Mod 1 BS II
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/220
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:01 PM on 9/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
221 Terms
1
New cards
What images are useful?
Diagnostic images!
2
New cards
In film-screen combinations, how is the image produced?
By visible light photons
3
New cards
What is the effect of faster screens on film-screen combinations?
Reduce dose but decrease image quality
4
New cards
What affects image quality in film-screen combinations?
Size and shape of phosphor crystals
5
New cards
Because film is double sided, how many screens are used in combination?
2
6
New cards
Describe standard screens
blue light-emitting, calcium tungstate
7
New cards
Describe rare earth screens
Green light-emitting gadolinium or lanthanum
8
New cards
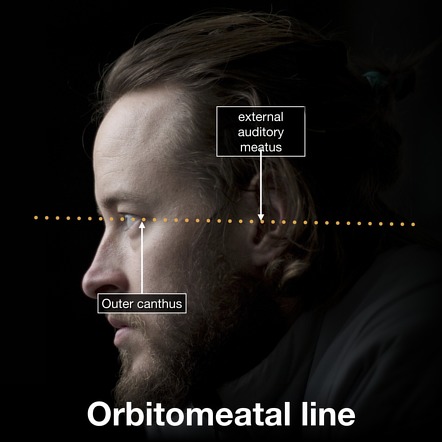
What is the canthomeatal plane?
From the corner of the eye to the middle ear
9
New cards
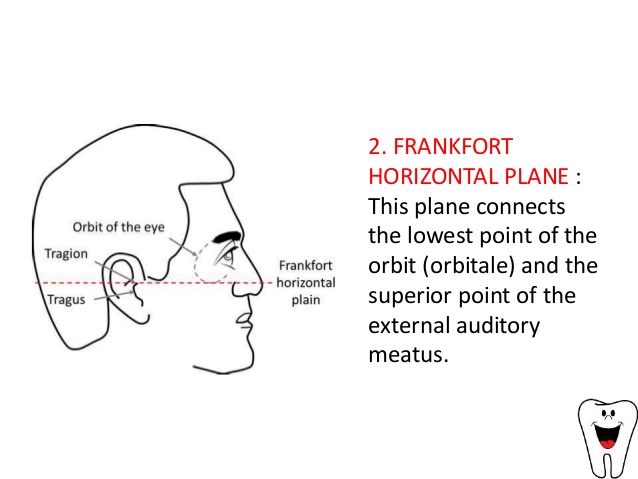
What is the frankfort plane horizontal?
From base of eye to ear and hits the mid-point of nose
10
New cards
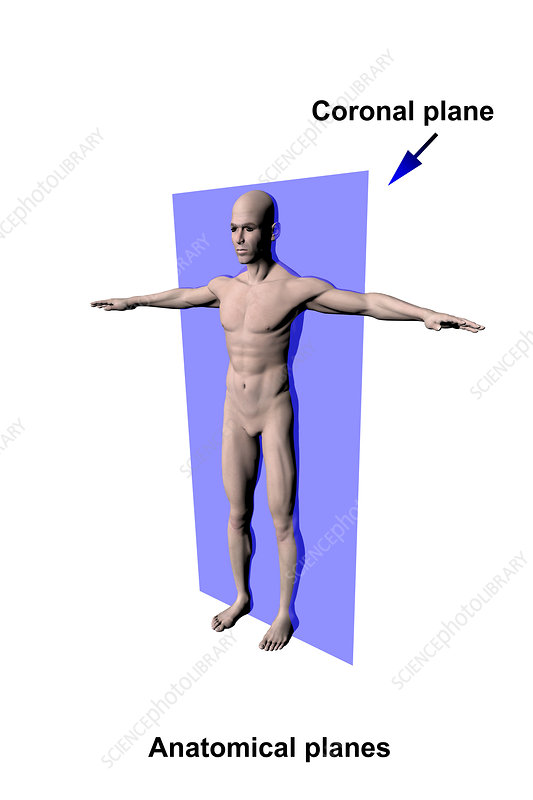
What is the coronal plane?
