Thyroid Lecture Review
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Dr. Koh's material
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
Where are some features of the thyroid gland?
- Highly vascularized
Hormones immediately released into blood
- Dynamic
Can change in size
What is the functional unit of the thyroid gland?
Follicle
What is thyroglobulin (TGn)?
A protein produced by follicular cells and stored in the lumen.
What does a colloid contain?
Abundance of thyroglobulin
What are thyroid hormone levels regulated by?
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Thyroid (HPT) axis
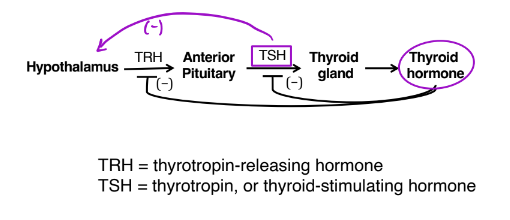
What does thyrotropin (TSH) do?
Regulate and control follicles via TSH receptor
What are the two thyroid hormones?
- Thyroxine (T4) (levothyroxine)
- Liothyronine (T3)
Why does the thyroid gland need iodine?
In order to synthesis thyroid hormones.
What happens when we have a deficiency in iodine?
- Increase activity of Na+/I- cotransporter
- Hypothyroid
Thyroid hypertrophy (goiter) → enlarges to collect iodine
What are functions of TSH?
- Increase uptake of iodine by thyroid
- Increase synthesis and secretion of T4 and T3
- Stimulate growth and development of thyroid
- Mediates most cases of goiters
What is iodinated within the colloid?
TGn
What causes T4 and T3 to be released into the blood?
Enzymatic cleavage of TGn
Which hormone does the thyroid gland synthesize more of?
T4
Why is T3 mostly in the circulation of blood?
Due to the removal of I from T4.
True or False: T3 has greater activity than T4.
True
What do T4 and T3 hormones bind to?
Plasma proteins
Thyroid-binding globulin (TBG)
Albumin
What function is the thyroid hormone best known for?
Regulates overall metabolic activity and energy expenditure
Since the thyroid hormone regulates metabolic activity, what is caused by that?
- Increase in basal metabolic rate (BMR)
- Increase in protein synthesis and catabolism
- Increase carbohydrate metabolism
- Increase lipid cholesterol metabolism
- Increase activity of the adrenergic nervous system
- Increase GI motility
What is the thyroid hormone essential for?
Growth and development
What type of patients is hypothyroidism (Gull’s disease) more common in?
Women and older patients
What are some signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism?
- Chronic fatigue; somnolence; face expressionless
- Poor circulation
- Muscle cramps
- Faulty hearing
- Unexplained weight gain (decreased metabolism)
- Cold, dry skin; hair loss
- Hypothermia, sensitivity to cold
- Constipation
- Decreased mental function and motor activity
- Reproductive disorders (infertility, menstrual irregularities)
- Cardiac difficulties (bradycardia, decreased BP, decreased cardiac output)
- Goiter (diffuse non-toxic goiter)
All the thyroid effects decreased
What is Myxedema?
Poor lymph drainage leads to SQ buildup of mucopolysaccharides
Severe hypothyroidism
What are some signs and symptoms of Myxedema?
- Puffy hands and feet
- Swelling of cheeks and tongue → slurred speech
- Puffy eyes (droopy eyelids as well)
- Decreased cardiovascular function, cardiac output, glomerular filtration, renal function
What should Myxedema NOT be treated with?
Diuretics
What can hypothyroidism cause?
- Hypercholesterolemia
- Decreased drug metabolism and elimination
- Increase in TSH levels
What is the most common type of hypothyroidism?
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
What is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis?
Chronic autoimmune thyroiditis
- Auto antibodies attach thyroid
- Damage, inflammation
What are some other types of hypothyroidism?
- Caused by a Thyroidectomy or 131^I treatment (too much removal or destroyed)
- Endemic (areas with low iodine levels)
What are drugs that induce hypothyroidism?
- Amiodarone (Cordarone)
- Iodine
- Lithium
What is cretinism?
Congenital Hypothyroidism (from birth)
What does cretinism cause?
- Mental retardation (irreversible)
- Growth retardation
What are the signs and symptoms of cretinism?
- Thick tongue
- Chocking episodes
- Poor feeding
- Hypothermia; dry, cool skin
- Short extremities
- Dry, brittle hair
- Overall inactivity, sluggish
- Goiter
What is myxedemic coma?
A severe and chronic complication of hypothyroidism.
What are some precipitating factors of myxedemic coma?
Stress (trauma, car accident), infection, hypothermia
What are the treatments for hypothyroidism?
- Iodine (for endemic only)
- Thyroid hormone replacement (T4)
Synthroid, Levothroid, Levoxyl, Levoxine, Levothyroxine Sodium
What is the preferred agent for hypothyroidism treatment?
Levothyroxine (T4)
How does levothyroxine interact with other drugs?
Inhibits absorption → should take on empty stomach
What are the side effects of levothyroxine caused by?
Due to overdose
What is the equivalent dose (mimics amount in our body) of levothyroxine?
100 µg
What treatment option is more potent but less commonly used for hypothyroidism treatment?
Liothyronine (T3)
Cytomel, Triostat
What are some characteristics of Liothyronine?
