EDUC 40 Midterm - UCI
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Behaviorism
the science of behavior that focuses on observable behavior only
What is classical conditioning?
Learning process pairing stimuli to elicit a response.
What is an unconditioned stimulus?
Stimulus that leads to automatic response.
Example: In Pavlov's Experiment, this is the presentation of food to the dog. This stimulus naturally and automatically triggers a salivation response without prior conditioning.
What is an unconditioned response?
Automatic response to unconditioned stimulus.
Example: In Pavlov's Experiment, this is the dog's salivation in response to the sight or smell of food. This reaction is unlearned and occurs naturally.
What is a neutral stimulus?
Stimulus that initially causes no response.
Example: In Pavlov's Experiment, this is the sound of a tuning fork or a bell initially, when it is yet to be associated with the food. Initially, this sound does not trigger salivation on its own.
What is a conditioned response?
Learned response to a previously neutral stimulus.
Example: In Pavlov's Experiment, this is the dog's salivation in response to the sound of the tuning fork or bell, after conditioning. This response is learned through the association between the bell (CS) and the food (US).
What is operant conditioning?
Learning through rewards and punishment to modify behavior.
What is positive reinforcement?
Adding desired stimulus to increase or maintain behavior.
Example: A student receives praise (positive/desired stimulus) after getting good grades. The praise encourages the student to continue studying hard.
What is negative reinforcement?
Removing undesired stimulus to increase or maintain behavior.
Example: A headache goes away (removal of a negative/undesired stimulus) after taking pain medication, increasing the likelihood that the person will use pain medication again for future headaches.
What is positive punishment?
Adding unwanted stimulus to decrease specific behavior.
Example: A child touches a hot stove and feels pain (addition of a negative/unwanted stimulus). This experience decreases the likelihood that the child will touch the stove again.
What is negative punishment?
Removing pleasant stimulus to decrease specific behavior.
Example: A teenager comes home after curfew, and their parents take away their gaming privileges (removal of a positive stimulus). This loss reduces the likelihood of the teenager coming home late again.
What is shaping?
Reinforcing behaviors that are progressively closer to the desired behavior, while also stopping reinforcement of already established behaviors.
Example: Training a dog to fetch by initially rewarding it for going towards the ball, then for picking it up, and finally for bringing it back.
Reinforcement Schedules
Rules that dictate the frequency and timing of reinforcements (e.g., fixed-ratio, variable-ratio, fixed-interval, variable-interval).
Fixed Ratio
Reinforces a response only after a specified number of responses.
Example: A salesperson receives a bonus for every fifth sale they make.
Fixed Interval
Reinforces a response only after a specified time has elapsed.
Example: A weekly paycheck.
Variable Ratio
Reinforces a response after an unpredictable number of responses.
Example: Slot machine.
Variable Interval
Reinforces a response at unpredictable time intervals.
Example: Random surprise quizzes in a class.
How do you know if a stimulus is reinforcing?
Frequency of the Behavior: After introducing the stimulus, does the frequency of the targeted behavior increase?
Consistency: Is the increase in behavior consistently observed following the presentation of the stimulus?
Timeliness: Is the increase in behavior closely tied in time to the presentation of the stimulus?
What is social learning theory?
Learning through observation and imitation of others.
What are the 4 conditions necessary for modeling?
Attention, retention, motor reproduction, motivation.
What is the Attention requirement in Modeling?
Learner must pay attention to model to learn from it
What is Retention requirement in Modeling?
Learner must retain/remember what information they receive from the model
What is Motor Reproduction requirement in Modeling?
Learner must be able to reproduce the modeled behavior
What is the Motivation requirement in Modeling?
Learner must be motivated to learn and demonstrate the modeled behavior
What are the three types of Models?
Live, Verbal, and Symbolic.
What is a live model?
A real life person who may be demonstrating, acting out and/or describing a behavior
Learning something over Zoom counts as a Live Model.
What is a symbolic model?
A real or fictional character displaying behaviour in books, movies, tv shows and other media.
This includes YouTube Videos!
What is a verbal model?
Verbal descriptions of how to successfully do a behavior.
What makes an effective model?
Similarity to the target, status of the model, and competence of the model.
Described in class as Competence, Prestige, Power, and Relevance to own circumstances.
The most effective model is one with the most similarity to the target.
What is the Observational Learning Effect?
Learning by observing others.
Also known as Modeling.
What is the Response Facilitation Effect?
A learner does a behavior they know how to do because they observed a model being rewarded for doing so.
Example: The learner begins to submit homework on time because they saw a classmate being praised and rewarded by the teacher for consistent timely submissions.
What is the Response Inhibition Effect?
A learner decreases or refrains from a behavior because they observed a model being negatively reinforced or punished for doing so.
Note: The learner does not have to know how to do the behavior.
Example: The learner stops using their phone in class because they observed another student being reprimanded by the teacher for doing so.
What is the Response Disinhibition Effect?
A learner engages in a previously suppressed or inappropriate behavior because they observed a model performing that behavior without being punished.
Example: The learner starts to joke around in class because they observed others doing so without any consequences, despite previously being told that class isn't the place for joking.