divides front and back
11
New cards
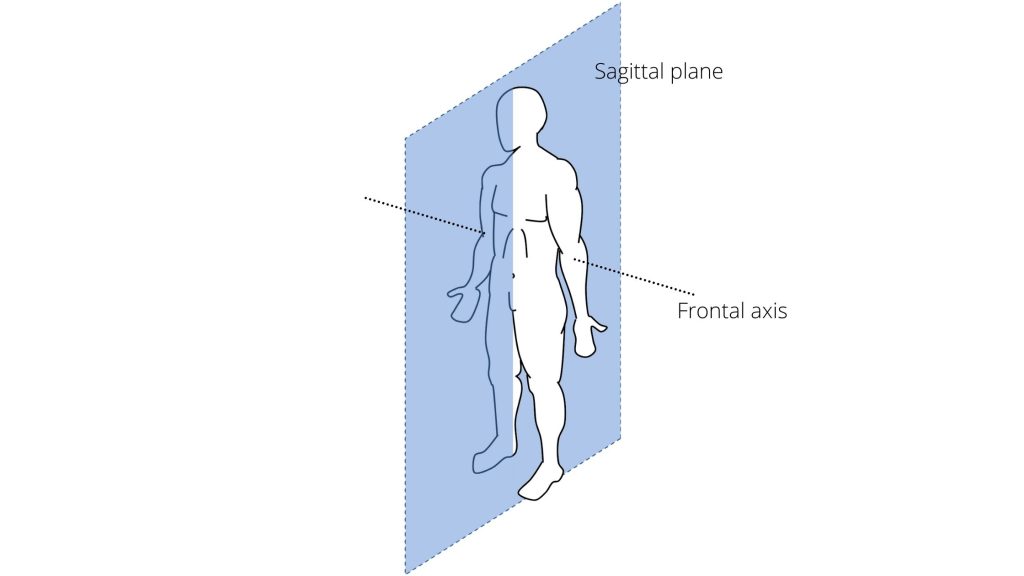
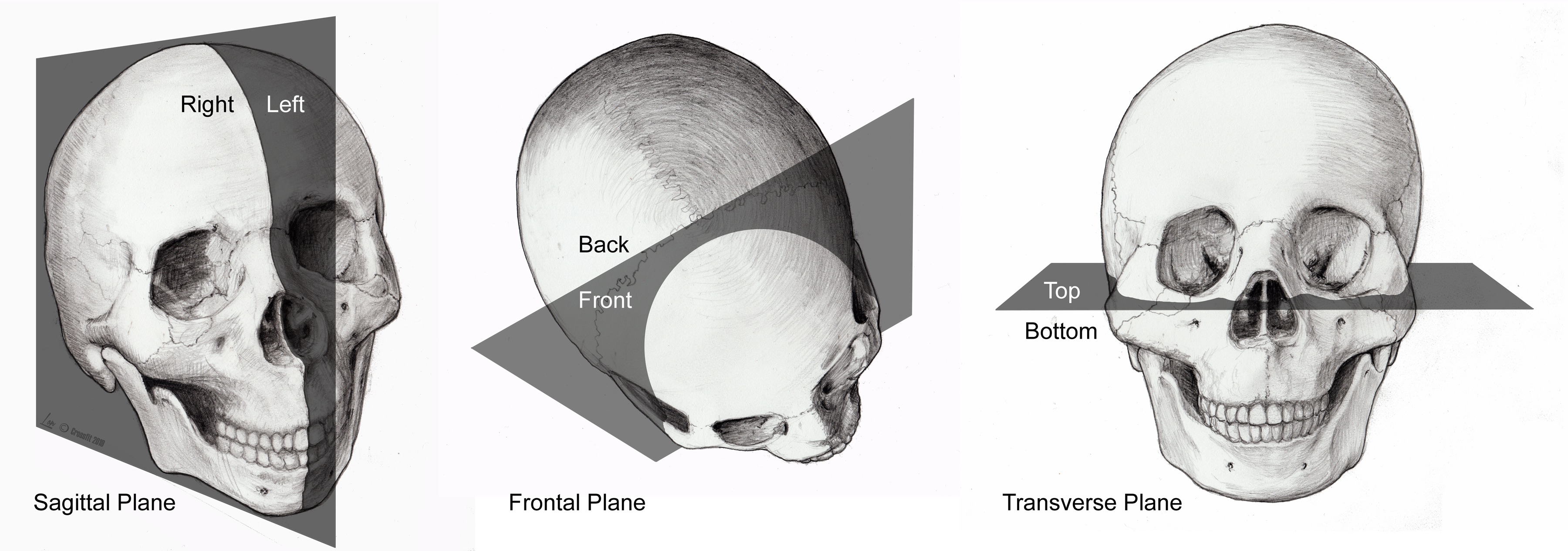
What is the sagittal plane?
divides left and right
12
New cards
What is the axial plane?
Cut horizontally above the eyebrows
13
New cards
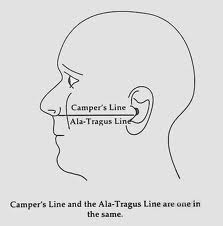
What is the ala-tragus plane?