- Shorter duration (have to take more)
- More potent
- Caution in CV disease
- Side effects: due to potency
- Equivalent dose: 25-30 µg
What are the naturally sourced agents that are less commonly used for hypothyroidism treatment?
Thyroid USP, desiccated thyroid
Armour Thyroid, Westhroid
What are some characteristics of thyroid USP?
- 4:1 ratio of T4:T3
- Limited shelf life
- Equivalent dose = 1 g
What are signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism (Graves’ disease)?
- Exaggerated TH effects
Increased appetite (polyphagia)
- Osteoporosis
- Increased RBC mass → increased menstrual flow
- Arrhythmias, tachycardia (increased HR)
- Exomphalos (bulging eyes)
- Goiter
What are the types of hyperthyroidism?
- Graves’ disease (diffuse toxic goiter; exophthalmic goiter)
- Nodular toxic goiter
- Drug-induced
What is Graves’ disease?
Auto immune disorder
Antibodies mimic TSH, overstimulate gland (increase TH)
No negative feedback loop
What are some characteristics of Graves’ disease?
- Diffuse toxic goiter
Diffuse: entire gland enlarges
Toxic: leads to thyrotoxicosis
Goiter: hypertrophy
- Exophthalmos
- Pretibia myxedema (thyroid dermopathy)
Deposit of tissue in front of the shin bone, causing ripples
- can feel good & bad (Wax and Wane)
What is nodular toxic goiter?
Isolated nodes or groups of cells in the thyroid gland become hyperactive and resistant to pituitary feedback regulation
Happens in 40-60-year-old patients
Do NOT observe exophthalmos
What are some characteristics of endemic goiter?
- Due to I deficiency
- Hypothyroidism
- Increased TSH
What drugs induce hyperthyroidism?
- Amiodarone
- Lithium
What are some antithyroid agents that are used for hyperthyroidism treatment?
- Thioamides (thioureyelenes)
methimazole (MTZ)(Tapazole)
propylthiouracil (PTU) (Propacil)
- Iodines
Radioactive iodine (RAI)
What is the MOA of action of thioamides?
- Inhibition of thyroperoxidase
- Inhibit monodeiodination of T4 (PTU only)
What are some advantages of thioamides?
- Cause no permanent damage → once off, thyroid function returns normally
- Concentrates in thyroid
What are some disadvantages of thioamides?
- Takes 1-2 months for effectiveness (must deplete T4/T3 stores in thyroid gland)
- May cause goiter (T4/T3 depletion increase TSH)
- Therapy is long; must be continual
- Not a cure
- Secreted in breast milk (MTZ)
- Pregnancy Category D (MTZ)
- Short half life (PTU)
What is a side effect of thioamides?
Agranulocytosis (low neutrophil count)
What are some characteristics of agranulocytosis caused by thioamides?
- PTU dose-related
- Look for fever, rapid developing sore throat
- Rapid onset (couple of days)
What are some characteristics of iodine that treat hyperthyroidism?
- Short term: effect wears off in ~ 2 months
- Reduce vascularity (blood flow) of thyroid gland
- Used in surgery prep and radiation emergency
What is the MOA of radioactive iodine?
Concentrates in the thyroid and destroys thyroid tissue
What are some pros of radioactive iodine?
Simple, convenient, permanent
What are some cons of radioactive iodine?
- 3-4 weeks for onset; 4 months for full effect
- can be too effective, too permanent
cause hypothyroidism rather than euthyroid
- Crosses placenta, damages fetus
What is a second line treatment for hyperthyroidism?
Surgery
What do we use the surgery for?
- To remove large nodular toxic goiters; always for malignancies
- Also used in pregnancy if necessary
What is a pro for surgery?
Very effective
What is a con of surgery?
- All disadvantages of surgery
- Occasional damage to parathyroids
What other agents can we use in combination with antithyroid agents?
Beta blockers
Why do we use beta blockers?
- To control CV symptoms (to control BP)
What beta blocker do we normally use?
Propranolol
What is a thyroid storm?
Life-threatening, exaggerated high levels of thyroid hormones
Go to ER!
What are some symptoms of thyroid storm?
- agitation
- confusion
- diarrhea
- restlessness, shaking
- hyperthermia (severe)
- sweating
- tachycardia
- skin is red hot
What can cause a thyroid storm?
- infection
- CV disease
- stress
What is the treatments for thyroid storm?
Give high doses!!! (EYG)
- beta blockers
- anti-arrhythmic
- antithyroid agents: thioamides (PTU), iodine
- ice bath, ice-packs, Tylenol (do not give aspirin → highly protein bound)
What type of patients should we not use TH?
- Obese patients or patients who have experienced weight gain
- Euthyroid patients
What does pregnancy induce?
Mild hyperthyroidism
- TH is essential for 1st trimester growth and development
- less hyperthyroidism during the 2nd and 3rd trimester
What does thyrotoxicosis cause in a mom who is pregnant?
- CV complications
- Preeclampsia
- Premature birth/miscarriage
What does thyrotoxicosis cause in the fetus?
- Low birth weight
- Thyroid storm
What does a crucial or urgent mom stay as?
Euthyroid (having a normal functioning thyroid)