day