From the nostril to the middle of the ear
14
New cards
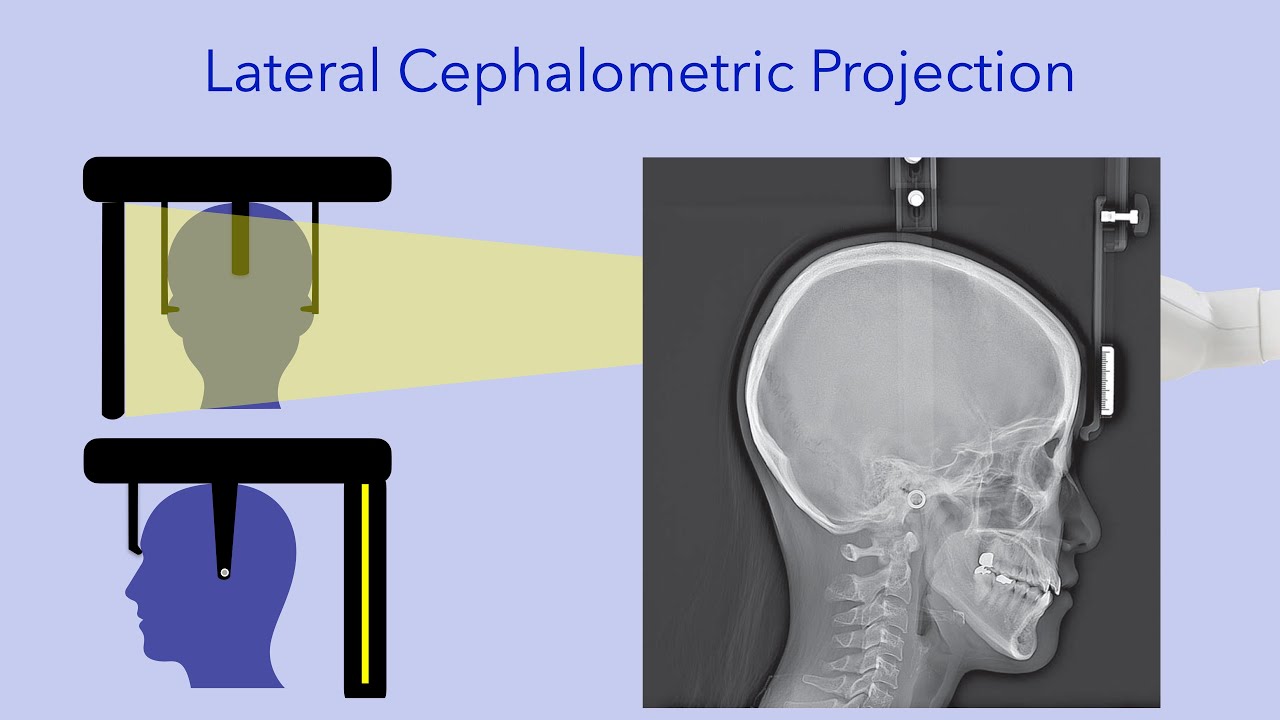
Describe the lateral cephalometric projection
Image receptor is parallel to pts side of interest with beam pointed perpendicular to the receptor
15
New cards
What does the submentovertex projection give insight to?
Skull base and condyle position as well as cheek bones and sinuses, looking down at the skull from above
16
New cards
What does the jug handle view of the submentovertex projection allow us to see?
The zygomatic arches

17
New cards
What is the Waters or Occipito-Menton projection?
canthomeatal plane forms 37 angle with image receptor, pt faces receptor
18
New cards
What does the waters projection give insight to?
Sinuses, cheek bones, septum and mandible
19
New cards
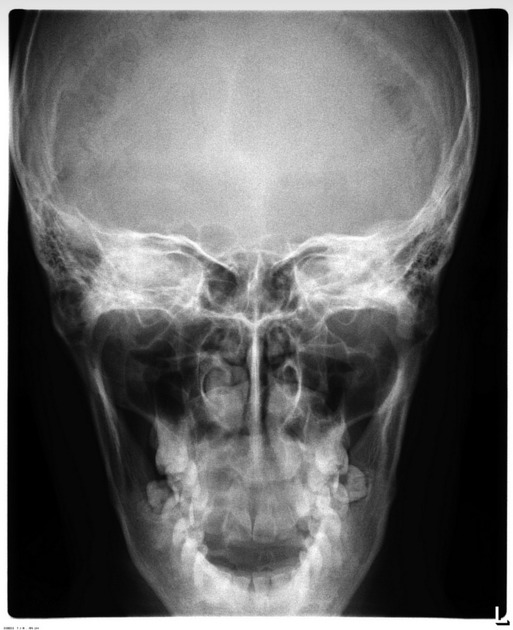
What is the towne's veiw of the skull?
The anterior-posterior view where pt facing away from receptor and chin tilted down -30 degrees
20
New cards
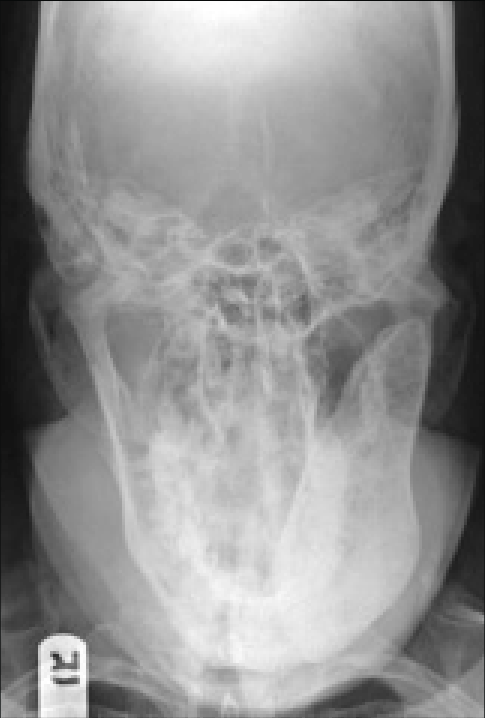
What is the reverse towne projection?