Self-efficacy
Belief in one's ability to succeed.
Types of Self-regulated learning behaviors
Planning, monitoring, and evaluating one's own learning.
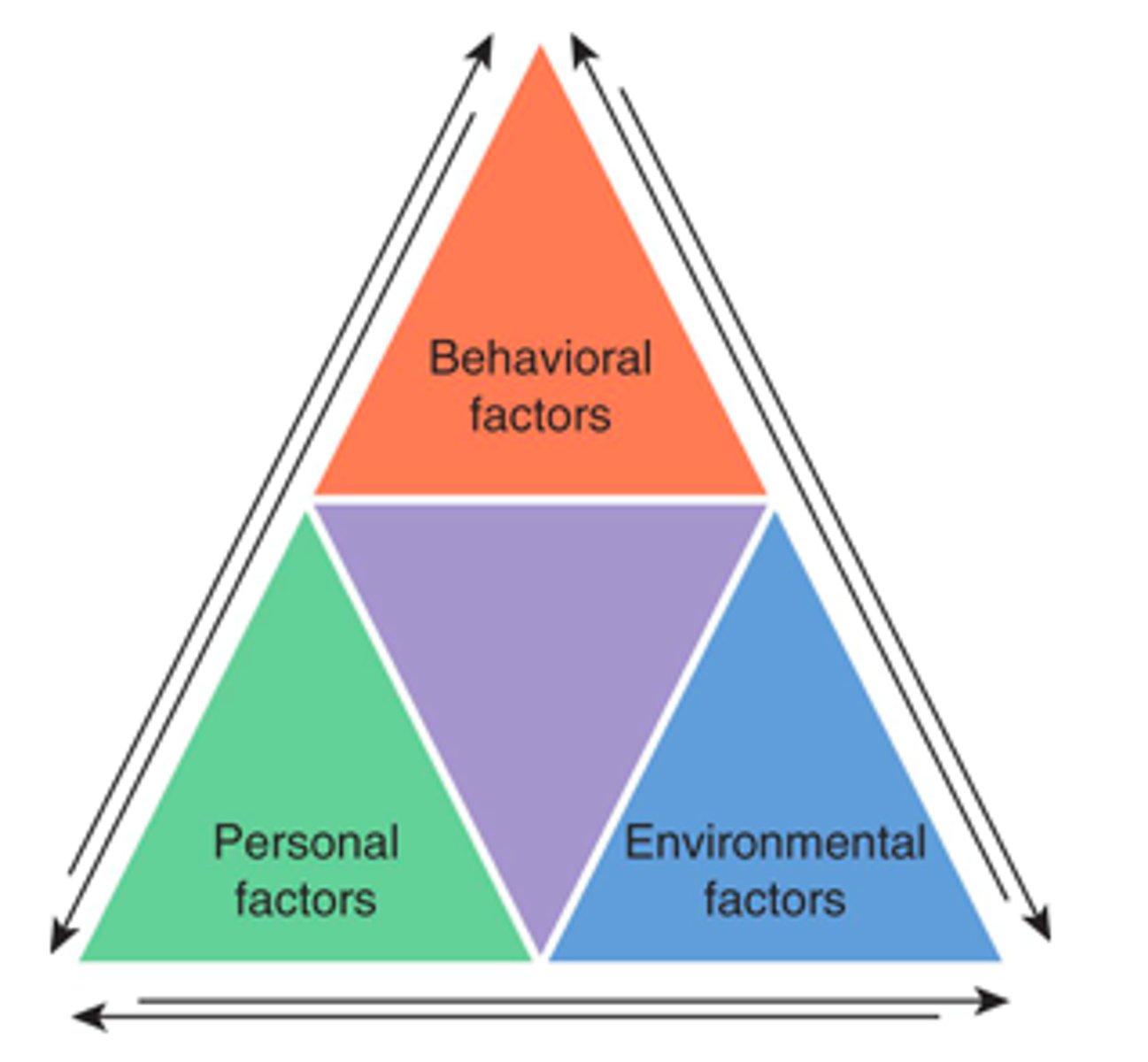
Reciprocal causation
Interaction between personal factors, behavior, and environment.
Constructivism
Learning theory emphasizing active construction of knowledge.
Individual Constructivism: Piaget
Cognitive development through assimilation, accommodation, and equilibration.
Scheme
Mental framework for organizing and interpreting information.
Assimilation
Process of incorporating new information into existing schemes.
Accommodation
Process of modifying existing schemes to fit new information.
Equilibration
A mechanism that Piaget proposed to explain how children shift from one stage of thought to the next.
Social Constructivism: Vygotsky
Learning through social interaction and cultural tools.
Zone of proximal development
Range of tasks a learner can perform with guidance.
Mediated learning experience
The role of instructors or more capable peers in guiding the learner's development.
Scaffolding
A variety of techniques that help students accomplish challenging tasks in instructional contexts
Dynamic assessment
An interactive approach to psychological assessment that emphasizes the ability of the learner to learn from instruction.
Constructivist principles in the classroom
Active learning, collaboration, and authentic tasks.