The pt is facing the receptor with mouth open and chin tilted down -30 degrees
21
New cards
What do MRIs help us study?
Soft tissues
22
New cards
Why would we use a panoramic image?
To see dentition, joints, cysts, trauma, can't get intraoral images
23
New cards
What are the advantages of panoramic images?
Broad coverage, low radiation dose, easy, quick
24
New cards
What are disadvantages of panoramic images?
Magnification of image, low resolution, ghost images, positioning errors, difficult to decipher
25
New cards
What happens when the mandible is at the center of the focal trough?
Minimal distortion of image
26
New cards
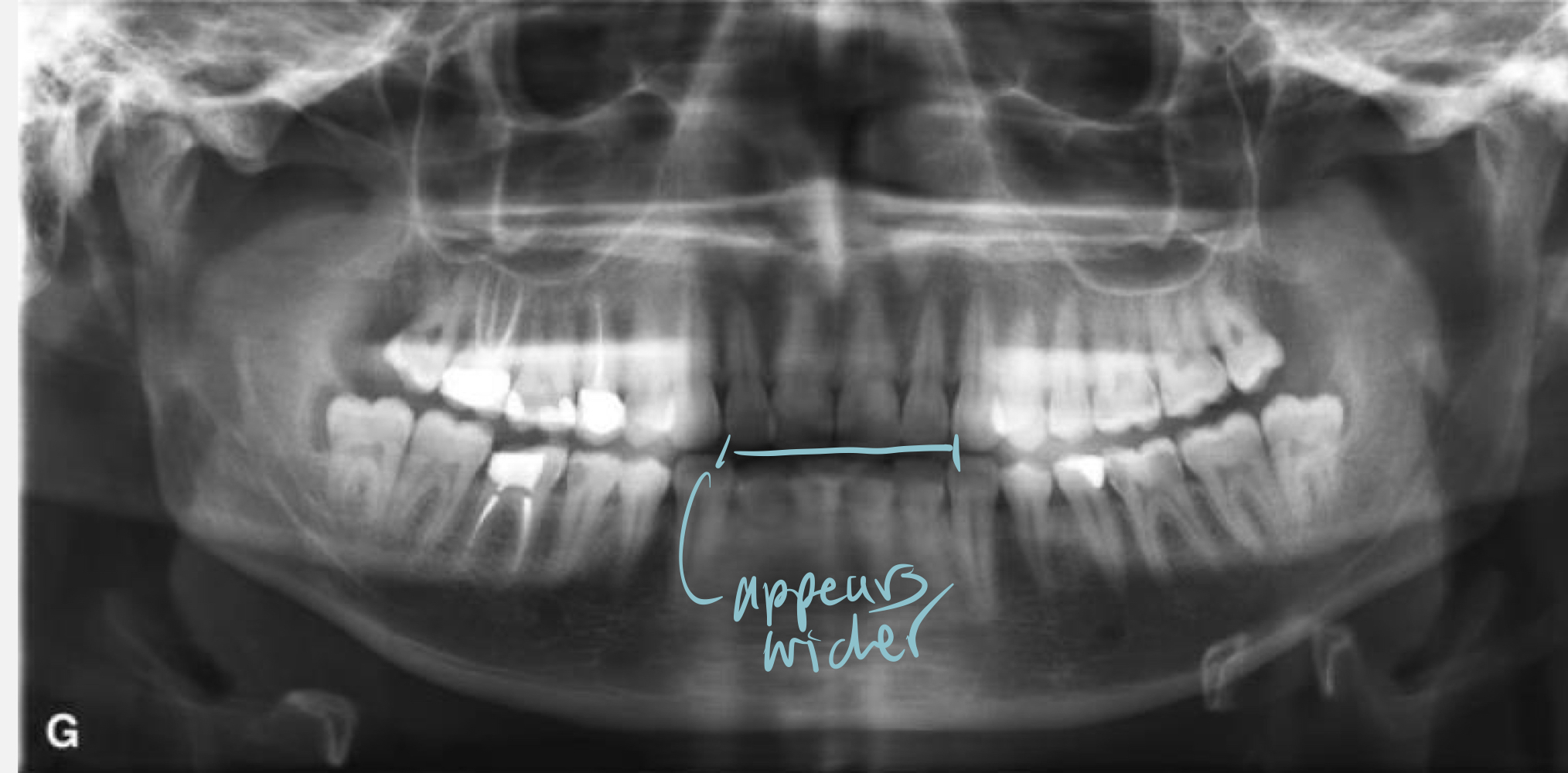
What happens if the mandible is posterior to focal trough?
Widening of image
27
New cards
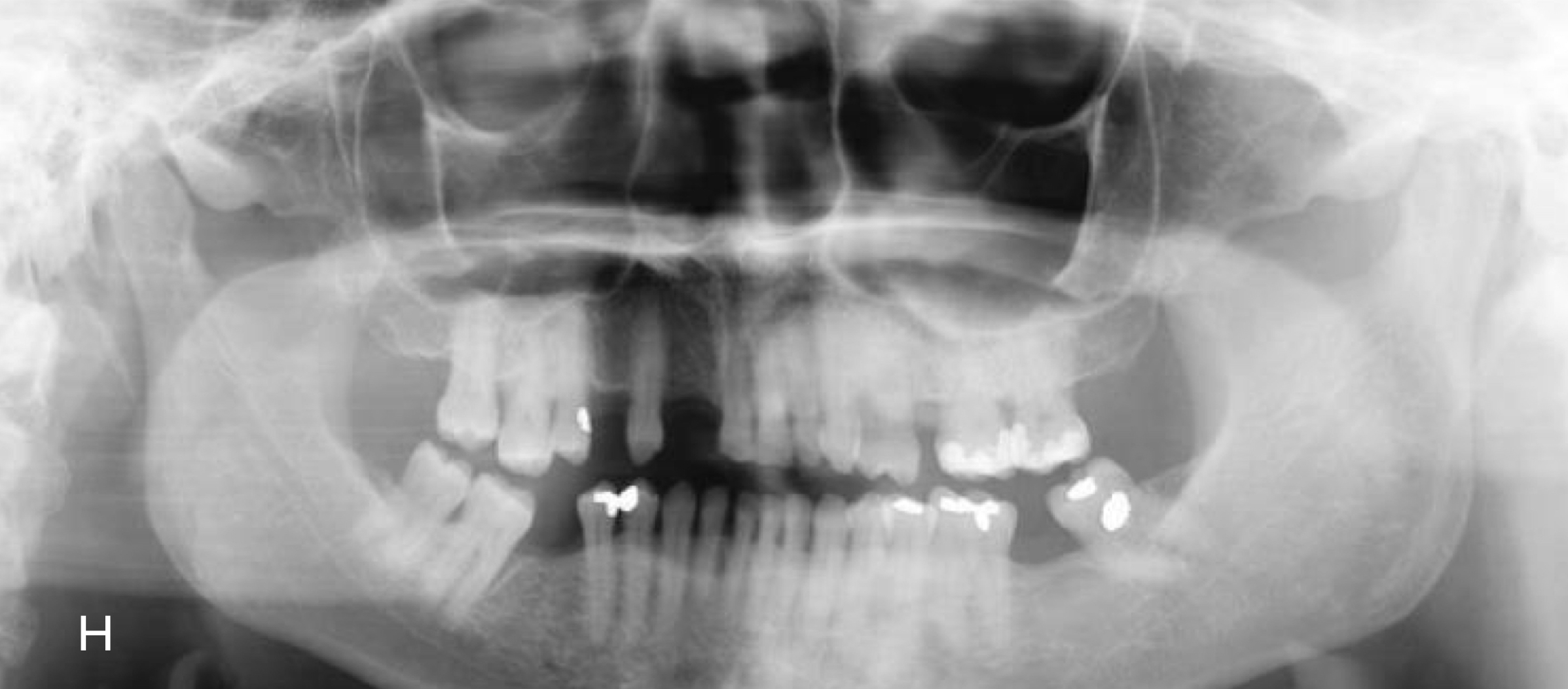
What happens if the mandible is anterior (too front) to the focal trough?
Lengthening of image
28
New cards
Why do we use an upward projection of the beam in panoramic images?
So that the beam spreads out and we can see vertical relationships of mandible and maxilla
29
New cards
If pt is rotated upward for a pan, what happens?
Overlapping images and hard palate obscures roots of teeth
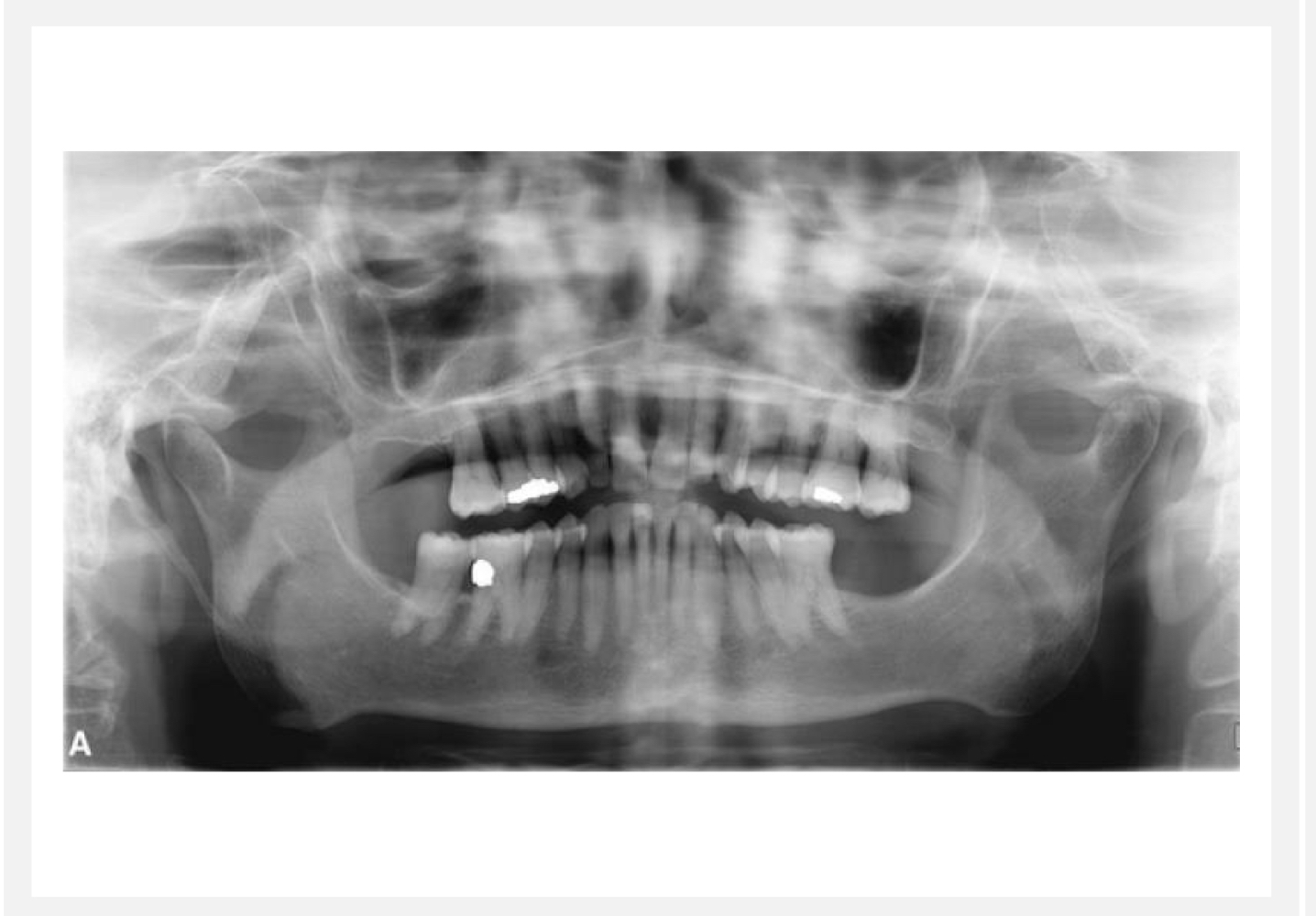
30
New cards
If the pt is rotated downward for a pan, what happens?
The anterior teeth are distorted and cutting off symphyseal region
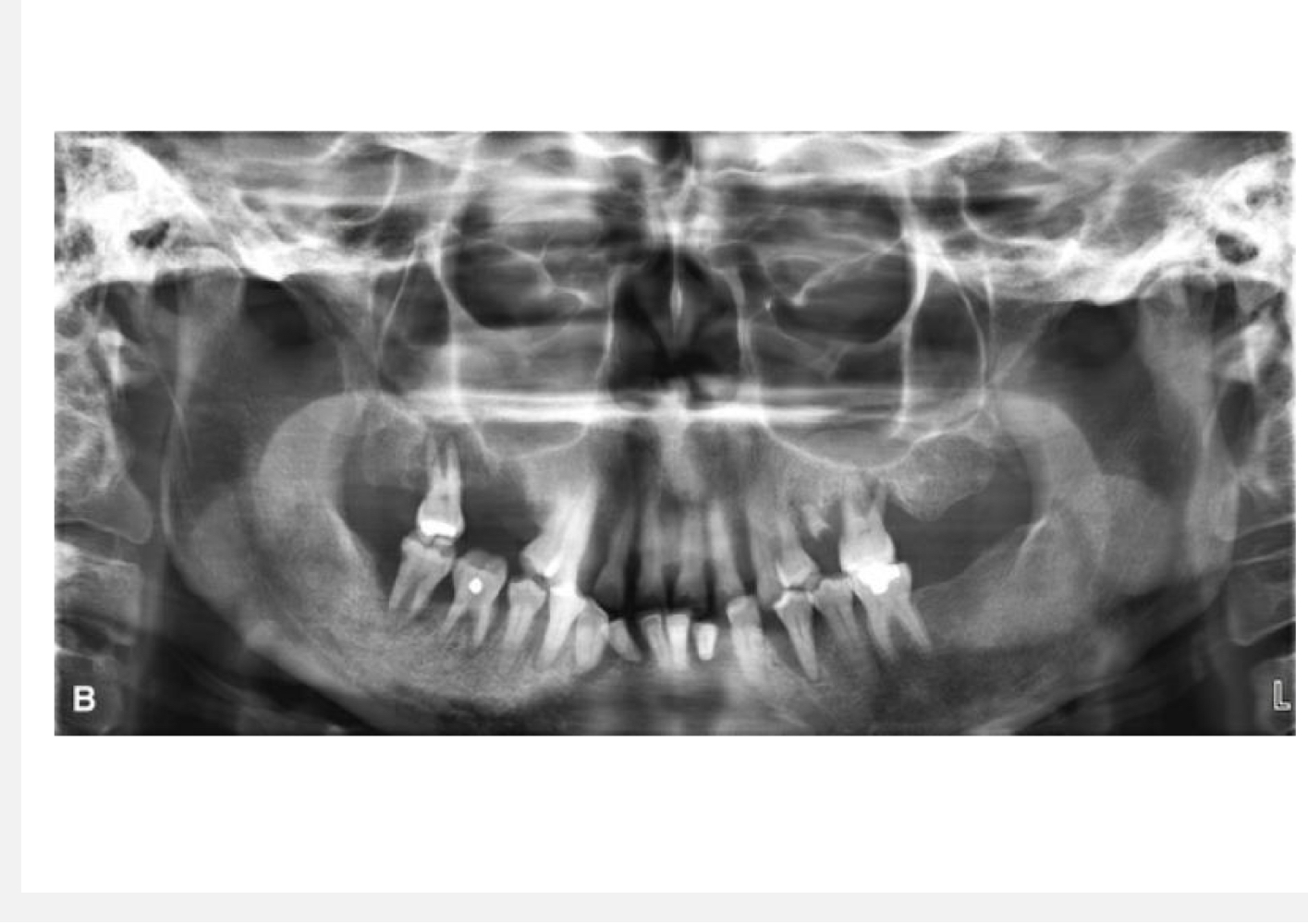
31
New cards
What happens if the tongue is not placed on the roof of the mouth?
Air is present and you cant see roots of teeth
32
New cards
What is Wilhelm Roentgen's contribution to dentistry?
Discovered x-rays
33
New cards
What is Otto Walkhoff known for?
The first dental radiograph
34
New cards
What was W.J. Morton known for?
The first radiograph of a skull
35
New cards
What was C. Edmund Kells known for?
The first dental radiograph on a LIVE person
36
New cards
What was William Rollins known for?
The first paper on the dangers of x-radiation
37
New cards
Who is considered the father of dental radiology?
Dr. C Edmund Kells
38
New cards
What is Howard Raper known for?
The introduction of oral and maxillofacial radiology to dental school curriculum, inventor of the bitewing, textbook on dental radiology
39
New cards
What are electrons?
Tiny, negatively charged particles
40
New cards
How do electrons travel around the nucleus?
In orbits that are maintained by electrostatic forces with the nuclei
41
New cards
Would an electron closer or farther from the nucleus have high energy?
Closer
42
New cards
What determines the binding energy of an electron?
The distance from the nucleus
43
New cards
What shell has the highest binding energy?
K shell —> need ≥70 keV to knockout
44
New cards
How is binding energy measured?
By electron volts
45
New cards
What is ionization?
The production of ions by converting an atom to ions
46
New cards
How does an atom become an ion?
An electron is ejected and the atom becomes positively charged (positive ion) and the electron plays the negative ion role
47
New cards
What is particulate radiation?
Tiny particles of matter that possess mass and travel in straight lines at high speed
48
New cards
What are the four types of particulate radiation?
Electrons, alpha particles, protons, and neutrons
49
New cards
Describe electrons
Fast moving beta particles emitted from the nucleus of radioactive atoms
50
New cards
What are alpha particlees?
Emitted from nuclei of heavy metals and exist as two protons and neutrons without electrons
51
New cards
What are protons?
Accelerated hydrogen nuclei with a mass and charge of 1
52
New cards
What are neutrons?
Accelerated particles with a mass of 1 and no electrical charge
53
New cards
What is the particle concept?
It characterizes electromagnetic radiation in terms of discrete bundles of energy called photons or quanta
54
New cards
Do photons have mass or weight?
No
55
New cards
How do photons travel?
as waves at the speed of light and move through space in a straight line
56
New cards
What is velocity?
The speed of the wave
57
New cards
What is wavelength?
The distance between crests
58
New cards
What is frequency?
the number of wavelengths that pass a fixed point in a given time frame
59
New cards
What are the three parts of the x-ray machines?
Control panel, extension arm and tubehead
60
New cards
What does the extension arm house?
the electrical wires that extend from the control panel to the tubehead
61
New cards
What is in the tubehead?
tightly sealed, heavy metal housing that contains the x-ray tube that produces dental x-rays
62
New cards
What is the purpose of insulating oil?
to prevent overheating
63
New cards
What is the purpose of the tubehead seal?
To permit exit of x-rays, seals oils and filters x-ray beam
64
New cards
What do aluminum disks do in the tubehead?
Filter non-penetrating, longer wavelength x-rays
65
New cards
What does the lead collimator do in the tubehead?
Restricts size of x-ray beam
66
New cards
What does the PID do?
Aims and shapes the x-ray beam
67
New cards
Describe the x-ray tube
Glass vacuum tube that includes leaded glass housing, cathode and anode
68
New cards
Describe the cathode
Negative electrode that has tungsten filament that produces electrons, molybdenum cup focuses electrons to a beam towards the tungsten target
69
New cards
How do electrons travel from the cathode to the anode?
By repellent forces of negative cathode and attractive forces of positive anode
70
New cards
Describe the anode
Positive electrode with tungsten plate that converts energy from electrons into x-ray photons
71
New cards
What is the purpose of a copper stem in the anode?
To dissipate heat away from the tungsten target
72
New cards
Describe tungsten
Most efficient in producing x-rays, high melting point and thermal conductivity
73
New cards
Describe filament circuits
3-5 volts, regulates flow to the filament, controlled by mA
74
New cards
Describe high-voltage circuits
65000-100000 volts (65-100kV), provides high voltage needed for x-ray, controlled by kV
75
New cards
How much energy is converted to x-rays?
Less than 1%
76
New cards
What is bremsstrahlung radiation?
When an e- gets close to the nucleus and “brakes” or slows down and results in an x-ray photon with lower energy → this is a braking or general radiation
77
New cards
What constitutes most x-rays that are produced?
Bremsstrahlung radiation
78
New cards
What is characteristic radiation?
Produced when high speed electron dislodges an inner shell electron from tungsten and causes ionization, electrons rearrange themselves
79
New cards
When does characteristic radiation occur?
≥70 kV
80
New cards
Describe compton scattering
57% of x-rays, degrades imaging and exposes pts, electron ejected from orbit
81
New cards
Describe coherent scattering
7% of x-rays and is minimal contribution to scattering, no loss of energy
82
New cards
Describe photoelectric absorption
27% of x-rays, basis of radiographic image formation
83
New cards
What does wavelength determine?
The energy and penetrating power of radiation
84
New cards
What length of x-rays have a greater penetrating power?
Shorter wavelengths
85
New cards
What does kilovoltage impact?
Quality, the penetrating ability of the x-ray
86
New cards
If voltage is increased, how are electrons impacted?
Their speed is increased and they strike the target with greater force
87
New cards
What kV do we need for dental imaging?
65-100 kV
88
New cards
What is the density of a dental radiograph?
The darkness
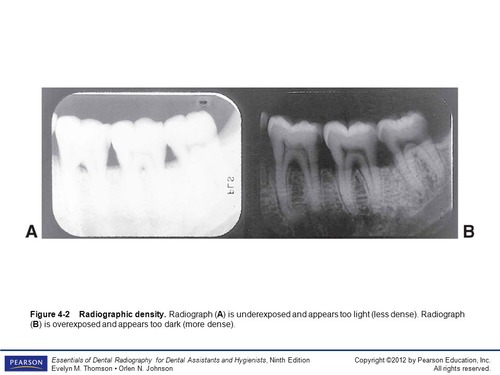
89
New cards
If we increase kV, what happens to the density?
The image will appear darker
90
New cards
If we decrease kV, what happens to the density?
The image will appear lighter
91
New cards
What is contrast?
How sharply dark and light areas are differentiated on an image
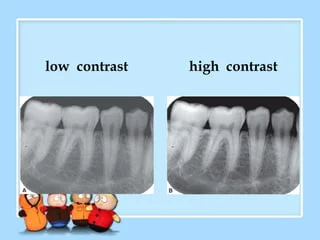
92
New cards
What is the impact of low kV on contrast?
High contrast, few shades of gray, good for detecting caries
93
New cards
What is the impact of high kV on contast?
Low contrast, many shades of gray, good for detection of periodontal/periapical disease
94
New cards
What does miliamperage affect?
The temperature of the cathode filament
95
New cards
If the mA is increased, what happens?
The temperature of the cathode filament increases and more electrons are produced meaning more x-rays are emitted
96
New cards
If we increase mA, what happens to density of image?
The image will appear darker
97
New cards
What is the inverse square law rule?
The intensity of the radiation is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source of radiation
98
New cards
What is the purpose of filtration?
To remove low energy photons, reduce intensity, and increase mean energy of the beam
99
New cards
What is inherent filtration?
Materials in the path of the photon beam from focal spot to exit point
100
New cards
What inherent filtration is there in dental x-rays?
Glass wall of tube, insulating oil, and barrier surrounding oil